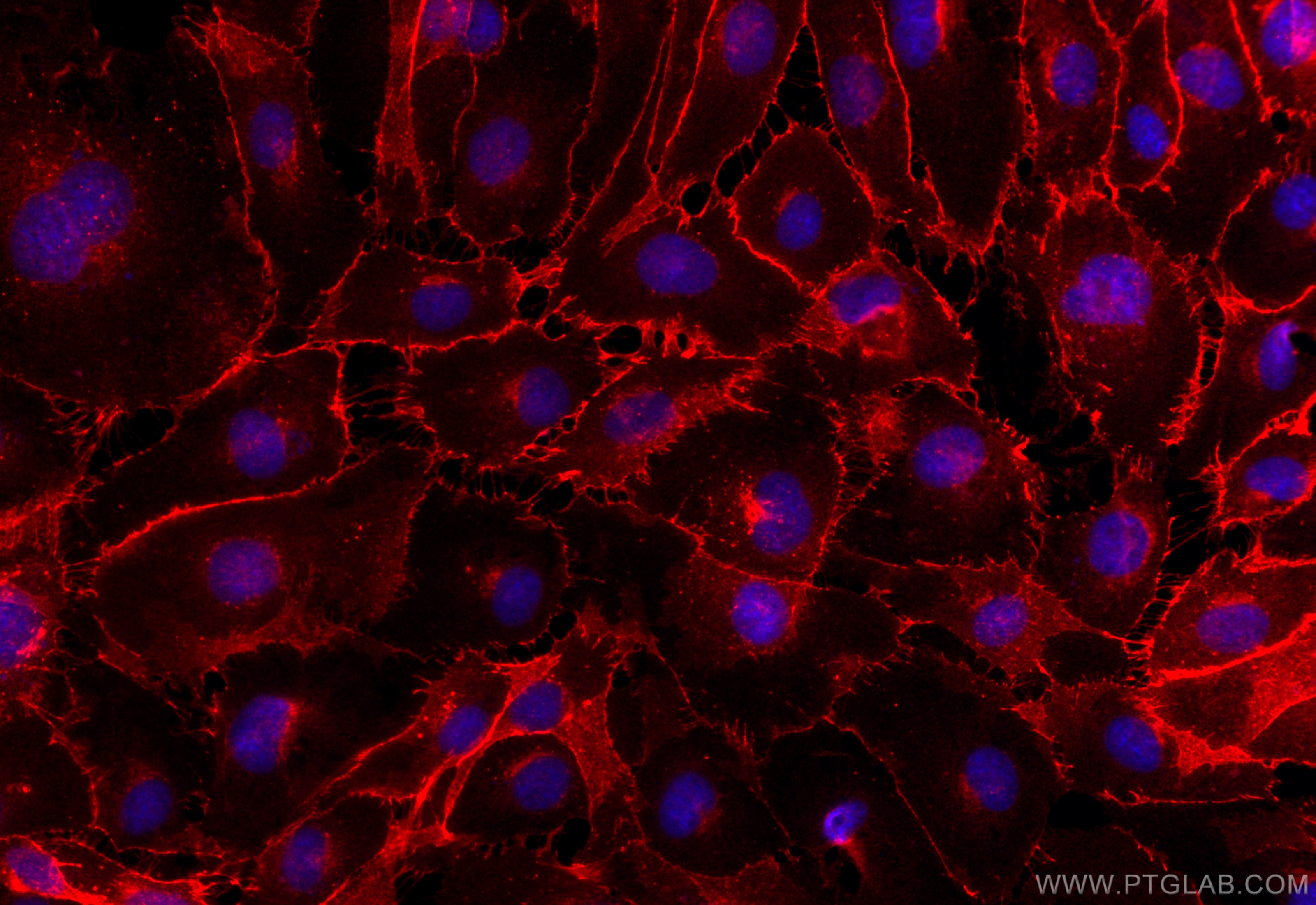
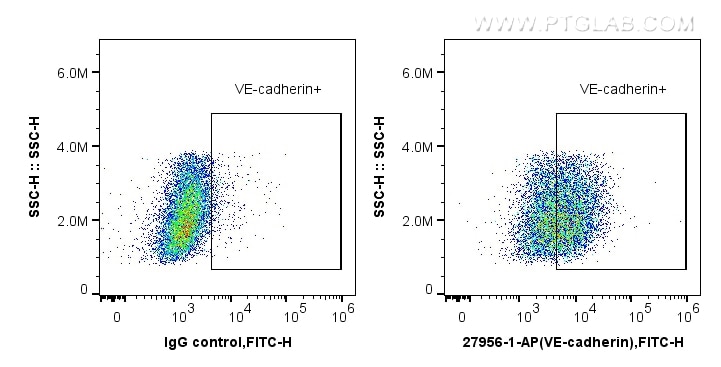
VE-cadherin/CD144 Polyklonaler Antikörper
VE-cadherin/CD144 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 27956-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
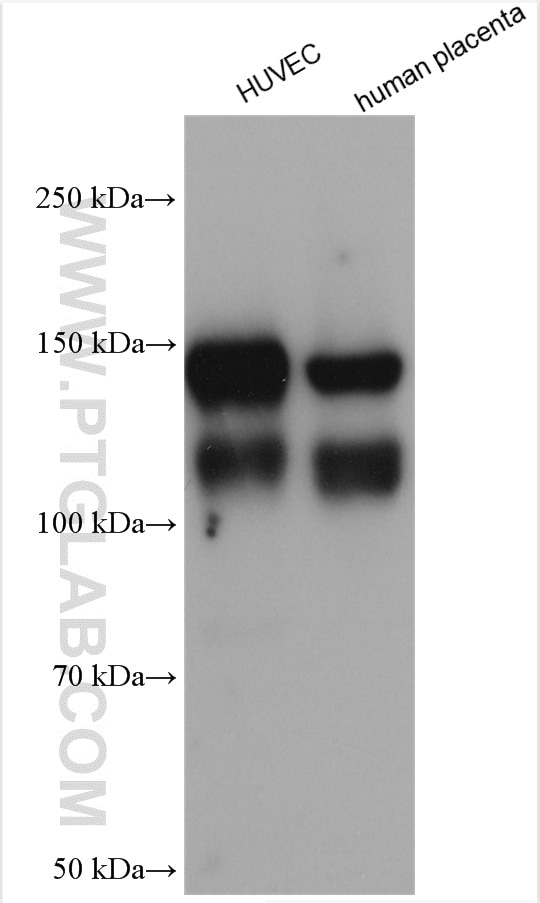
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HUVEC-Zellen, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe |
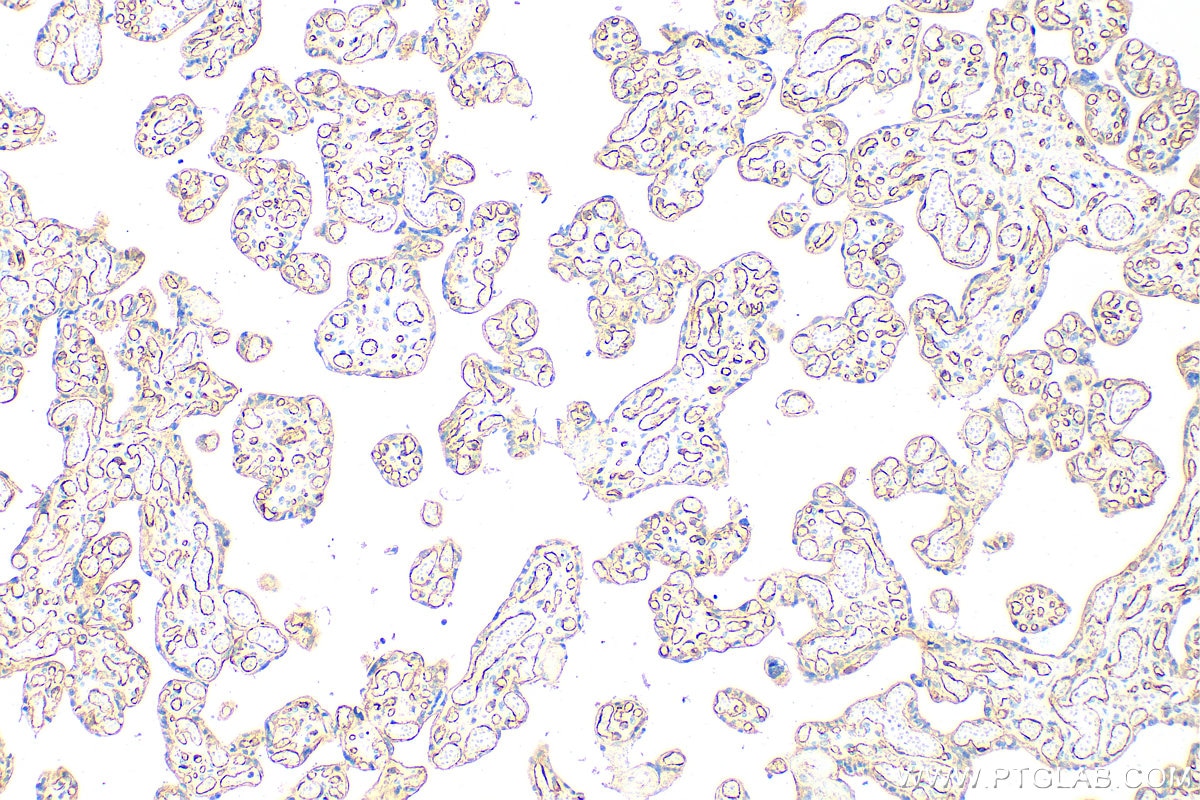
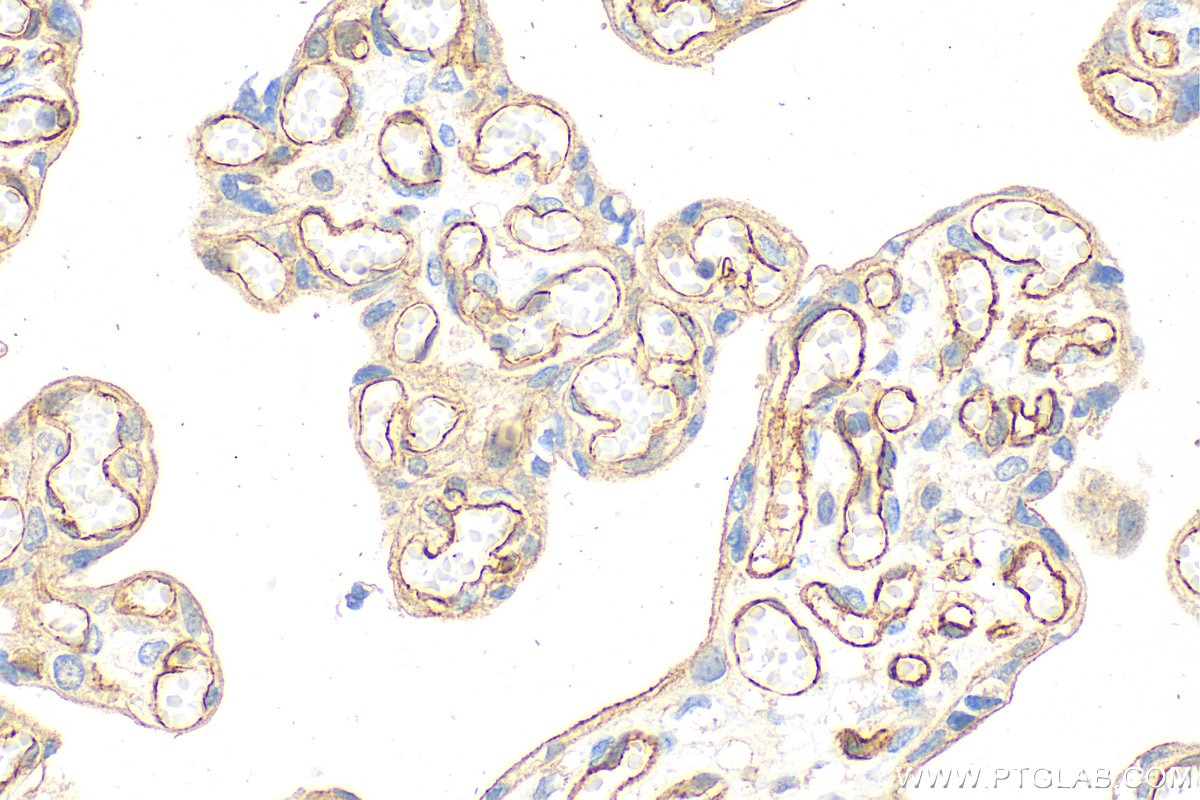
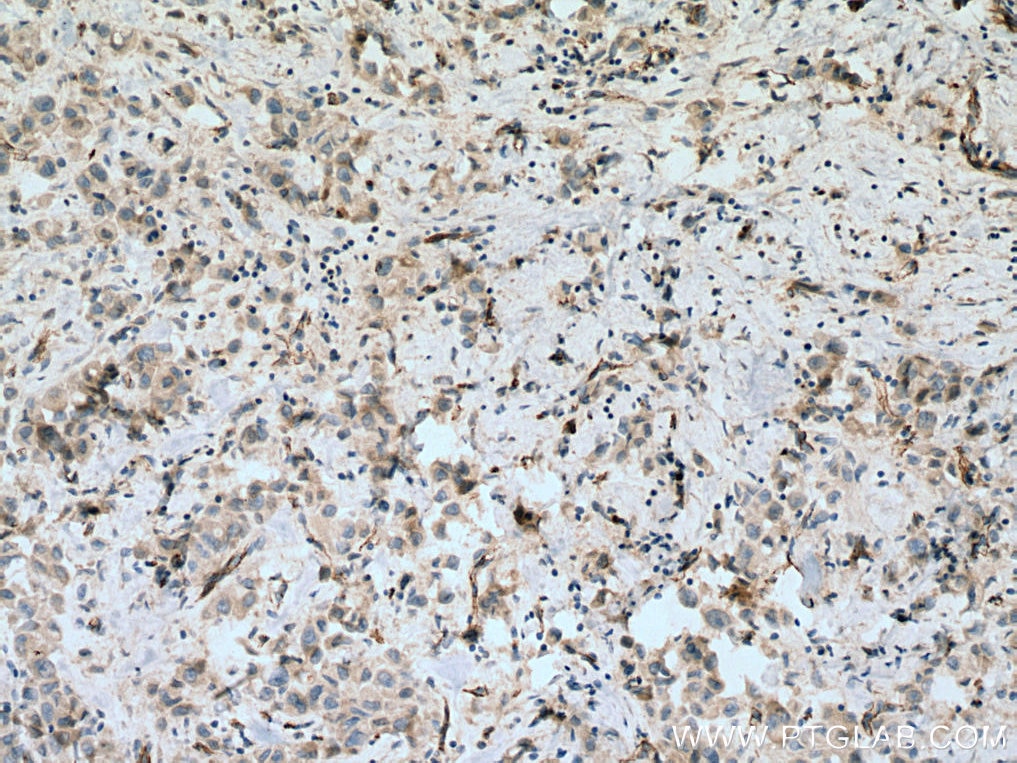
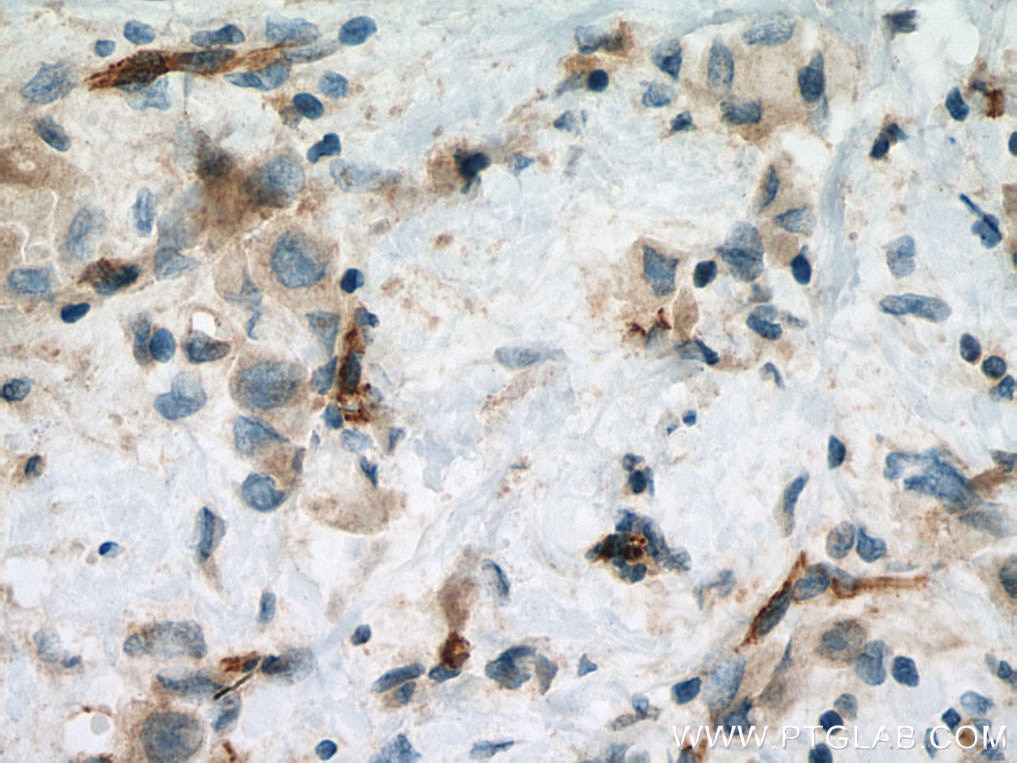
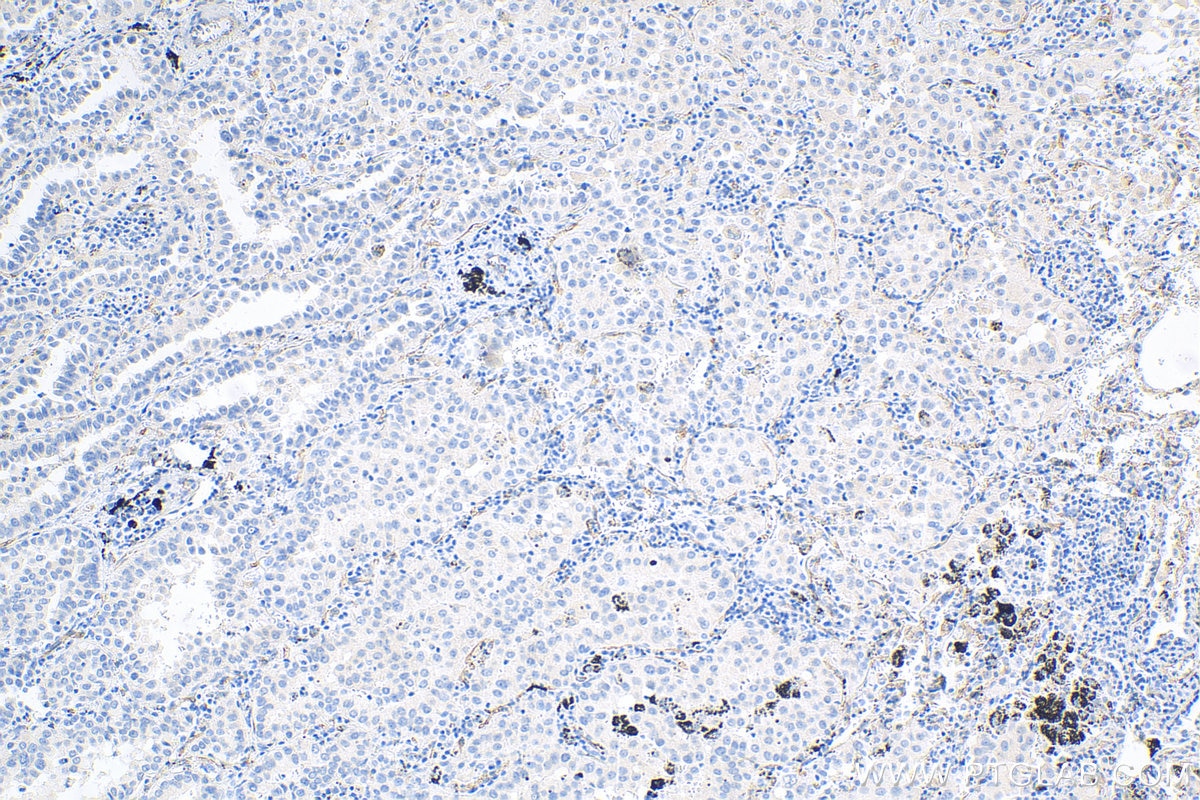
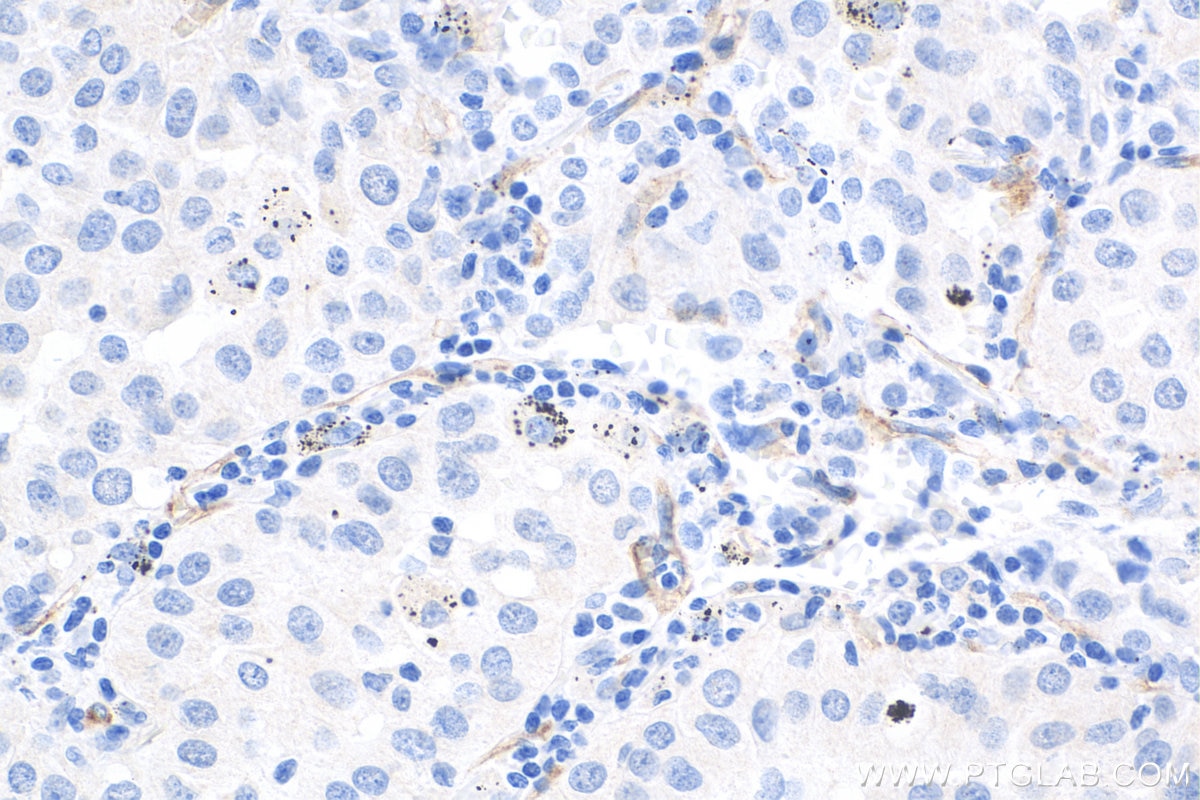
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Plazenta-Gewebe, humanes Mammakarzinomgewebe, humanes Lungenkarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
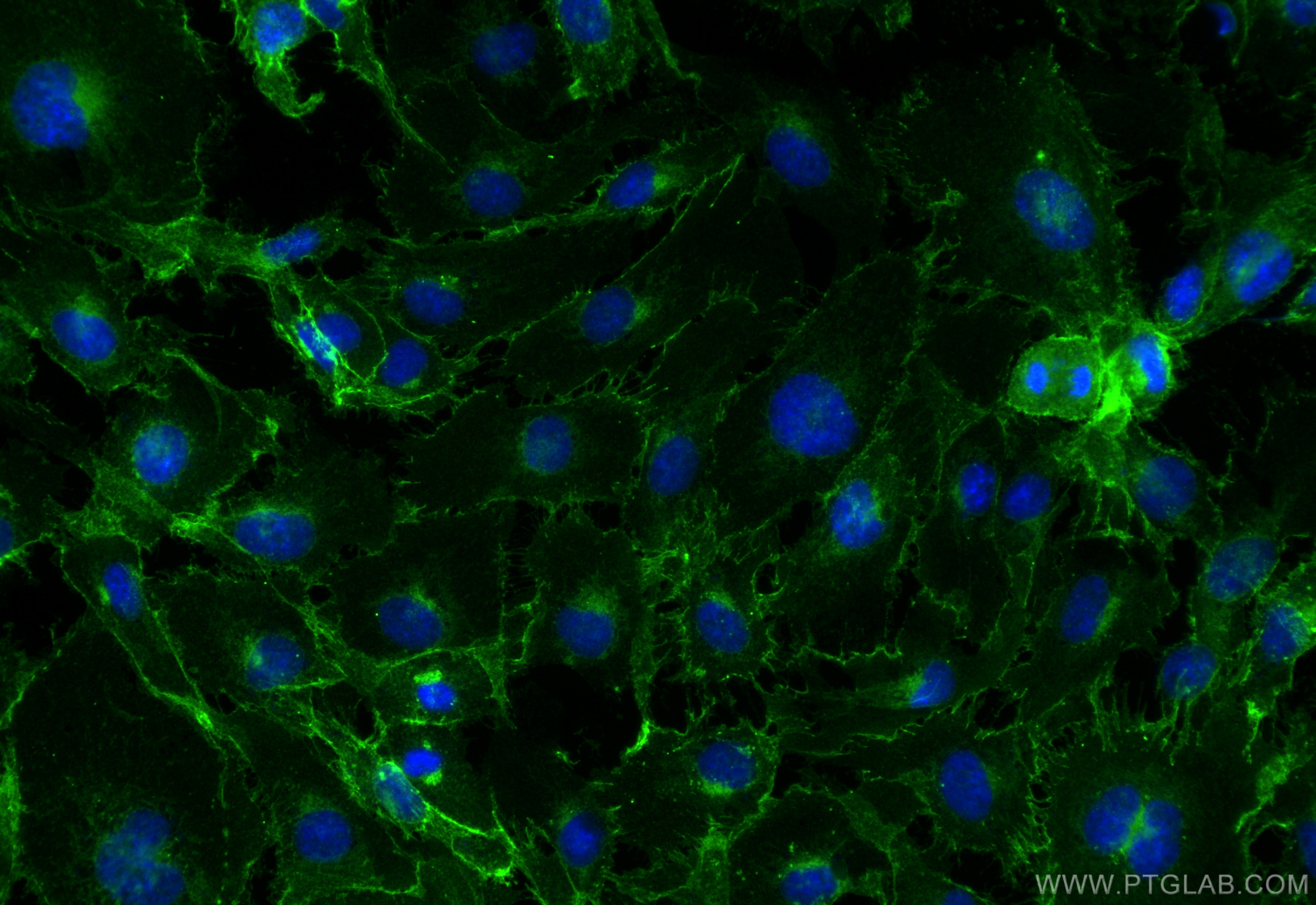
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HUVEC-Zellen |
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC | HUVEC-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) | FC : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 16 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 12 publications below |
Produktinformation
27956-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC, ELISA VE-cadherin/CD144 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | VE-cadherin/CD144 fusion protein Ag27487 |
| Vollständiger Name | cadherin 5, type 2 (vascular endothelium) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 88 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 120-140 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_001795 |
| Gene symbol | VE-cadherin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1003 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Cadherins are a family of transmembrane glycoproteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion and play an important role in the maintenance of normal tissue architecture. Vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin), also known as Cadherin-5 (CDH5) or CD144, is a member of the type II classical cadherin family of cell adhesion proteins (PMID: 21269602). VE-cadherin is expressed specifically in endothelial cells and mediates homophilic adhesion in the vascular endothelium (PMID: 1522121; 8555485; 21269602). VE-cadherin plays a role in the organization of lateral endothelial junctions and in the control of permeability properties of vascular endothelium (PMID: 1522121). VE-cadherin has also been shown to be required for angiogenesis (PMID: 16473763; 18162609). The calculated molecular weight of VE-cadherin is 88 kDa and the apparent molecular weight of 120-140 kDa is higher due to post-translational glycosylation and phosphorylation (PMID: 10460833; 29894844). Full-length VE-cadherin can be proteolytically cleaved to generate a fragment of 90-100 kDa (PMID: 9786462; 22064597).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 27956-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 27956-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 27956-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| FC protocol for VE-cadherin/CD144 antibody 27956-1-AP | Download protocol |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun FNIP1 abrogation promotes functional revascularization of ischemic skeletal muscle by driving macrophage recruitment | ||
Adv Healthc Mater Colon-Targeted Ginseng Polysaccharides-Based Microspheres for Improving Ulcerative Colitis via Anti-Inflammation and Gut Microbiota Modulation | ||
Bioengineering (Basel) Organotypic 3D Co-Culture of Human Pleura as a Novel In Vitro Model of Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Biofilm Development | ||
Pharmaceuticals (Basel) CXCL8 Promotes Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Endothelial Cells and Protects Cells from Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis via CXCR2-Mediated Activation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway | ||
World J Diabetes Tongxinluo promotes endothelium-dependent arteriogenesis to attenuate diabetic peripheral arterial disease | ||
Front Cell Infect Microbiol Analysis of miRNAs Involved in Mouse Heart Injury Upon Coxsackievirus A2 Infection. |