- Featured Product
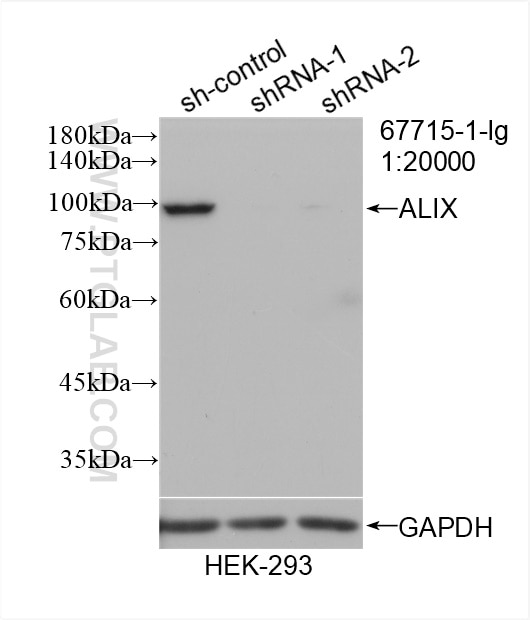
- KD/KO Validated
Alix Monoklonaler Antikörper
Alix Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1H9D9
Kat-Nr. : 67715-1-Ig
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
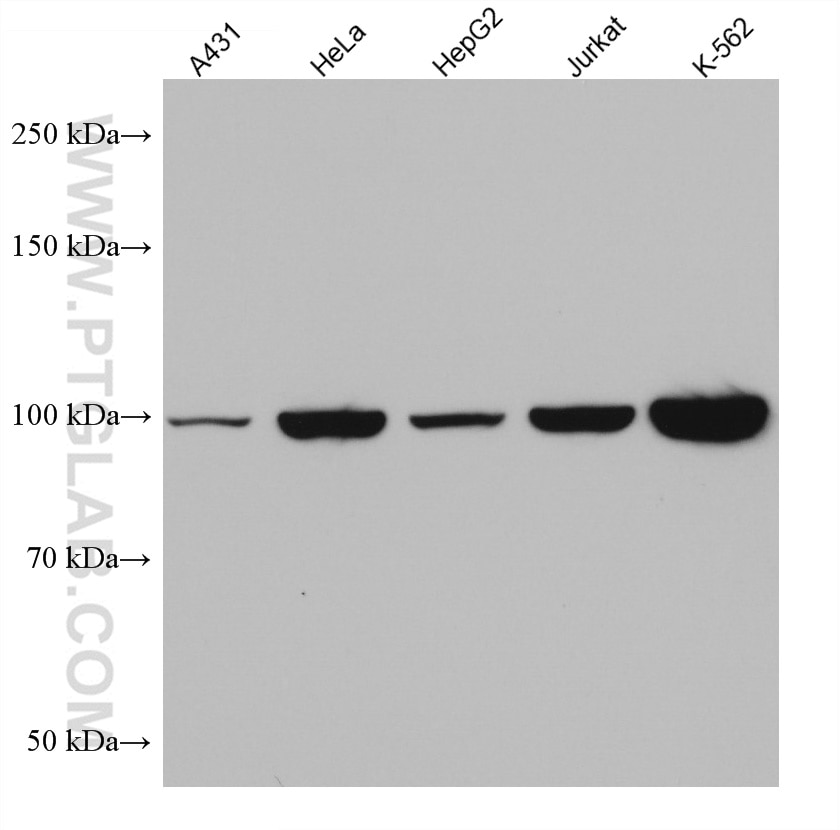
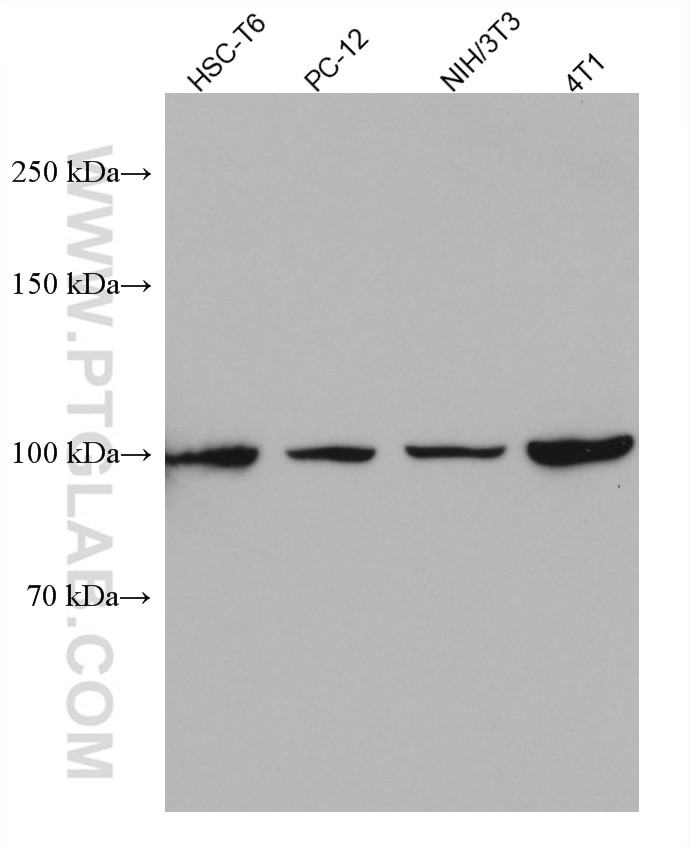
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HSC-T6 cells, 4T1-Zellen, A431-Zellen, HEK-293-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen, Jurkat-Zellen, K-562-Zellen, NIH/3T3-Zellen, PC-12-Zellen |
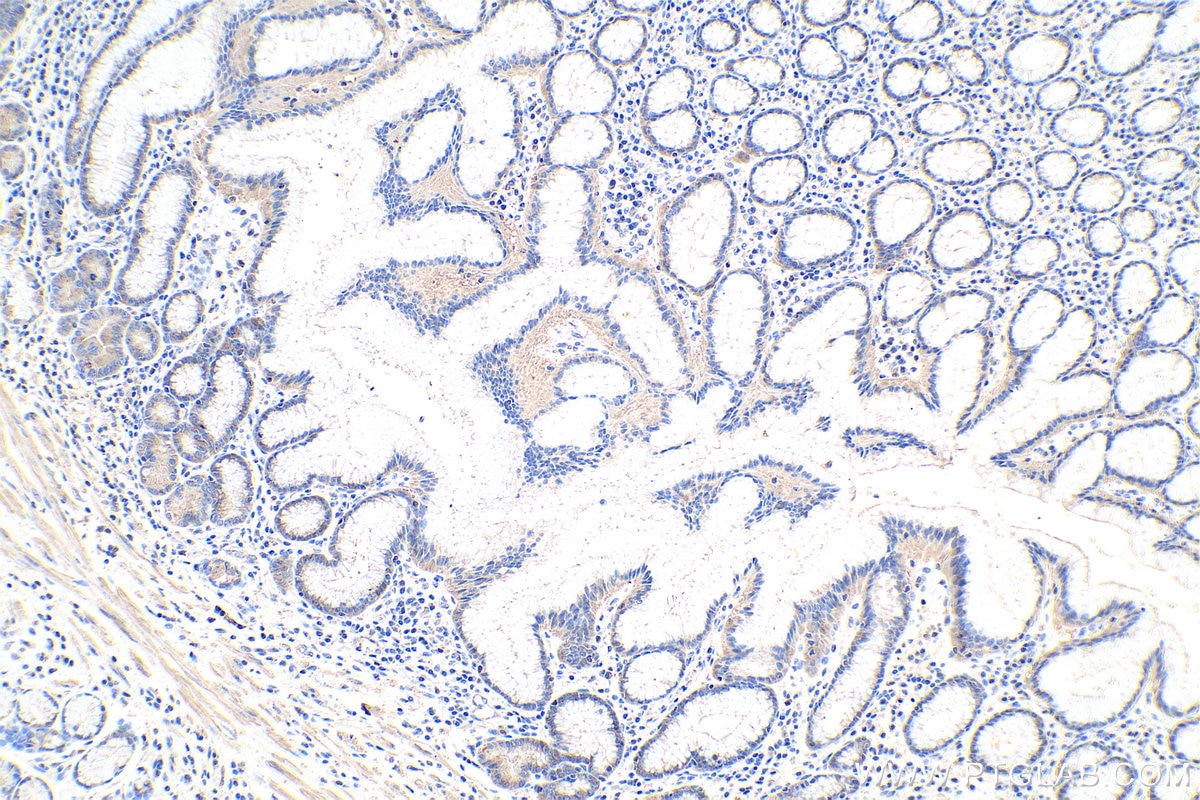
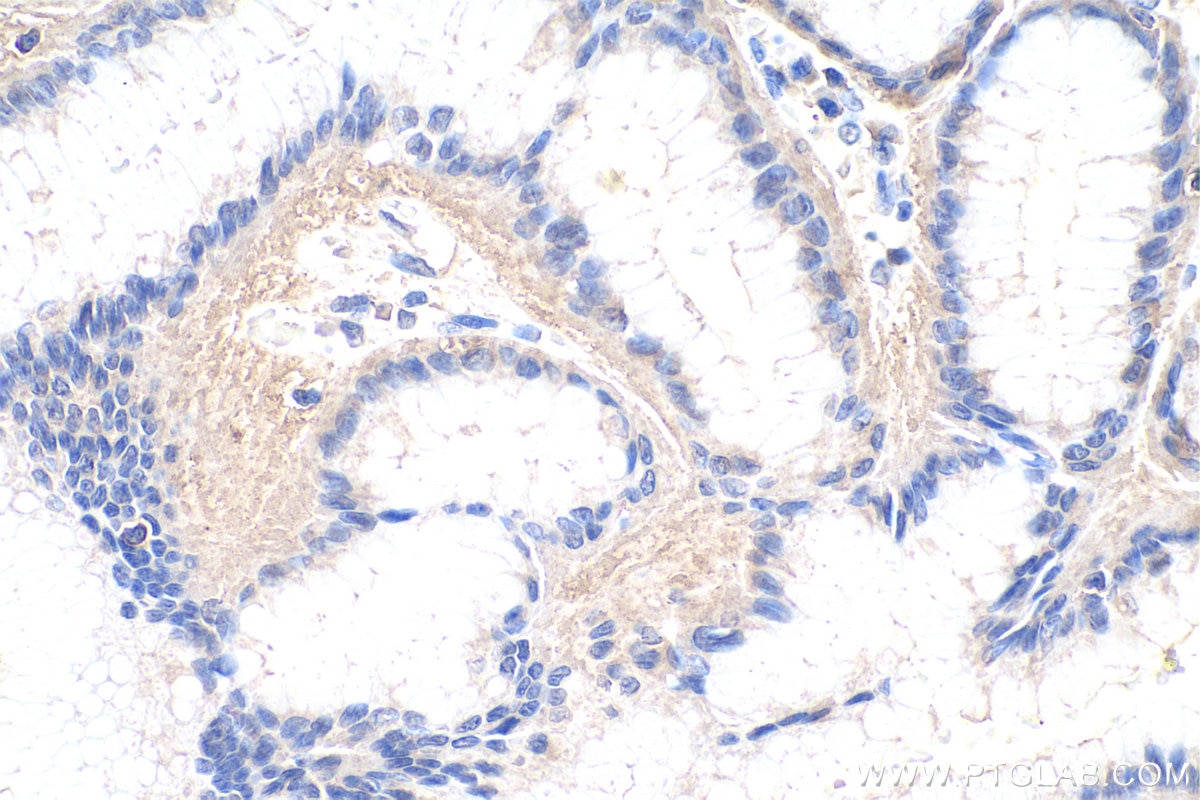
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Magenkrebsgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
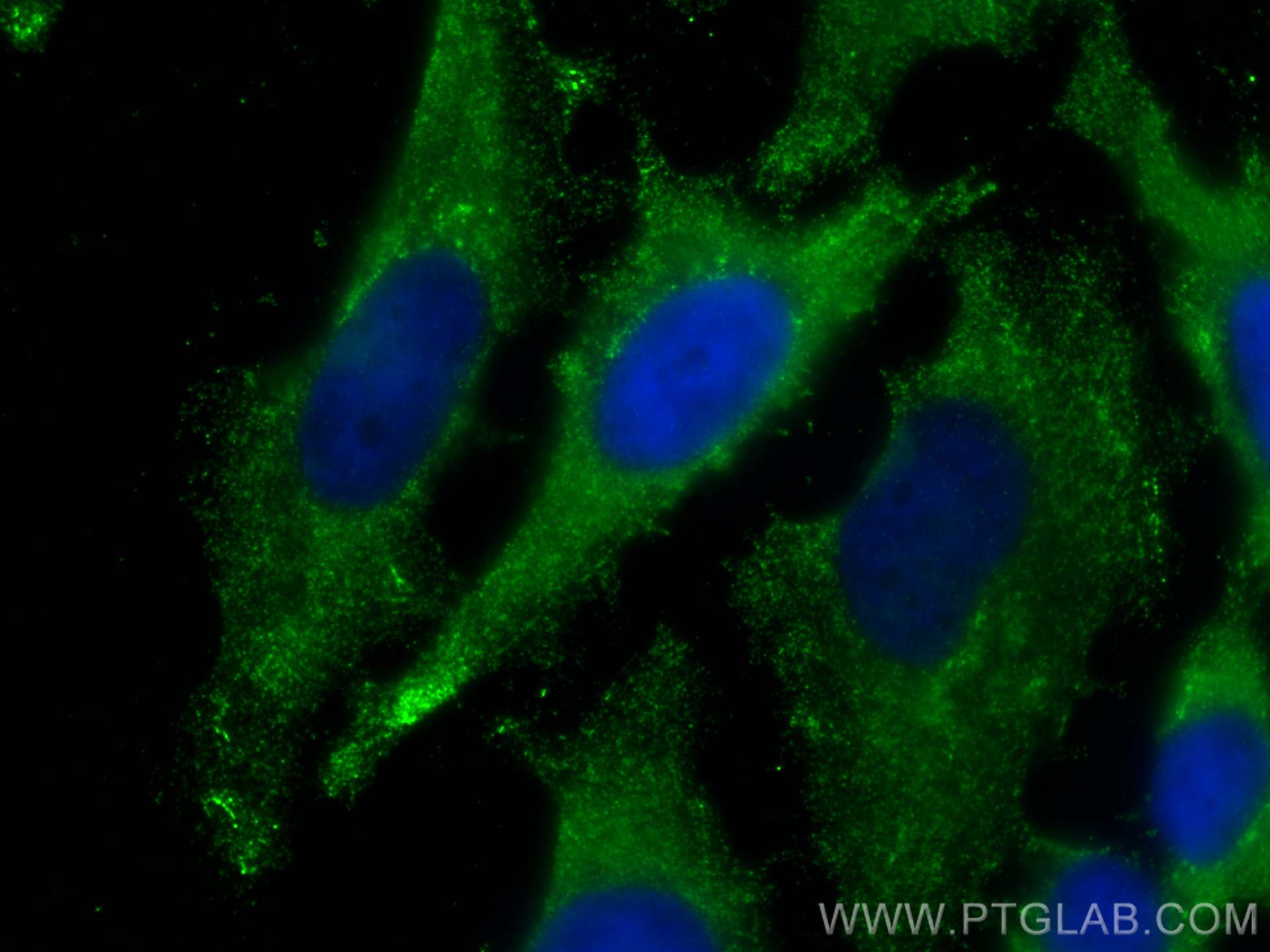
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HeLa-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:20000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:4000-1:16000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 16 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
67715-1-Ig bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA Alix und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Affe, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Alix fusion protein Ag30437 |
| Vollständiger Name | programmed cell death 6 interacting protein |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 868 aa, 96 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 100 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC020066 |
| Gene symbol | Alix |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10015 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
ALG-2-interacting protein 1 (ALIX), also known as AIP1 or Hp95, is encoded by PDCD6IP gene and is involved in cell death through mechanisms involving its binding partner ALG-2 (apoptosis-linked gene-2). ALG-2 is a 22-kDa protein containing five serially repetitive EF-hand structures and is defined as a regulator of calcium-induced apoptosis following endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. ALIX interacts with ALG-2 through its C-terminal proline-rich region and participates in formation of multivesicular bodies. Recent finding suggest that ALIX is a critical component of caspase 9 activation and apoptosis triggered by calcium.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Alix antibody 67715-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Alix antibody 67715-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for Alix antibody 67715-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Stem Cell Res Ther Tremella polysaccharide microneedles loaded with magnetic dental pulp stem cell intracellular vesicles used for androgenic alopecia | ||
Environ Pollut TDCPP Disrupts ALG-2/ALIX-Mediated ESCRT-III Recruitment: Implications for Lysosomal Membrane Repair and Neurotoxicity | ||
Cell Mol Biol Lett Downregulation of exosomal miR-7-5p promotes breast cancer migration and invasion by targeting RYK and participating in the atypical WNT signalling pathway | ||
J Thromb Haemost Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote venous thrombosis through podoplanin/CLEC-2 interaction in podoplanin-negative lung cancer mouse model | ||
Psychiatry Clin Neurosci Human in vivo evidence of reduced astrocyte activation and neuroinflammation in patients with treatment-resistant depression following electroconvulsive therapy | ||
J Microsc A method for extraction of exosomes from breast tumour cells and characterisation by transmission electron microscopy |