Signal Transduction
Use Proteintech’s phospho antibodies, available against over 140 common PTMs, to help you better identify and better understand the critical phosphorylation events that drive signaling pathways forward.
Detail Validation
To verify their specificity for the target modification, Proteintech’s phospho antibodies are validated with cell treatments that utilize relevant pathway agonists and inhibitors to either stimulate or block expression of the desired phosphorylation signal. This approach followed by downstream western blot analysis alongside total protein control antibodies ensures that these products are specific for phosphorylated forms of their target only.
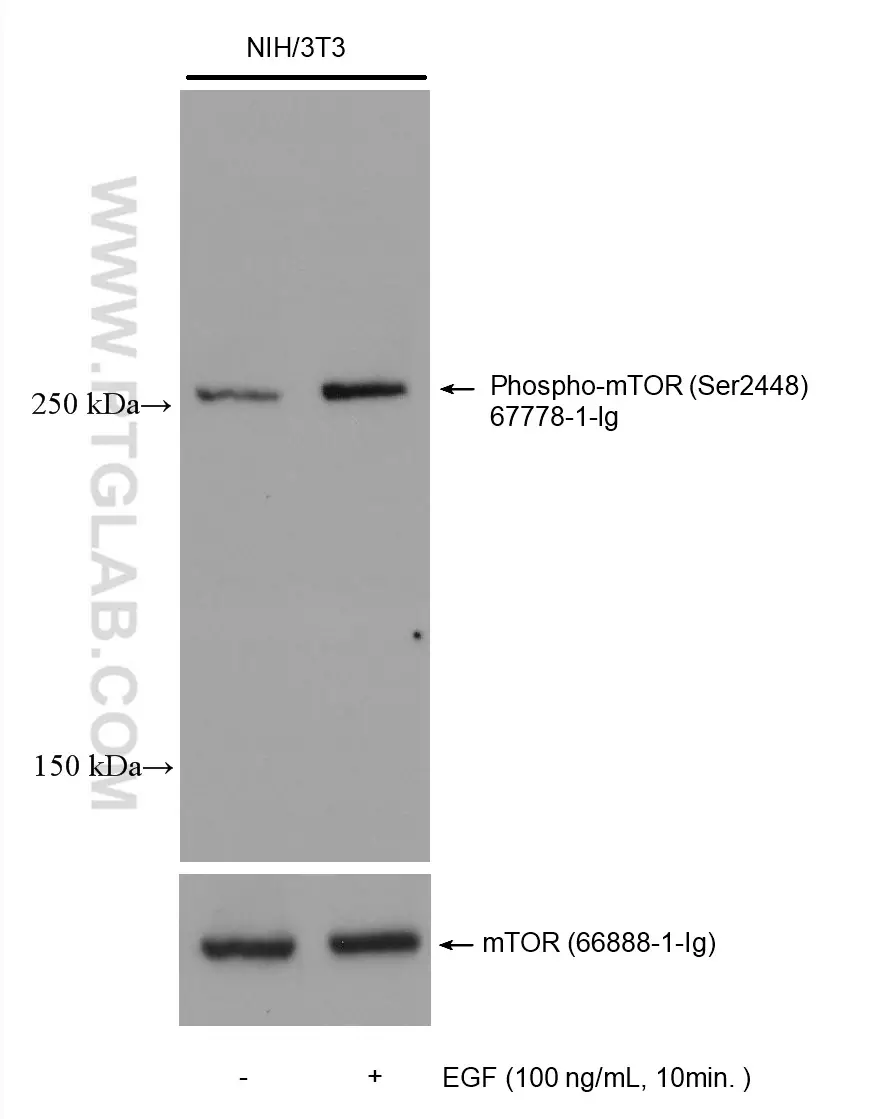
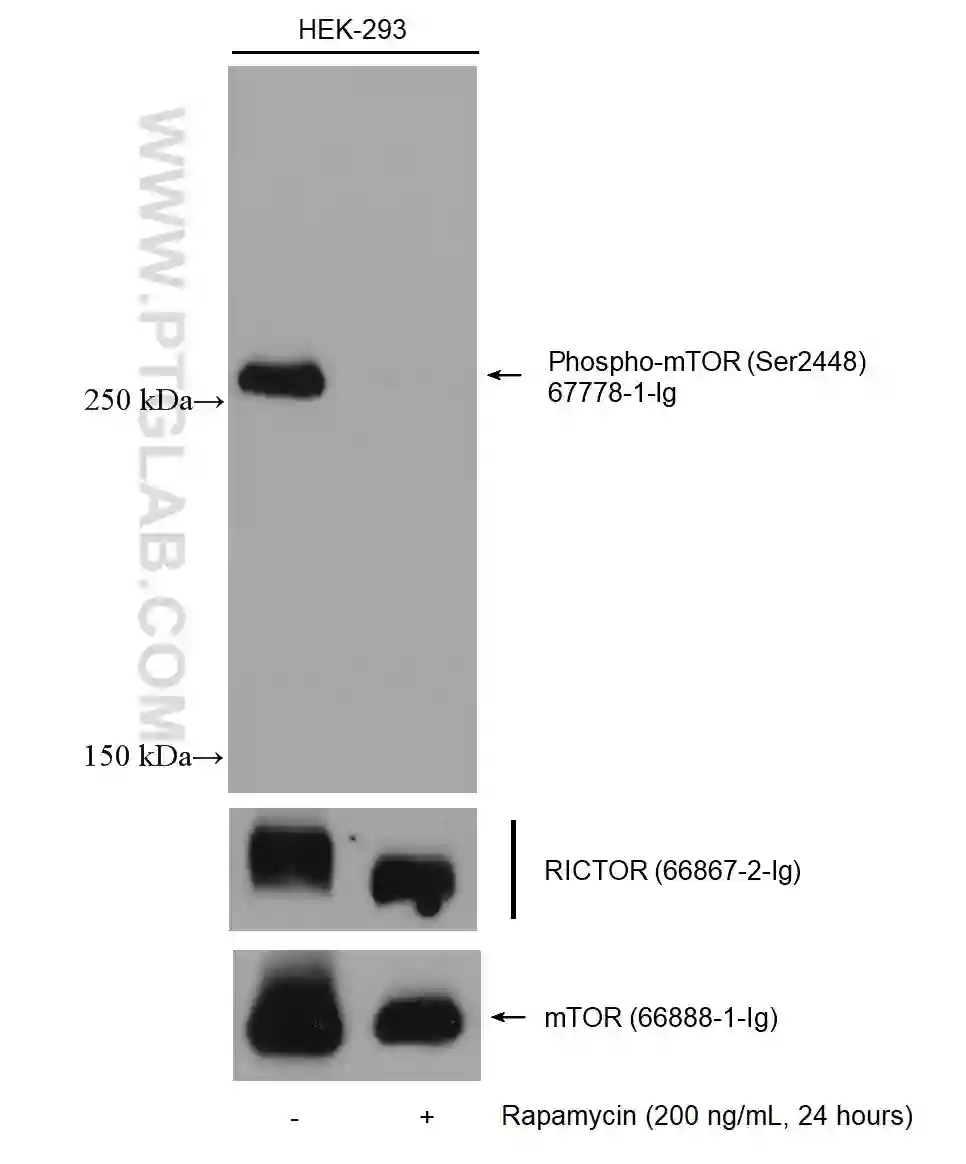
Image description: WB analysis of phospho MTOR signal following treatment with either pathway agonist (EGF) or MTOR-inhibitor (rapamycin). On the left side, NIH3T3 cells were not-treated or treated with 100 ng/mL EGF for 10 min followed lysis and downstream western analysis with phospho-MTOR antibody (67778-1-Ig).
On the right side, HEK293 cells were non-treated or treated with 200 ng/mL Rapamycin for 24 hours followed by lysis and downstream western analysis with phospho-MTOR antibody (67778-1-Ig).
In addition to WB, many phospho antibodies have also been validated in additional applications including IHC, IF, and FC.
Cell treatments have also been used to validated certain phospho antibodies for IHC and IF
Binary Signal
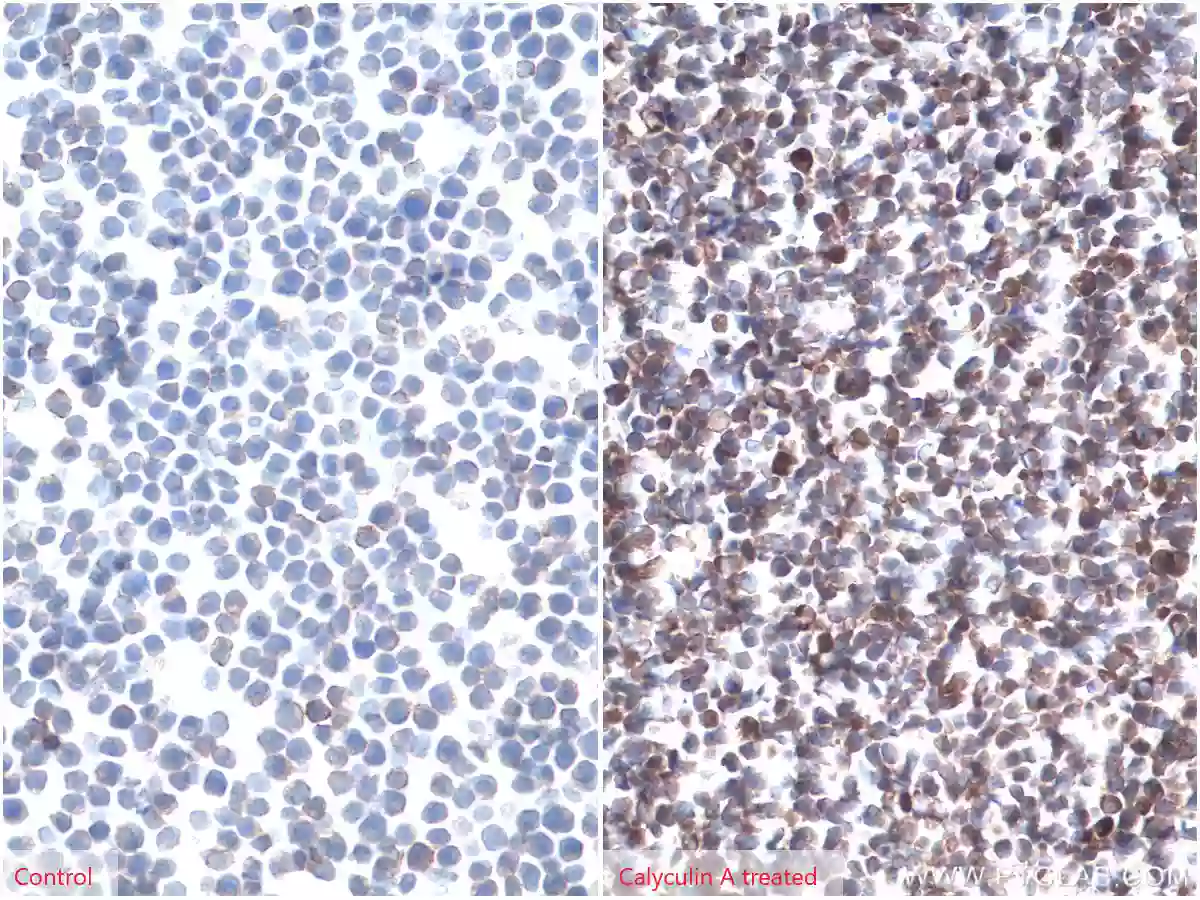
IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded untreated (left) or calyculin A treated (right) Jurkat cells slide using Phospho-AKT (Ser473) antibody (66444-1-Ig) at a dilution of 1:8000 (under 40x lens)
Dynamic Signal
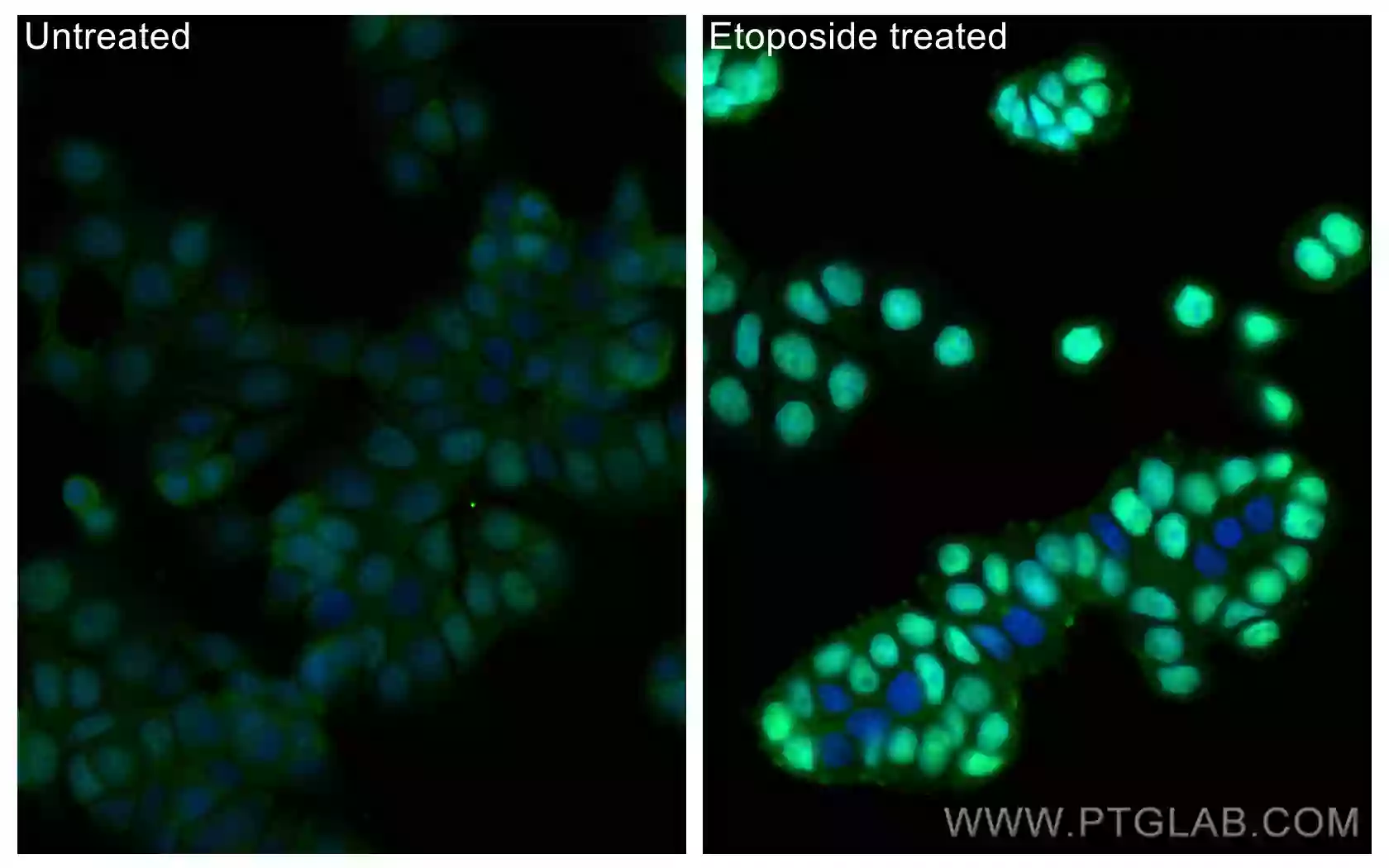
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed etoposide treated HT-29 cells using CoraLite Plus 488 Phospho-P53 (Ser15) Recombinant Antibody (CL488-80195, clone: 2J21) at dilution of 1:200.
Top Cited Products
Phospho-AKT (Ser473) Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, FC |
Phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) Polyclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications: | WB, IP |
Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, IF, FC |
Phospho-JNK (Tyr185) Recombinant Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Applications: | WB |
Interactive Signaling Posters
|
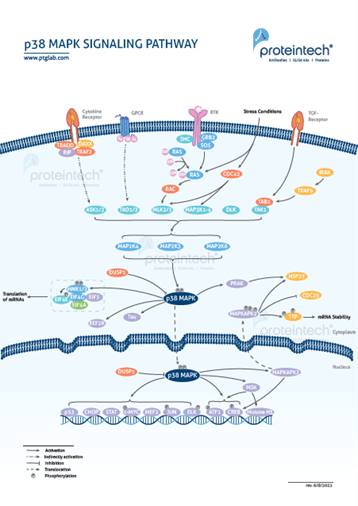
The p38 MAPK signaling pathway is a multi-tiered cascade characterized by sequential protein phosphorylation events. It is anchored by p38 MAPK protein, which plays a major role in regulating inflammation, cell differentiation, cell cycle progression, and nuclear fragmentation during apoptosis. |
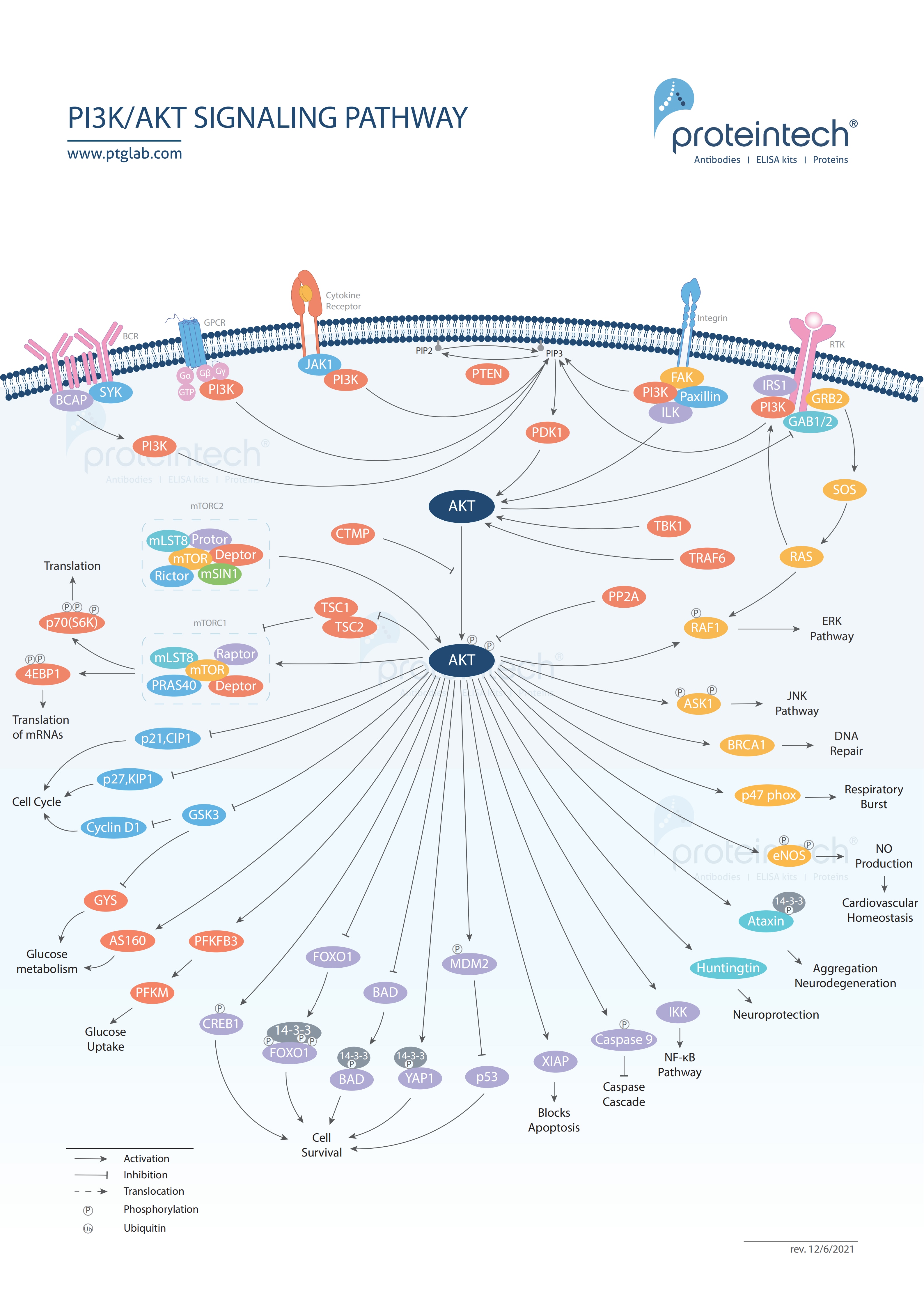
PI3K is a lipid kinase that activates downstream intracellular signaling pathways anchored by AKT. These pathways regulate several important processes including growth, proliferation, metabolism, motility, and apoptosis. They can also trigger strong, pro-survival responses within tumor cells due to abnormal rates of activation |
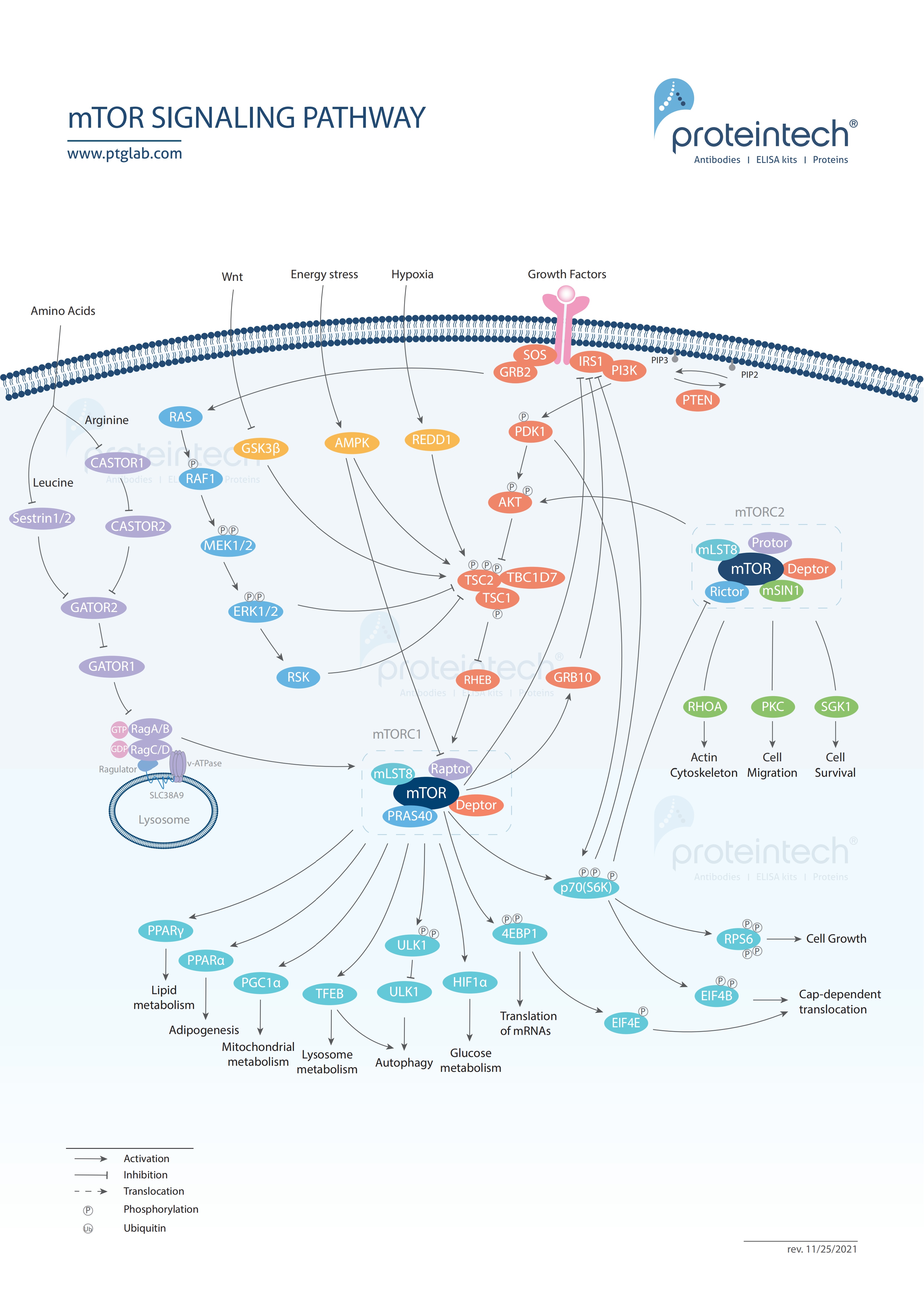
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) forms a center of a signaling pathway that plays a critical role in regulating cell metabolism, proliferation, and survival. mTOR signaling is often involved in regulating tumor metabolism in cancer and disease pathology in Alzheimer’s. |
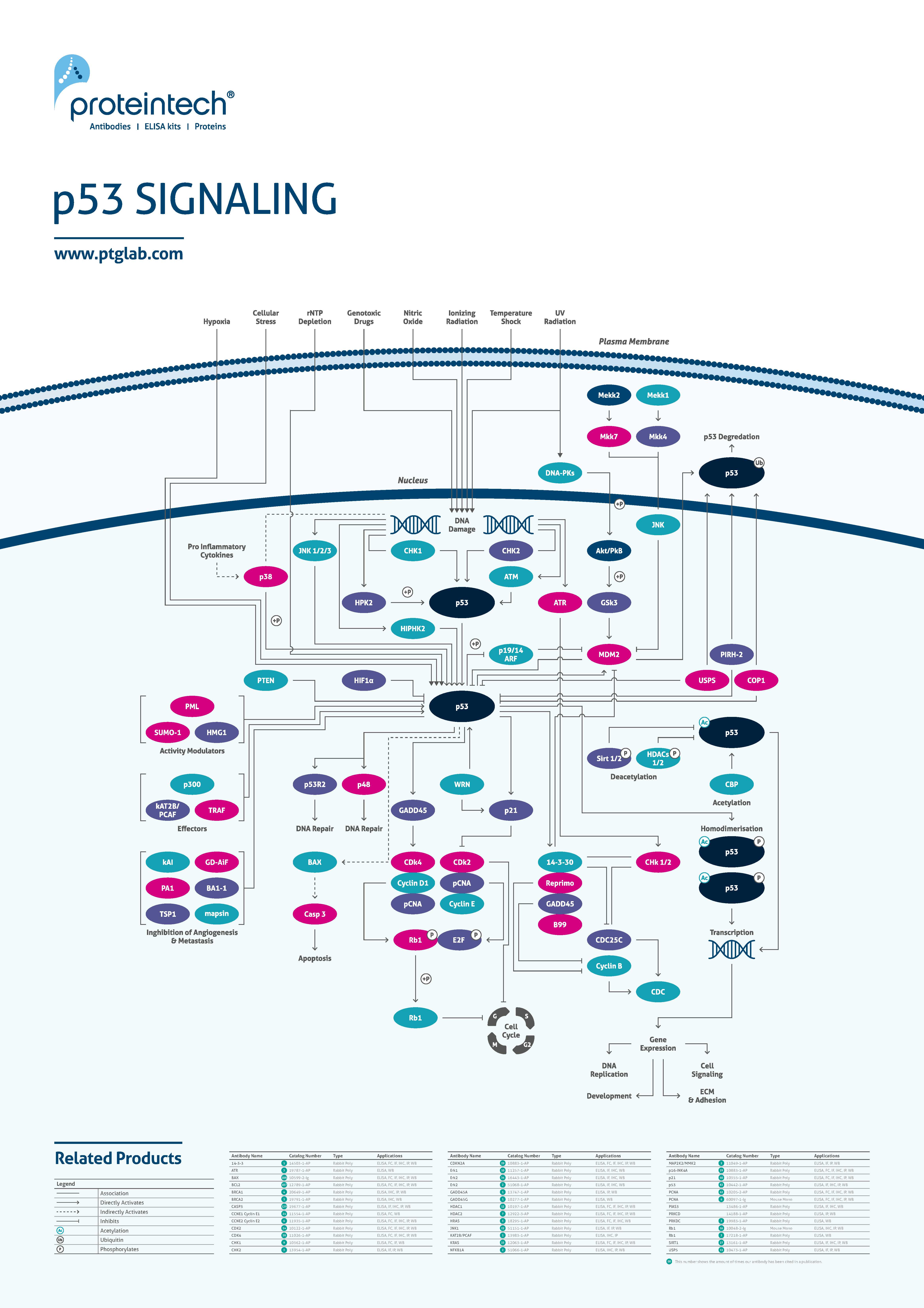
The p53 signaling pathway controls progression through the cell cycle. The p53 protein can arrest the cycle before DNA replication and before cell division in response to various stress signals. As such this pathway can function to halt tumor progression and initiate apoptosis in tumor cells where DNA has been damaged beyond repair. |
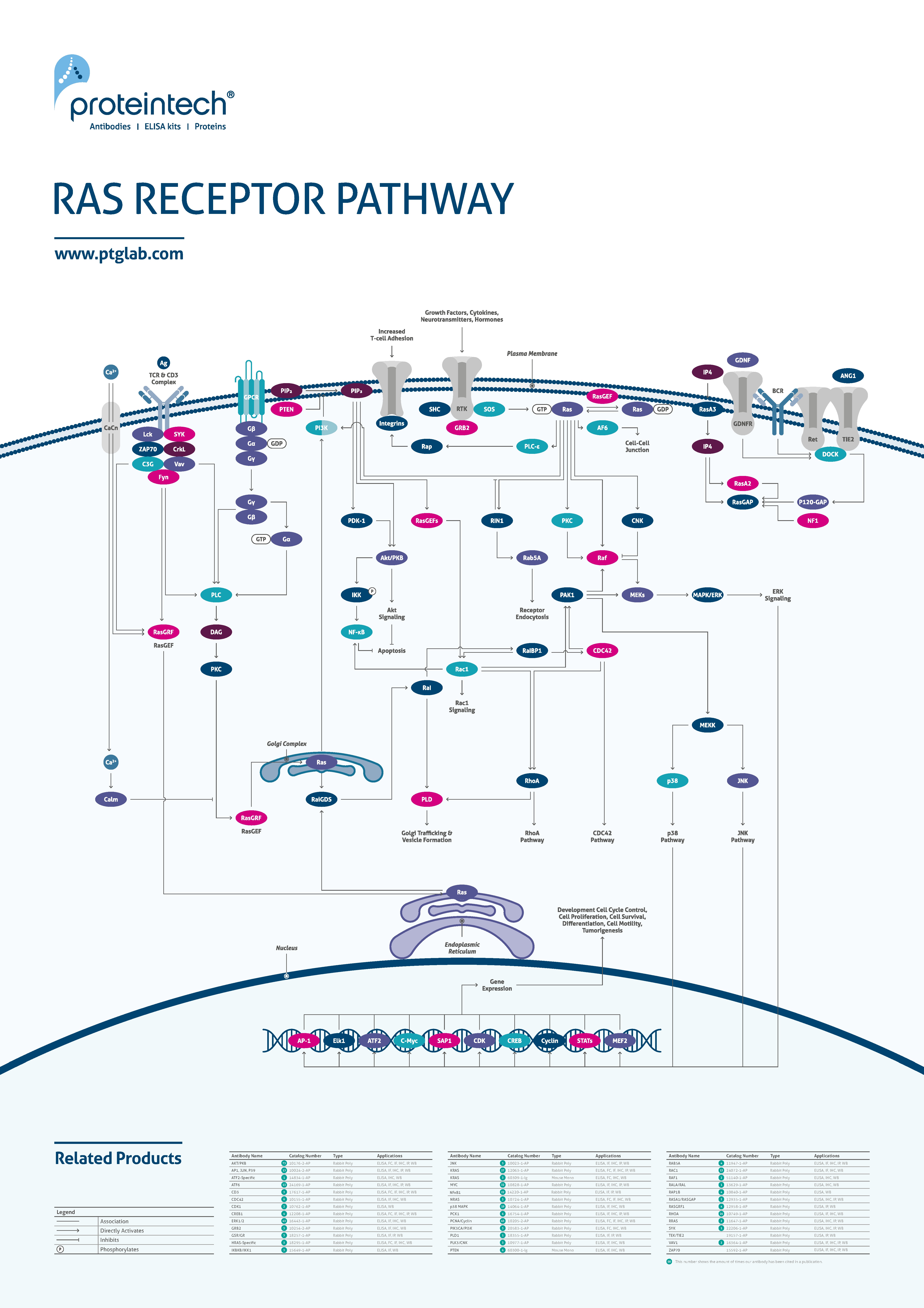
Ras proteins require binding with GTP to become active. Upon activation, the Ras signaling pathway can regulate several processes including cell proliferation, apoptosis, cytoskeletal remodeling, and protein secretion. Mutations within tumors cause many Ras pathways to become constitutively active, resulting in uncontrolled growth. |