CDC27; APC3 Monoklonaler Antikörper
CDC27; APC3 Monoklonal Antikörper für FC (Intra)
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2b
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
FC (Intra)
Konjugation
CoraLite® Plus 647 Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
2F10G2
Kat-Nr. : CL647-67239
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
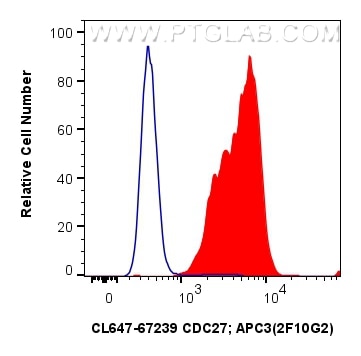
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC (Intra) | K-562-Zellen |
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC | K-562-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) | FC : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
CL647-67239 bindet in FC (Intra) CDC27; APC3 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2b |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CDC27; APC3 fusion protein Ag25588 |
| Vollständiger Name | cell division cycle 27 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 92 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 90-100 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC011656 |
| Gene symbol | CDC27 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 996 |
| Konjugation | CoraLite® Plus 647 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 654 nm / 674 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Vor Licht schützen. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr stabil. Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
CDC27/APC3 is a component of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/cyclosome), which is composed of eight subunits and highly conserved in eukaryotic cells. The APC/cyclosome complex acts as a cell cycle-regulated E3 ubiquitin ligase which mediates ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of target proteins, and lead to the progression control through mitosis and the G1 phase of the cell cycle.