- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
Beta Arrestin 1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
Beta Arrestin 1 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 15361-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
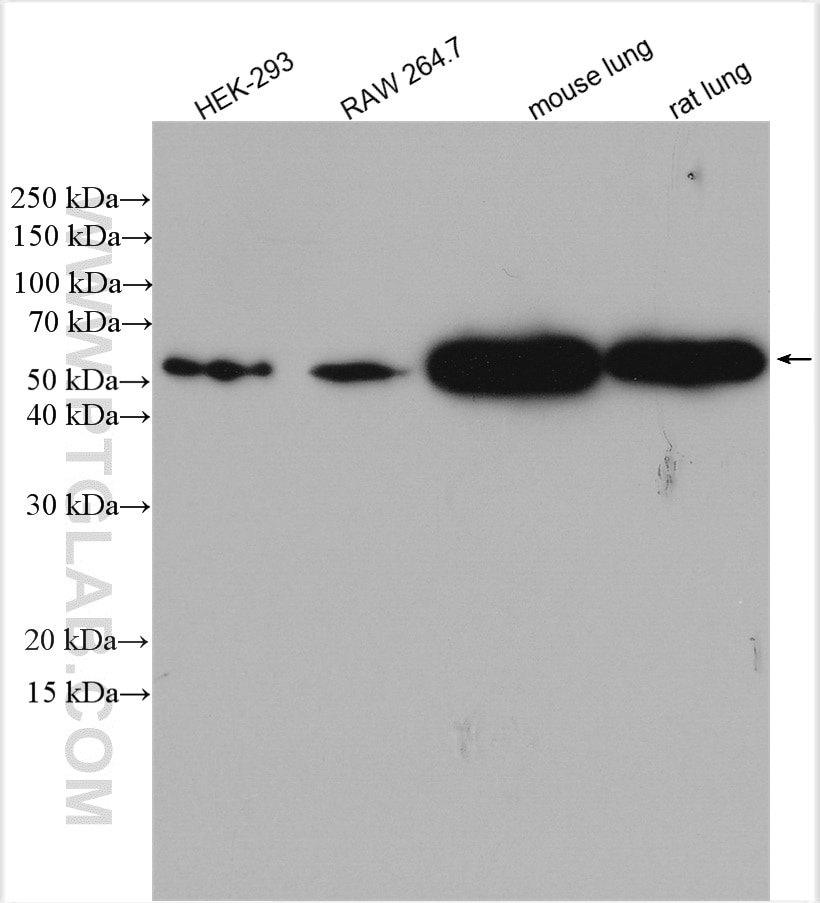
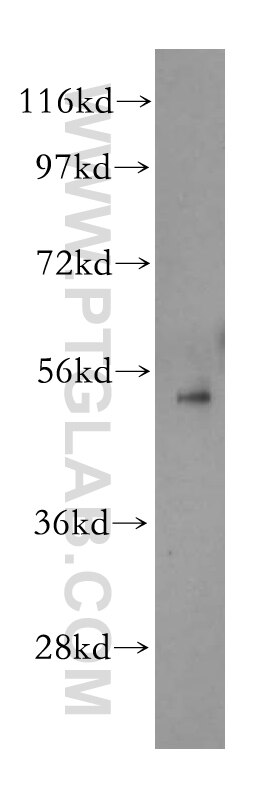
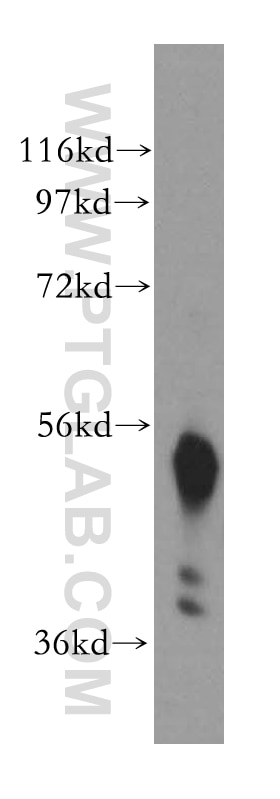
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HEK-293-Zellen, A549-Zellen, Mauslungengewebe, Rattenlungengewebe, RAW 264.7-Zellen, U-937-Zellen |
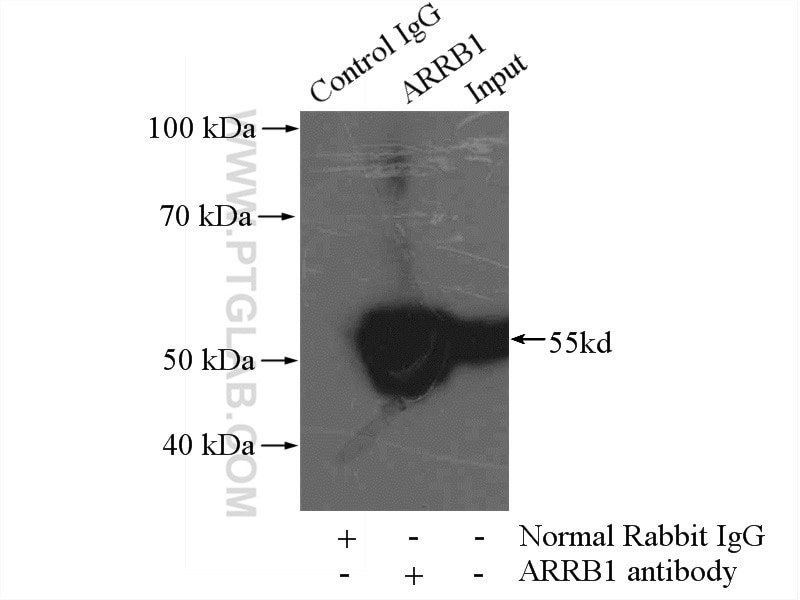
| Erfolgreiche IP | Mauslungengewebe |
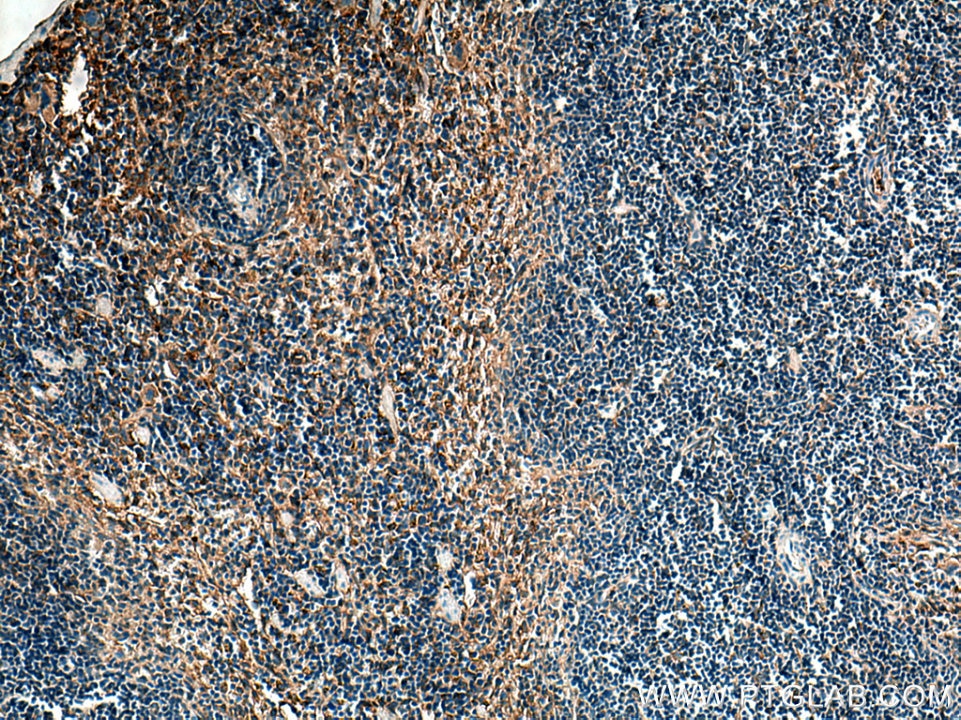
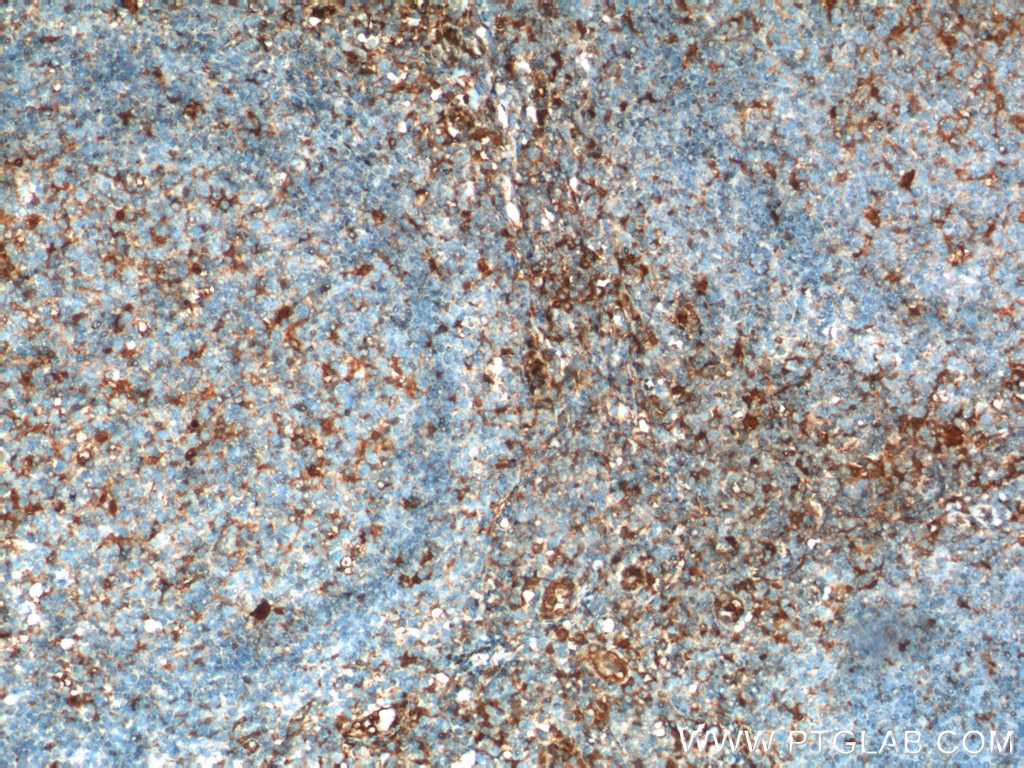
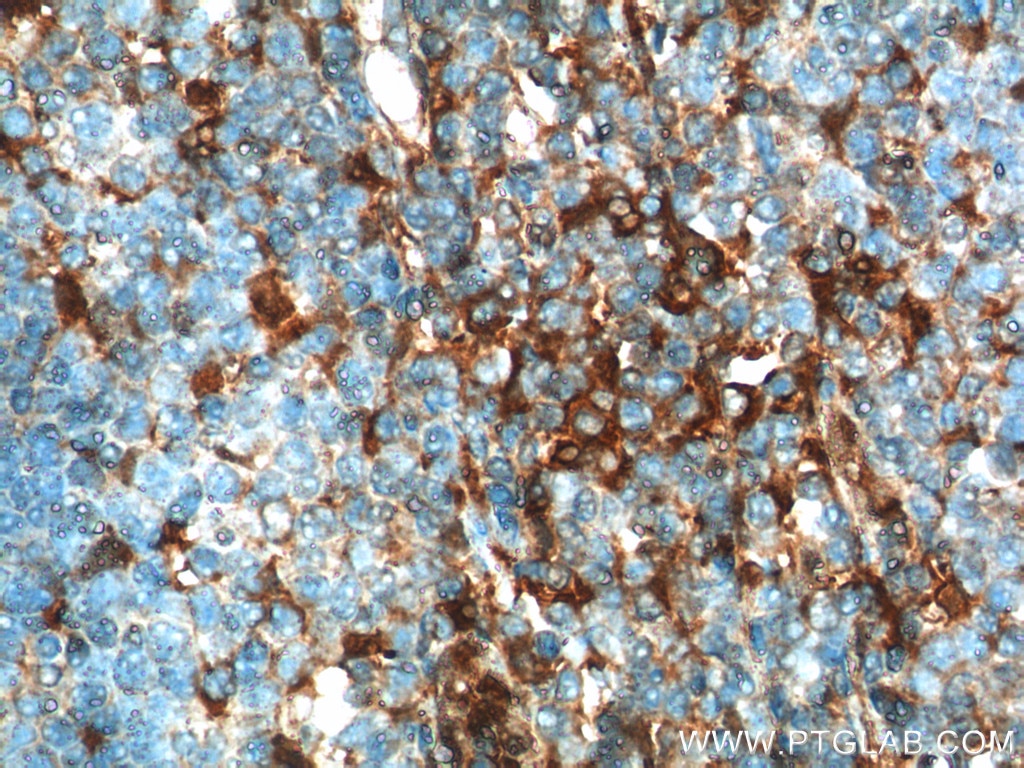
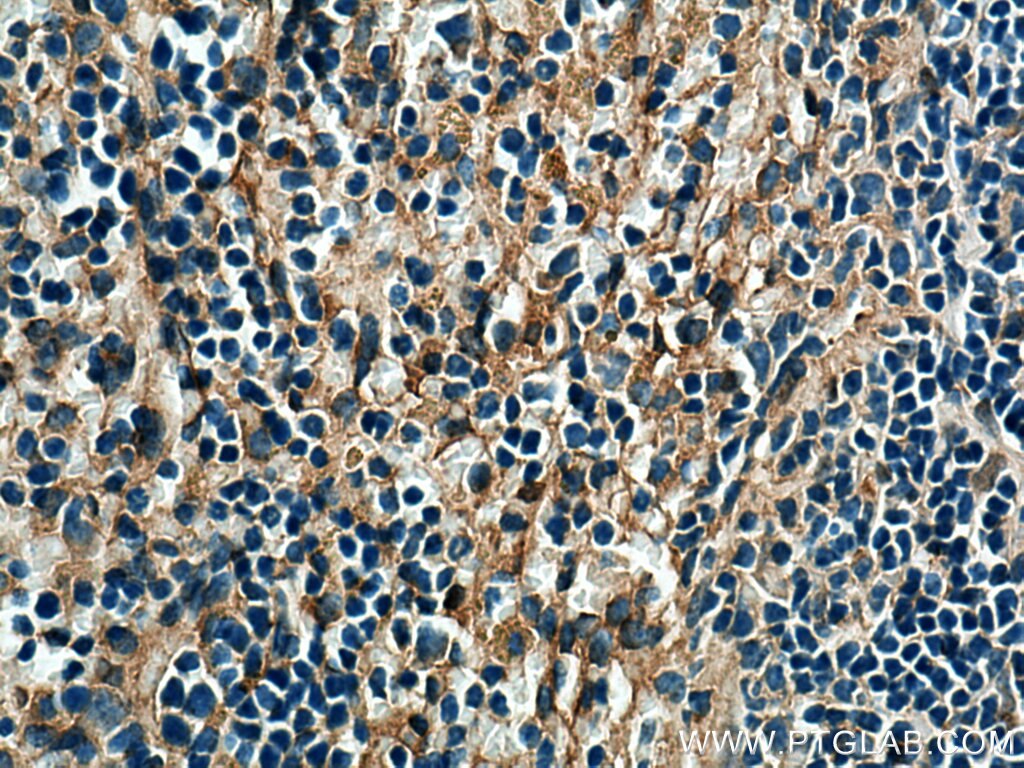
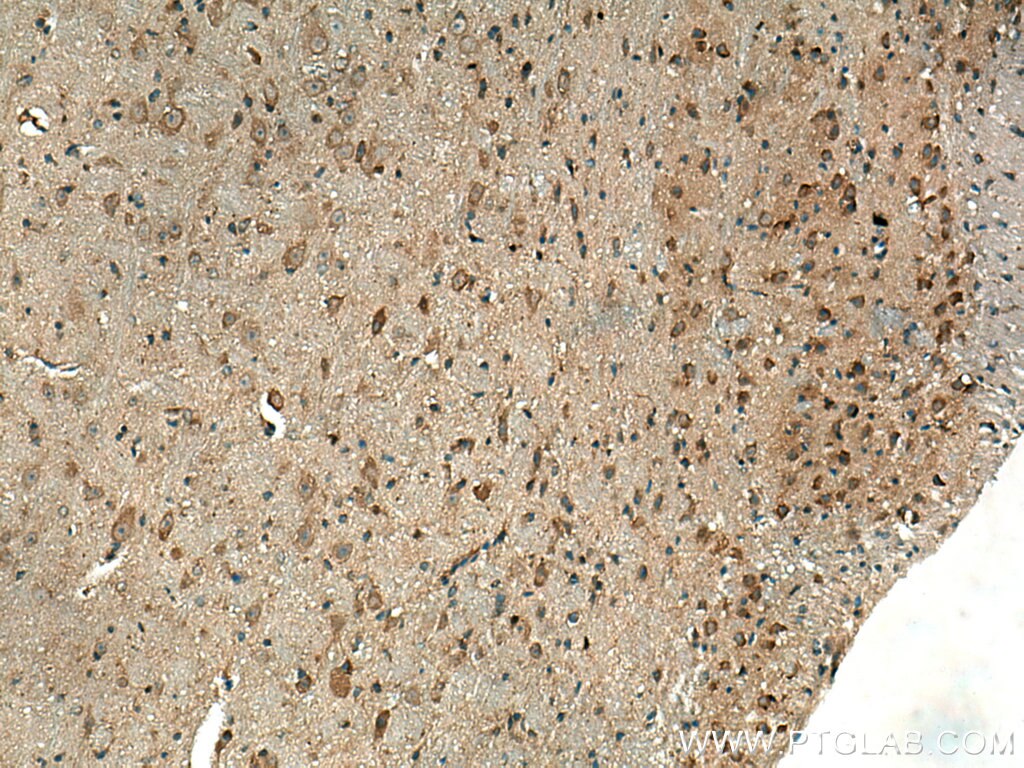
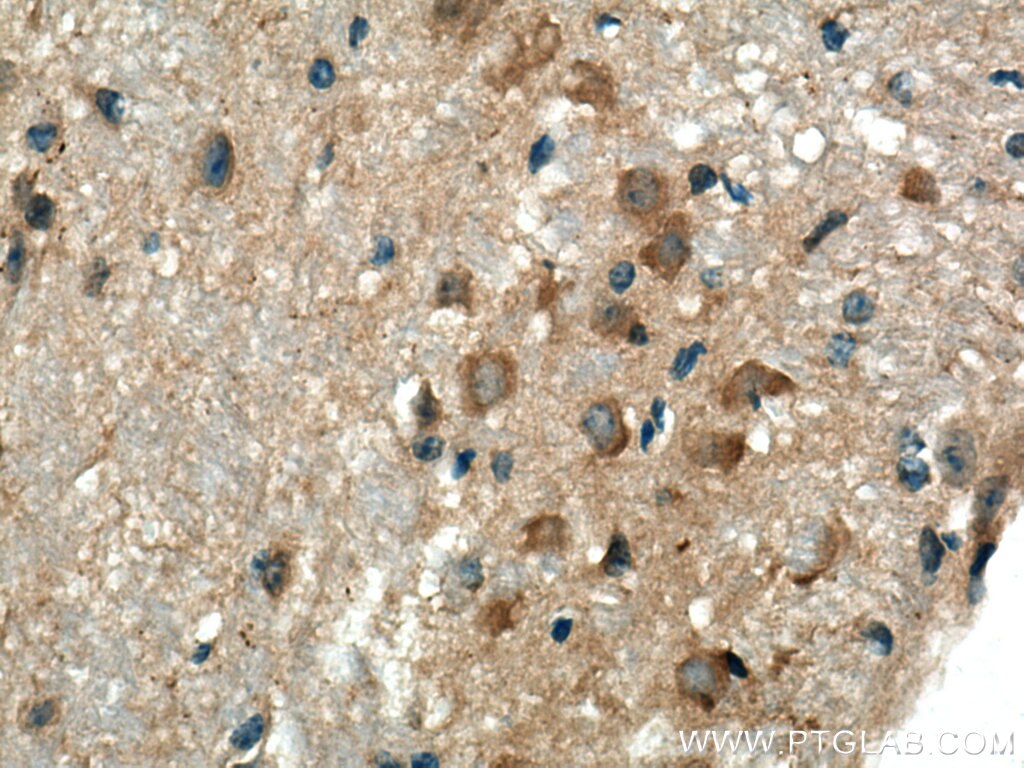
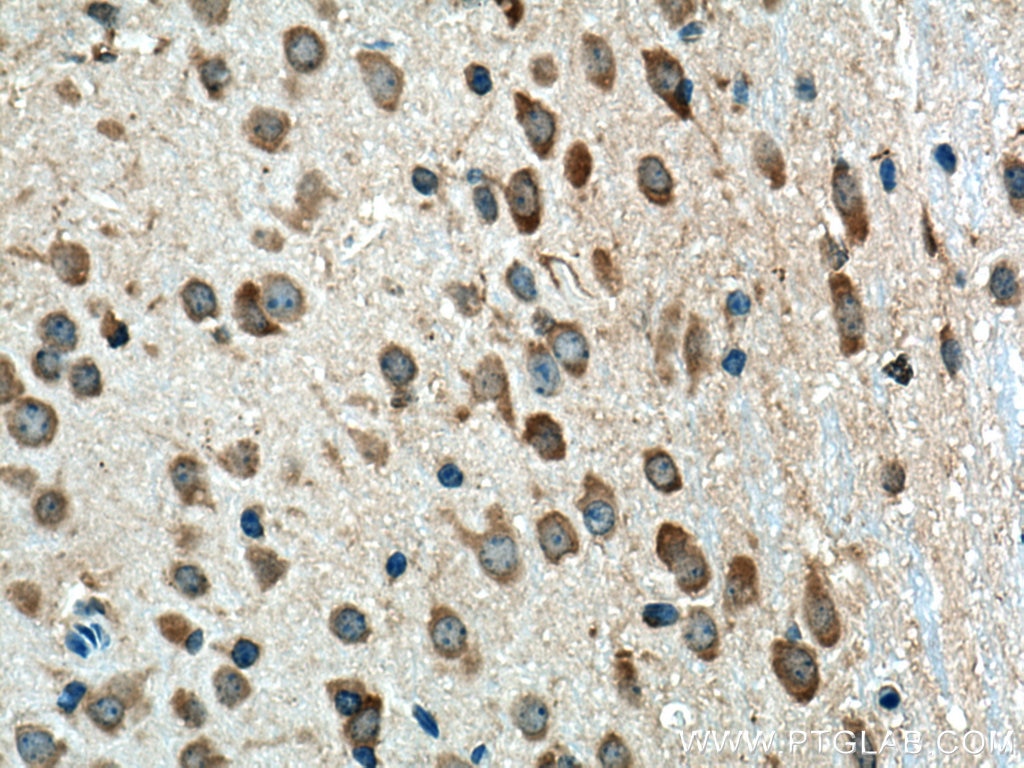
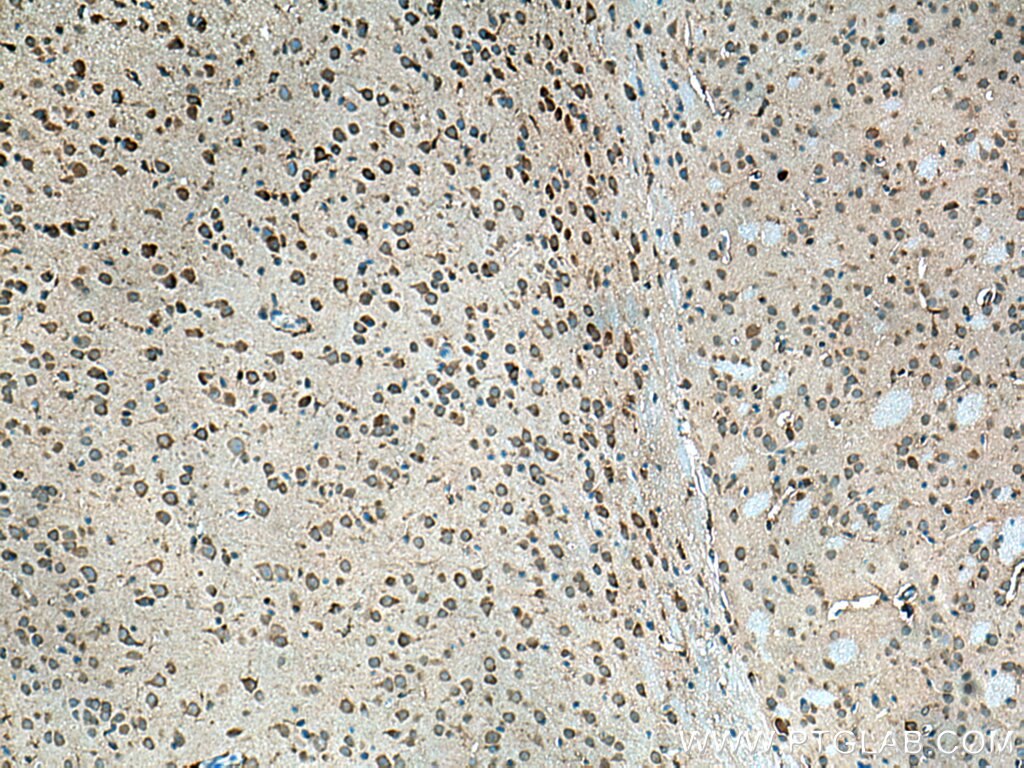
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Tonsillitisgewebe, Maushirngewebe, Maus-Cerebellum-Gewebe, Mausmilzgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
15361-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA Beta Arrestin 1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Beta Arrestin 1 fusion protein Ag7608 |
| Vollständiger Name | arrestin, beta 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 47 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 47-55 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC003636 |
| Gene symbol | Beta Arrestin 1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 408 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
β-Arrestins (ARRBs), the best known regulators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling, are versatile and multifunctional adapter proteins that regulate diverse cellular functions, including cell growth, apoptosis and immune responses. Overexpression of beta Arrestin 1 has been found in various cancers, indicating it as a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Recently expression of ARRB1 in saliva has been identified as a candidate circadian biomarker. ARRB1 migrated as a doublet of two bands of 45 and 55 kDa (PMID:28947386).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Beta Arrestin 1 antibody 15361-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Beta Arrestin 1 antibody 15361-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IP protocol for Beta Arrestin 1 antibody 15361-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab Autonomous sensing of the insulin peptide by an olfactory G protein-coupled receptor modulates glucose metabolism.
| ||
J Cell Biol BBSome trains remove activated GPCRs from cilia by enabling passage through the transition zone. | ||
Cell Death Dis β-Arrestins promote podocyte injury by inhibition of autophagy in diabetic nephropathy. | ||
J Biol Chem An ionic lock and a hydrophobic zipper mediate the coupling between an insect pheromone receptor BmOR3 and downstream effectors.
| ||
PLoS One Cell Survival Following Radiation Exposure Requires miR-525-3p Mediated Suppression of ARRB1 and TXN1. | ||
Oncol Rep Blue light irradiation inhibits the growth of colon cancer and activation of cancer‑associated fibroblasts. |