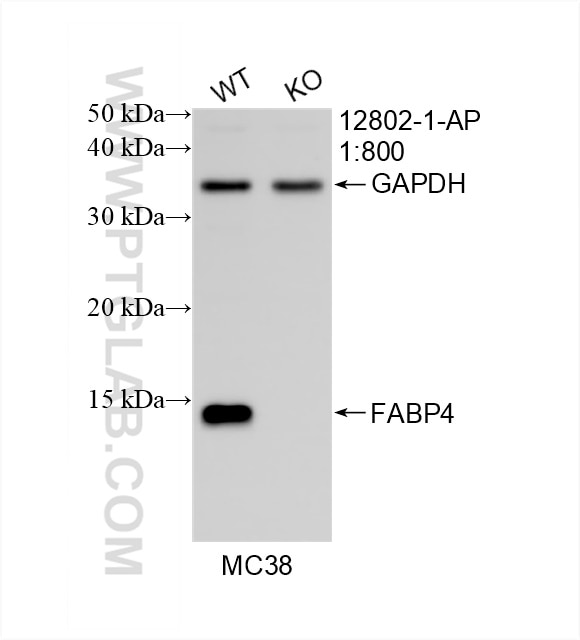
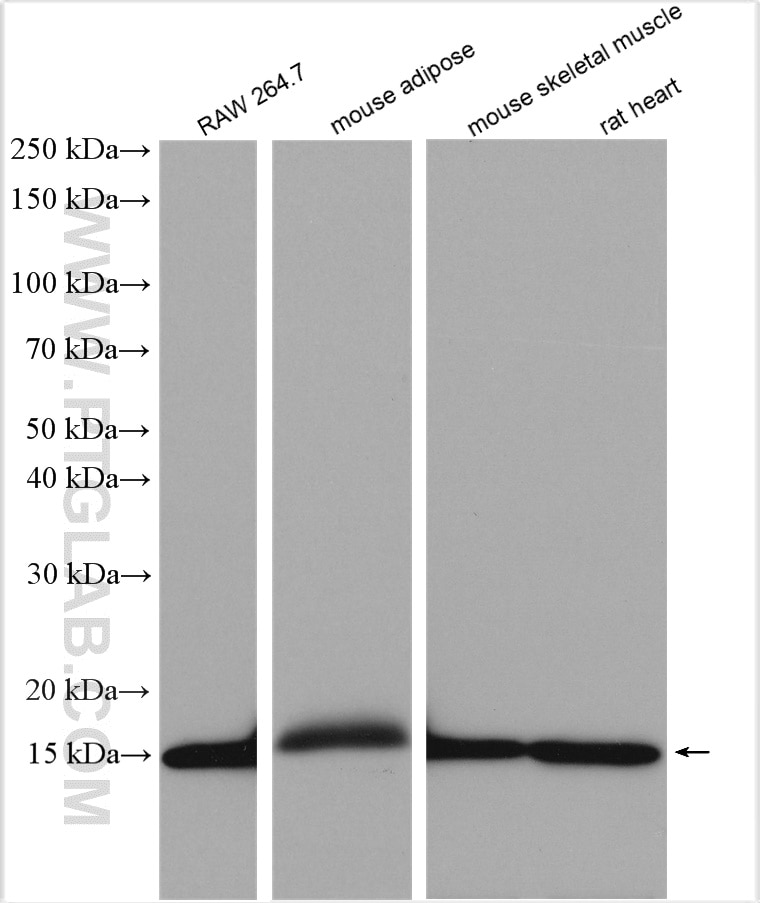
- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
FABP4 Polyklonaler Antikörper
FABP4 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
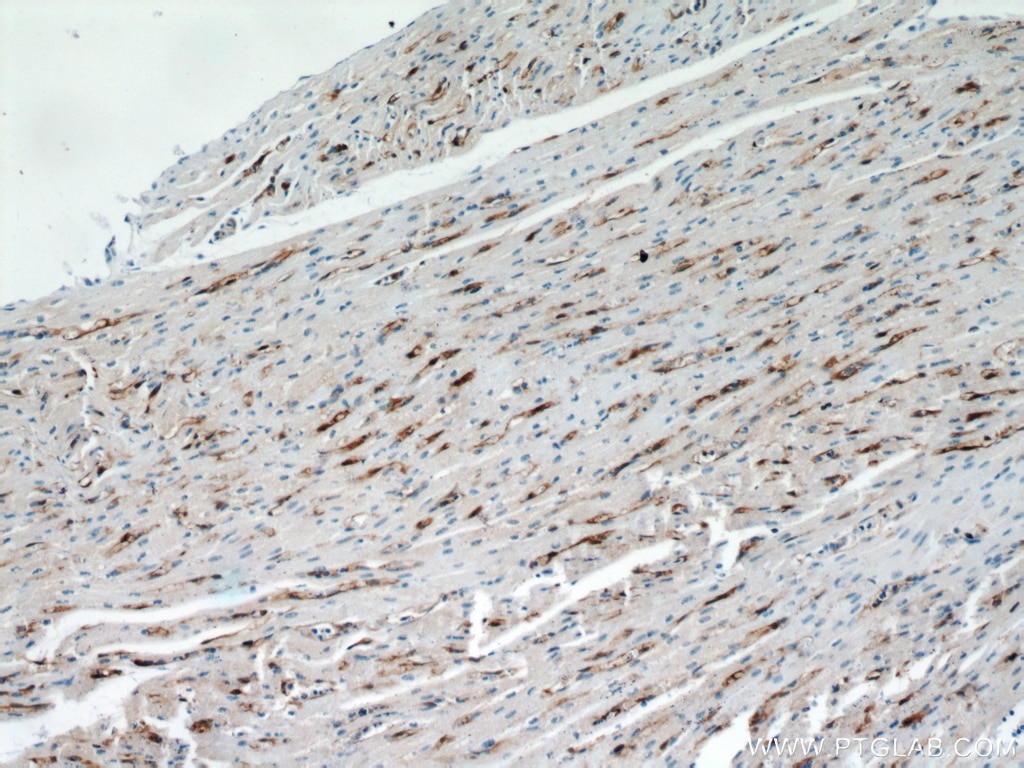
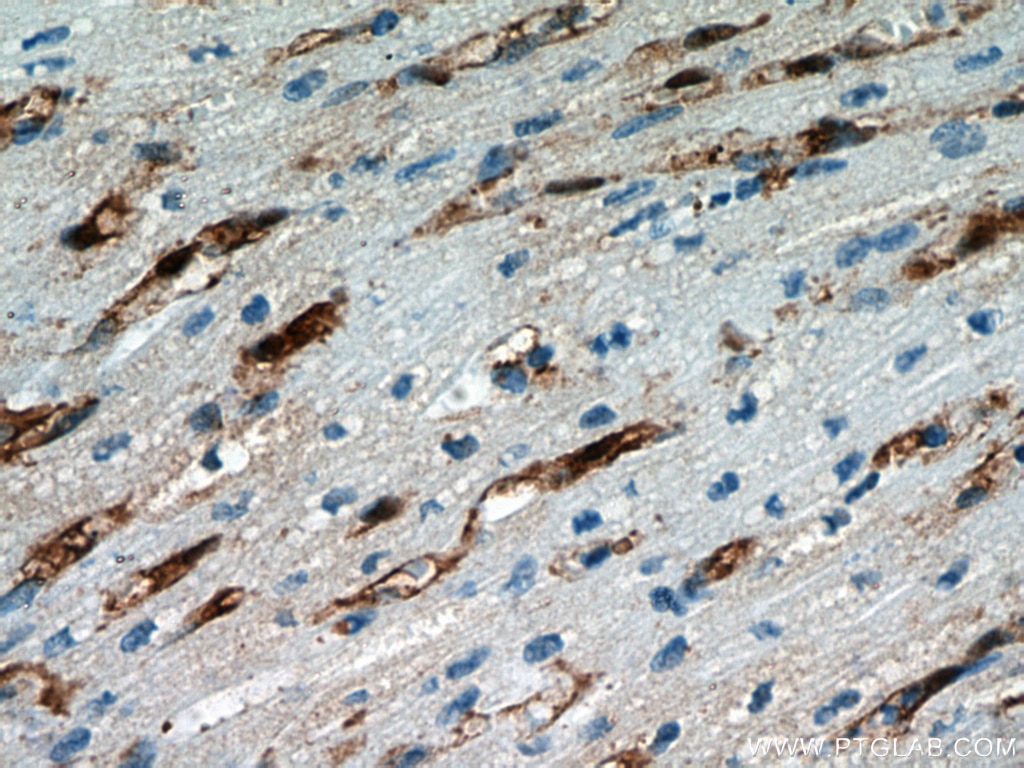
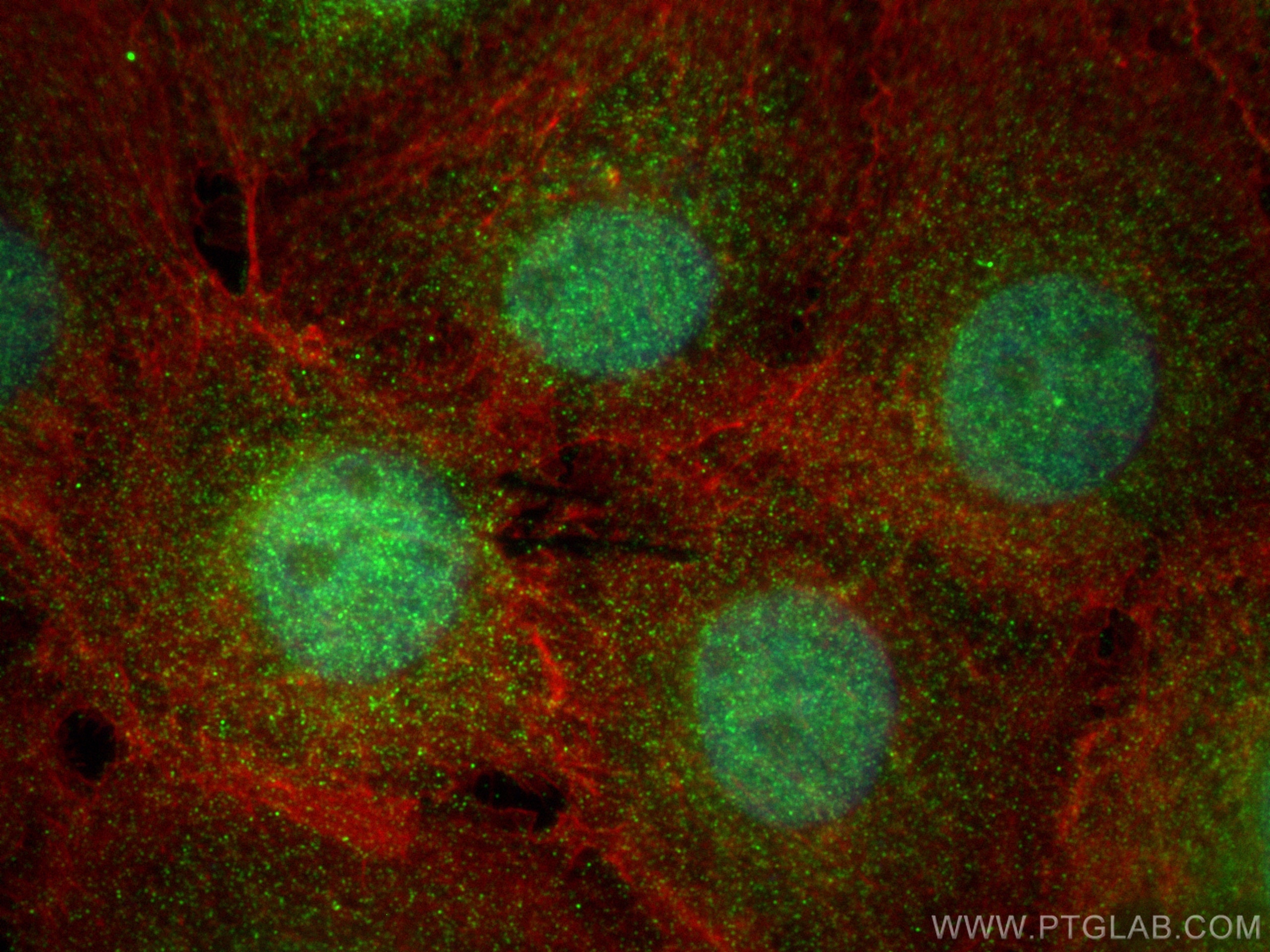
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 12802-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
12802-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA FABP4 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | FABP4 fusion protein Ag3912 |
| Vollständiger Name | fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 132 aa, 15 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 15 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC003672 |
| Gene symbol | FABP4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2167 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 is a member of the FABP family which abundantly expressed, fatty acid carrier proteins. FABPs are capable of binding a variety of hydrophobic molecules such as long-chain fatty acids and are important for their uptake and intracellular trafficking. It was first identified as an adipocyte-specific protein, important for the maintenance of lipid and glucose metabolism. It is also detected in macrophages, where it participates in regulating inflammation and cholesterol trafficking via NFκB and PPAR. In more recent studies, FABP4 has been found in a variety of endothelial cells, where it has been identified as a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation and possibly angiogenesis. Pathologically, FABP4 has been associated with the development of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cancer and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. FABP4 has been identified as a novel prognostic factor for both adverse cardiovascular events and breast cancer.