- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
DNAJC10 Polyklonaler Antikörper
DNAJC10 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 13101-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
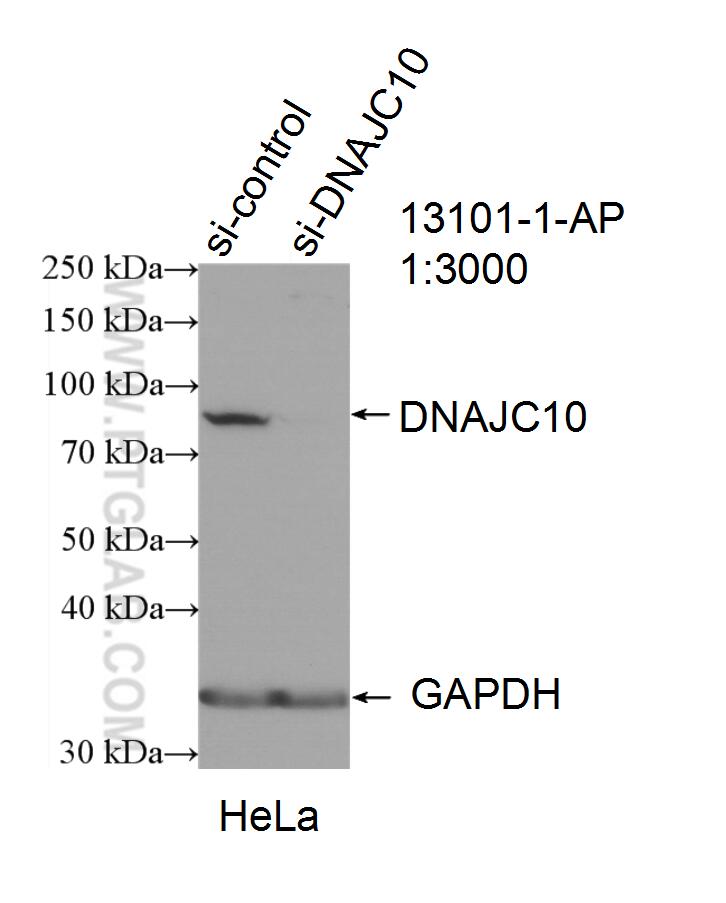
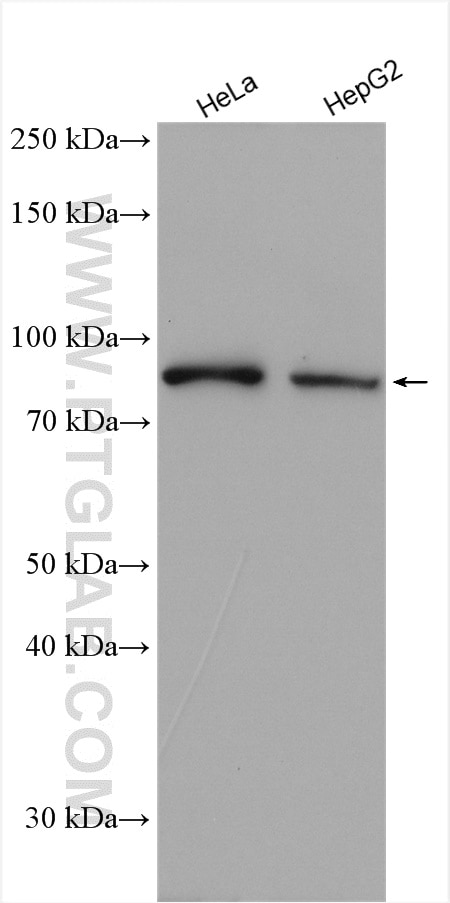
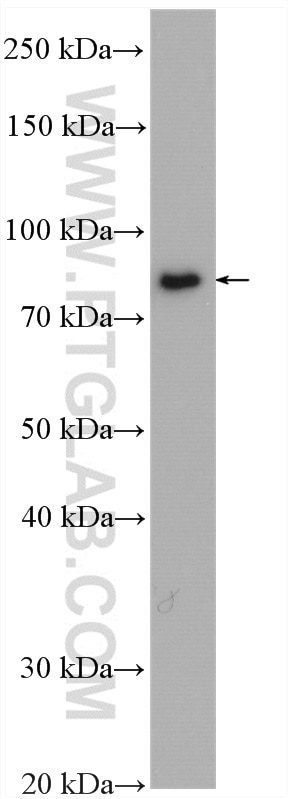
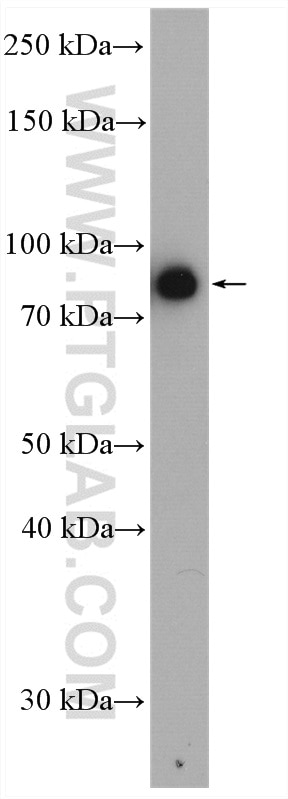
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HeLa-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen, Mauslebergewebe |
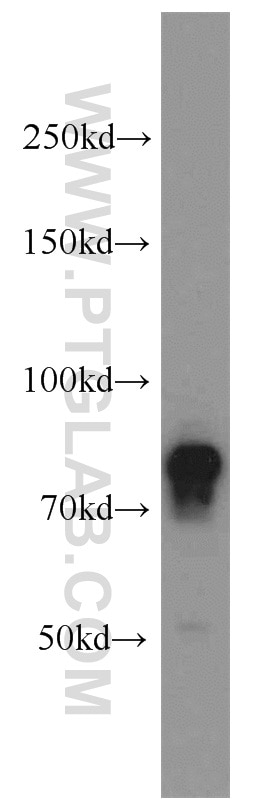
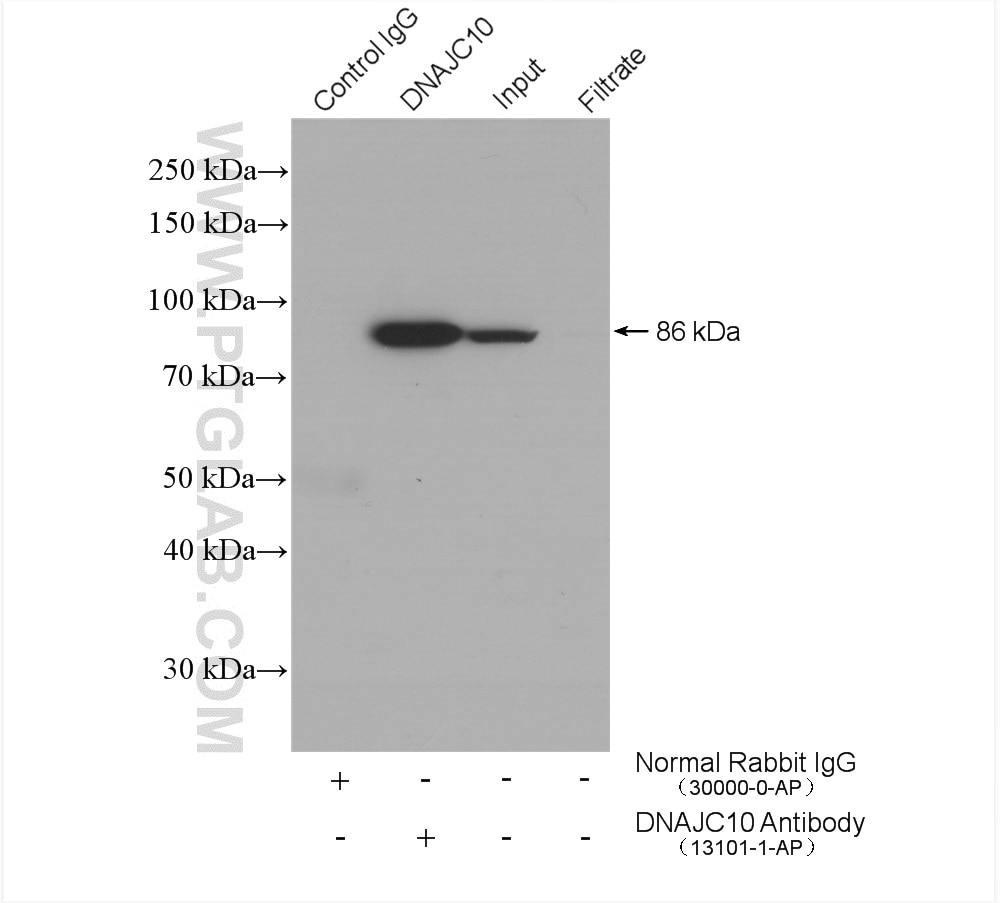
| Erfolgreiche IP | HeLa-Zellen |
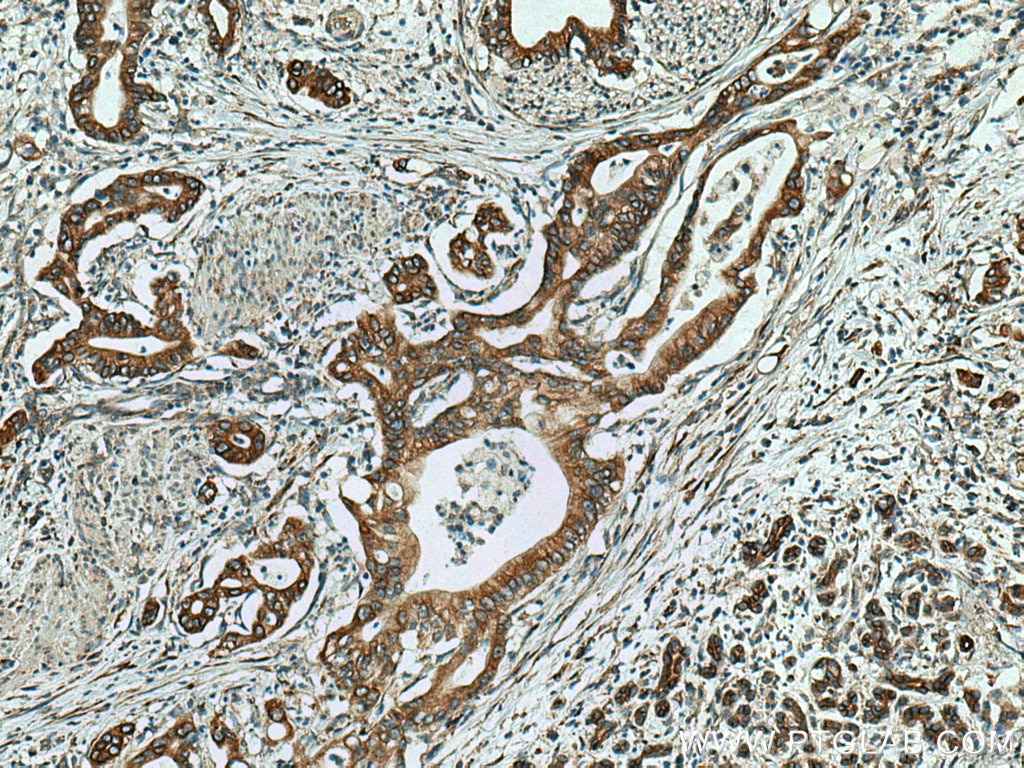
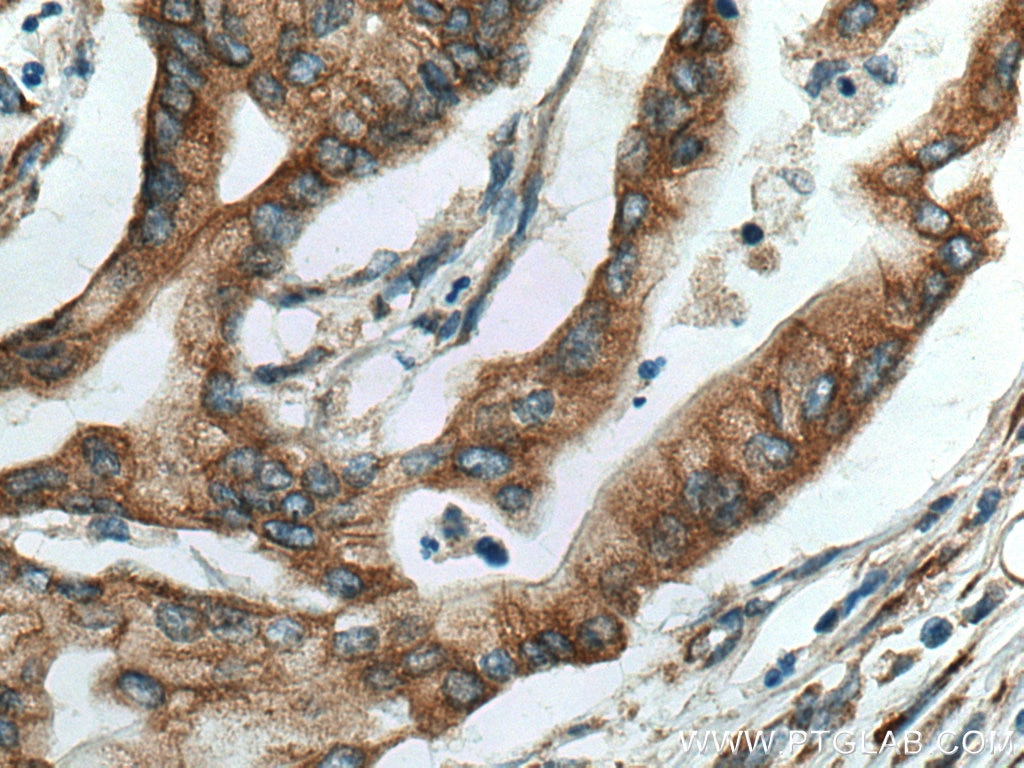
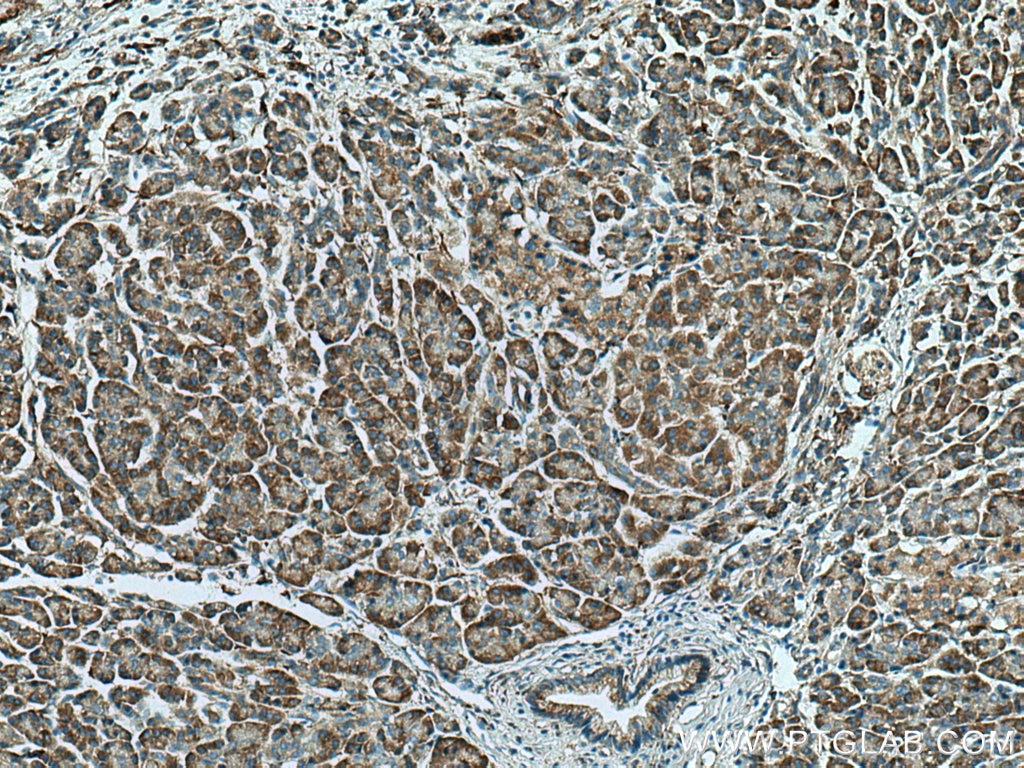
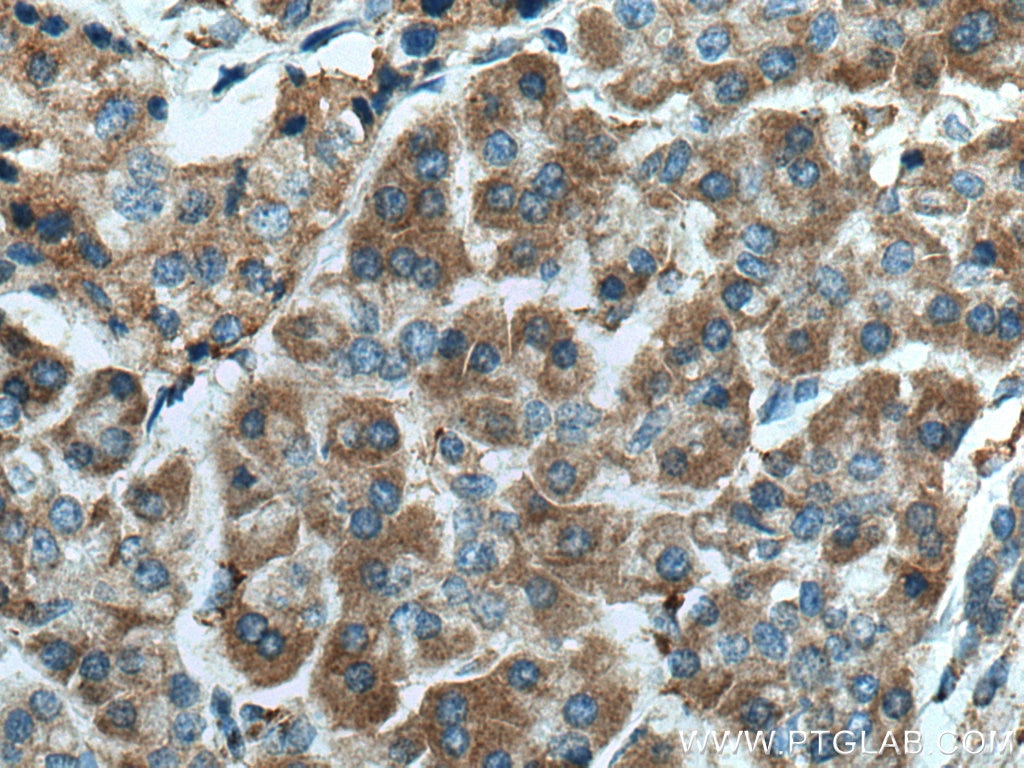
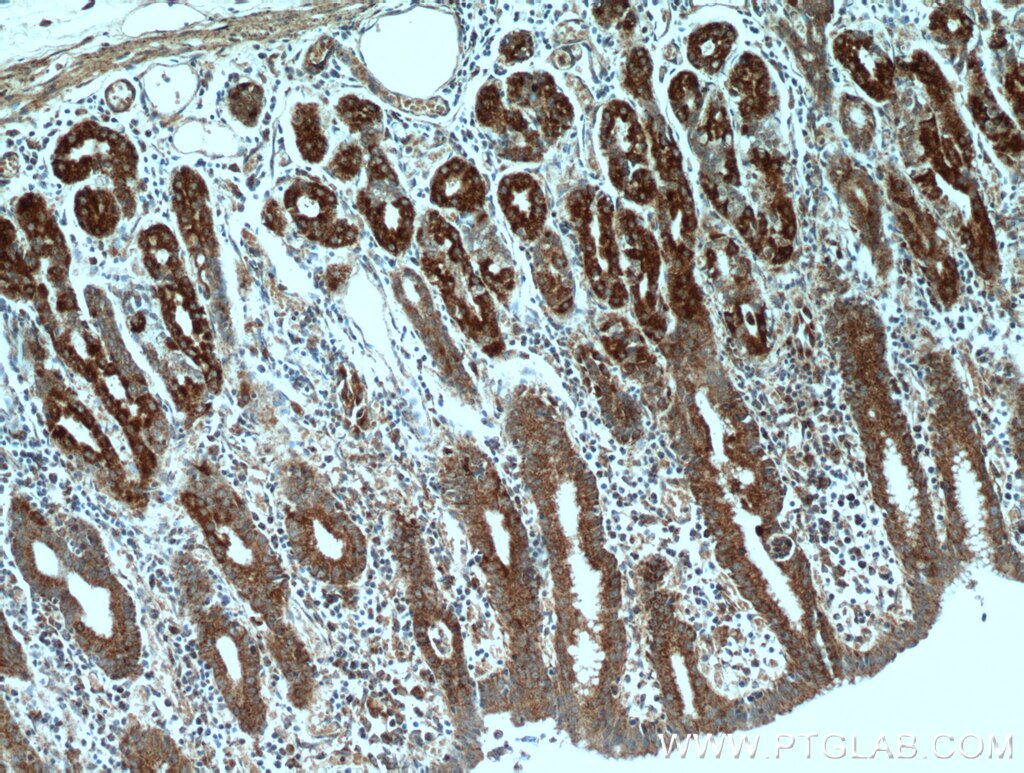
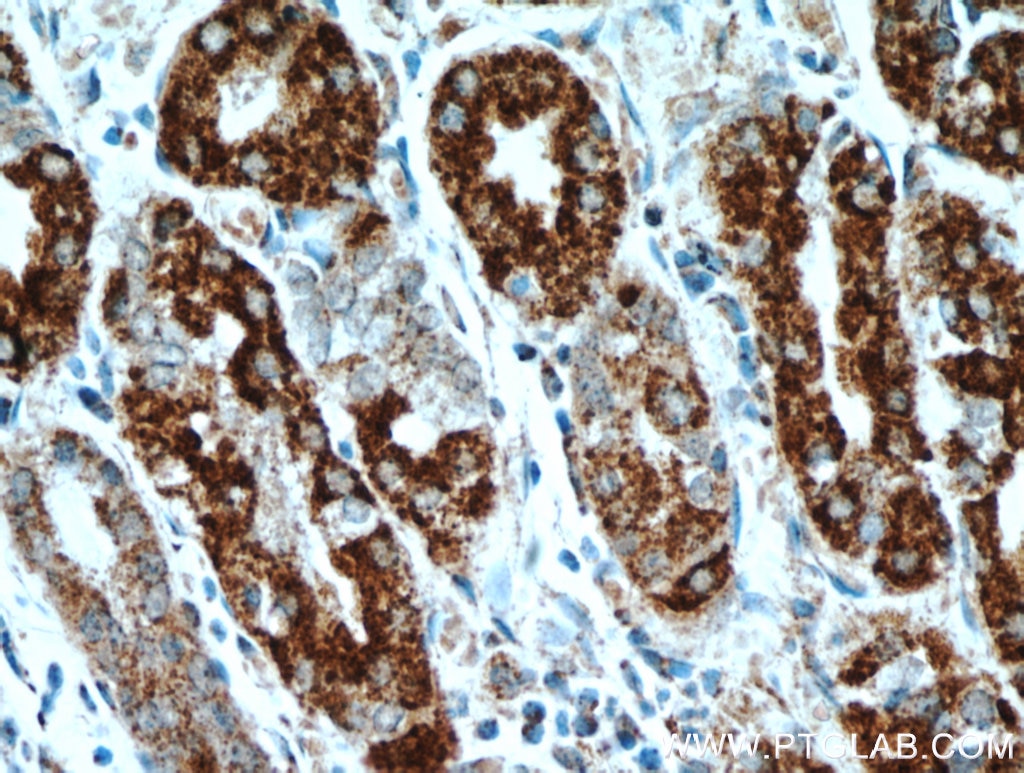
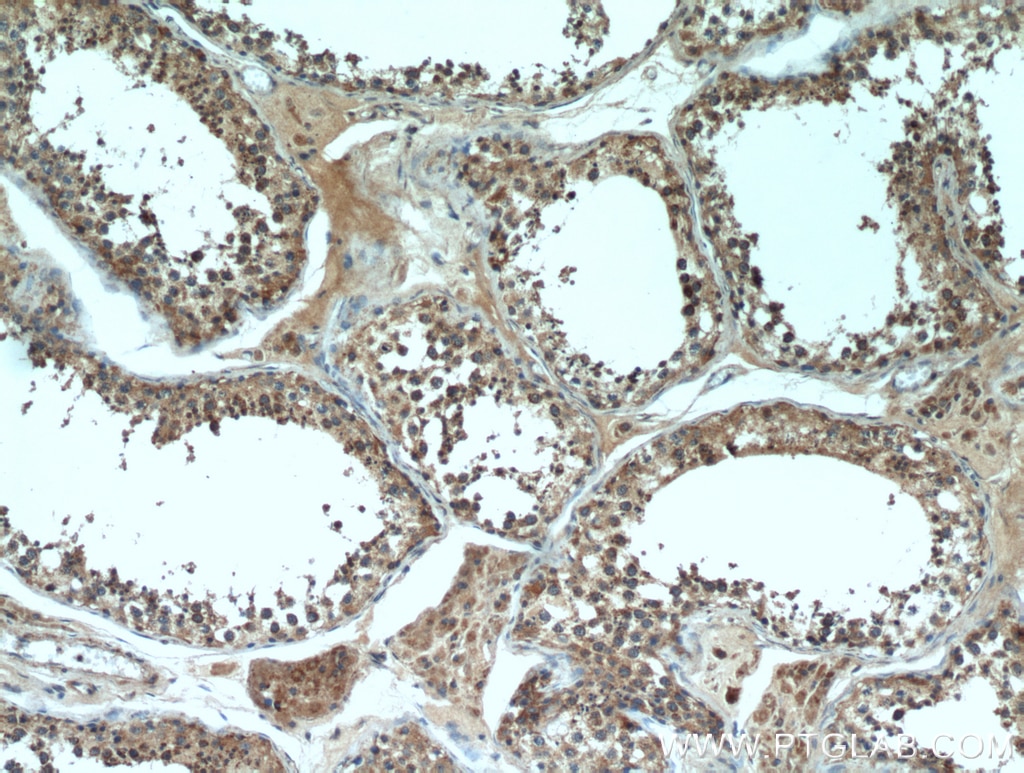
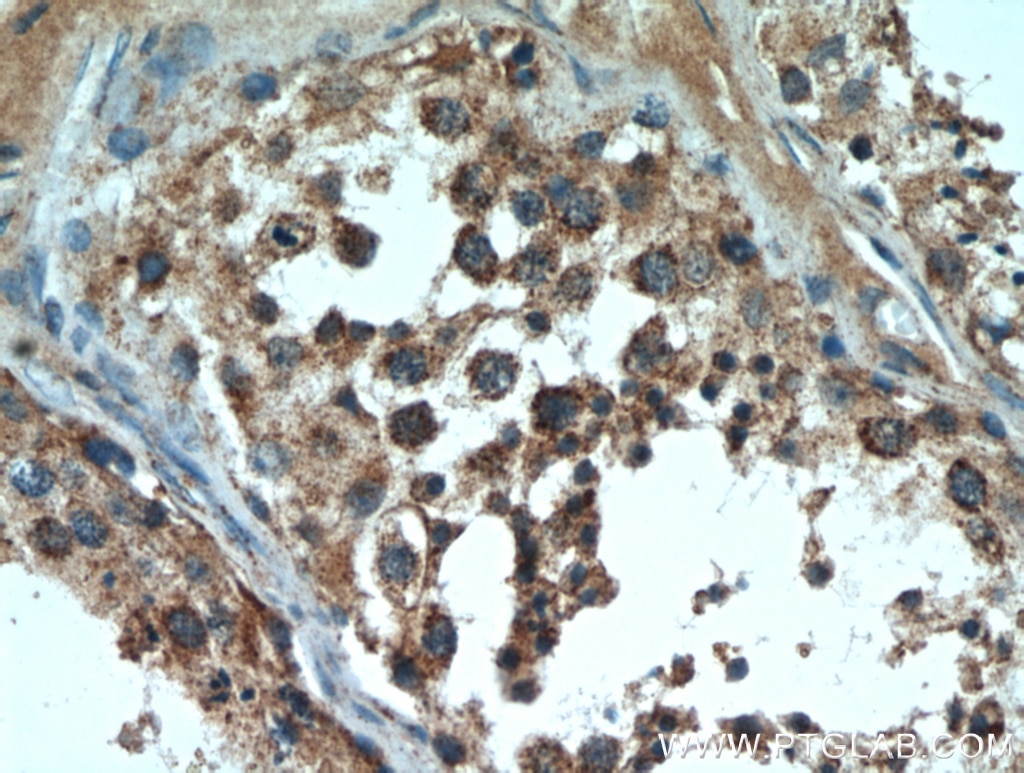
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Pankreaskarzinomgewebe, humanes Magengewebe, humanes Hodengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
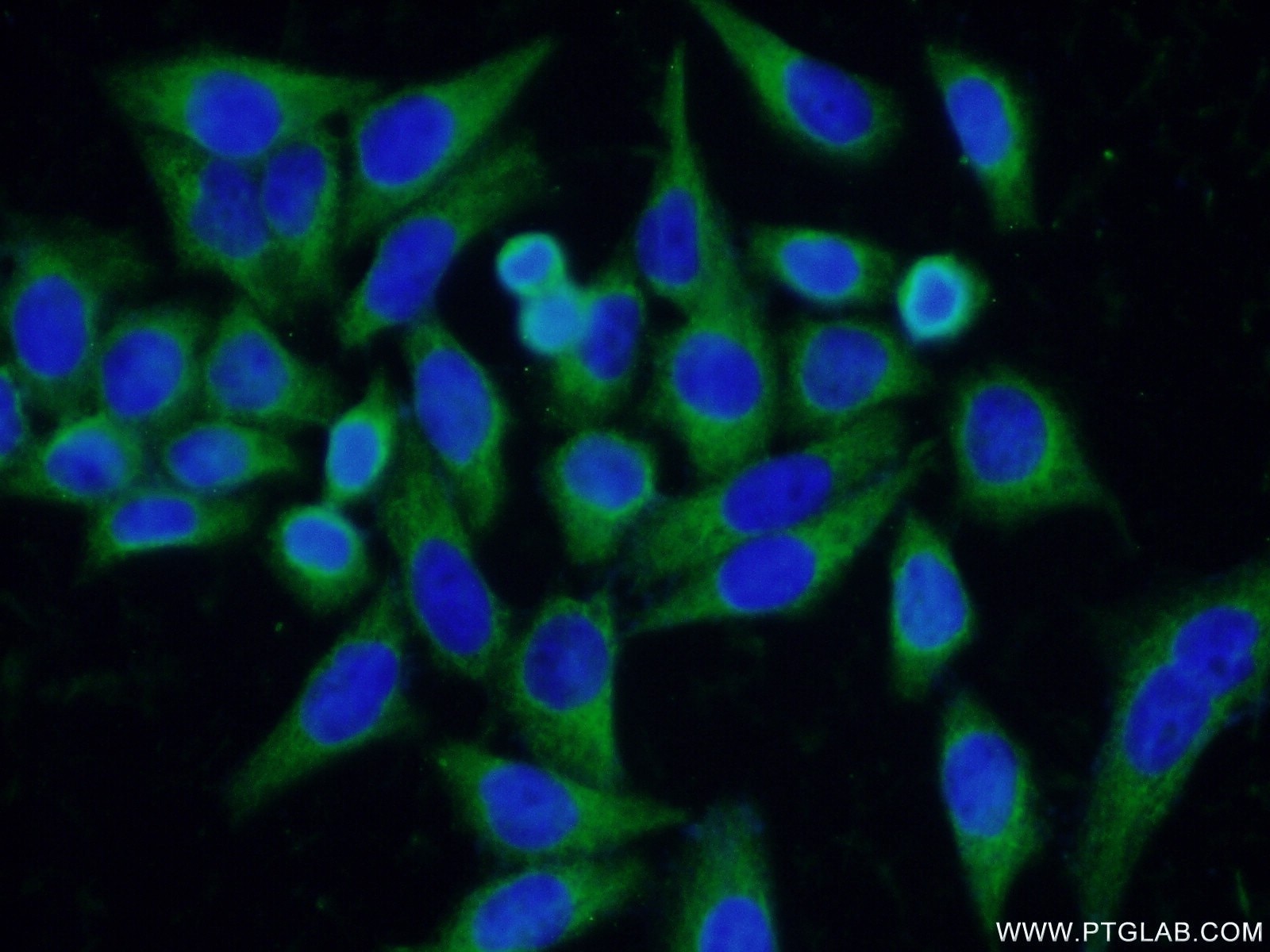
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HeLa-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 13 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
13101-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA DNAJC10 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | DNAJC10 fusion protein Ag3737 |
| Vollständiger Name | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 10 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 793 aa, 91 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 80-90 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC034713 |
| Gene symbol | DNAJC10 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 54431 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
DNAJC10(DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 10)is also named as ERDJ5. The human ER-resident protein (ERdj5) ubiquitously expresses and is abundant in secretory tissues such as pancreas and testis and it may be involved in assisting protein folding and quality control in the ER(PMID:12411443). The deduced 793-amino acid protein has a calculated molecular mass of about 91 kD. ERDJ5 contains an N-terminal hydrophobic sequence, followed by a type III DnaJ domain, 4 thioredoxin-like domains, and a C-terminal KDEL endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retention signal. It can be modified by N-linked glycosylation(PMID:12446677). The ERdj5 antibody displays a higher affinity for endogenous ERdj5u.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DNAJC10 antibody 13101-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for DNAJC10 antibody 13101-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for DNAJC10 antibody 13101-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for DNAJC10 antibody 13101-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
PLoS Pathog A cytosolic chaperone complexes with dynamic membrane J-proteins and mobilizes a nonenveloped virus out of the endoplasmic reticulum. | ||
Mol Cell Proteomics Thyroglobulin Interactome Profiling Defines Altered Proteostasis Topology Associated With Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis | ||
Diabetes Unbiased Profiling of the Human Proinsulin Biosynthetic Interaction Network Reveals a Role For Peroxiredoxin 4 in Proinsulin Folding. | ||
Mol Cell Proteomics Thyroglobulin Interactome Profiling Defines Altered Proteostasis Topology Associated With Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis. | ||
Biochem J Opposing regulation of endoplasmic reticulum retention under stress by ERp44 and PDIA6 |