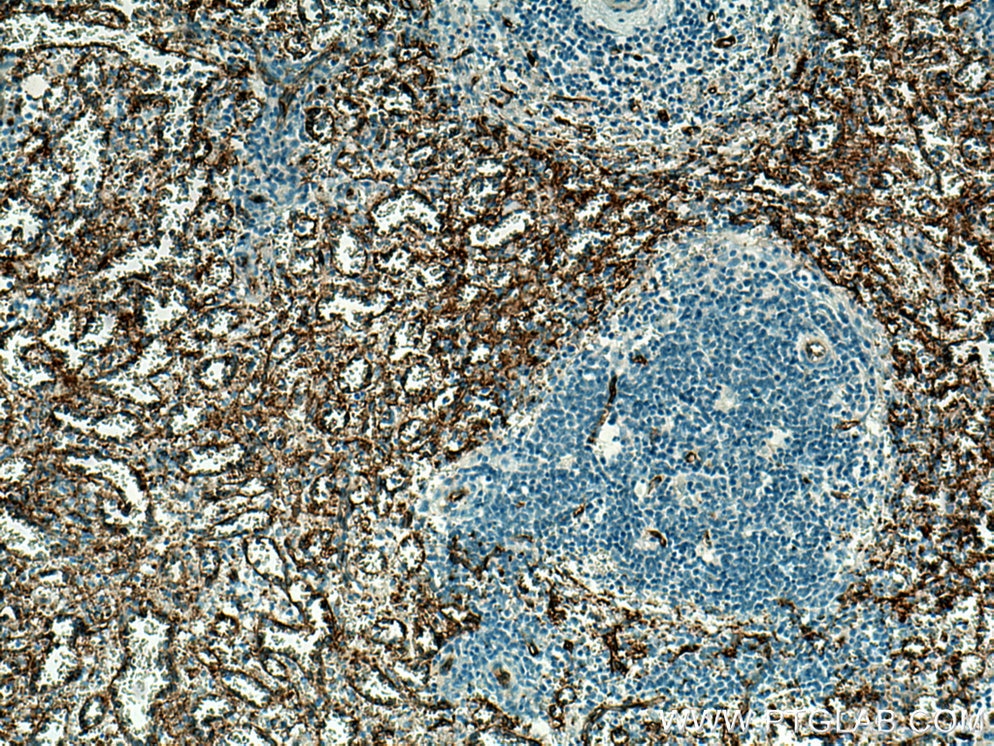
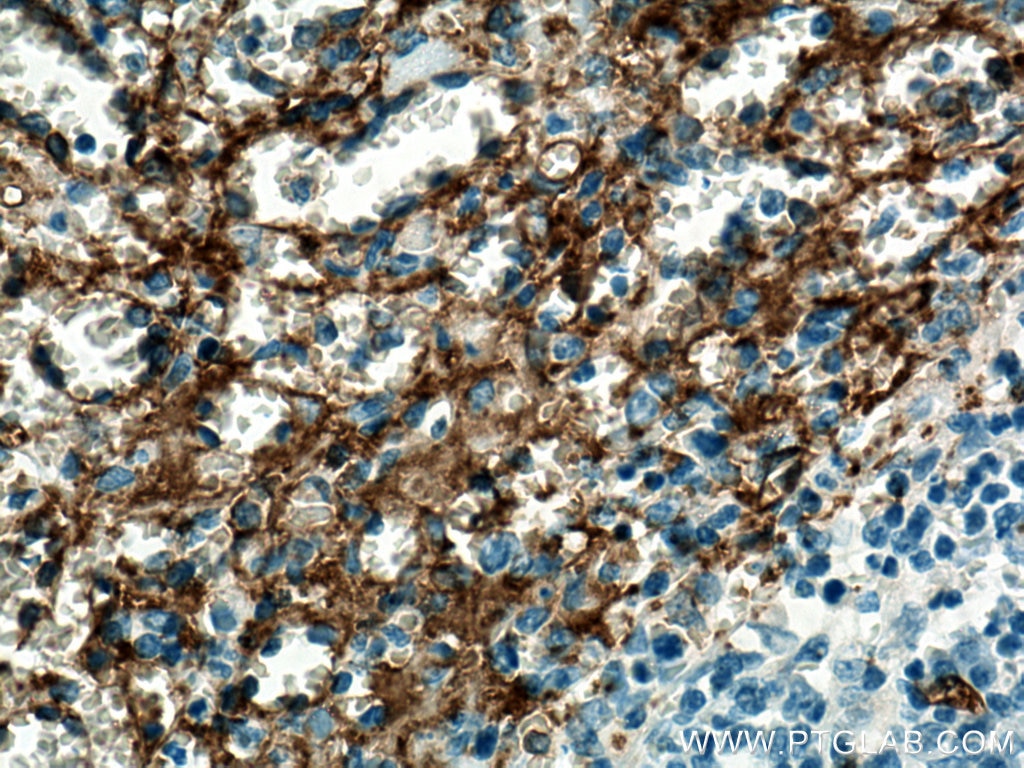
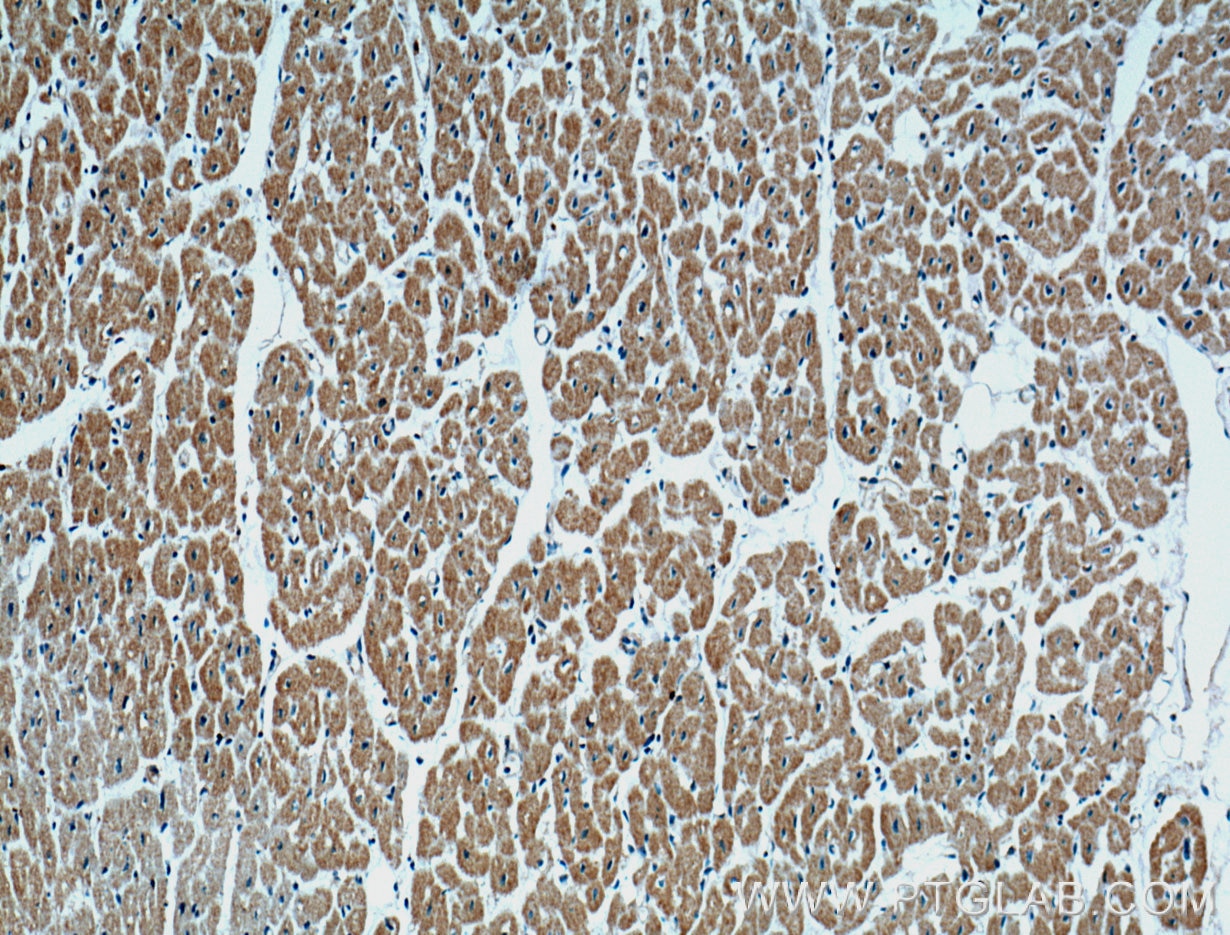
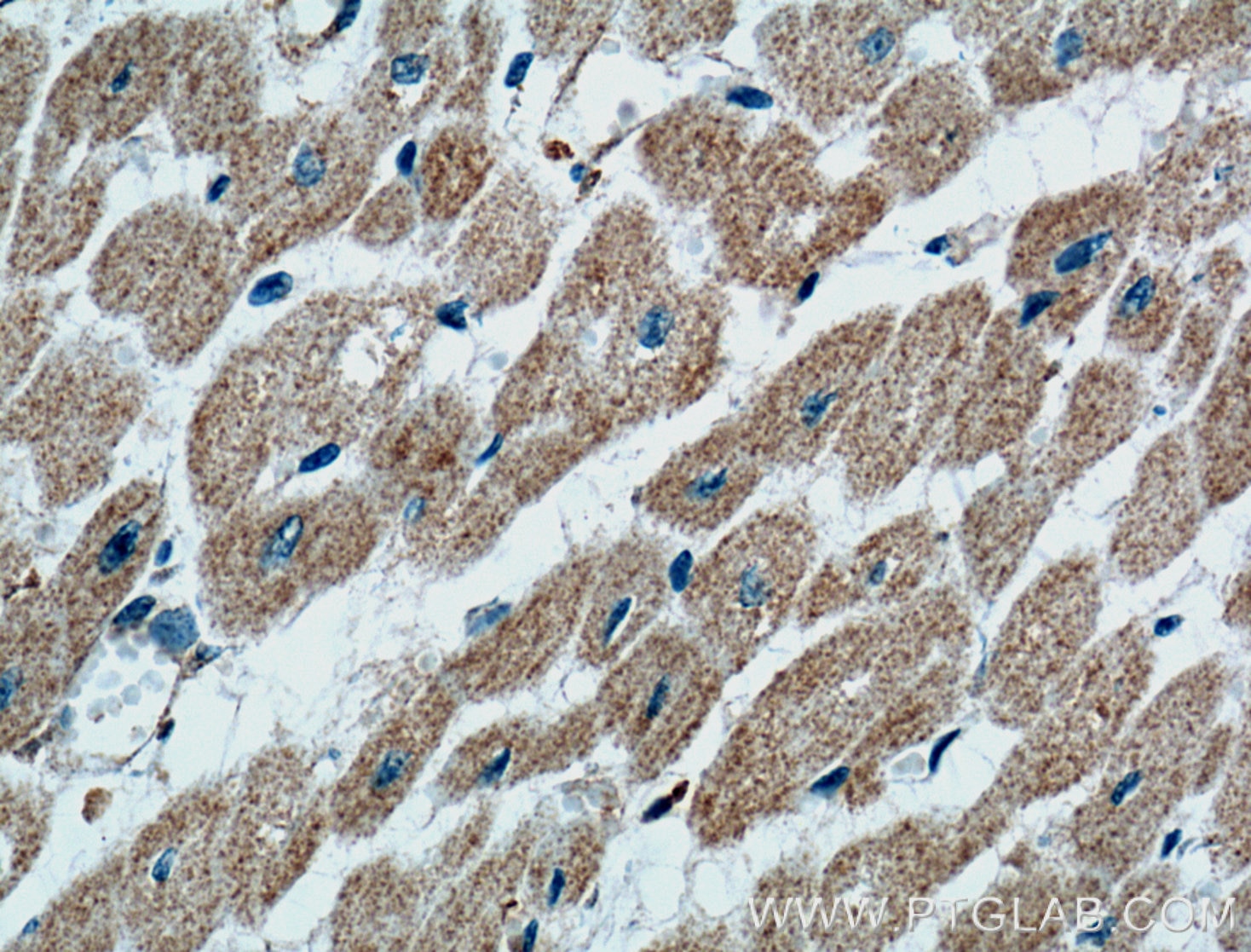
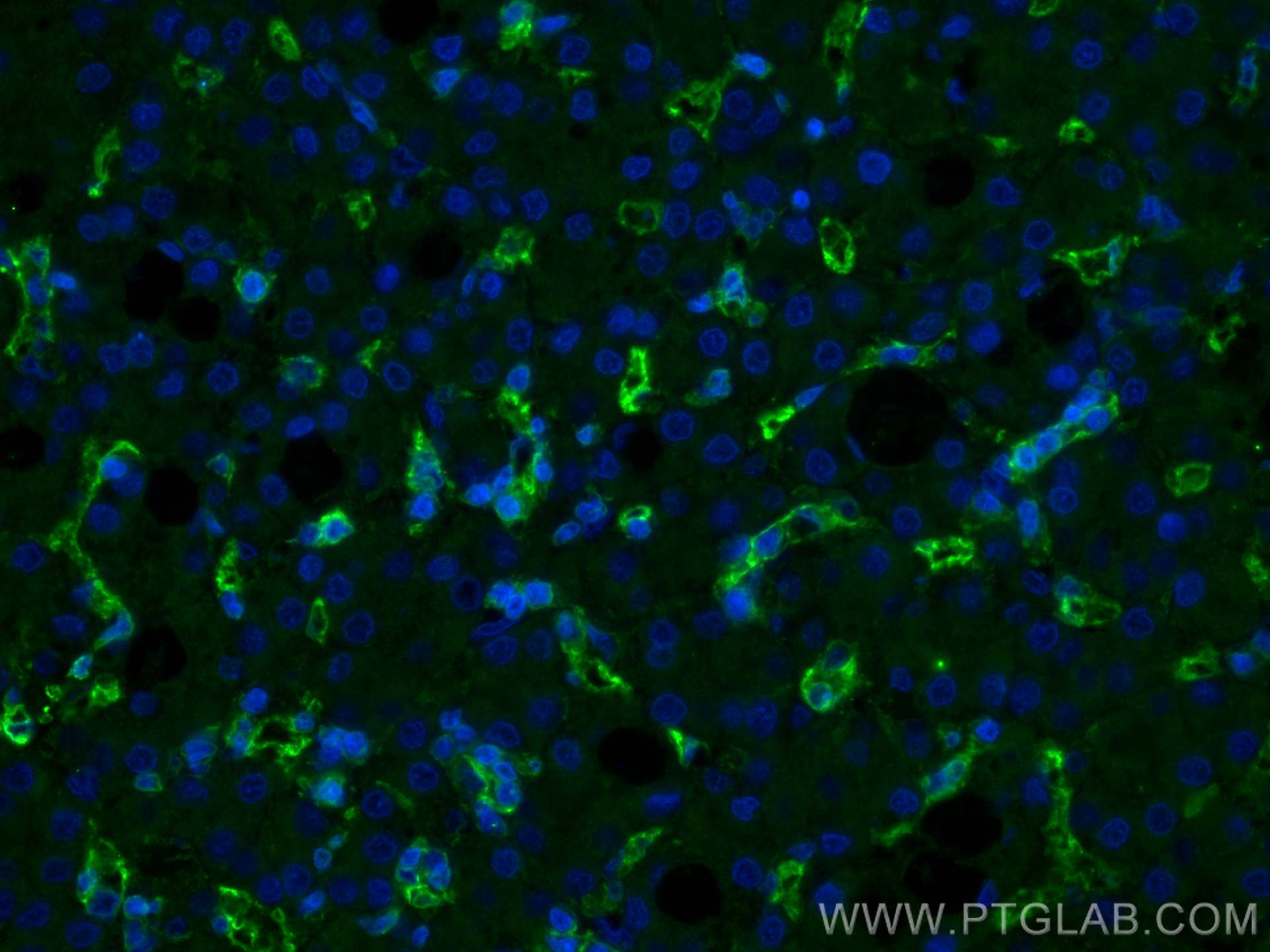
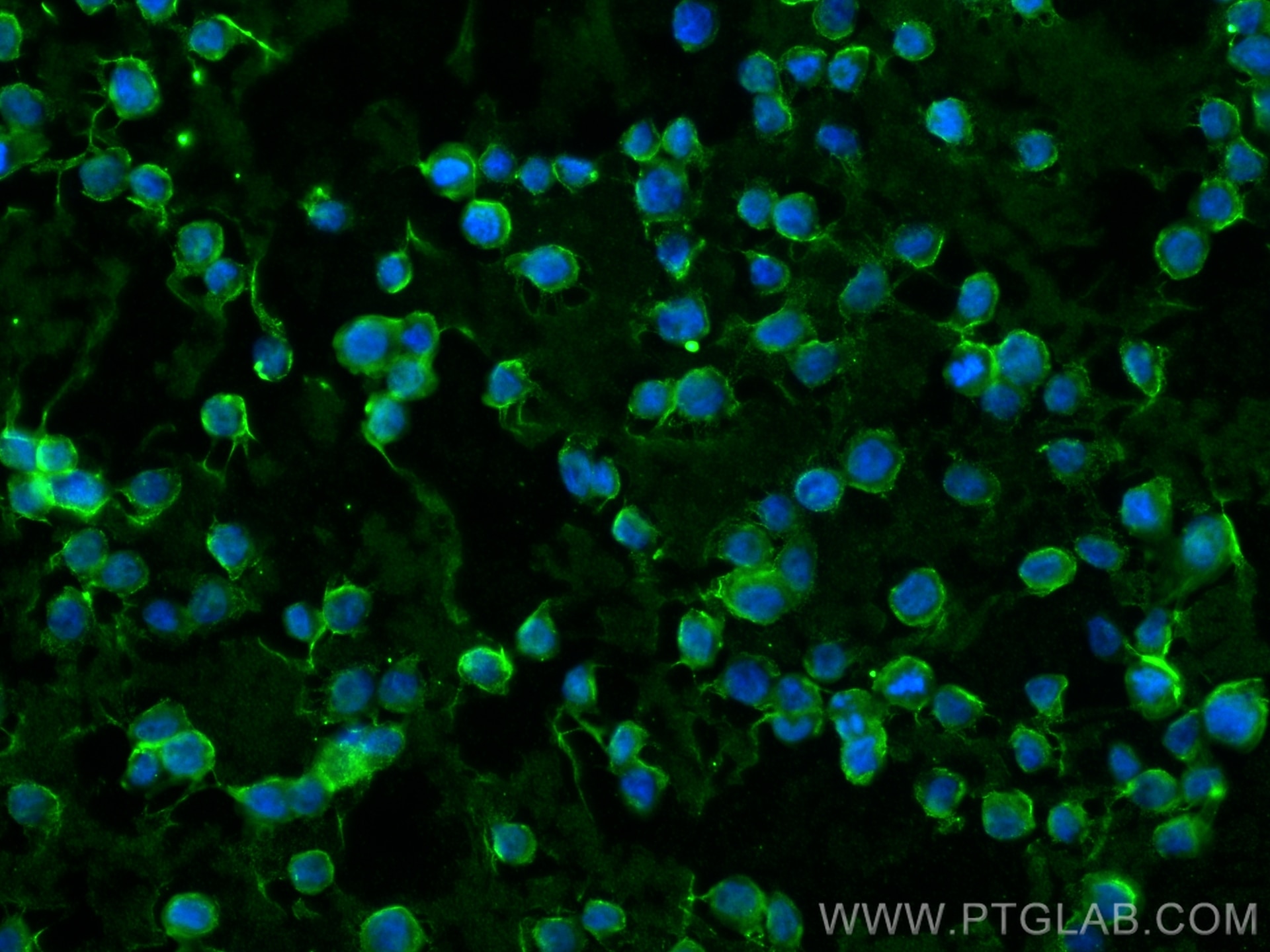
CD36 Monoklonaler Antikörper
CD36 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1A8C5
Kat-Nr. : 66395-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
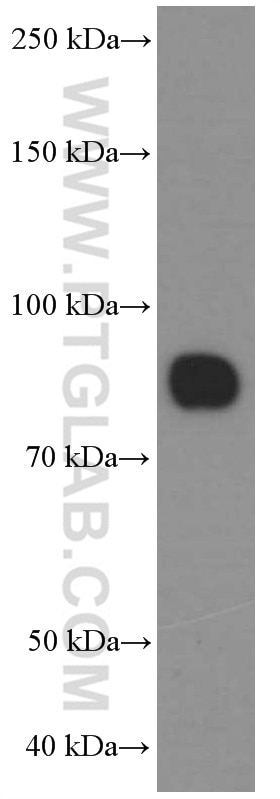
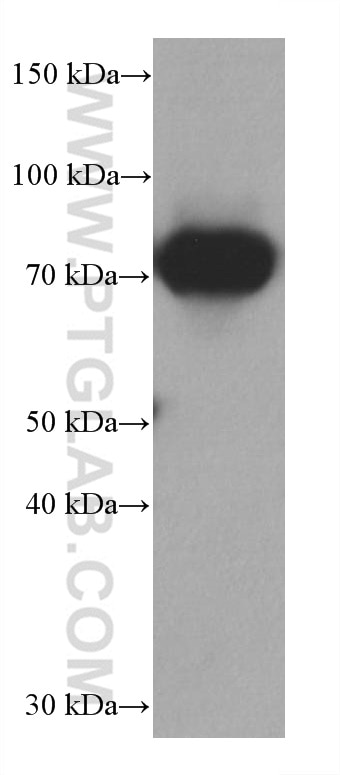
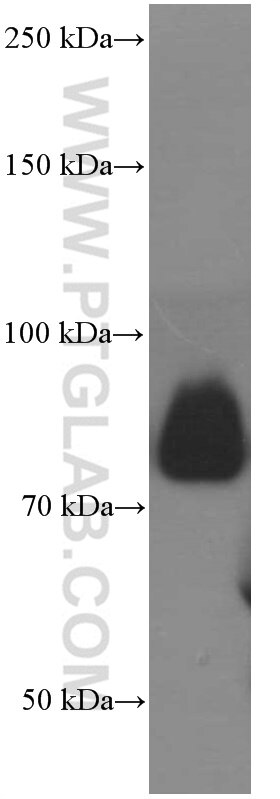
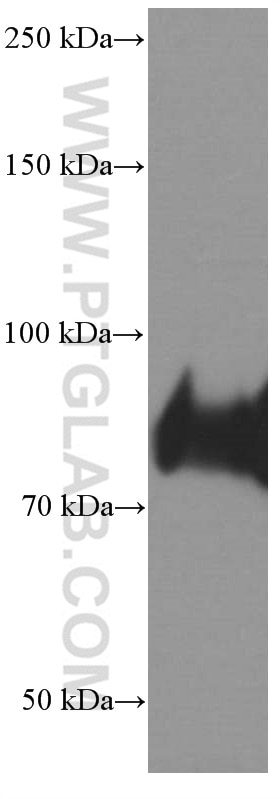
66395-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA CD36 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CD36 fusion protein Ag13541 |
| Vollständiger Name | CD36 molecule (thrombospondin receptor) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 472 aa, 53 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 88 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC008406 |
| Gene symbol | CD36 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 948 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Function
CD36, also known as platelet glycoprotein 4, is an integral membrane glycoprotein that acts as a scavenger receptor. CD36 can bind to multiple ligands, including thrombospondin-1, collagen, oxidized phospholipids, oxidized low-density lipoprotein, and long-chain fatty acids. CD36 can also bind to erythrocytes parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum and apoptotic cells. CD36 mediates different biological processes, acting as a signaling hub in angiogenesis, inflammatory response, and fatty acid metabolism.
Tissue specificity
CD36 is present on the surface of various cells types, such as adipocytes, monocytes, macrophages, platelets, microvascular endothelial cells, dendritic cells, and hematopoietic precursors of red cells.
Involvement in disease
-
Mutations in CD36 can give rise to platelet glycoprotein IV deficiency, a type of macrothrombocytopenia.
-
Polymorphisms in CD36 can increase susceptibility to malaria.
-
AAGIC haplotype at the CD36 locus increases the risk of coronary heart disease.
-
Disruption of CD36-dependent pathways and certain SNPs in the CD36 gene are attributed to impaired fatty acid metabolism, glucose intolerance, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, diabetes, and cardiomyopathy.
Isoforms
Apart from the full-length protein (isoform 1), one additional shorter isoform has been reported (PMID: 7509795). Other alternative isoforms have also been detected on the mRNA level (PMID: 17673938).
Post-translational modifications
The extracellular domain of CD36 is extensively glycosylated. Glycosylation is needed for the transport of CD36 to the plasma membrane, as well as mediating recognition and binding to ligands. Cytoplasmic tails of transmembrane domains can be phosphorylated and play a role in signal transduction. Intracellular domains can be additionally acetylated, ubiquitinated, and palmitoylated (PMID: 28919632).
Cellular localization
CD36 is present on the cell surface.