CCDC67 Polyklonaler Antikörper
CCDC67 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 24579-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
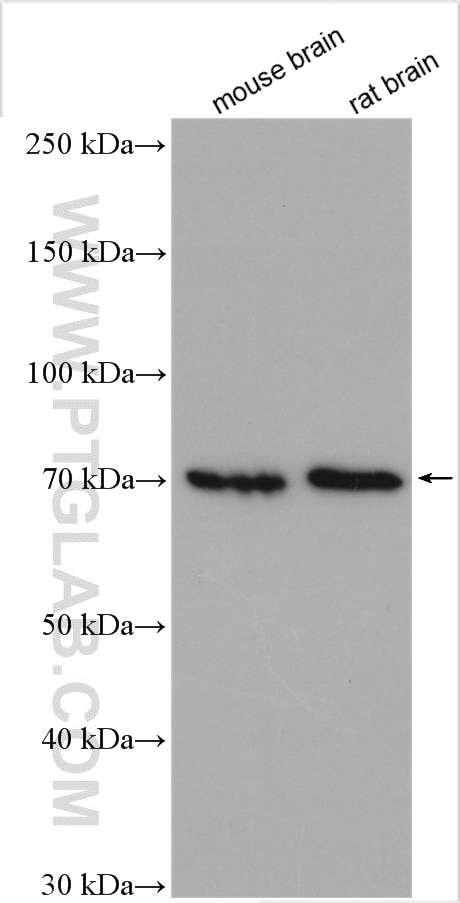
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Maushirngewebe, Rattenhirngewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
Produktinformation
24579-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA CCDC67 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CCDC67 fusion protein Ag18358 |
| Vollständiger Name | coiled-coil domain containing 67 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 604 aa, 71 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 71 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC031247 |
| Gene symbol | CCDC67 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 159989 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CCDC67 antibody 24579-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun CDC20B is required for deuterosome-mediated centriole production in multiciliated cells. | ||
Development Novel dynamics of human mucociliary differentiation revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing of nasal epithelial cultures. | ||
Biol Open Biophysical and biochemical properties of Deup1 self-assemblies: a potential driver for deuterosome formation during multiciliogenesis. |