COQ5 Polyklonaler Antikörper
COQ5 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 17453-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
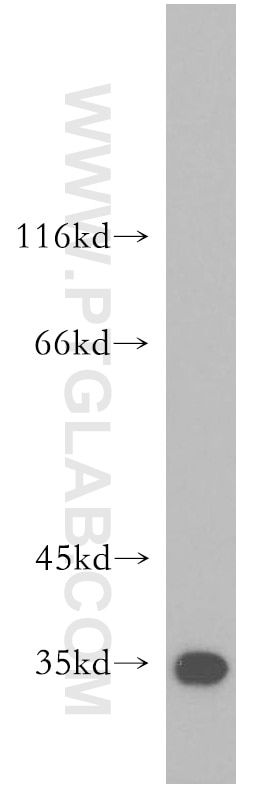
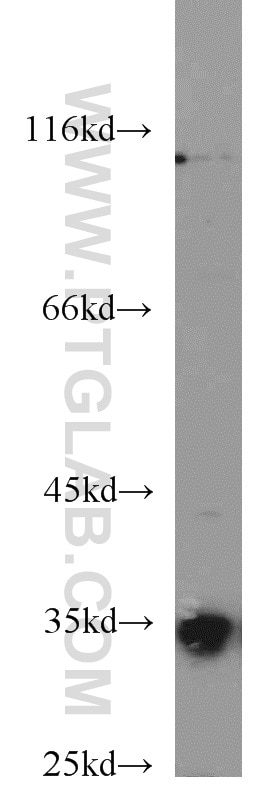
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Mausherzgewebe, Mauslebergewebe |
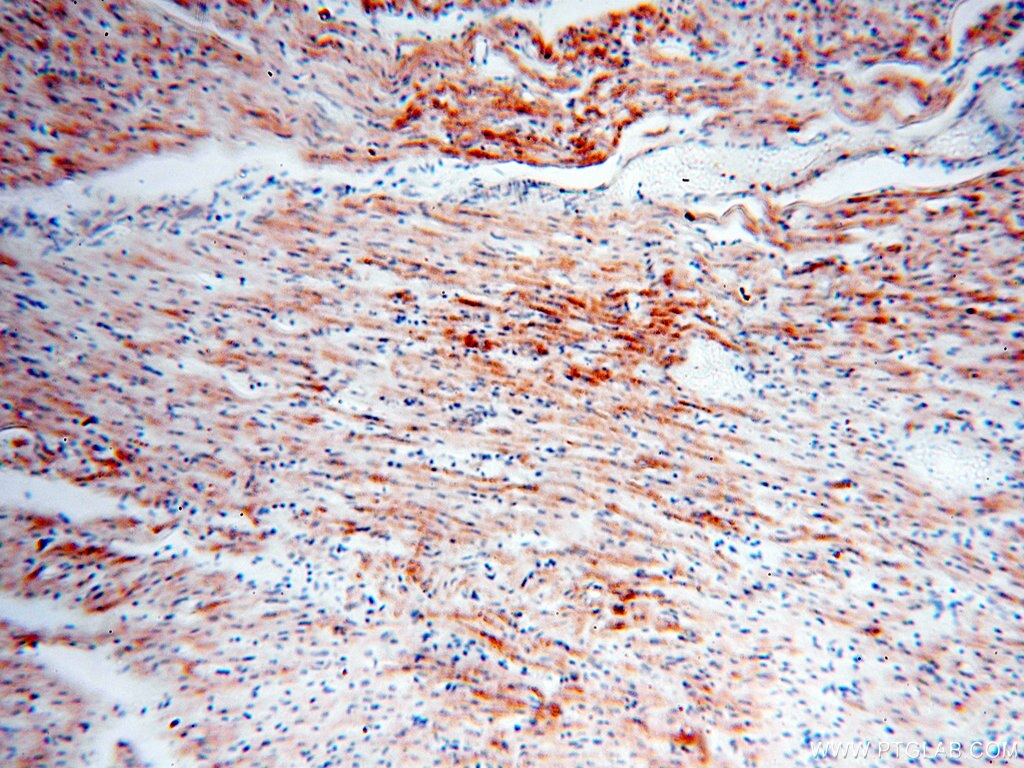
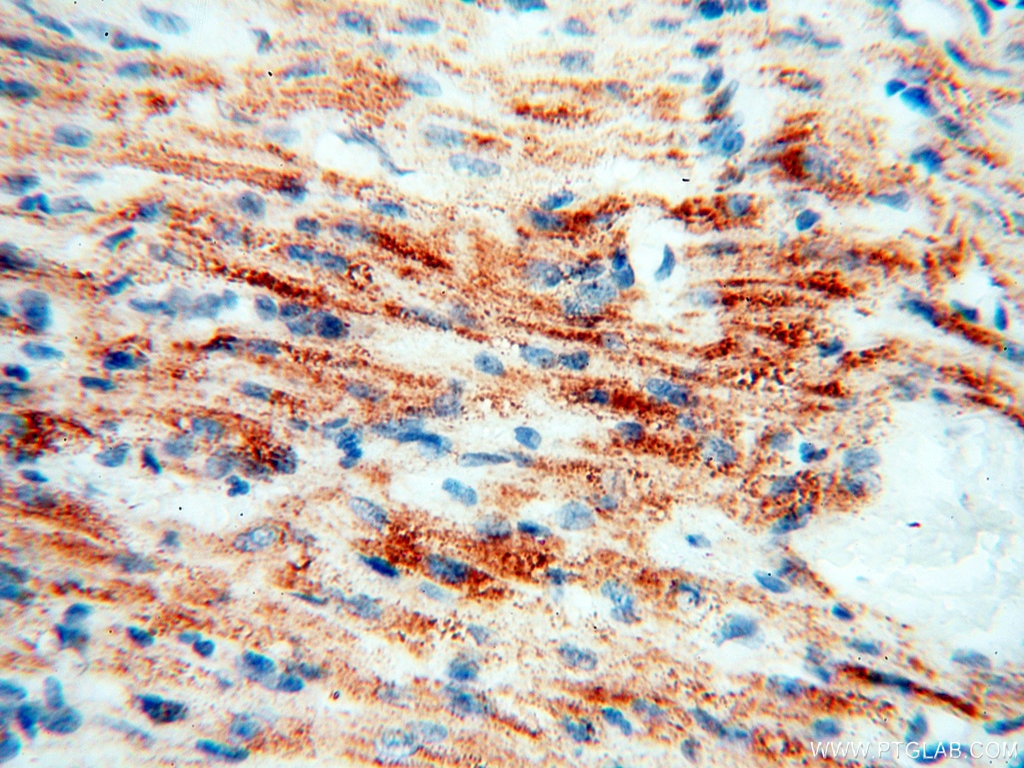
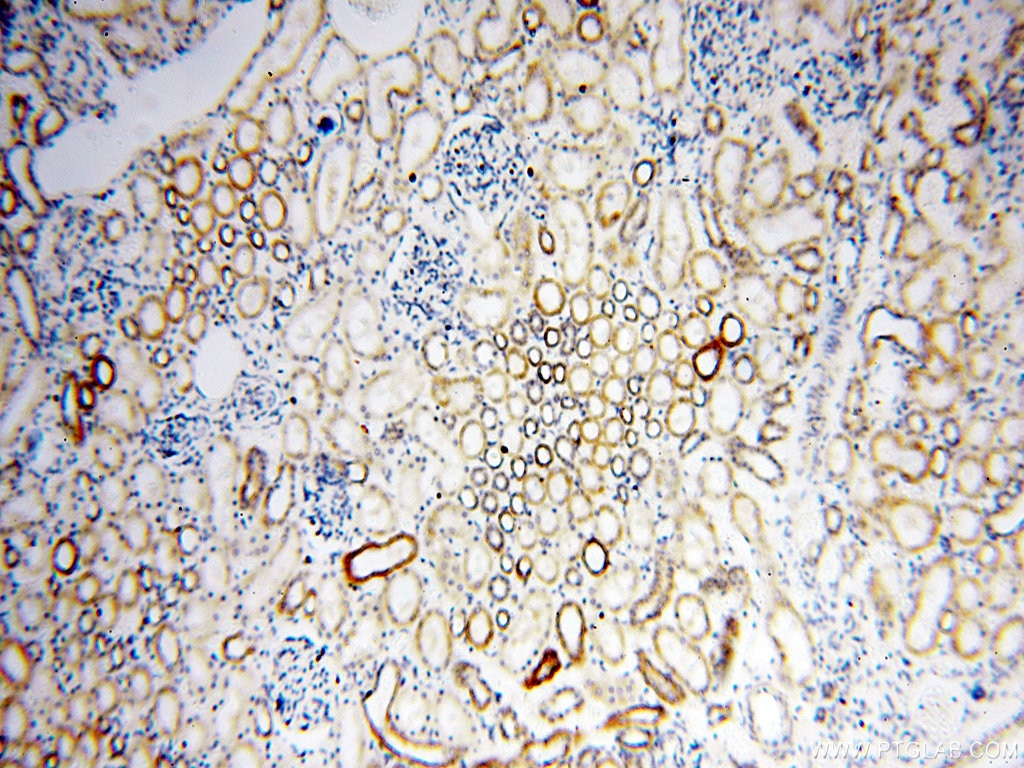
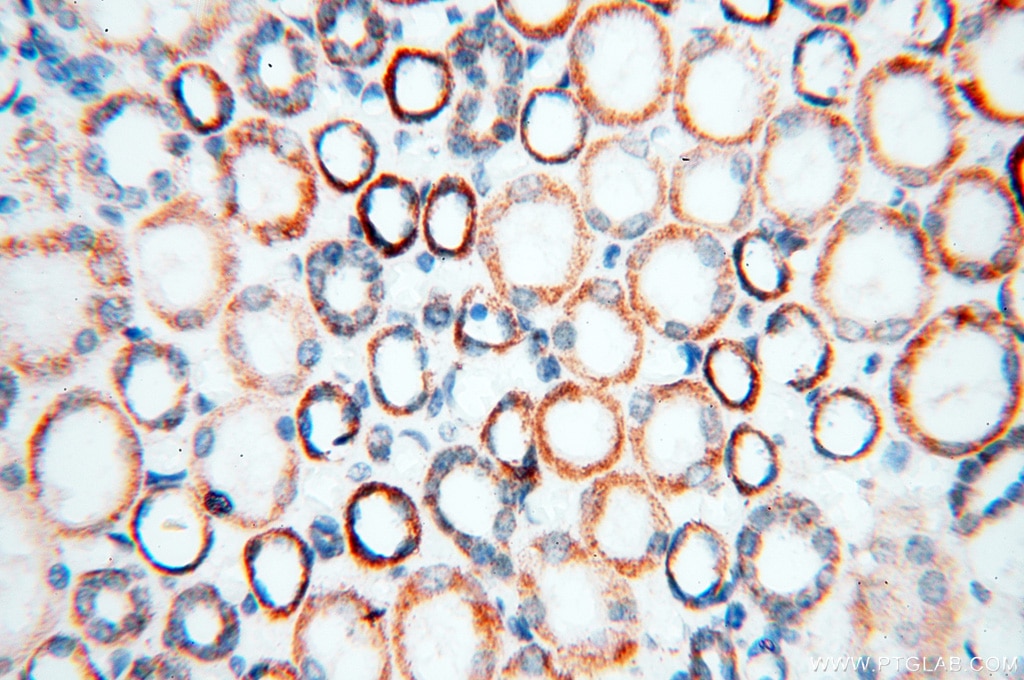
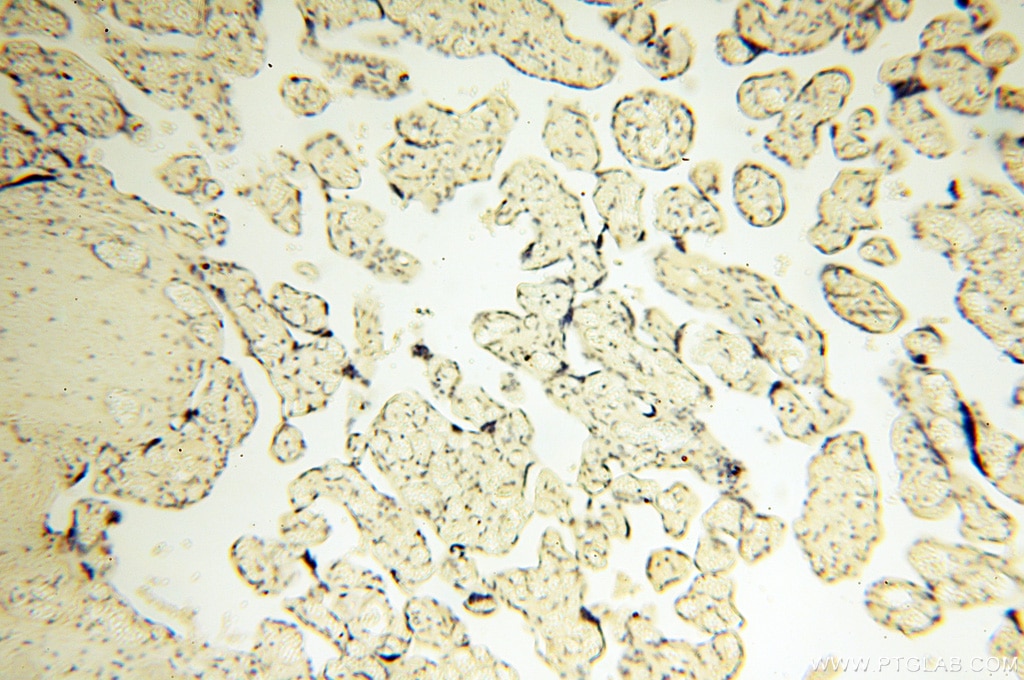
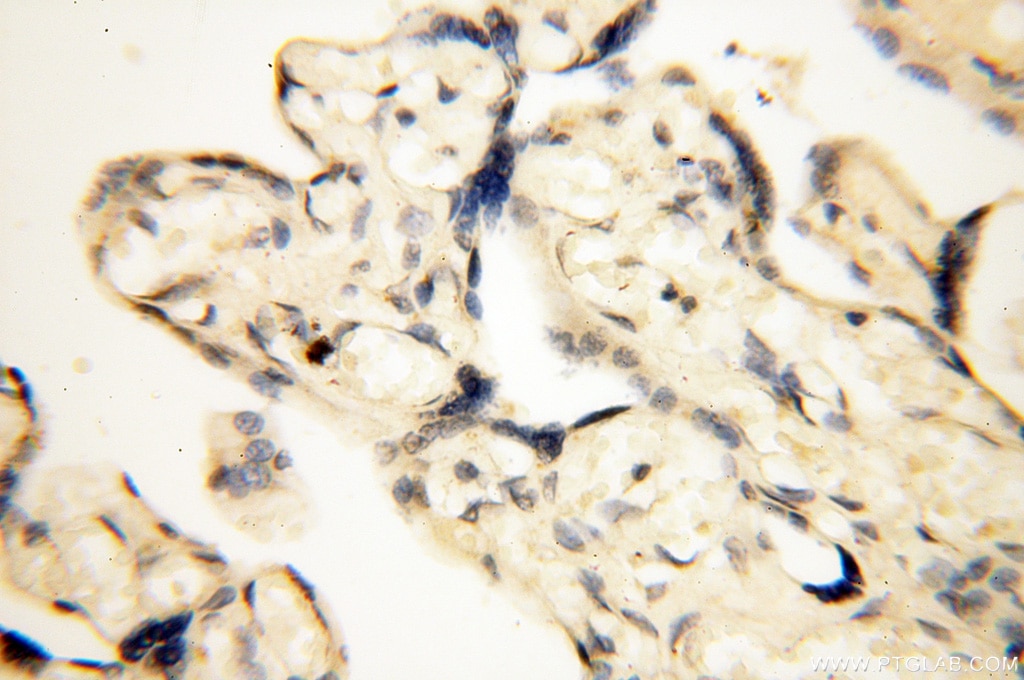
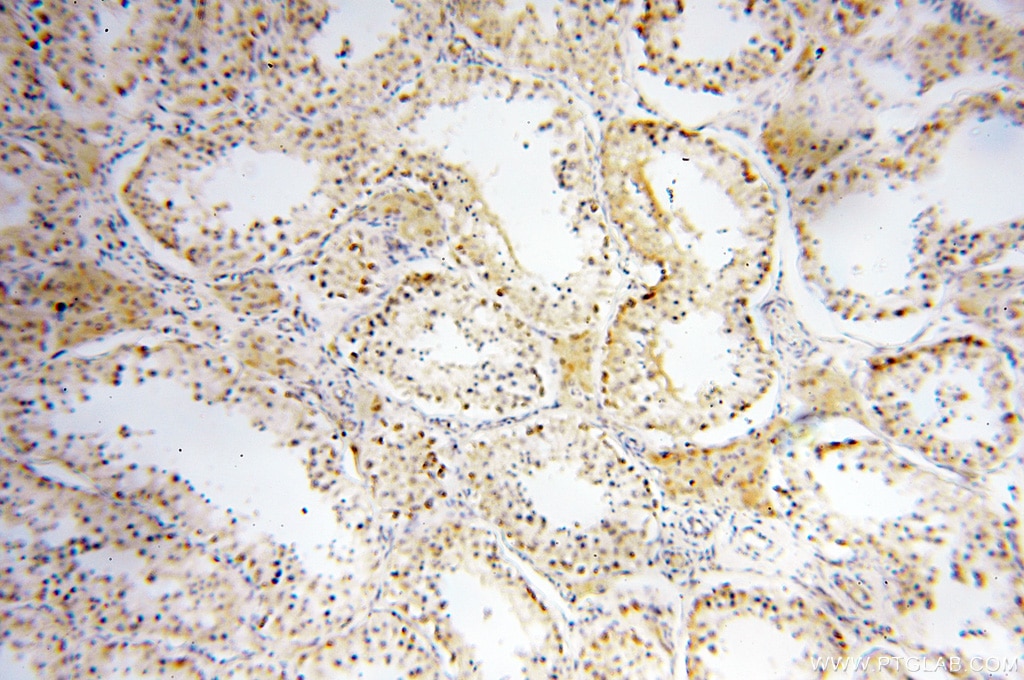
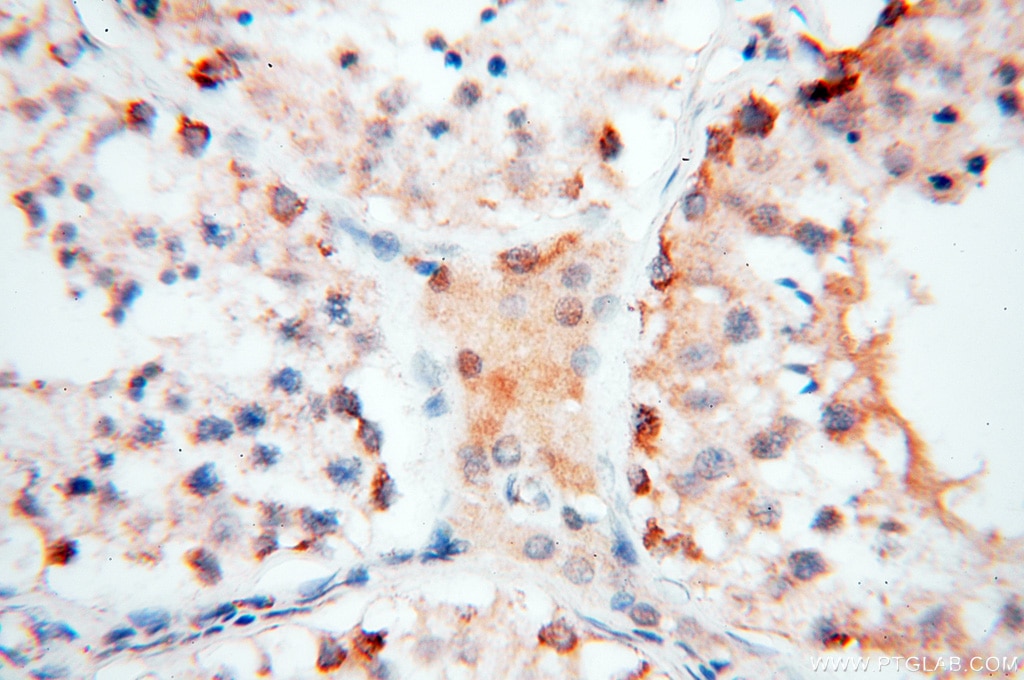
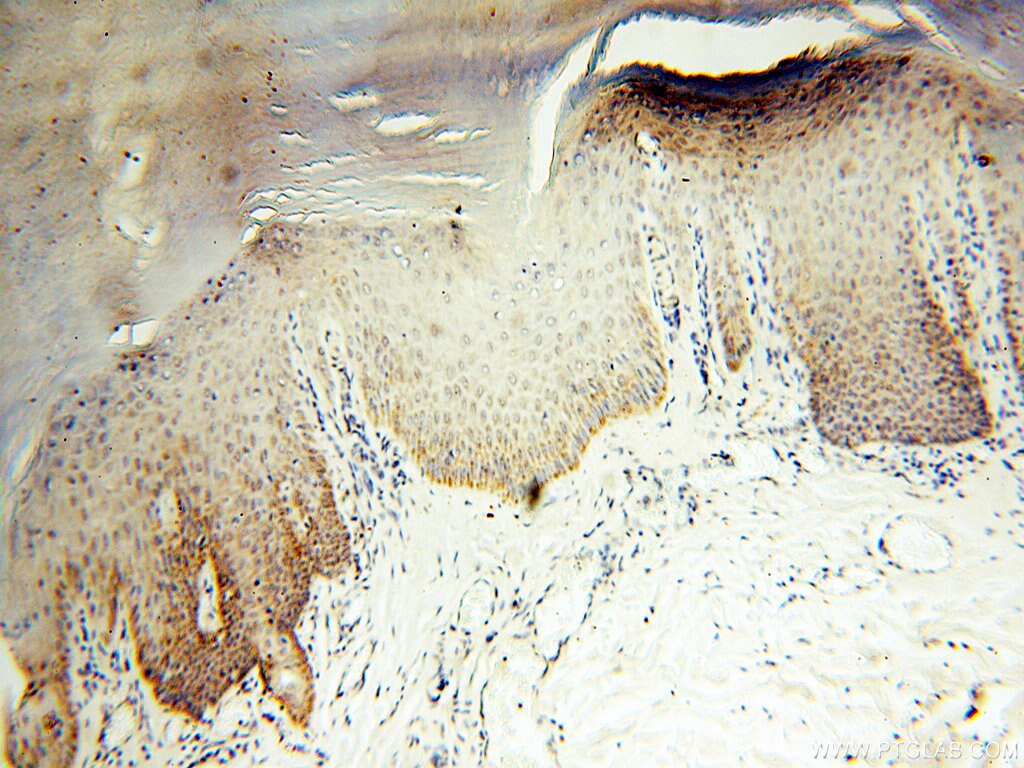
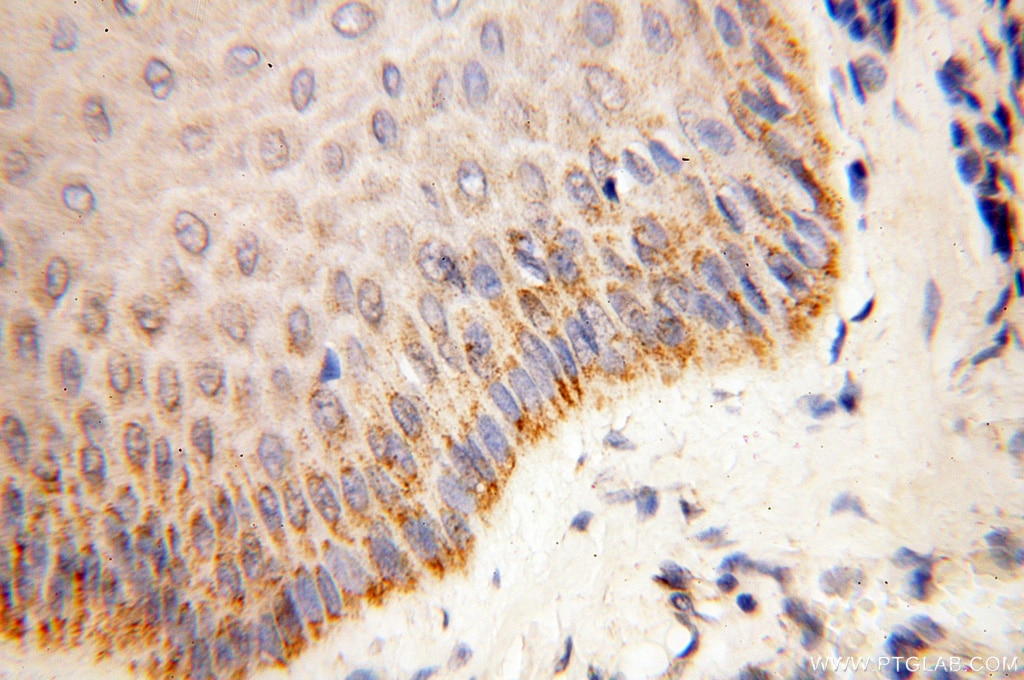
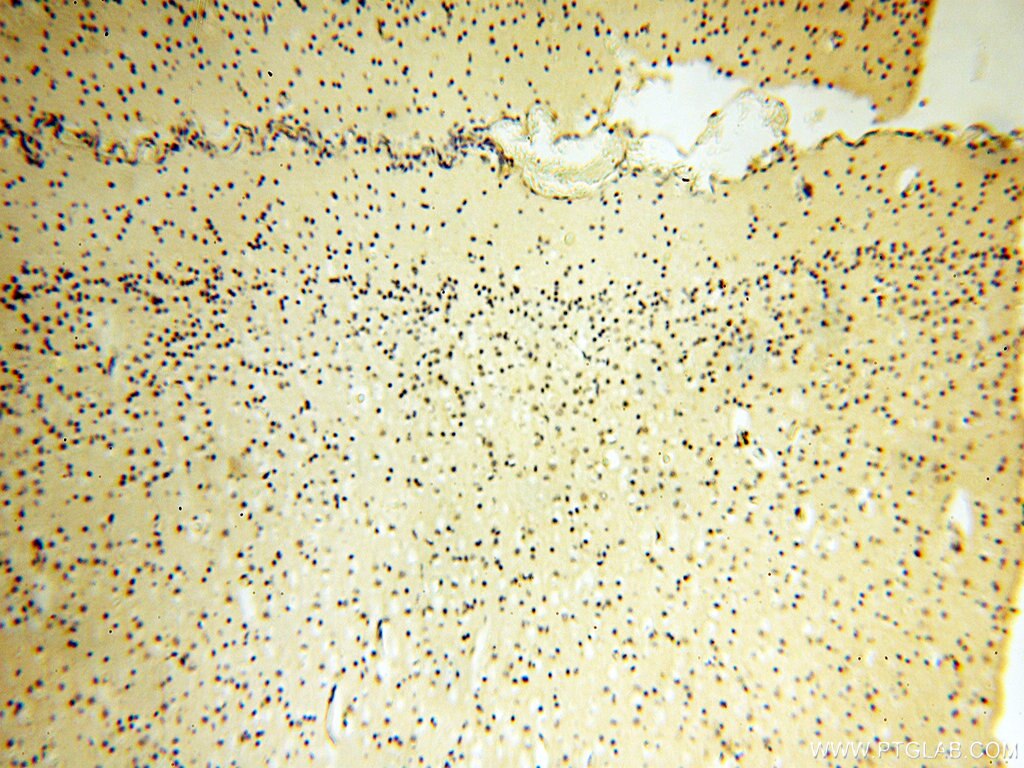
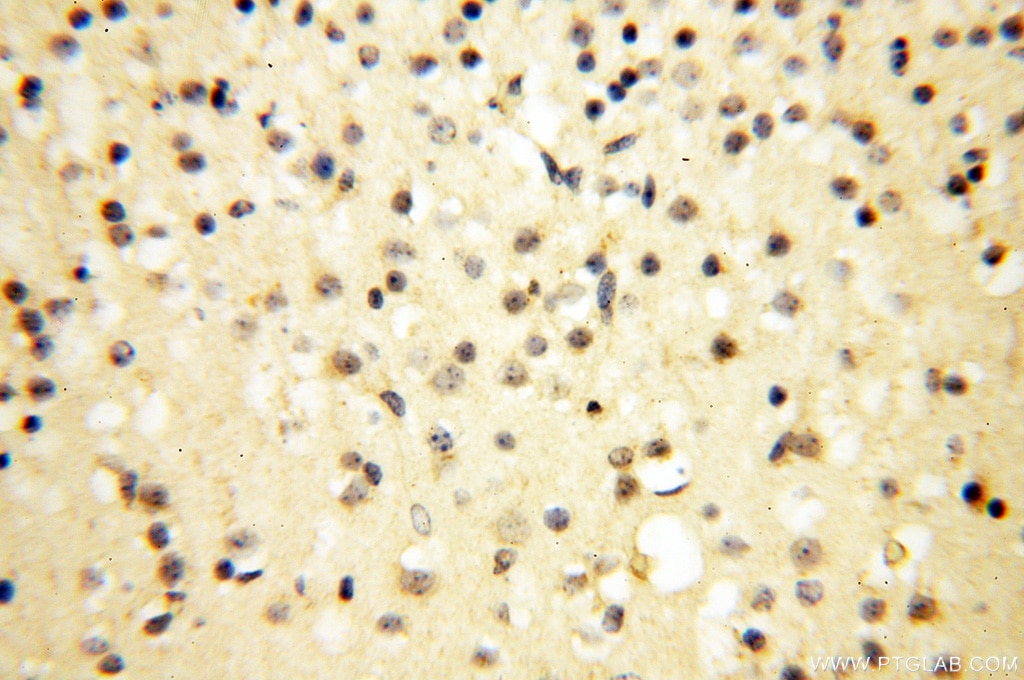
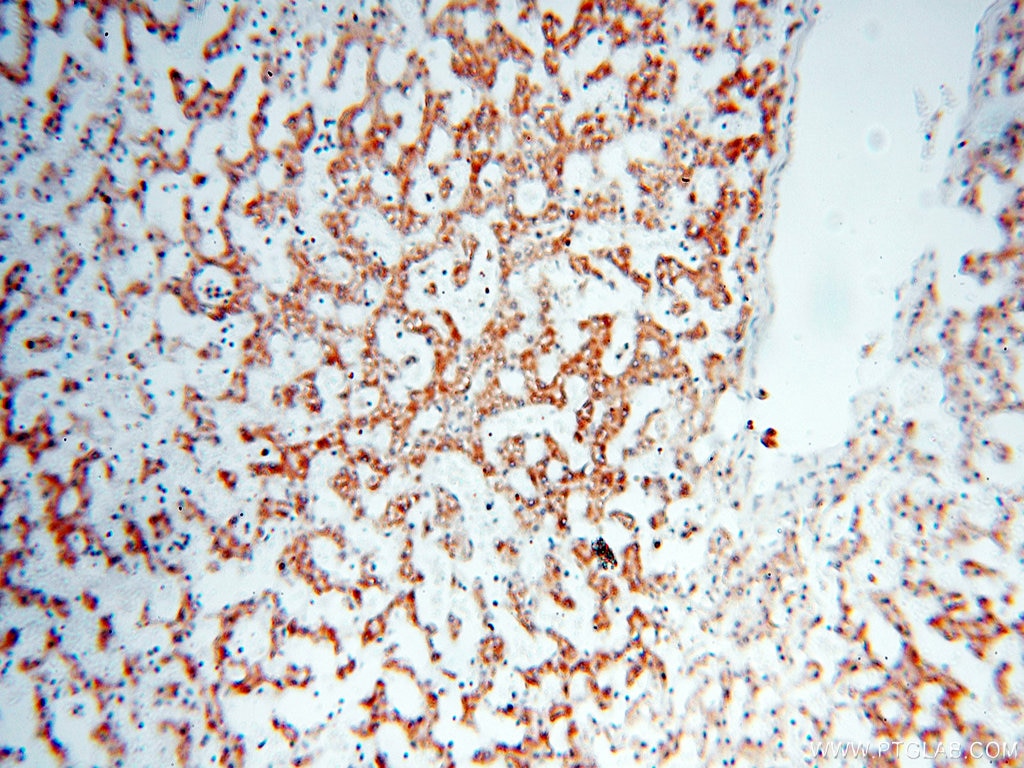
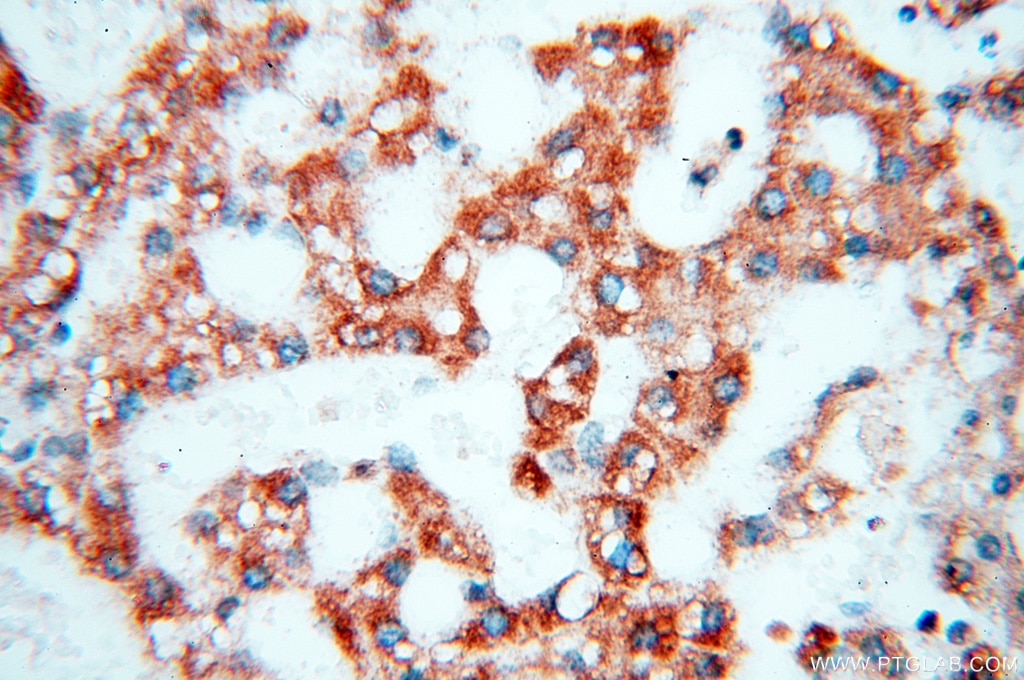
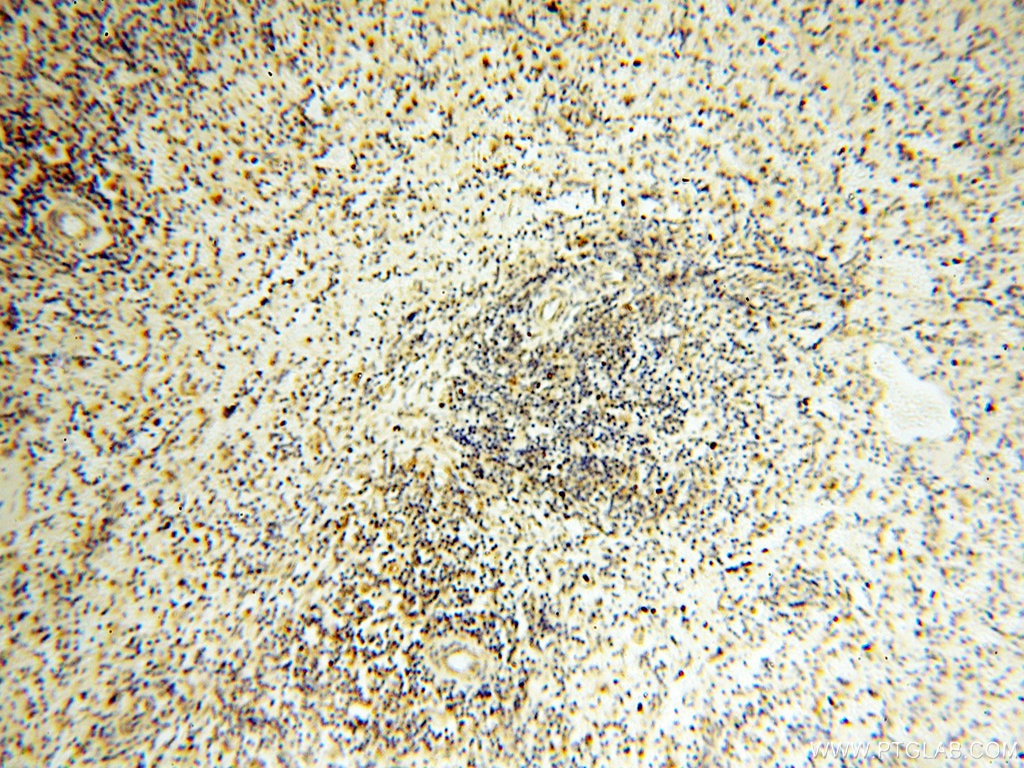
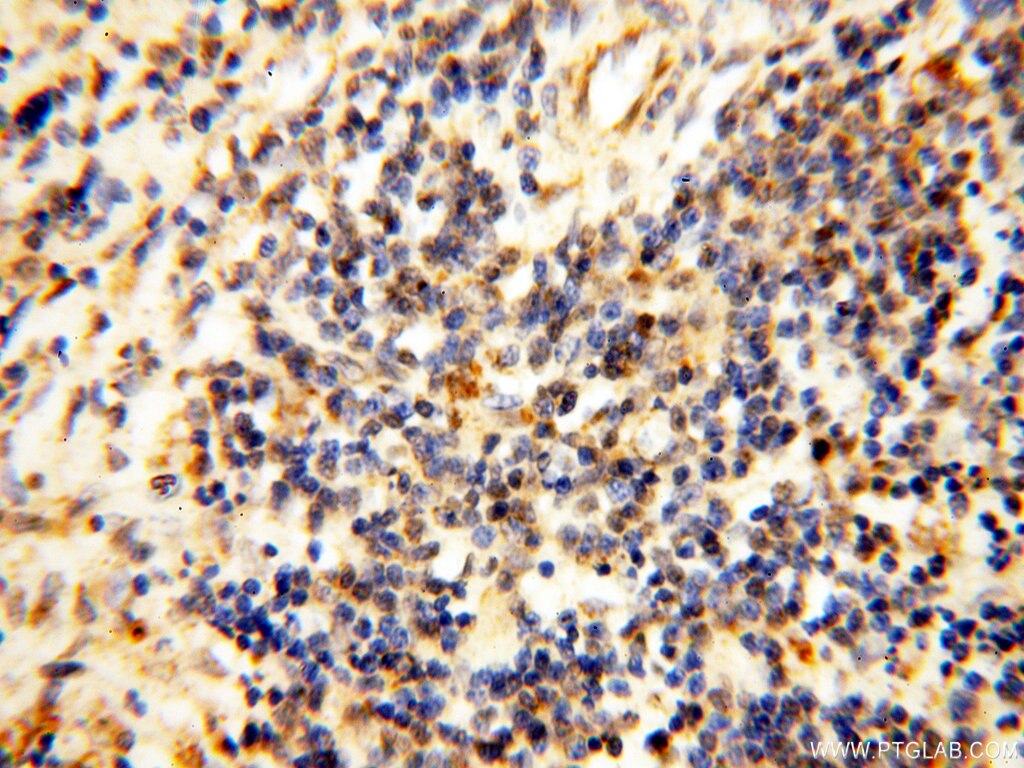
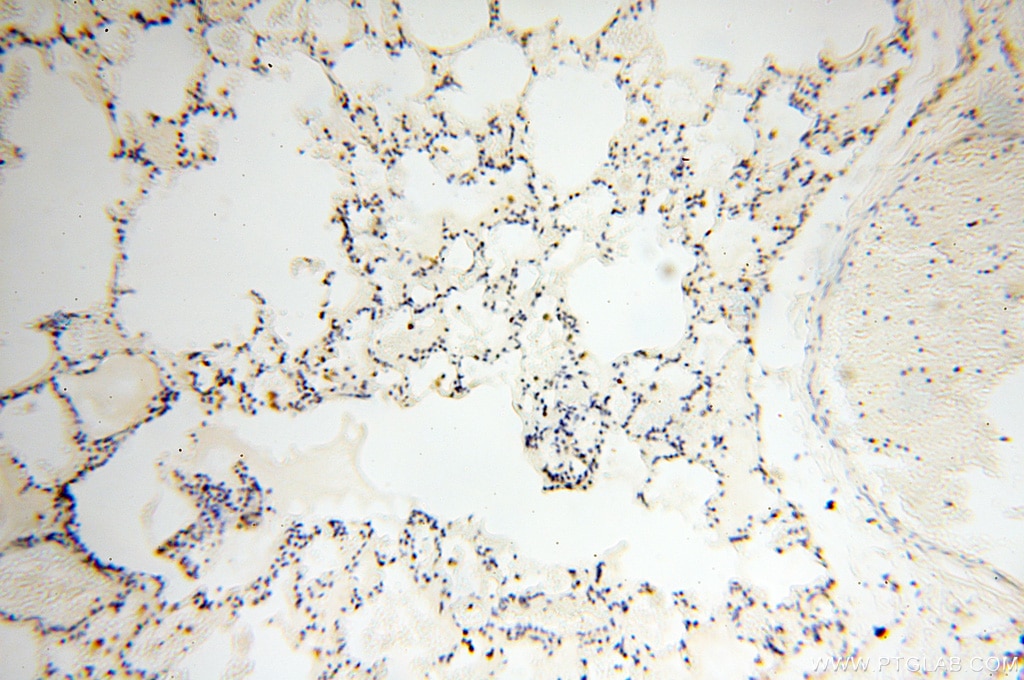
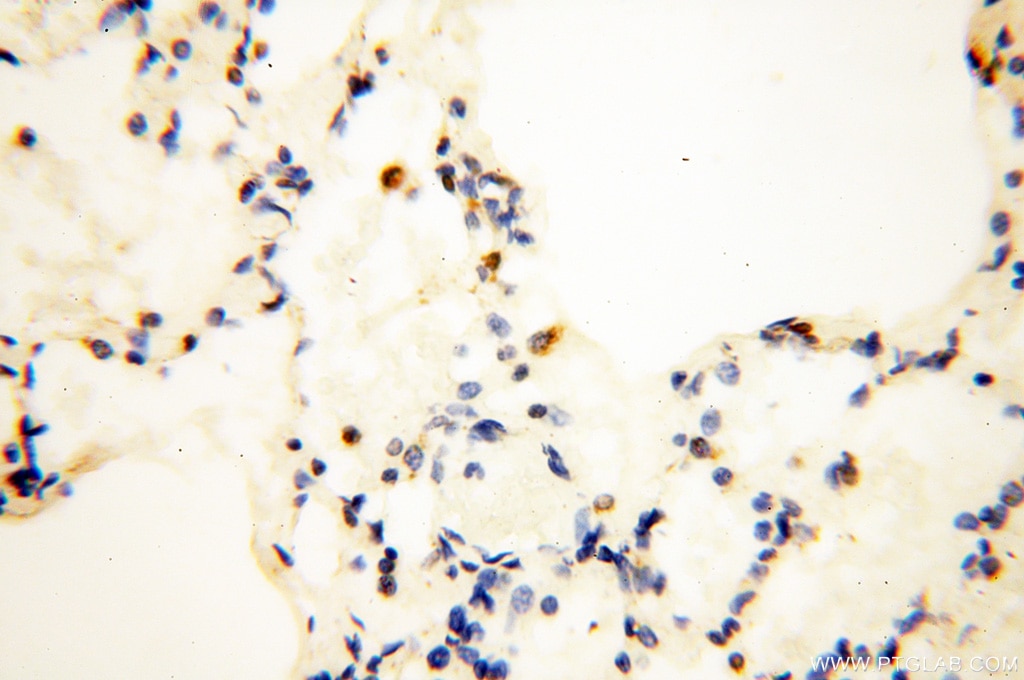
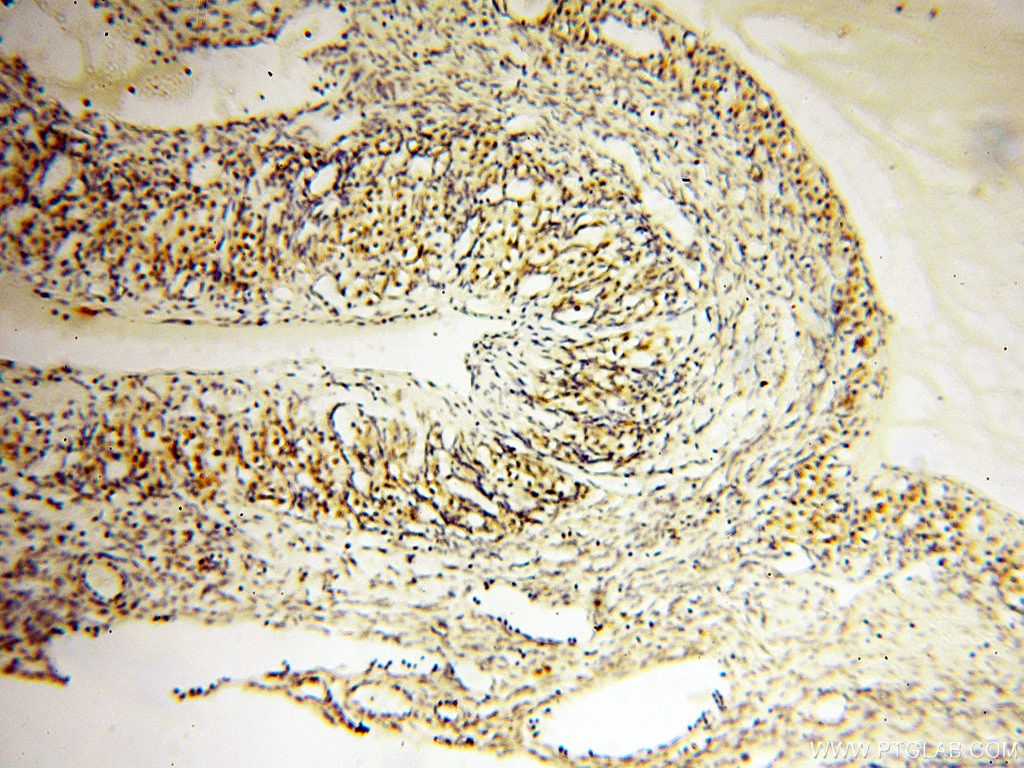
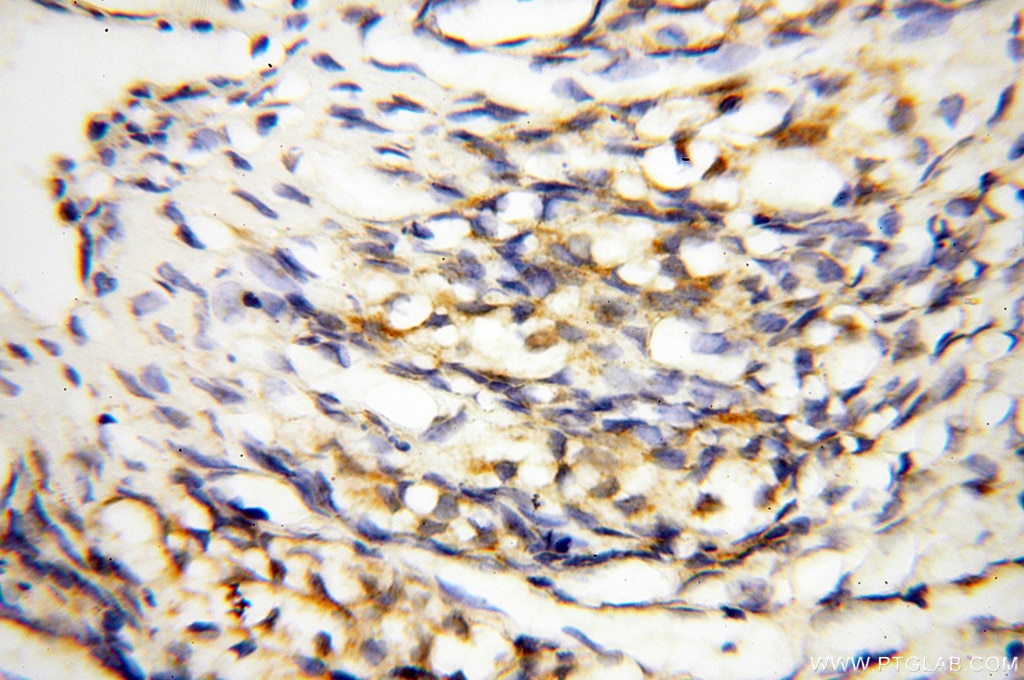
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Herzgewebe, humanes Hirngewebe, humanes Nierengewebe, humanes Lebergewebe, humanes Lungengewebe, humanes Eierstockgewebe, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe, humanes Hautgewebe, humanes Milzgewebe, humanes Hodengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 8 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
17453-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA COQ5 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | COQ5 fusion protein Ag10203 |
| Vollständiger Name | coenzyme Q5 homolog, methyltransferase (S. cerevisiae) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 327 aa, 37 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 32 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC107874 |
| Gene symbol | COQ5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 84274 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
COQ5 catalyzes the only C-methylation involved in the biosynthesis of coenzyme Q (Q or ubiquinone) in humans and yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In humans, mutations in several COQ genes cause primary Q deficiency, and a decrease in Q biosynthesis is associated with mitochondrial, cardiovascular, kidney and neurodegenerative diseases (PMID: 25152161). Endogenous human COQ5 protein primarily existed as a mature form (m-COQ5, ~32 kDa) without the mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) in the mitochondria of human cells, in addition to the minor precursor form (p-COQ5, 37 kDa) of the full-length protein (PMID: 27155576).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for COQ5 antibody 17453-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for COQ5 antibody 17453-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
EMBO Mol Med β-RA reduces DMQ/CoQ ratio and rescues the encephalopathic phenotype in Coq9 R239X mice. | ||
Redox Biol The Q-junction and the inflammatory response are critical pathological and therapeutic factors in CoQ deficiency. | ||
J Am Soc Nephrol ADCK4 Deficiency Destabilizes the Coenzyme Q Complex, Which Is Rescued by 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid Treatment. | ||
EMBO Mol Med The clinical heterogeneity of coenzyme Q10 deficiency results from genotypic differences in the Coq9 gene. | ||
Sci Rep Reduction in the levels of CoQ biosynthetic proteins is related to an increase in lifespan without evidence of hepatic mitohormesis. |