- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
EIF5B Polyklonaler Antikörper
EIF5B Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 13527-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
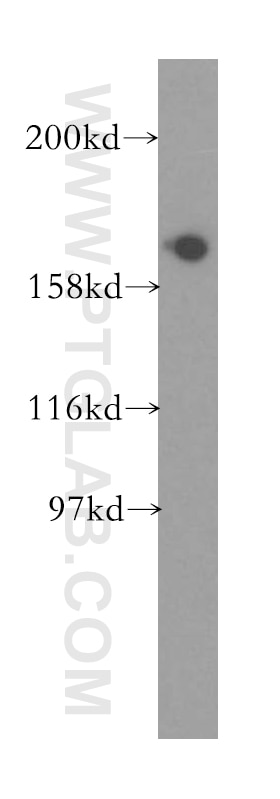
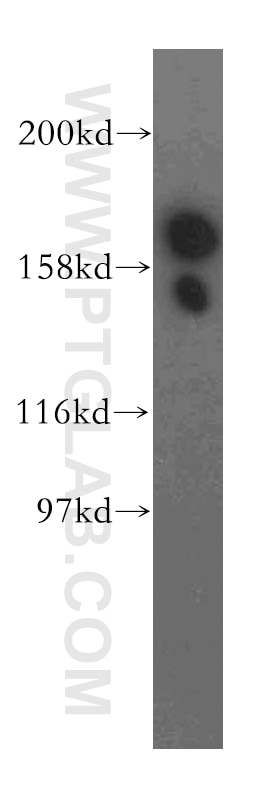
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Maushirngewebe, A549-Zellen |
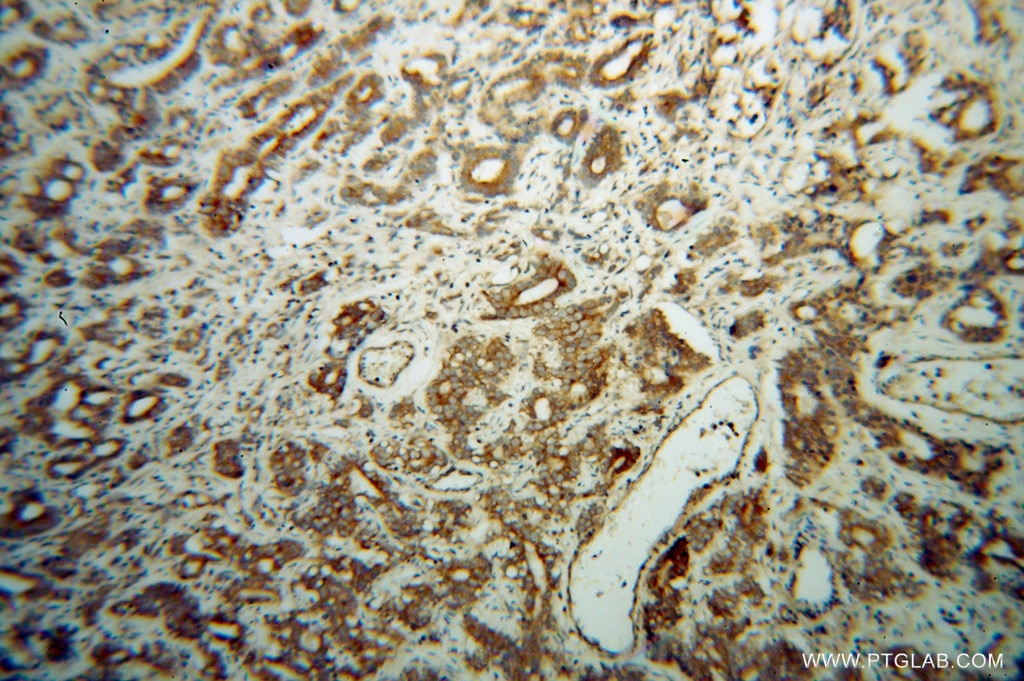
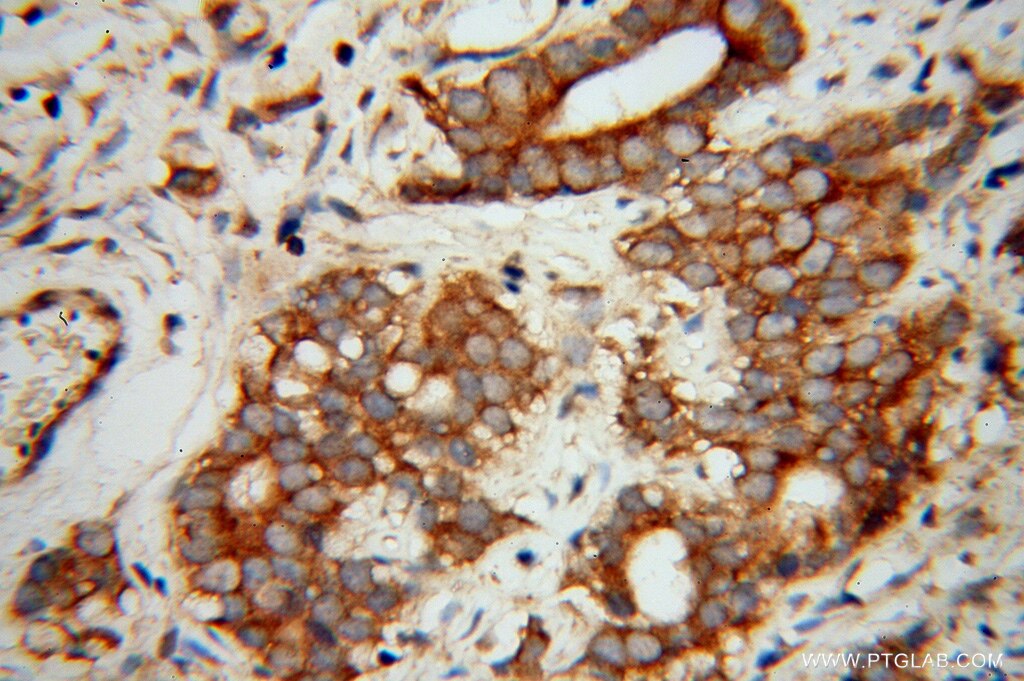
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Gliomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
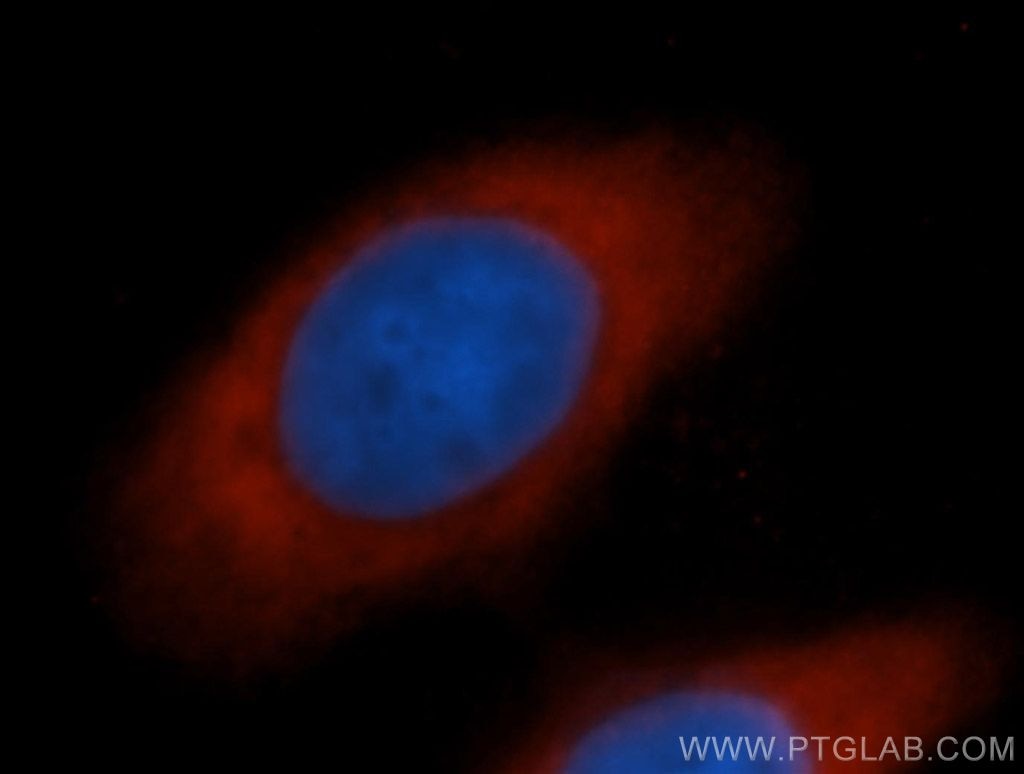
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | MCF-7-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
Produktinformation
13527-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA EIF5B und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Hausschwein |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | EIF5B fusion protein Ag4404 |
| Vollständiger Name | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 1220 aa, 139 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 175 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC032639 |
| Gene symbol | EIF5B |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9669 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Translation initiation requires the delivery of the initiator methionine tRNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit. The initiator methionine tRNA is delivered by the heterotrimeric complex EIF2 in a ternary complex with GTP that interacts with the 40S subunit. The resulting complex then binds to an mRNA and scans for the AUG start codon. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (EIF5B) plays a role in recognition of the AUG codon in conjunction with translation factor eIF2, which functions to general translation initiation by promoting the binding of the formylmethionine-tRNA to ribosomes, and promotes joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit. A single crossreactive polypeptide of 175 kDa was detected, whereas the predicted size of the protein was 139 kDa. This size discrepancy may be the result of posttranslational modifications of EIF5B or, perhaps more likely, of unusual behavior in SDS-PAGE caused by the highly charged N-terminal region of EIF5B (PMID: 10200264 ).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for EIF5B antibody 13527-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for EIF5B antibody 13527-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for EIF5B antibody 13527-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Mol Life Sci eIF2A, an initiator tRNA carrier refractory to eIF2α kinases, functions synergistically with eIF5B. | ||
bioRxiv Start codon-associated ribosomal frameshifting mediates nutrient stress adaptation
| ||
bioRxiv LARP1 senses free ribosomes to coordinate supply and demand of ribosomal proteins
| ||
Sci Adv Hepatovirus translation requires PDGFA-associated protein 1, an eIF4E-binding protein regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress responses | ||
J Virol VP3 protein of Senecavirus A promotes viral IRES-driven translation and attenuates innate immunity by specifically relocalizing hnRNPA2B1 |
Rezensionen
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Bill (Verified Customer) (12-23-2019) | This antibody give every strong signal on EIF5B.
|