Histone H3K4me2 antibody (mAb) (Clone MABI 0303)
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Wide Range Predicted
Applications
ChIP, ChIP-Seq, DB, ICC, IF, WB
CloneNo.
MABI 0303
Cat No : 39079,39679 39679
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Tested Applications |
ChIP, ChIP-Seq, DB, ICC, IF, WB
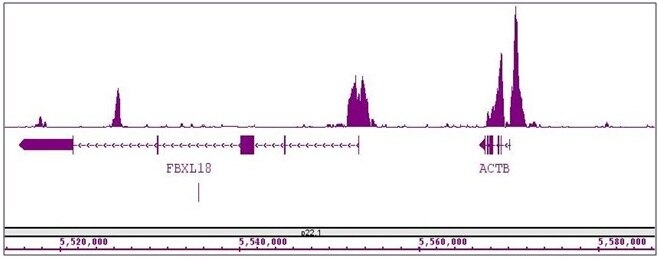
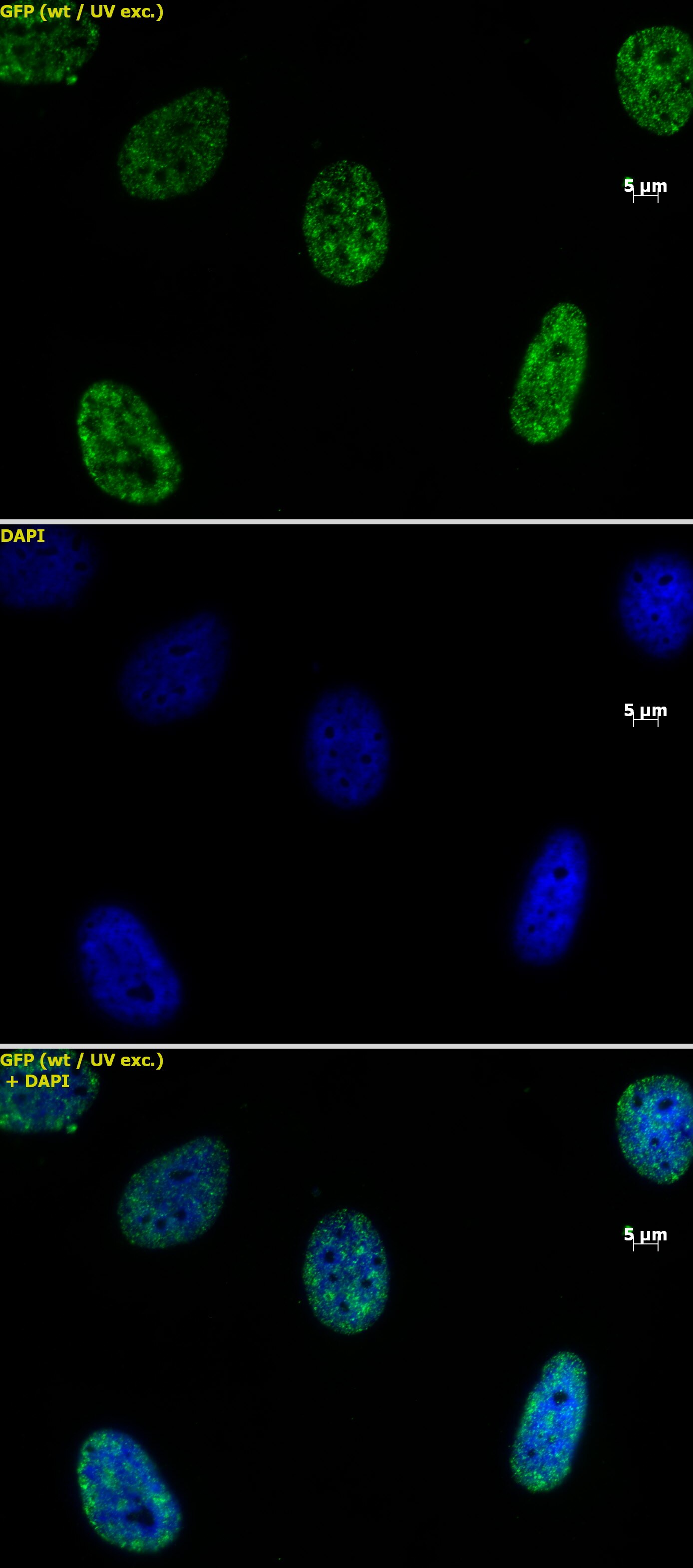
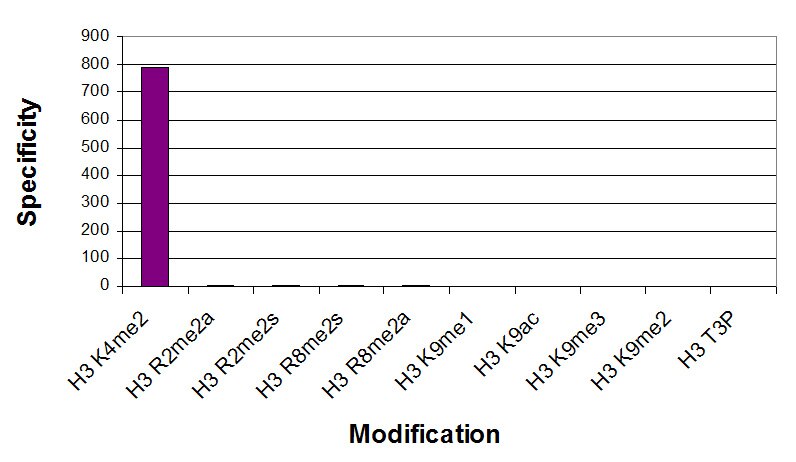
Applications Validated by Active Motif: ChIP: 5 - 10 ug per ChIP ChIP-Seq: 5 - 10 ug each ICC/IF: 1 - 2 ul/ml dilution WB: 2 - 5 ug/ml dilution DB: 1 ug/ml dilution ChIP-Seq validation was performed by Active Motif's Epigenetics Services; the complete data set is available in the UCSC Genome Browser by clicking here. For Histone H3K4me2, we also offer AbFlex Histone H3K4me2 Recombinant Antibody (rAb). For details, see Catalog No. 91321. |
| Tested Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Wide Range Predicted |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Modification | Methylated |
| Immunogen | This Histone H3 dimethyl Lys4 antibody was raised against a synthetic peptide containing dimethyl Lys4 of human histone H3. |
| Full Name | Histone H3K4me2 antibody (mAb) (Clone MABI 0303) |
| Synonyms | histone H3, histone, H3, histone-H3, histoneH3, pAb, monoclonal, H3K4me2, Histone H3 dimethyl Lys4, Histone H3 dimethyl Lysine 4, Histone H3 dimethyl Lys 4, Histone H3 dimethyl K4, Histone H3 dimethyl K 4, Histone H3 di-methyl Lys4, Histone H3 di-methyl Lysine 4, Histone H3 di-methyl Lys 4, Histone H3 di-methyl K4, Histone H3 di-methyl K 4, Histone H3 2Me Lys4, Histone H3 2Me Lysine 4, Histone H3 2Me Lys 4, Histone H3 2Me K4, Histone H3 2Me K 4, Histone H3 Me2 Lys4, Histone H3 Me2 Lysine 4, Histone H3 Me2 Lys 4, Histone H3 Me2 K4, Histone H3 Me2 K 4, antibody, antibodies, MABI, Clone MABI 0303, chip, chromatin immunoprecipitation, H3K4Me2, peptest, 61315 |
| Molecular weight | 17 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_003522 |
| RRID | AB_2793302 |
| Purification Method | Protein G Chromatography |
| Buffer | PBS pH 7.5 containing 30% glycerol, 0.3 M NaCl, and 0.035% sodium azide. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
Background Information
Histone H3 is one of the core components of the nucleosome. The nucleosome is the smallest subunit of chromatin and consists of 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped around an octamer of core histone proteins (two each of Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3 and Histone H4). Histone H1 is a linker histone, present at the interface between the nucleosome core and DNA entry/exit points. Histone H1 is responsible for establishing higher-order chromatin structure. Chromatin is subject to a variety of chemical modifications, including post-translational modifications of the histone proteins and the methylation of cytosine residues in the DNA. Reported histone modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, glycosylation, ADP-ribosylation, carbonylation and SUMOylation; these modifications play a major role in regulating gene expression. The methylation of histones can occur on two different residues: arginine or lysine. Histone methylation can be associated with transcriptional activation or repression, depending on the methylated residue. Lysine 4 of histone H3 can be mono-, di- or trimethylated by different histone methyltransferases (HMTs) such as SET1 or ASH1. Methylation of Lys4 is often associated with transcriptional activation. The demethylase LSD1 is able to demethylate histone H3 Lys4.