DDR2 Monoklonaler Antikörper
DDR2 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1E9A10
Kat-Nr. : 67126-1-Ig
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Jurkat-Zellen, HEK-293-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
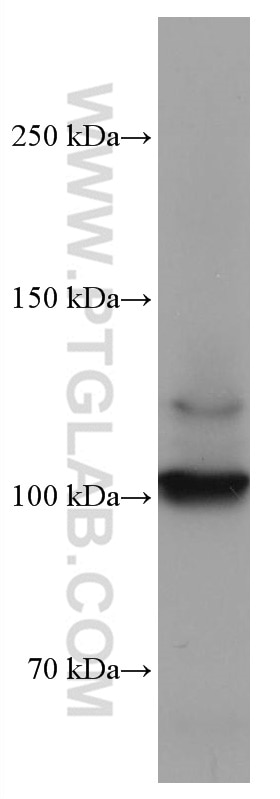
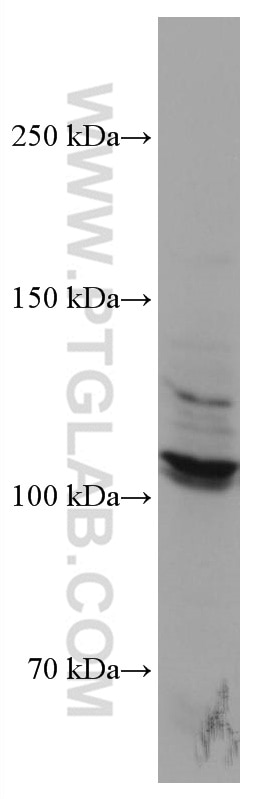
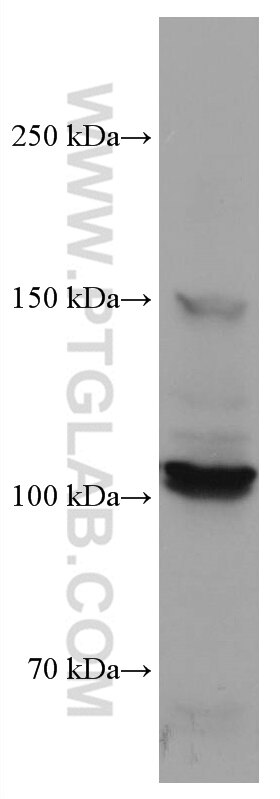
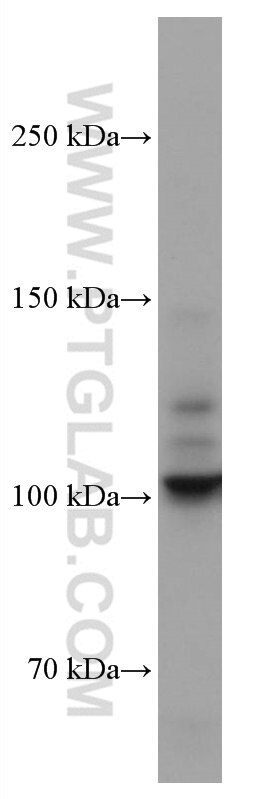
67126-1-Ig bindet in WB, IF, ELISA DDR2 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | DDR2 fusion protein Ag28340 |
| Vollständiger Name | discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 2 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 97 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 100-110 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_001014796 |
| Gene symbol | DDR2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4921 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
DDR2 (Discoidin domain receptor 2) belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family and is activated by collagen-binding.DDR2 is implicated in several physiological and pathological processes, including wound healing, angiogenesis, ovulation, spermatogenesis, extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and fibrosis, and tumor progression (PMID: 25805889). Moreover, DDR2 is prominently present in the fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, myofibroblasts, and chondrocytes (PMID: 37834343).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DDR2 antibody 67126-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Cell Mol Med The role and mechanism of transforming growth factor beta 3 in human myocardial infarction-induced myocardial fibrosis. | ||
Int J Biol Macromol Human type III collagen-derived biomaterial with high antitumor activity inhibits breast cancer cell autophagy, proliferation, and migration through DDR1 |