DDIT4L Polyklonaler Antikörper
DDIT4L Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
Maus
Anwendung
WB, IHC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 12094-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
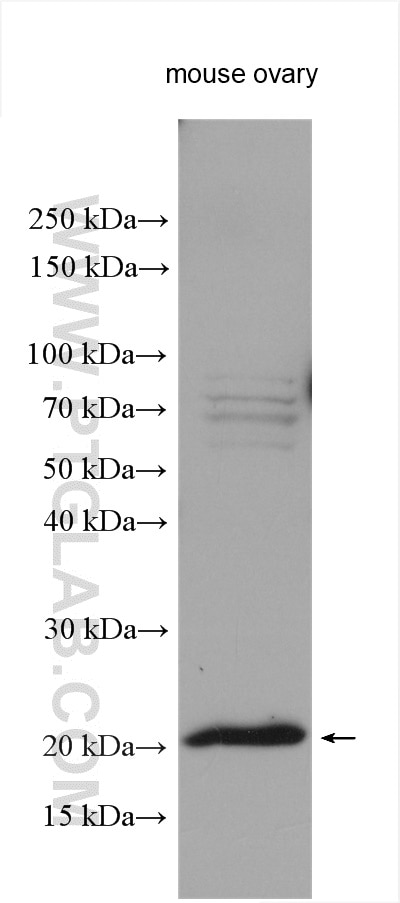
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Maus-Eierstockgewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
12094-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, ELISA DDIT4L und zeigt Reaktivität mit Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | Maus |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | DDIT4L fusion protein Ag2735 |
| Vollständiger Name | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4-like |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 193 aa, 22 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 22 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC013592 |
| Gene symbol | DDIT4L |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 115265 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4-like protein(DDIT4L), encoded by the stress responsive gene REDD2, is a negative regulator of mTOR signaling, and expressed predominantly in skeletal muscle. It regulates the TOR signaling pathway upstream of the TSC1-TSC2 complex and downstream of AKT1. Also, DDIT4L involves in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced macrophage death sensitivity.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DDIT4L antibody 12094-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Cell Sci Oocyte-dependent activation of MTOR in cumulus cells controls the development and survival of cumulus-oocyte complexes. | ||
J Nutr Amino Acid- and Insulin-Induced Activation of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 in Neonatal Piglet Skeletal Muscle Involves Sestin2-GATOR2, Rag A/C-mTOR, and RHEB-mTOR Complex Formation. | ||
J Cell Biochem Regulation of REDD1 by insulin-like growth factor-I in skeletal muscle and myotubes. | ||
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab Disruption of REDD1 gene ameliorates sepsis-induced decrease in mTORC1 signaling but has divergent effects on proteolytic signaling in skeletal muscle. |