- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
CXCL16 Monoklonaler Antikörper
CXCL16 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2a
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus
Anwendung
WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
2H7B3
Kat-Nr. : 60123-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
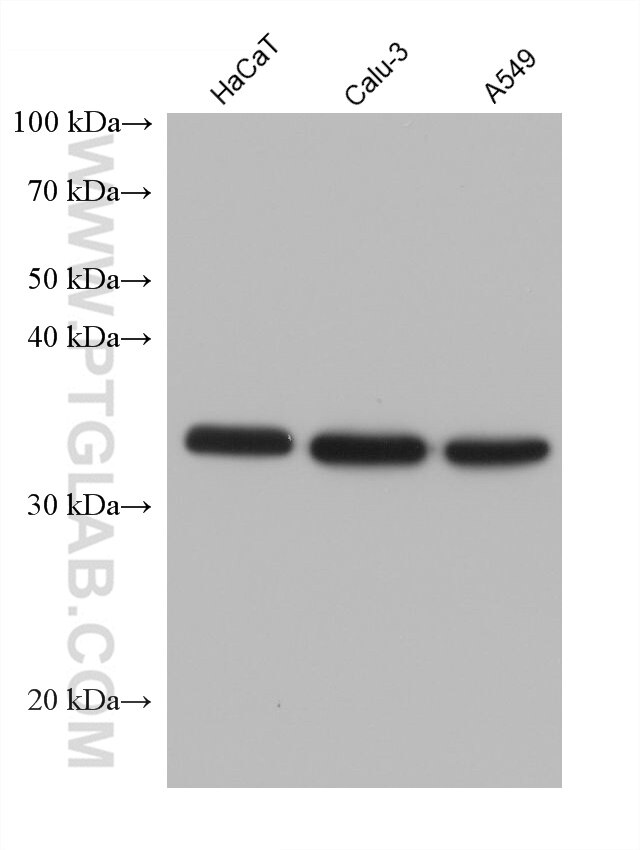
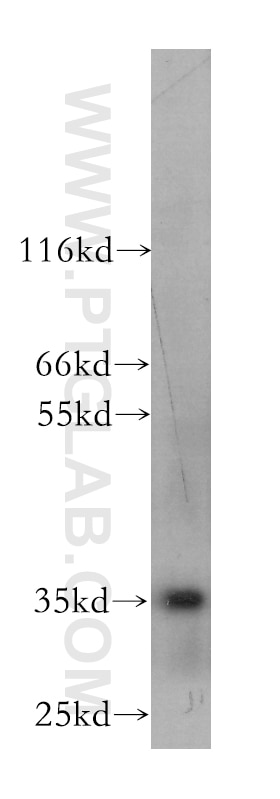
60123-1-PBS bindet in WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA CXCL16 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2a |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CXCL16 fusion protein Ag4883 |
| Vollständiger Name | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 273 aa, 30 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 35 kDa, 60 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC017588 |
| Gene symbol | CXCL16 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 58191 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
CXCL16 is a recently discovered cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family, which is synthesised in plasmacytoid dendritic cell as a transmembrane molecule. It exists in a transmembrane and soluble form. The transmembrane form of CXCL16 functions as an adhesion molecule for CXCR6-expressing cells, whereas the soluble form of CXCL16 mediates infiltration of circulating cells into sites of injury. CXCL16, has been proposed as an important pathogenic mediator in inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, glomerulonephritis, or prostate cancer. CXCL16 has been implicated in some forms of renal disease such as lupus nephritis and antiglomerular basement membrane nephritis. CXCL16 also plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of angiotensin II-induced renal injury and fibrosis through regulation of macrophage and T cell infiltration and bone marrow-derived fibroblast accumulation.