CD40 Rekombinanter Antikörper
CD40 Rekombinant Antikörper für WB, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
Maus
Anwendung
WB, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
240874B2
Kat-Nr. : 83972-5-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
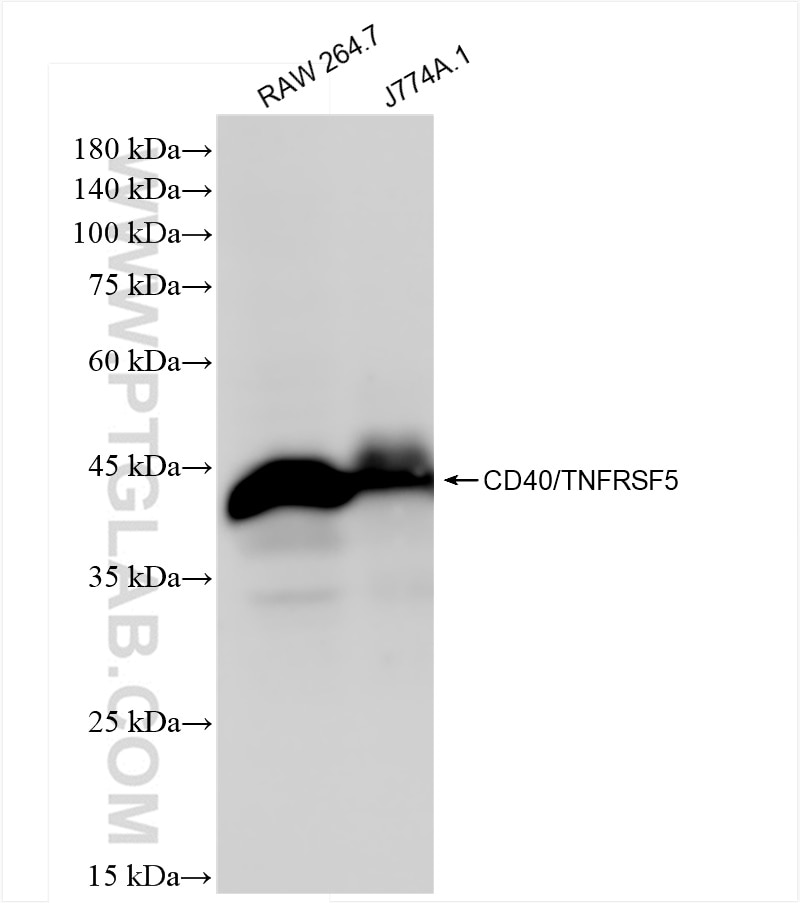
83972-5-PBS bindet in WB, Indirect ELISA CD40 und zeigt Reaktivität mit Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Rekombinant |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Rekombinantes Protein |
| Vollständiger Name | CD40 antigen |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 32 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 40-45 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_011611.2 |
| Gene symbol | Cd40 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 21939 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein A purfication |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Cluster of differentiation 40 (CD40) is a costimulatory protein located on antigen presenting cells and is required for their activation. CD40 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor (TNFR) family.
What is the molecular weight of CD40?
The molecular weight of CD40 is 43 kDa.
What is the cellular localization of CD40?
CD40 can be secreted by cells or found in the cell membrane.
What is the tissue specificity of CD40?
CD40 is expressed in B cells and primary carcinoma cells but is also found in dendritic cells and macrophages (PMID: 10209159).
What is the function of CD40?
CD40 acts as a receptor for TNFSF5/CD40LG, which is expressed on activated T cells. This interaction is essential for B cell proliferation, expression of activation markers, immunoglobulin production, and isotype switching (PMID: 8809473). This interaction is also crucial for the formation of memory B cells and germinal centers, and signaling through CD40 prevents apoptosis of germinal center B cells.
What is the role of CD40 in disease?
Defects in CD40 lead to hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome type 3 (HIGM3) (PMID: 11675497). This is an autosomal recessive disorder that includes the inability of B cells to undergo isotype switching, a key step in the final differentiation of the humoral immune response, and an inability to mount an antibody-specific immune response.