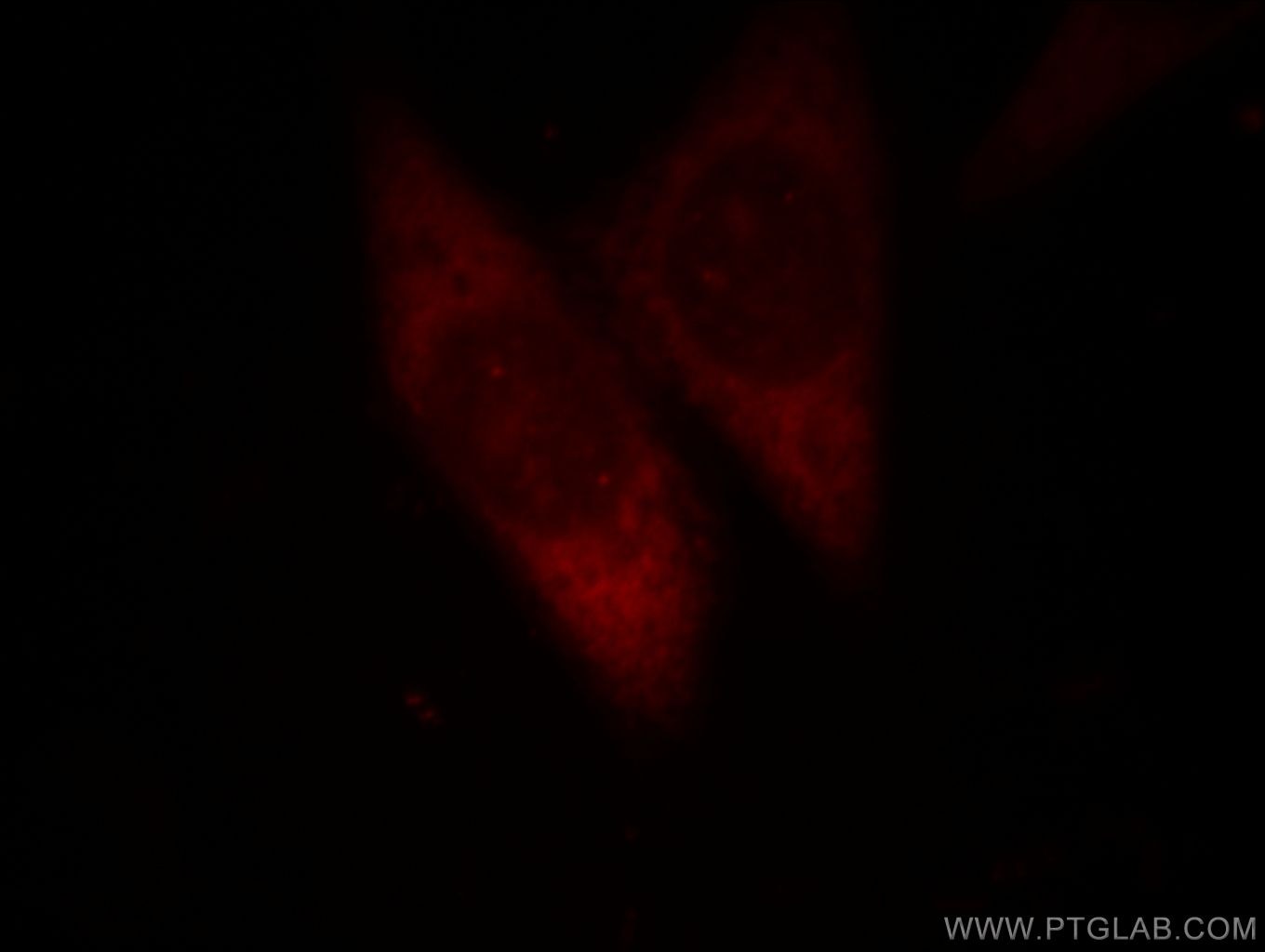
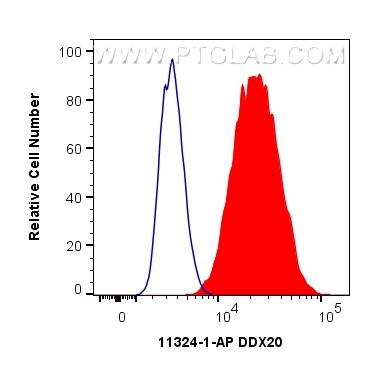
- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
DDX20 Polyklonaler Antikörper
DDX20 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 11324-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
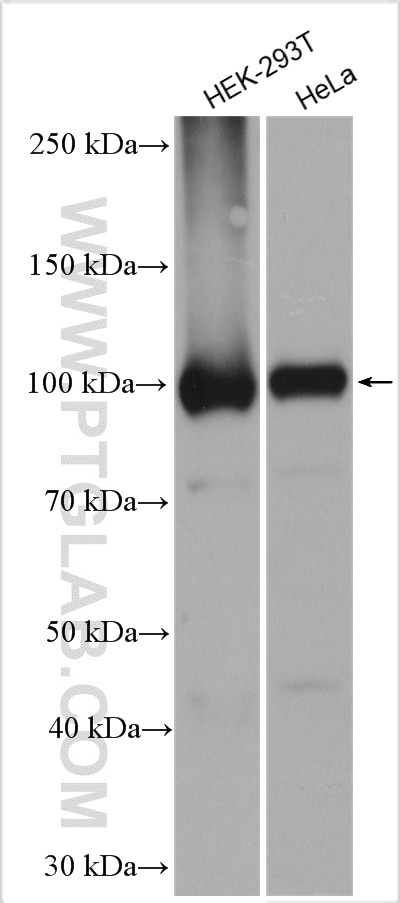
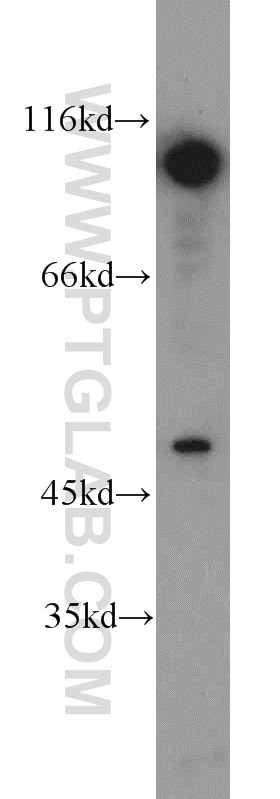
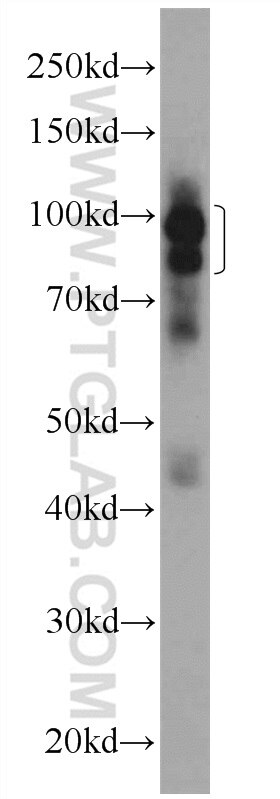
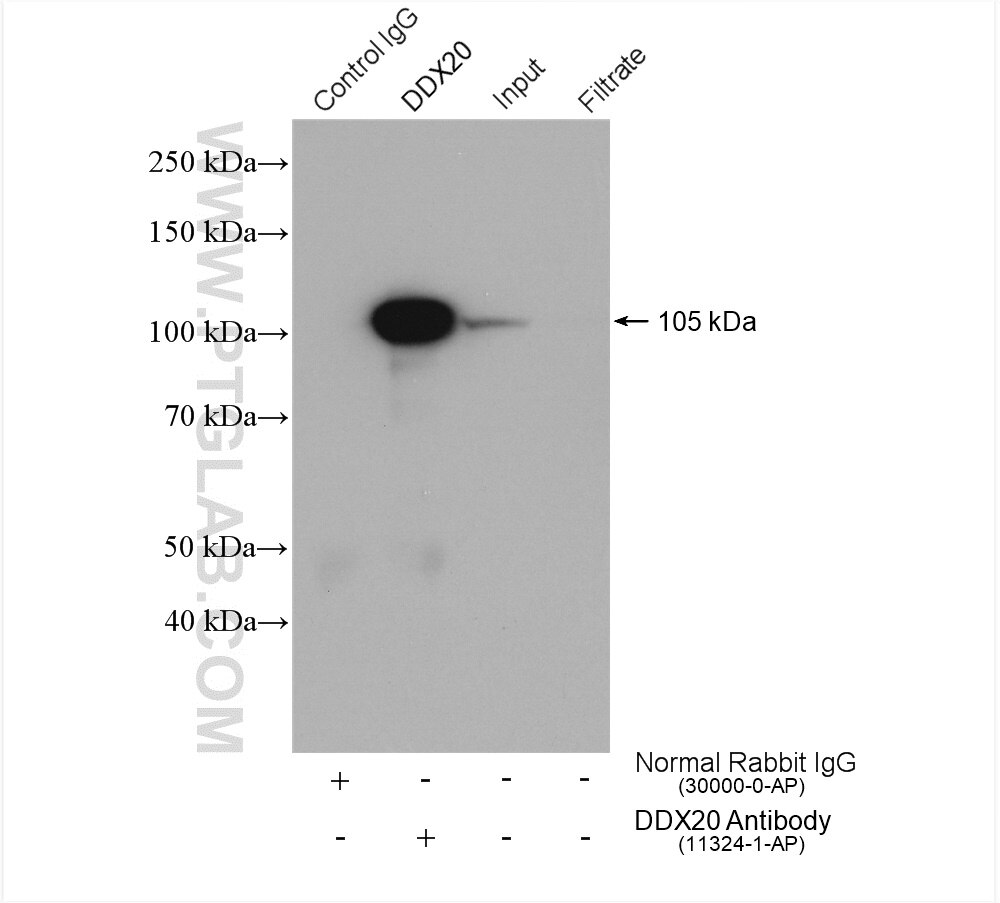
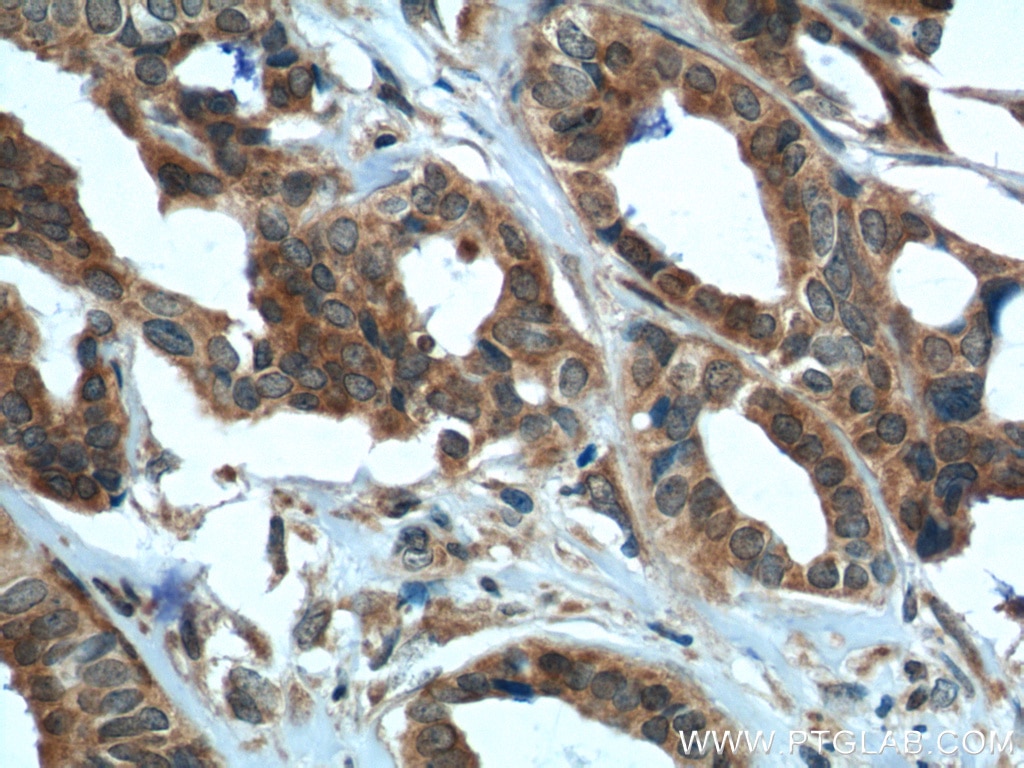
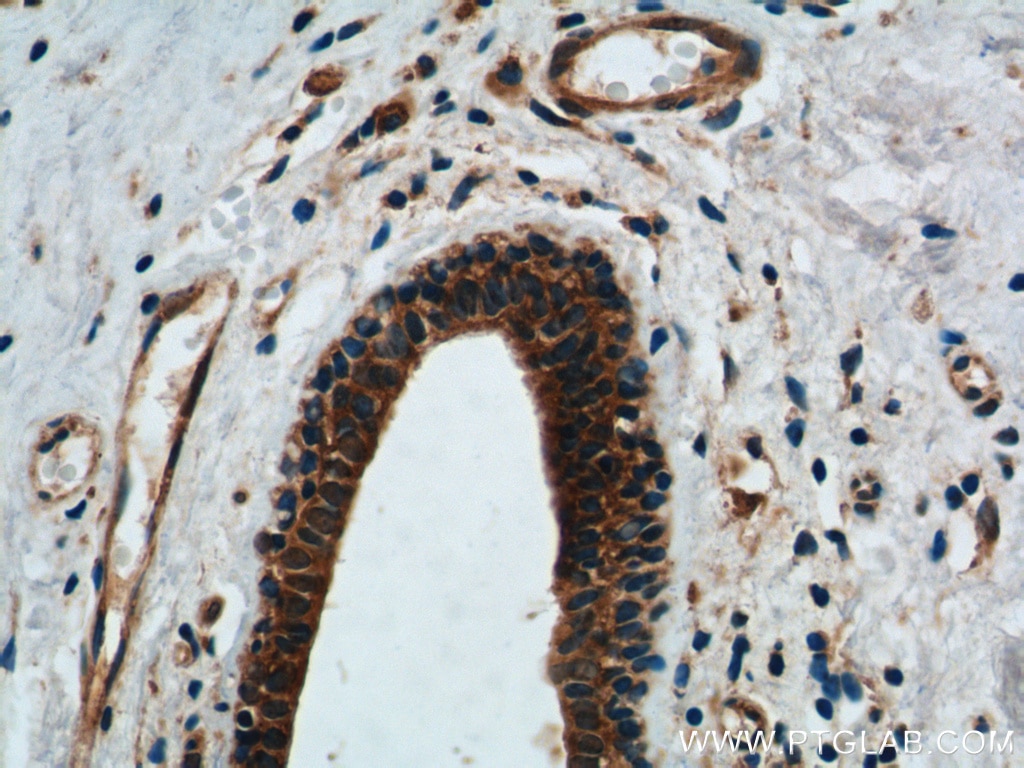
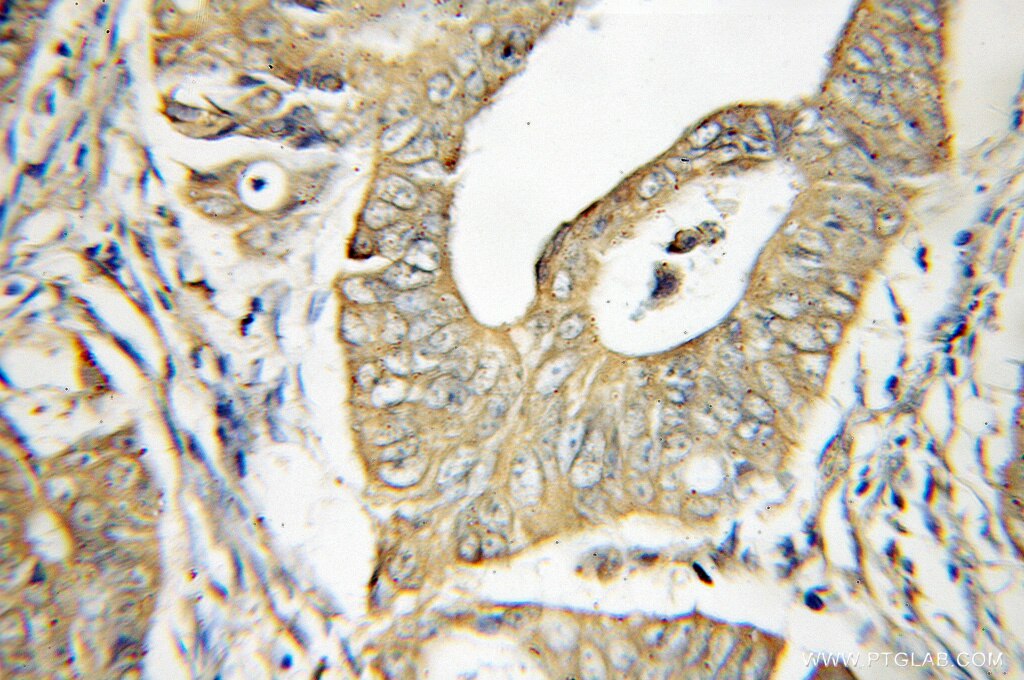
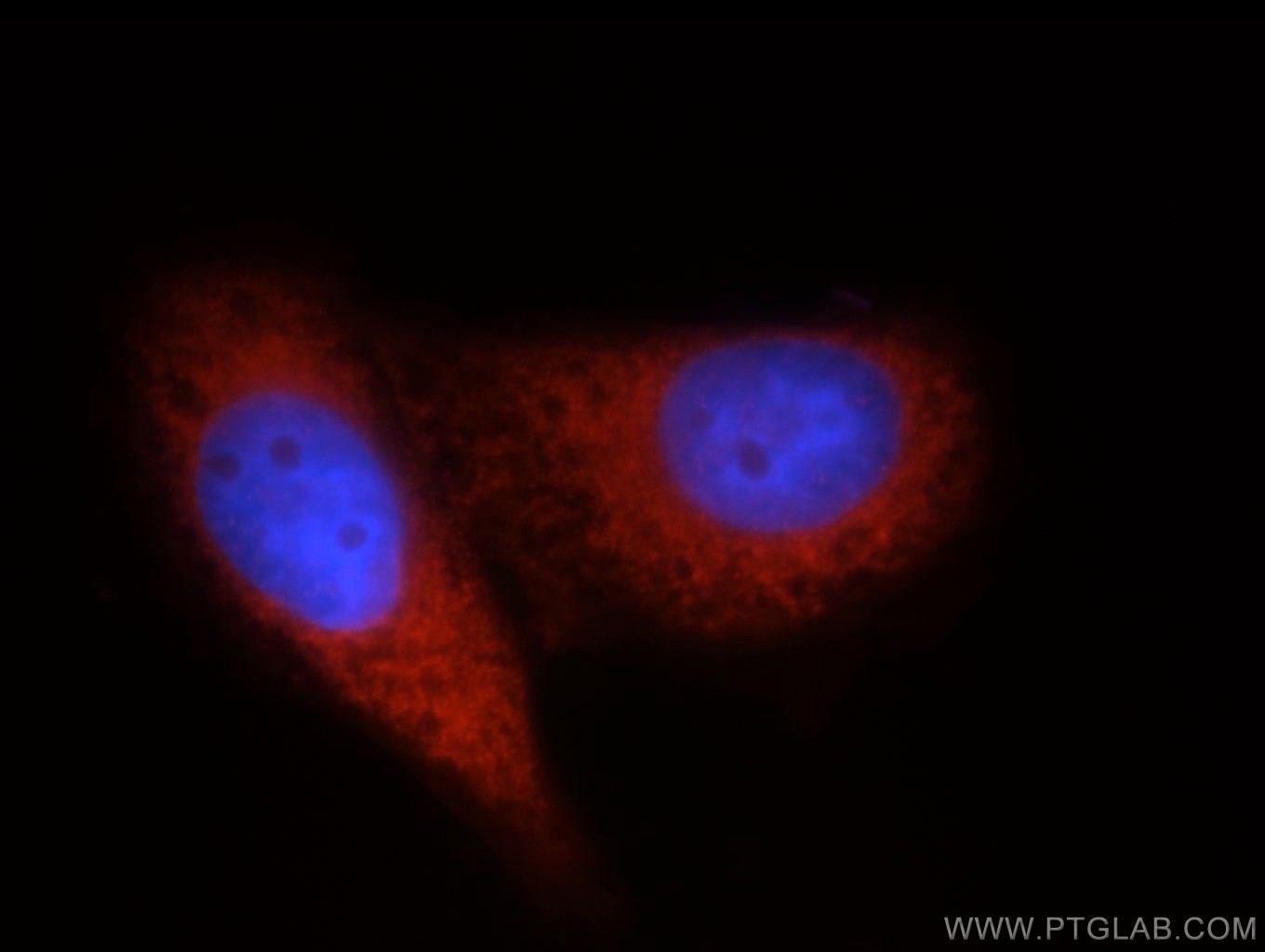
11324-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA DDX20 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | DDX20 fusion protein Ag1863 |
| Vollständiger Name | DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 20 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 824 aa, 92 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 100 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC011556 |
| Gene symbol | DDX20 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 11218 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 20 (DDX20), also known as DP103 or Gemin3, is a member of the DEAD box protein family expressed ubiquitously. DEAD family proteins use energy from ATP hydrolysis for RNA chaperoning and RNPase activity (PMID: 27121695). As a core member of the survival motor neuron (SMN) complex, DDX20 participate in small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) biogenesis. Second, DDX20 have direct roles in gene expression in view of its implication in transcription and post-transcriptional gene silencing. Addition, the false expression of DDX20 could have deleterious effects on cellular homeostasis thus leading to cancer development and progression (PMID:29523774). Anymore, DDX20 could be identified as a biomarker and metastasis-driving oncogene of human breast cancer (PMID: 25083991). The detected weight of DDX20 is slightly higher than the theoretical molecular weight that is because of phosphorylation after translation.