- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
ACSS1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
ACSS1 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IP, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
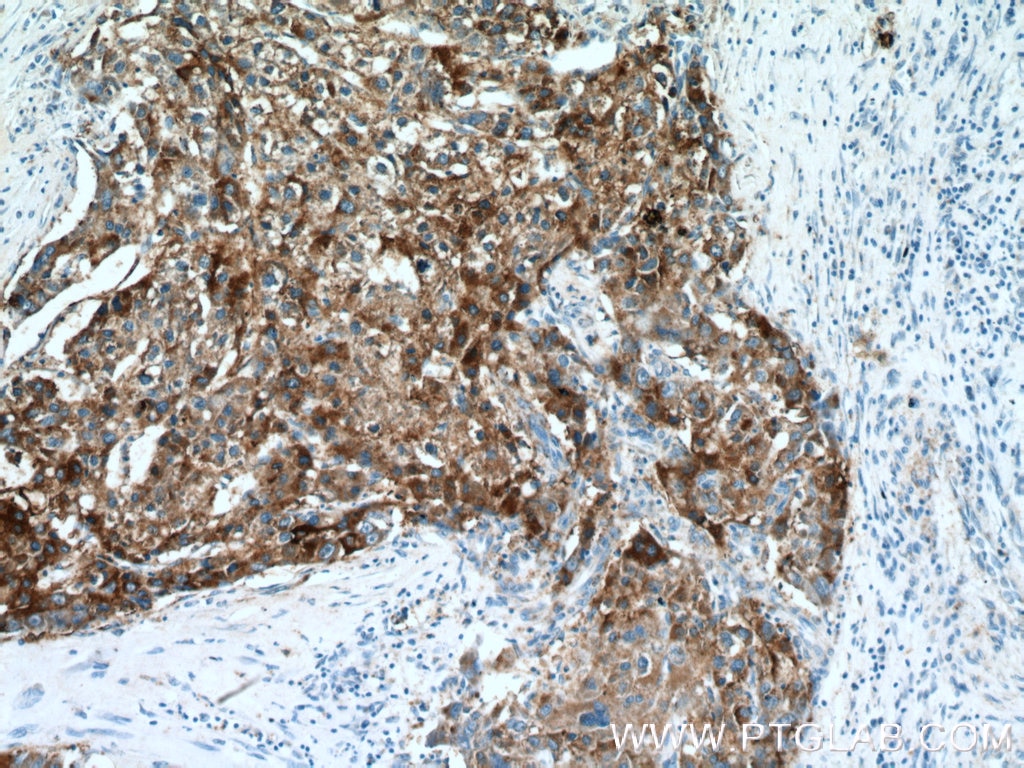
WB, IHC, IP, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 17138-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
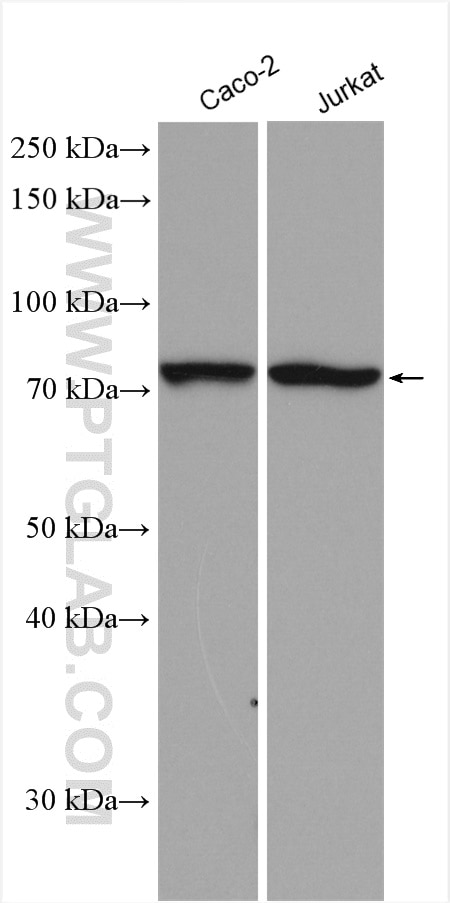
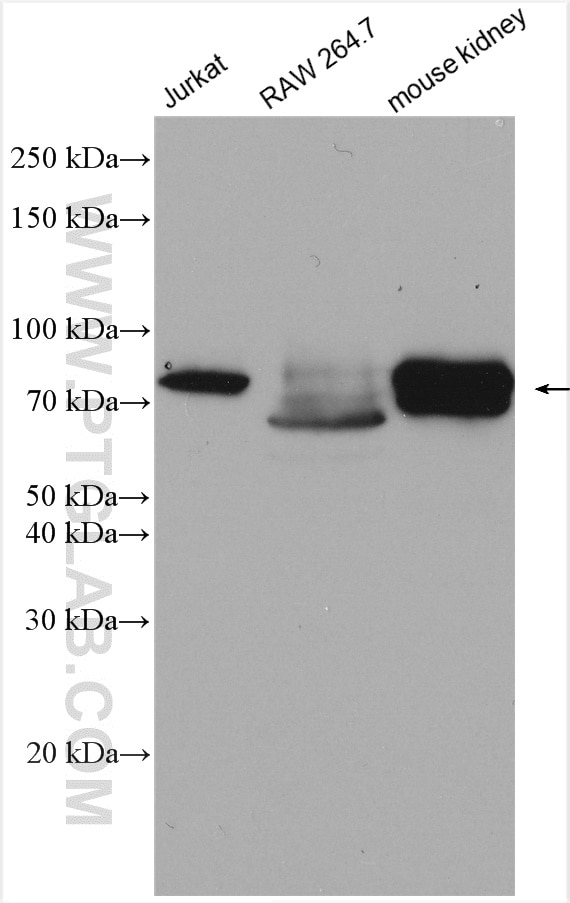
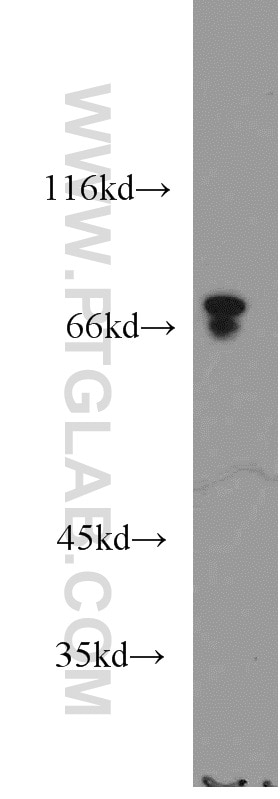
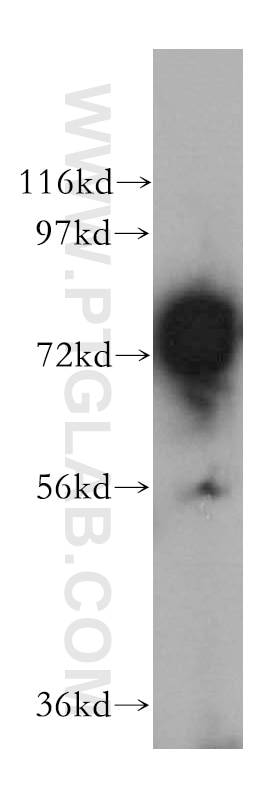
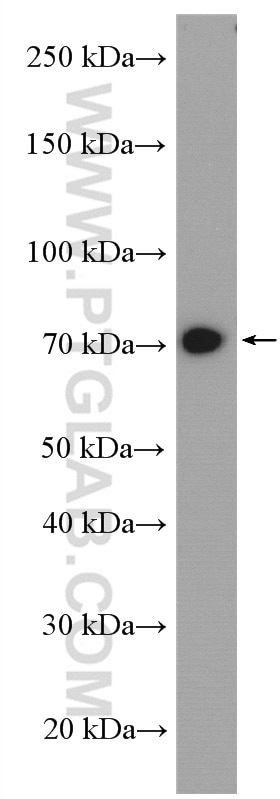
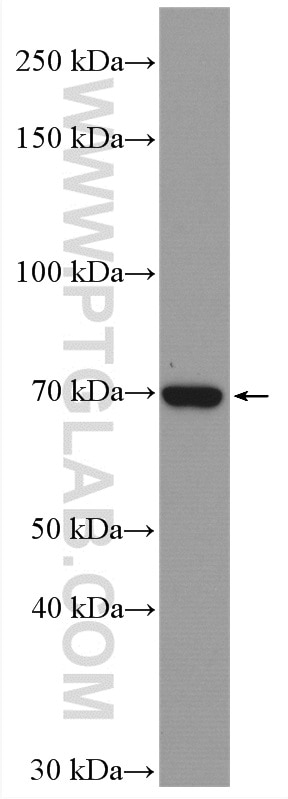
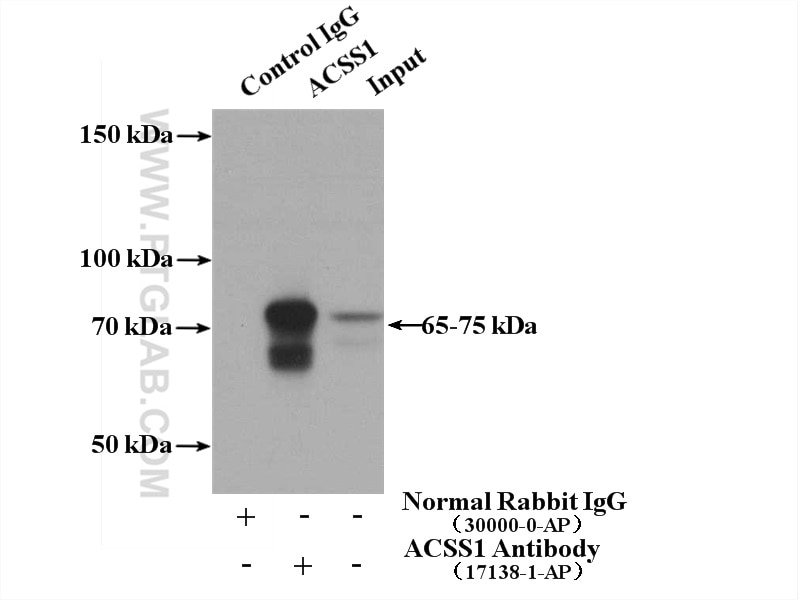
17138-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IP, Indirect ELISA ACSS1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | ACSS1 fusion protein Ag10896 |
| Vollständiger Name | acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family member 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 689 aa, 75 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 70-75 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC039261 |
| Gene symbol | ACSS1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 84532 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
The ACSS (acetyl-CoA synthetase) enzyme is the sole known mammalian enzyme that can catalyze the conversion of free acetate into acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). The three known isoforms of human ACSS are termed ACSS1, ACSS2, and ACSS3. The main substrate of ACSS1 and ACSS2 is acetate, while the preferential substrate of ACSS3 is propionate. Two acetate related enzymes, ACSS1(GeneID: 84532) and ACSS2 (GeneID:55902) difer in their tissue distribution and subcellular localization. On the one hand, as a mitochondrial matrix enzyme, ACSS1 is expressed mainly in cardiac and skeletal muscle as well as brown adipose tissue. On the other hand, as a nuclear and cytoplasmic enzyme, ACSS2 is strongly expressed in the liver, kidney and heart and moderately expressed in the brain and testis.ACSS2 participates in lipid synthesis and facilitates protein acetylation by generating acetyl-CoA, while ACSS1 is involved in acetate oxidation. The functional diferences in these enzymes involve energy production through the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Due to its more thorough utilization of intracellular acetate, ACSS2 is expressed in almost all cell types under diferent physiological conditions.