TRAPPC9/NIBP Polyklonaler Antikörper
TRAPPC9/NIBP Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 19549-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
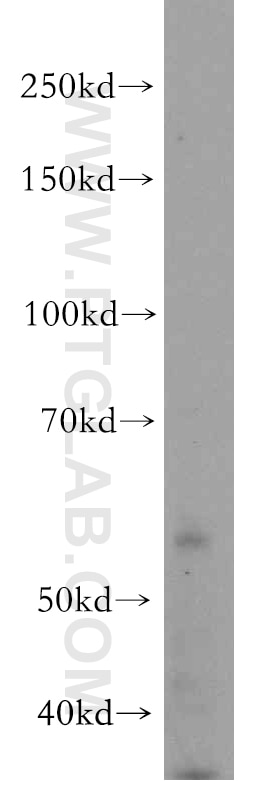
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | SH-SY5Y-Zellen, humanes Hirngewebe, Mausnierengewebe |
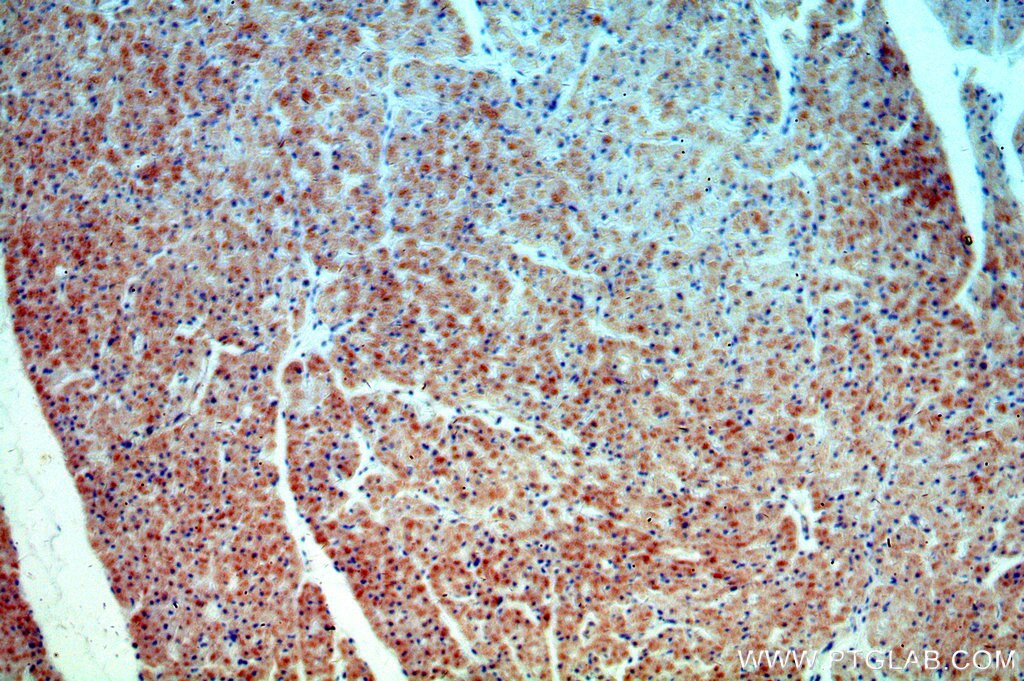
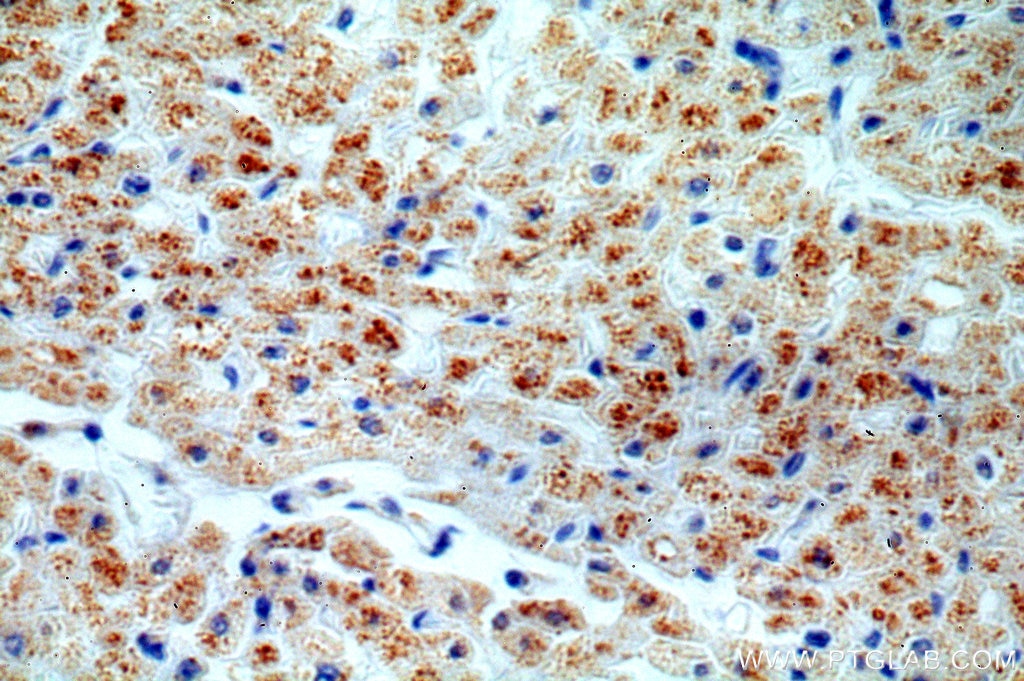
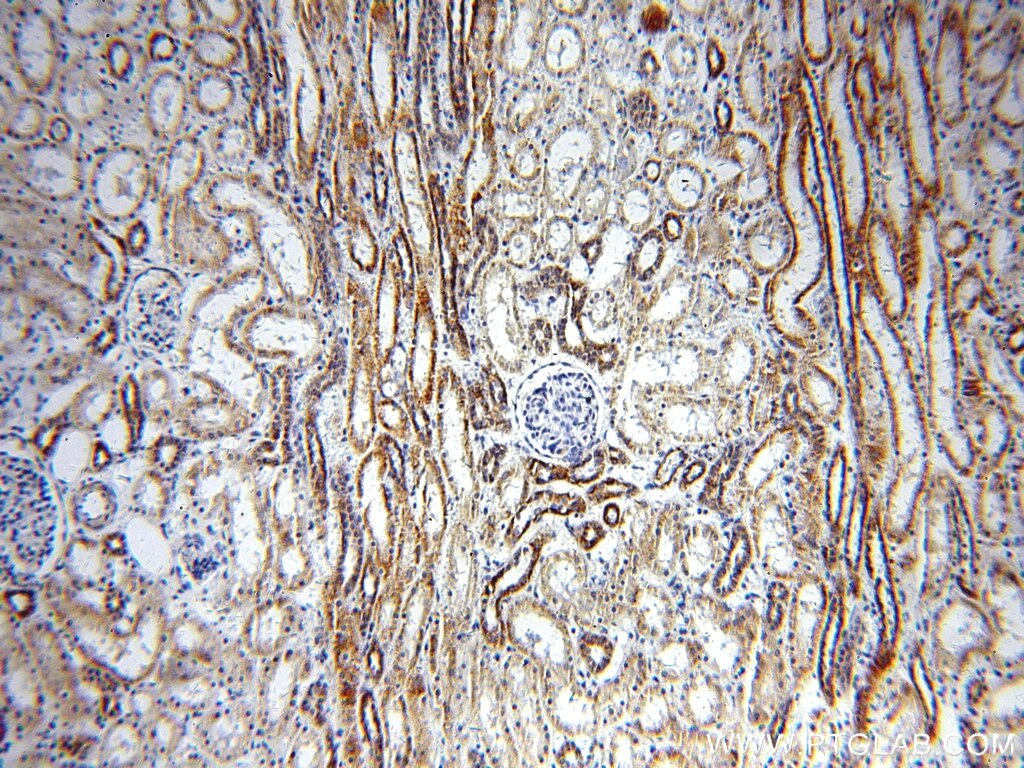
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Herzgewebe, humanes Nierengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:3000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
19549-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, ELISA TRAPPC9/NIBP und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | trafficking protein particle complex 9 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 139 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 56 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_031466 |
| Gene symbol | NIBP/Trappc9 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 83696 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
TRAPPC9, also named NIK- and IKBKB-binding protein (NIBP), is involved in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and directly interacts with IKK-beta and MAP3K14. TRAPPC9 functions as an activator of NF-kappa-B via increased phosphorylation of the IKK complex. TARPPC9 may also function in neuronal cells differentiation and defects in TRAPPC9 are the cause of mental retardation autosomal recessive type 13 (MRT13), which is characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptative behavior. TARPPC9 is a component of the multisubunit TRAPP (transport protein particle) complex and it may play a role in vesicular transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi.