SRY Polyclonal antibody
SRY Polyclonal Antibody for IHC, WB,ELISA
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
human, mouse
Applications
WB, IHC,ELISA
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Cat no : 17930-1-AP
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
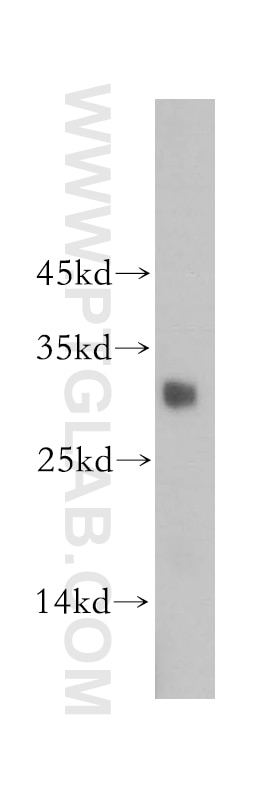
| Positive WB detected in | human testis tissue |
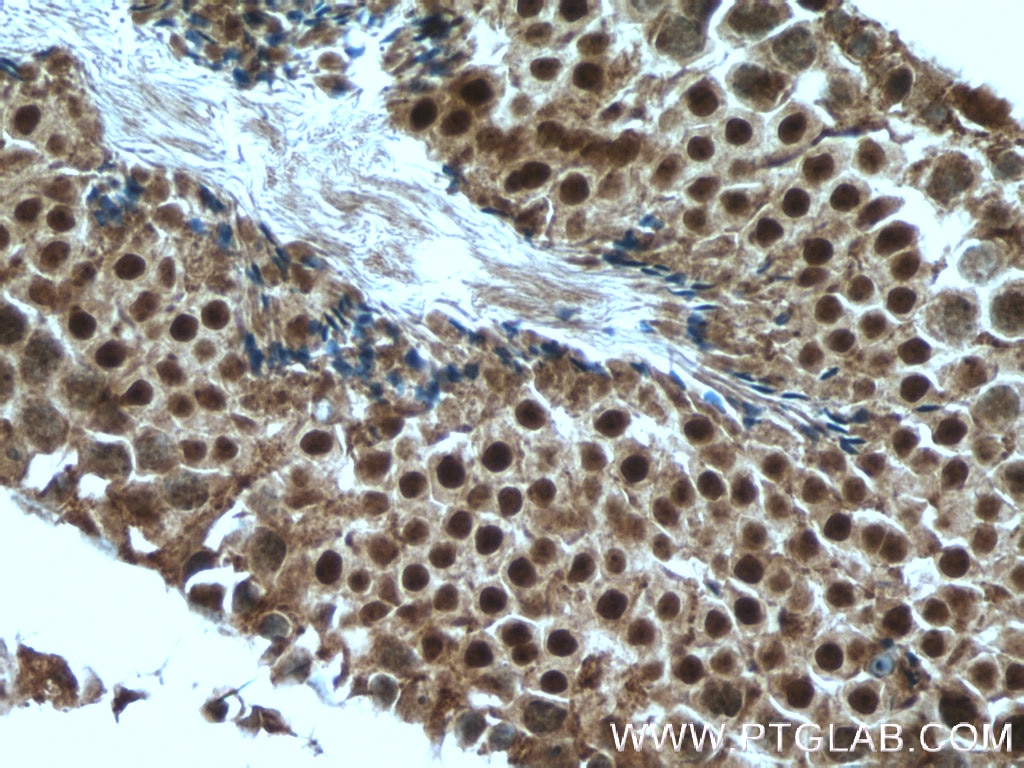
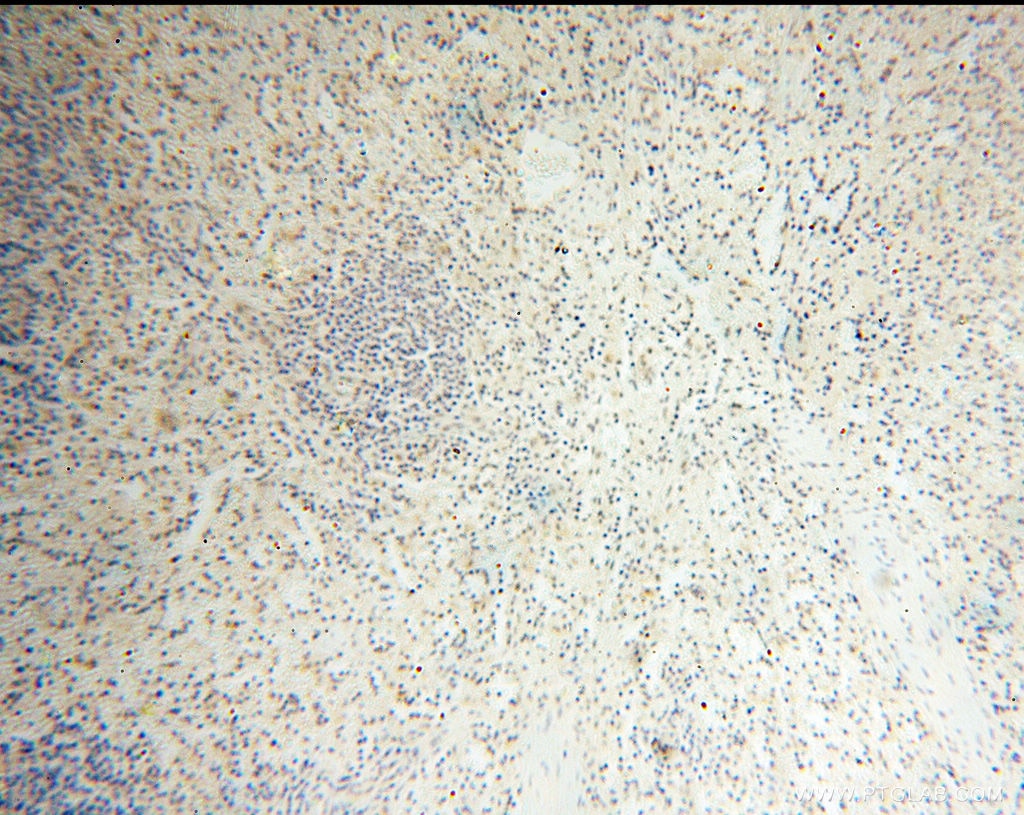
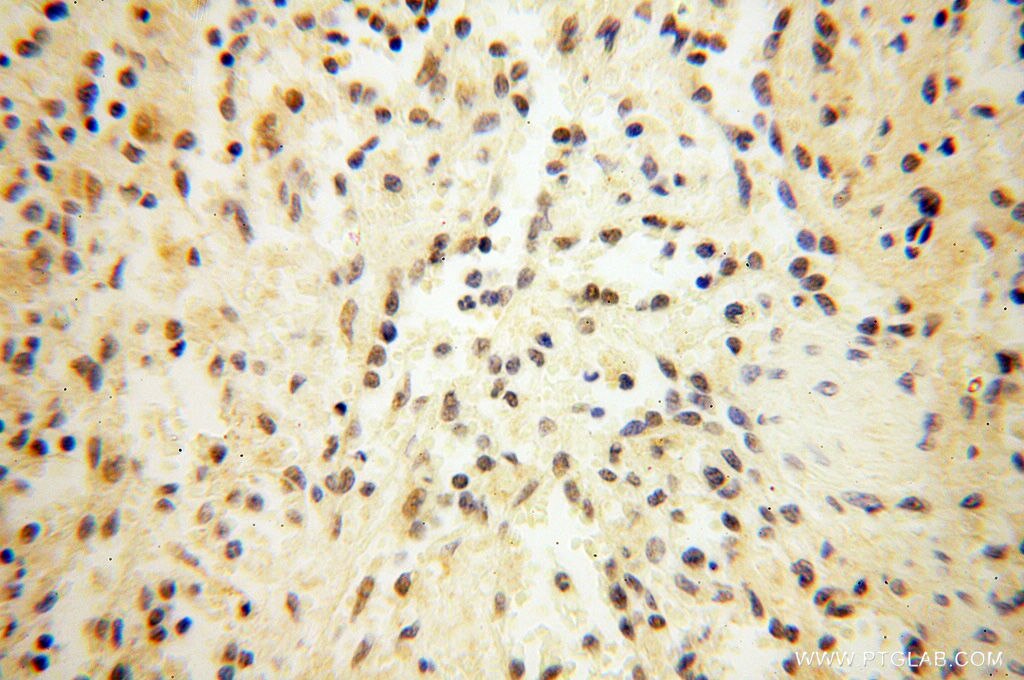
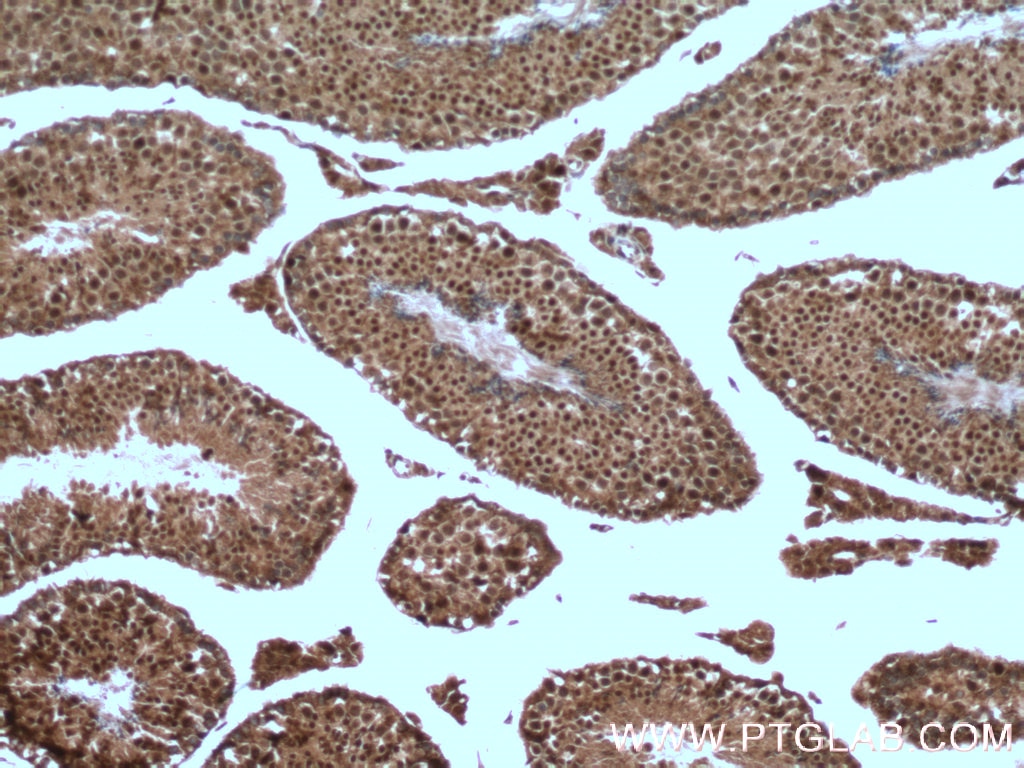
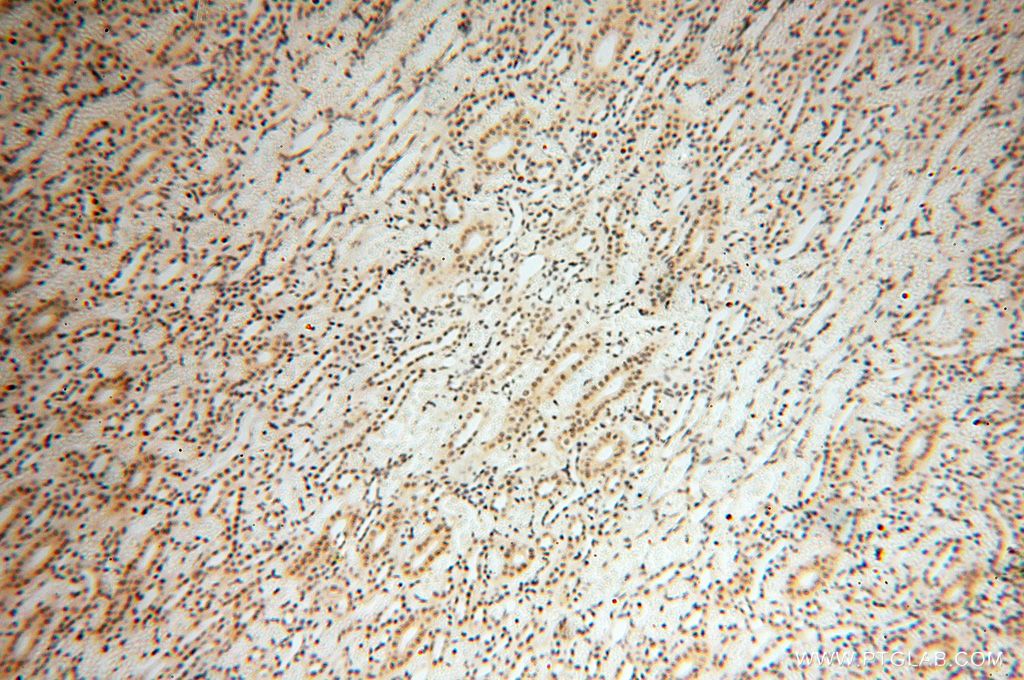
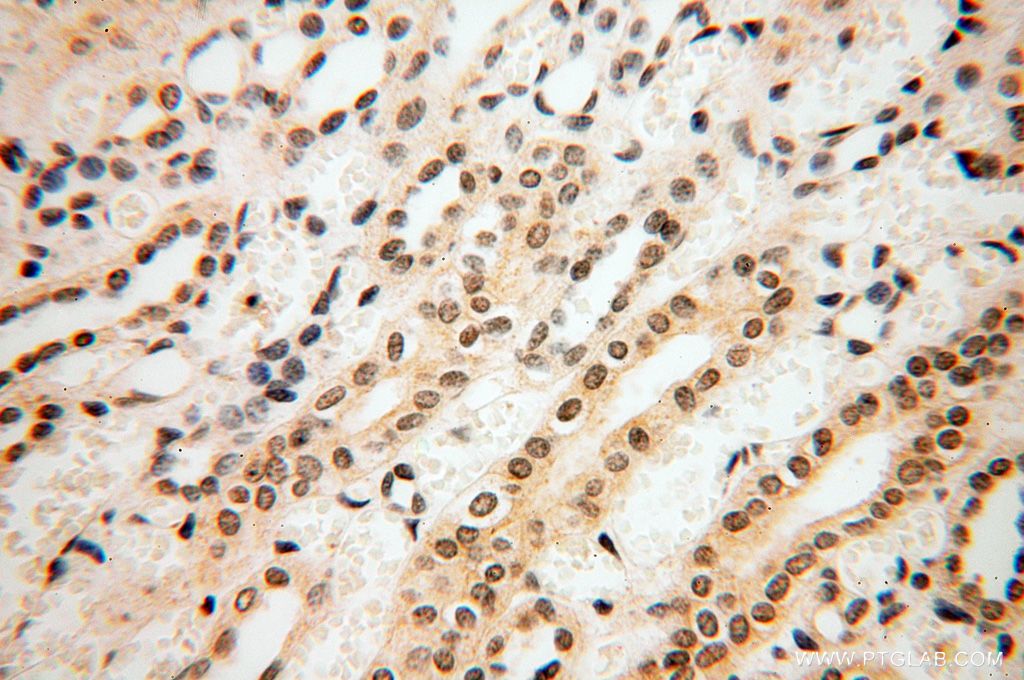
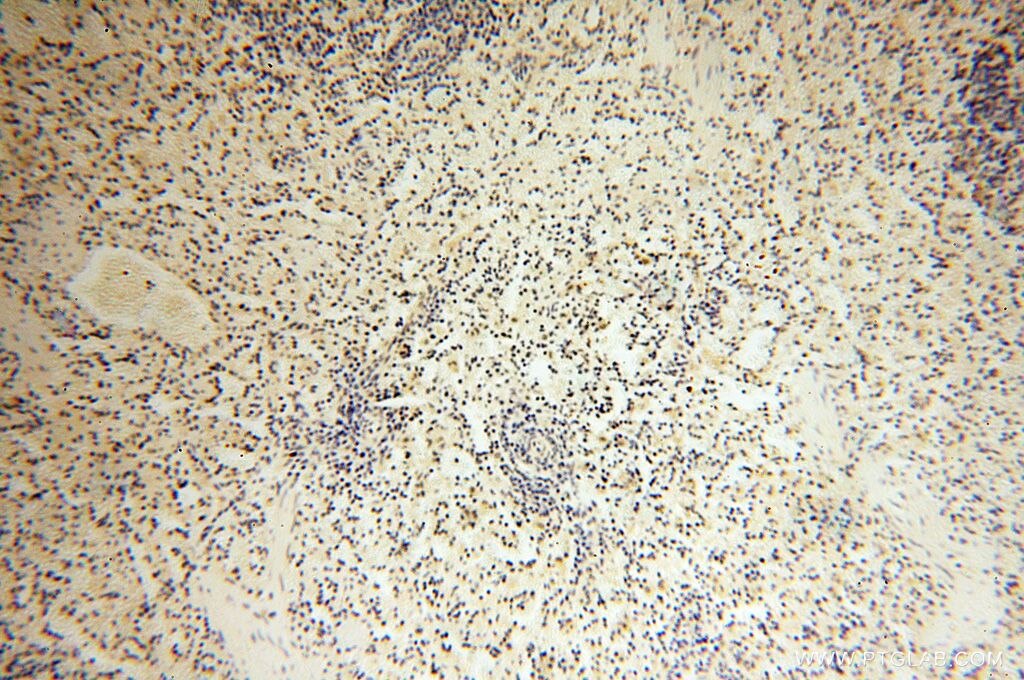
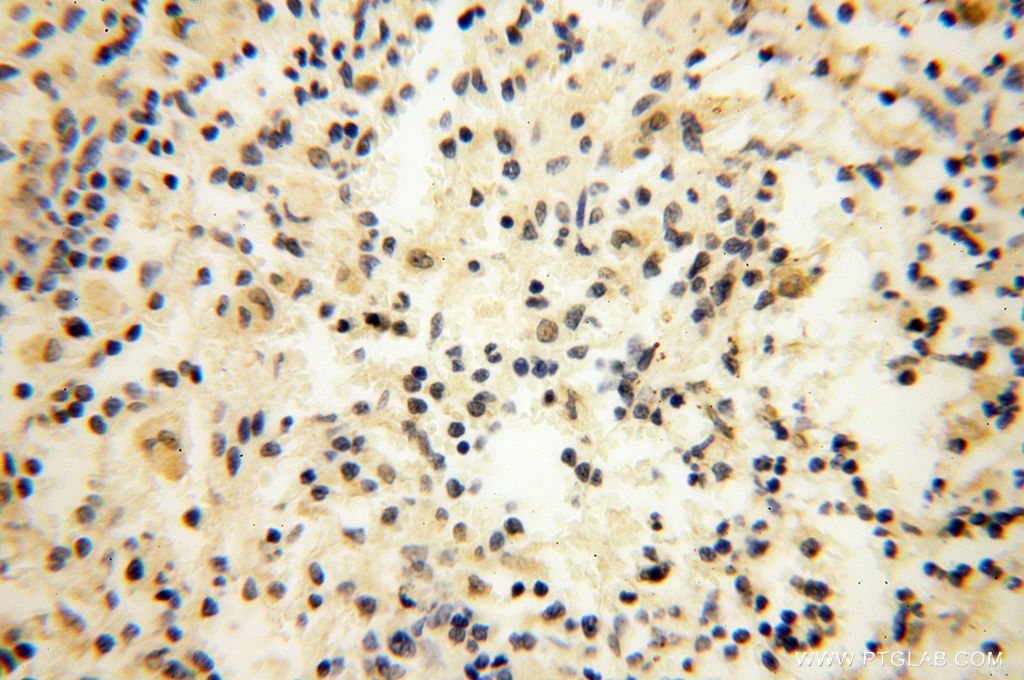
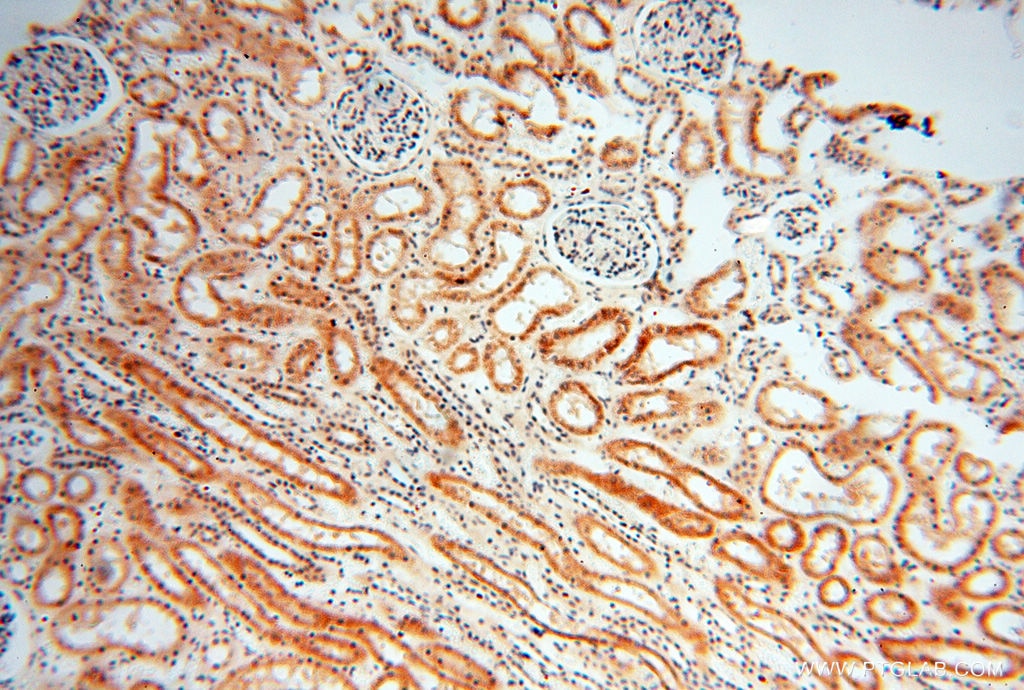
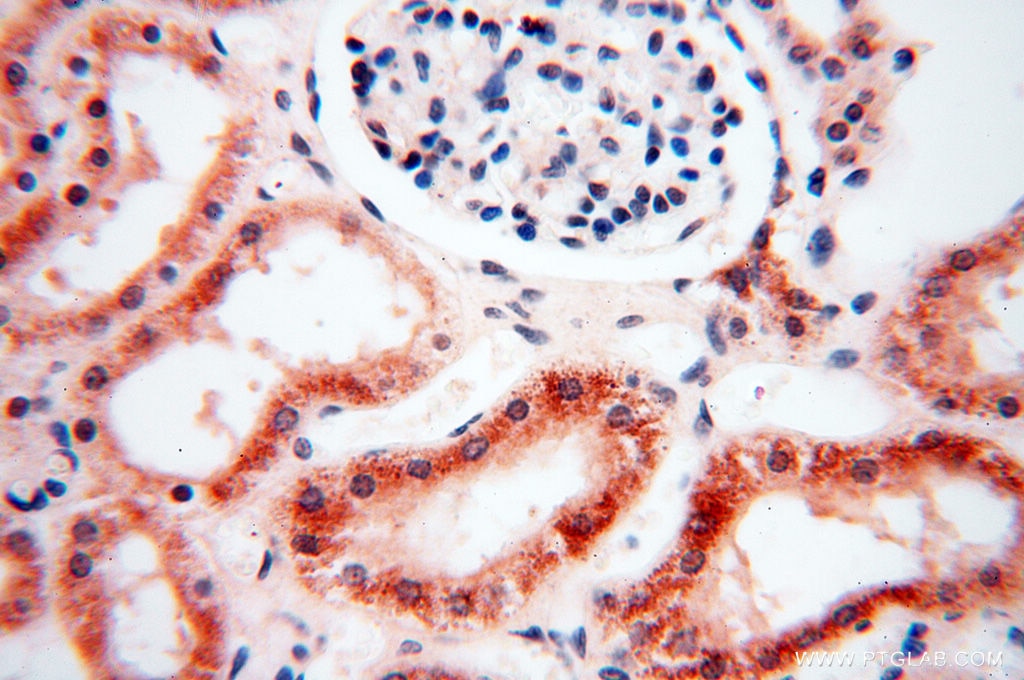
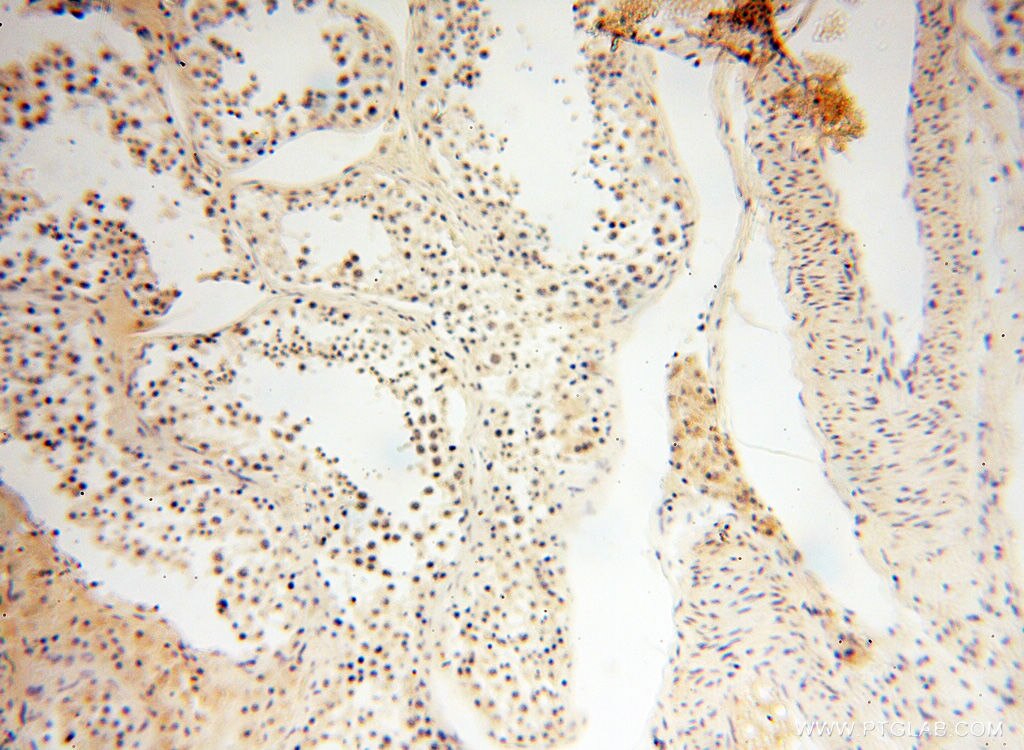
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse testis tissue, human testis tissue, human spleen tissue, human kidney tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
17930-1-AP targets SRY in WB, IHC,ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SRY fusion protein Ag12360 |
| Full Name | sex determining region Y |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 204 aa, 24 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 30 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC074924 |
| Gene Symbol | SRY |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6736 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
SRY (sex-determining region Y protein) is a tran-scriptional activator required for male sex determination in mammals. This protein, also referred to as testis-determining factor (TDF), is an HMG box protein that initiates the formation of testis from undifferentiated gonad. The DNA-binding activity of SRY is required for normal testis formation. This DNA-binding activity is thought to be regulated by PKA, which phosphorylates SRY in vivo. Mutations in SRY have been associated with 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis, in which the gonads fail to develop in XY phenotypic females.