- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
FABP5 Monoklonaler Antikörper
FABP5 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1C6E12
Kat-Nr. : 66299-1-Ig
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
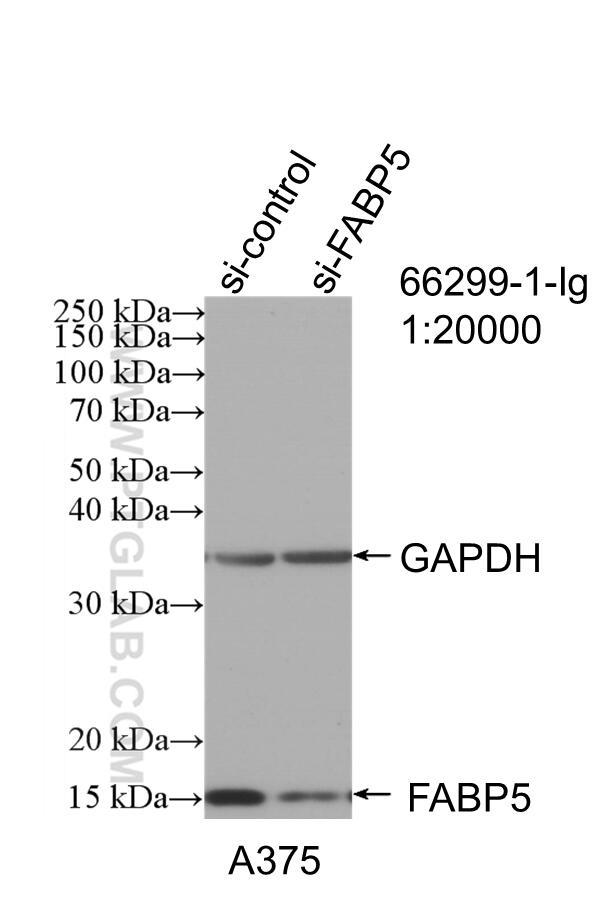
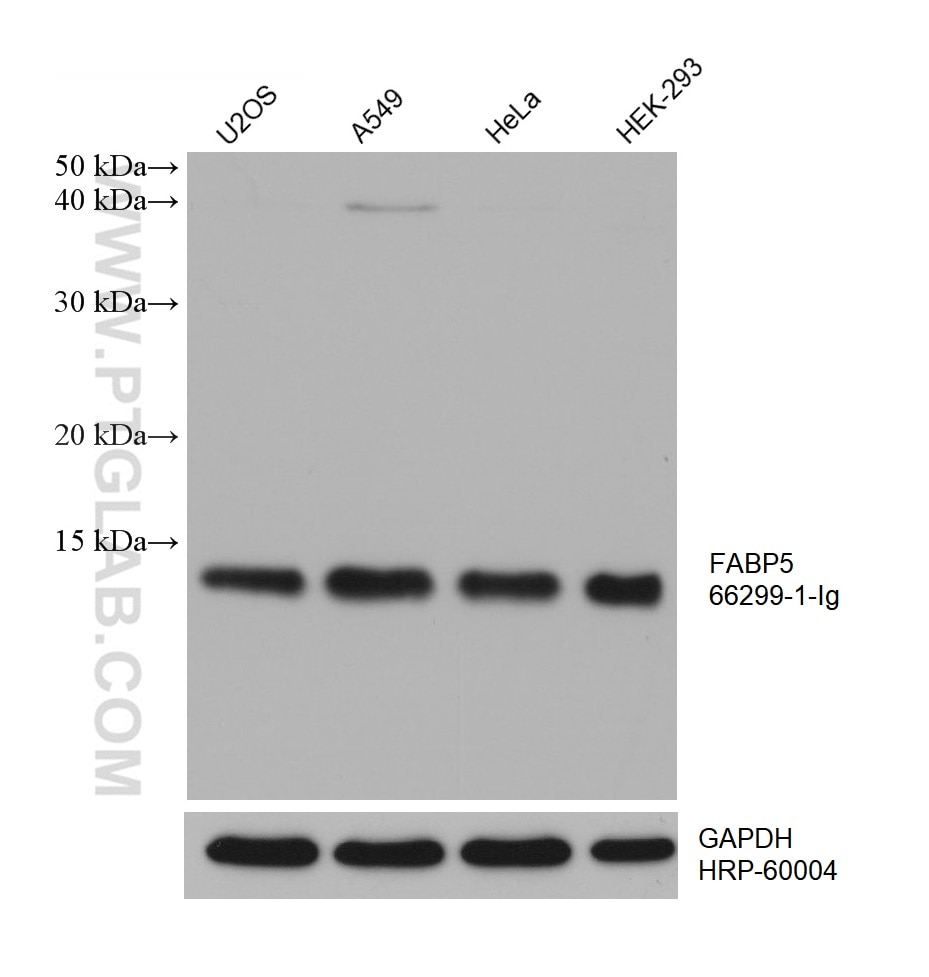
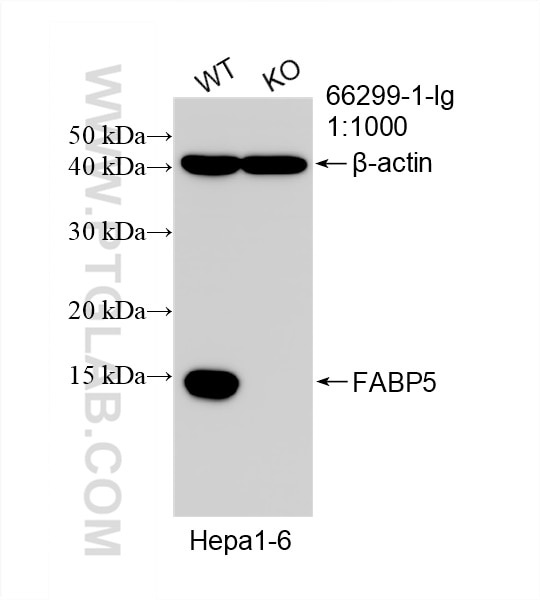
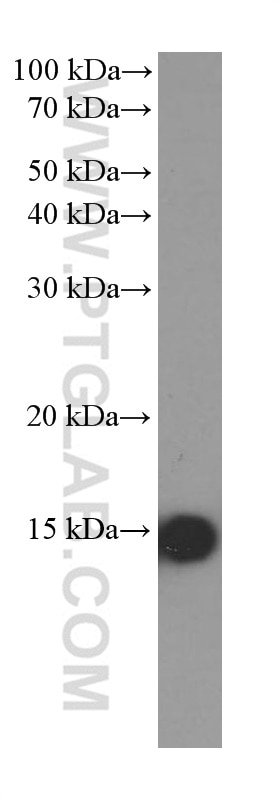
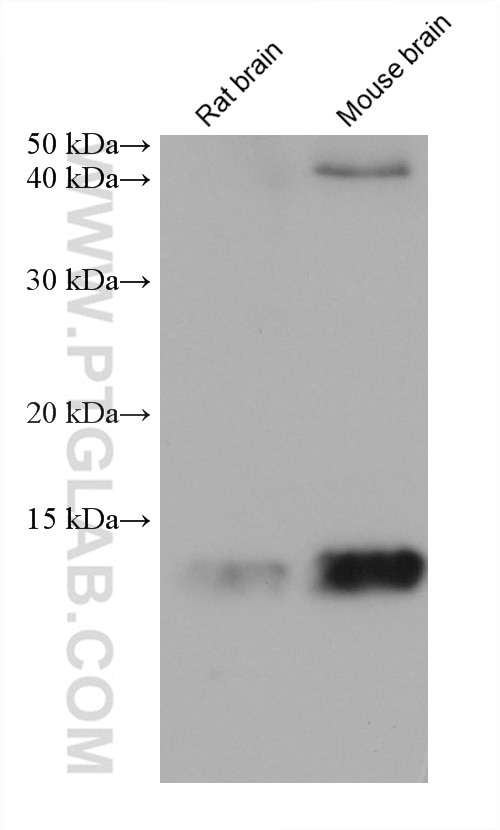
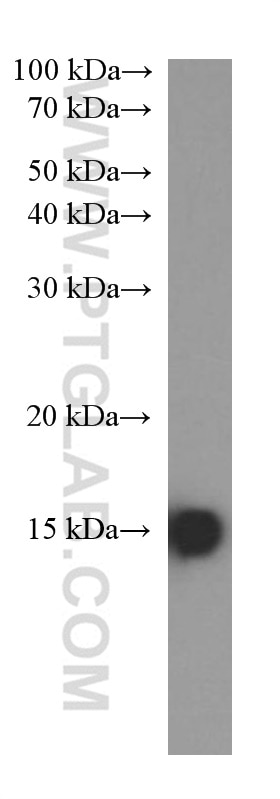
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | A375-Zellen, A549-Zellen, fetales humanes Hirngewebe, HEK-293-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, Hepa1-6-Zellen, Maushirngewebe, Rattenhirngewebe, U2OS-Zellen |
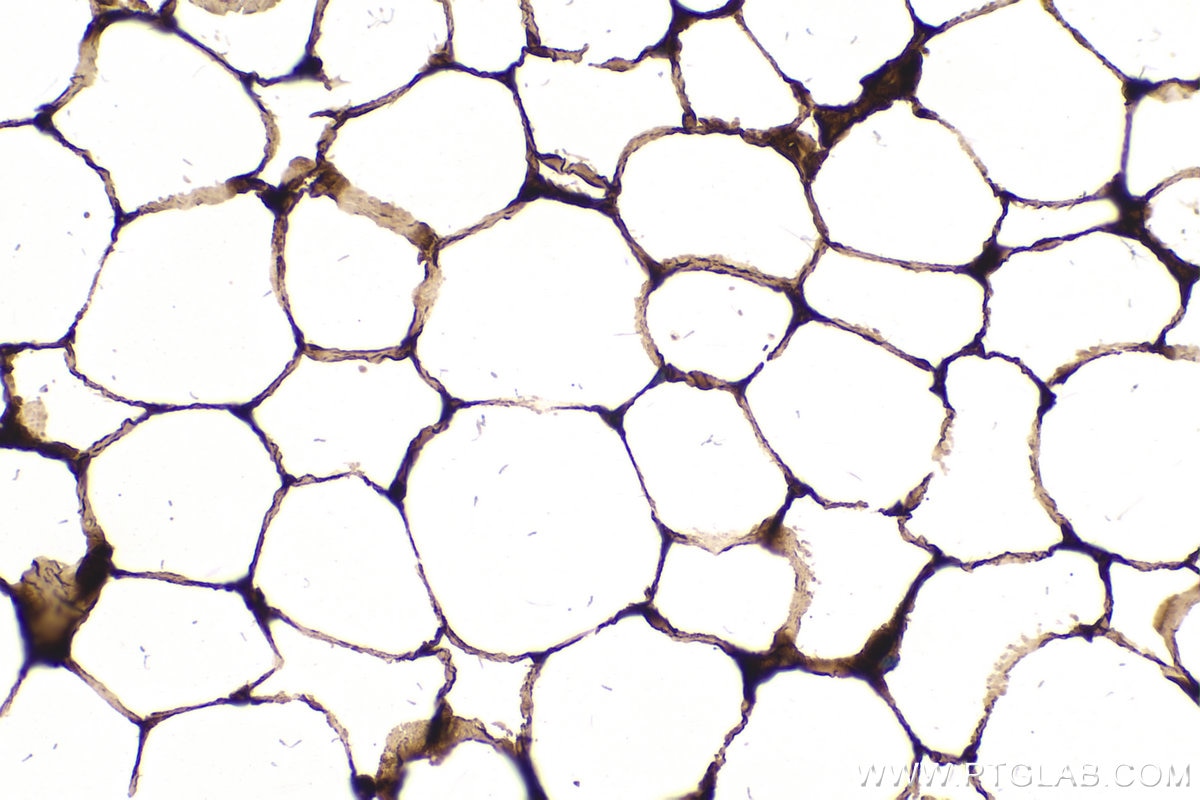
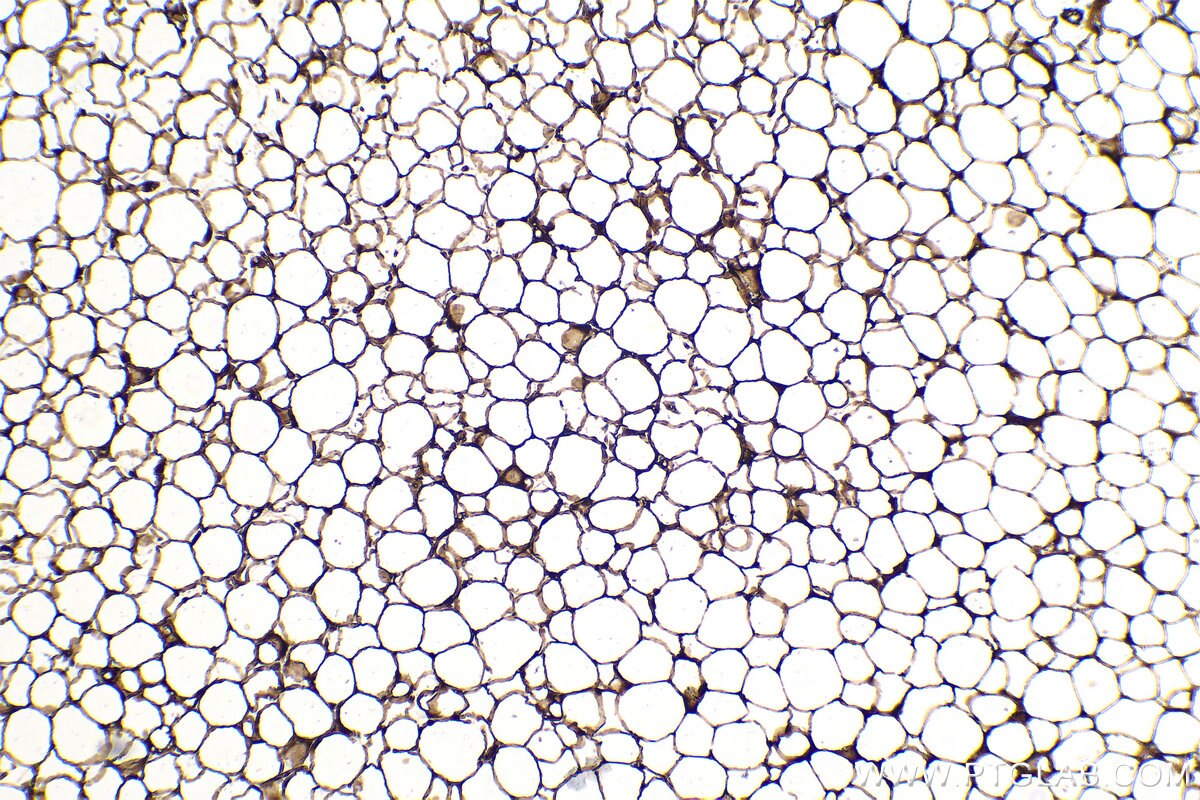
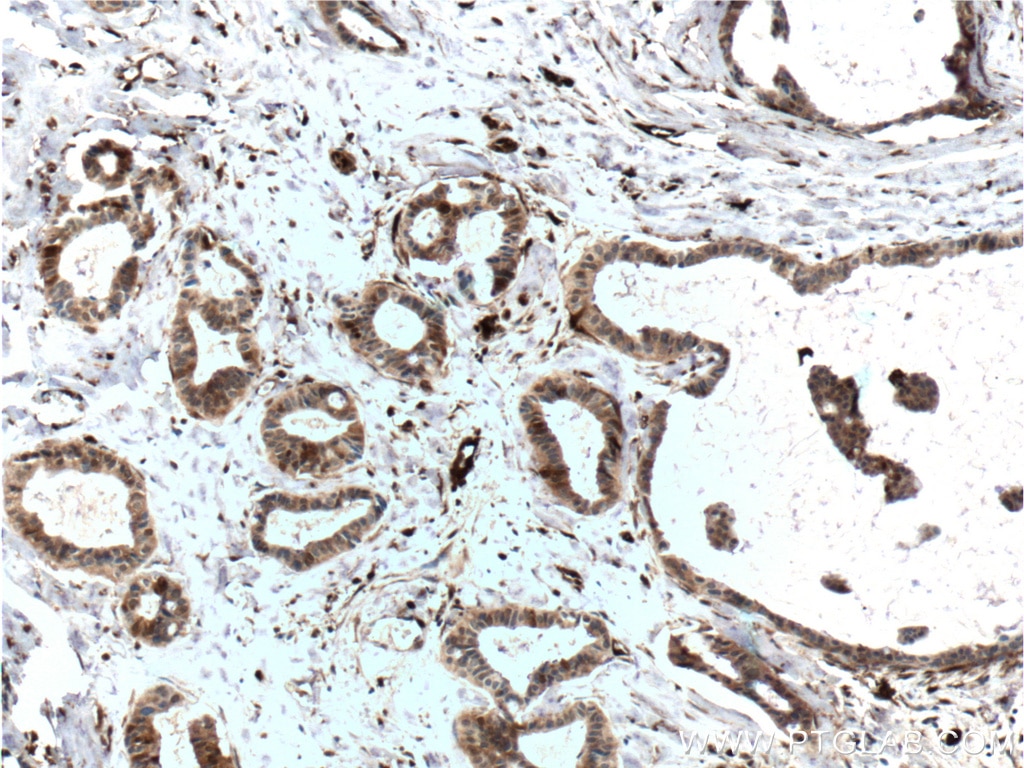
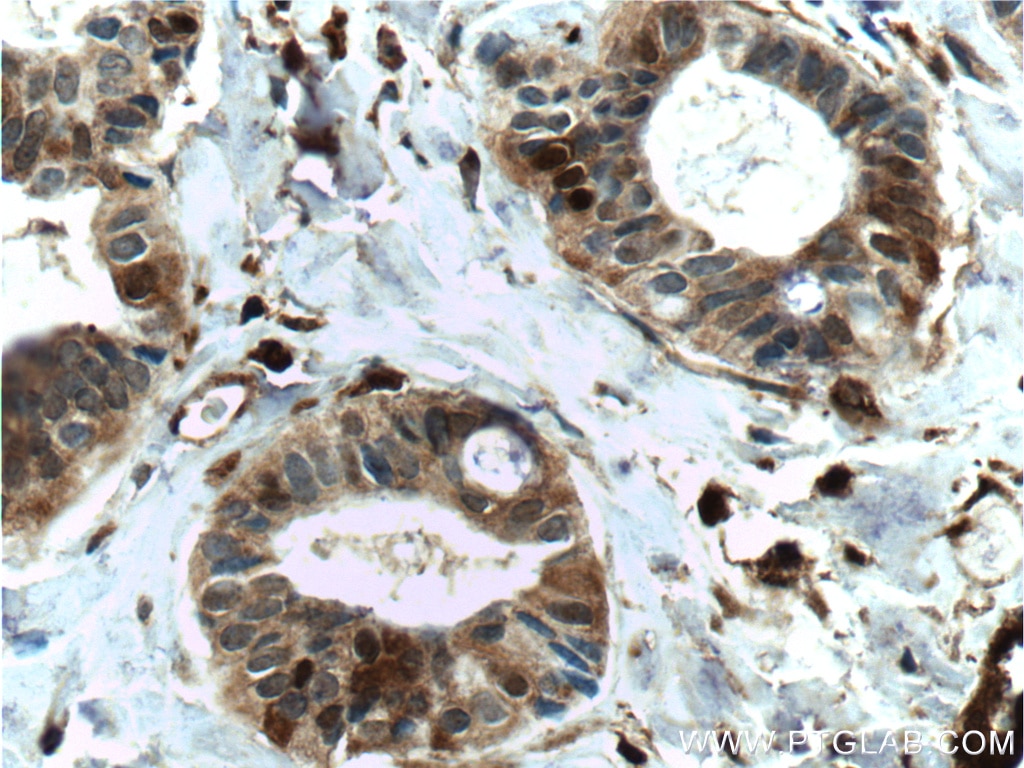
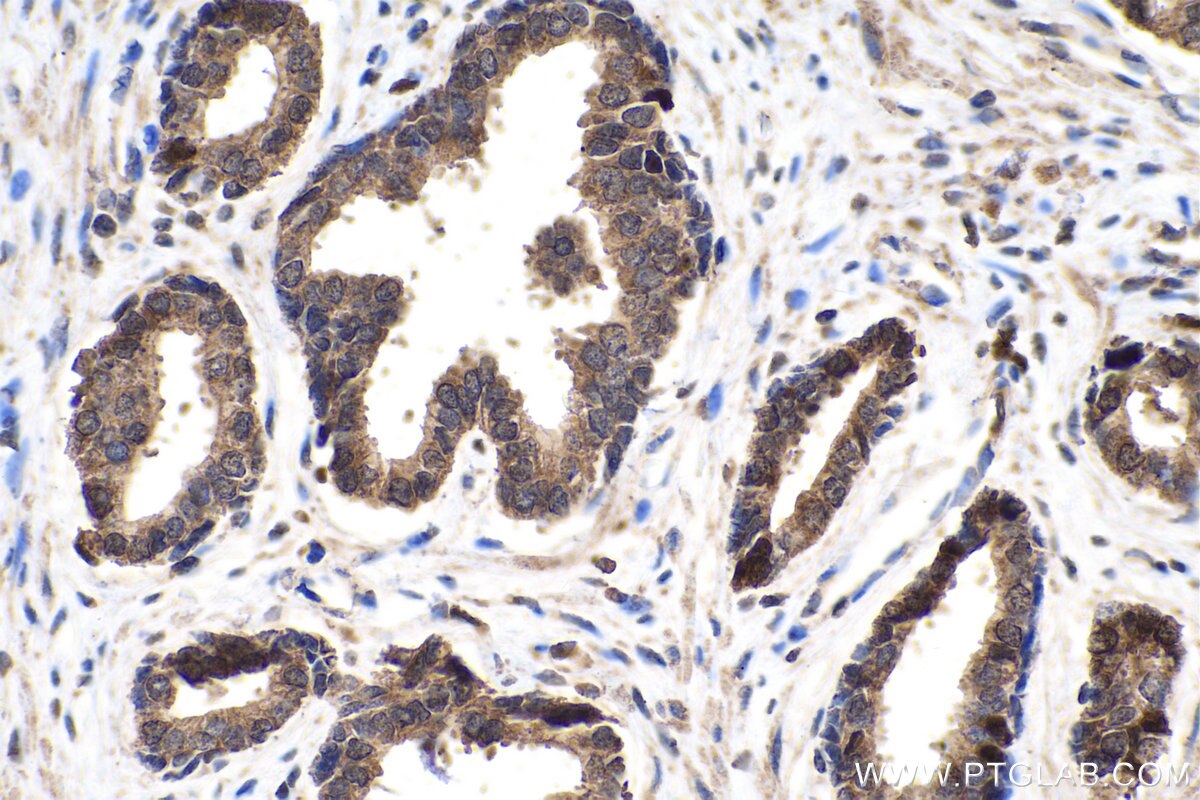
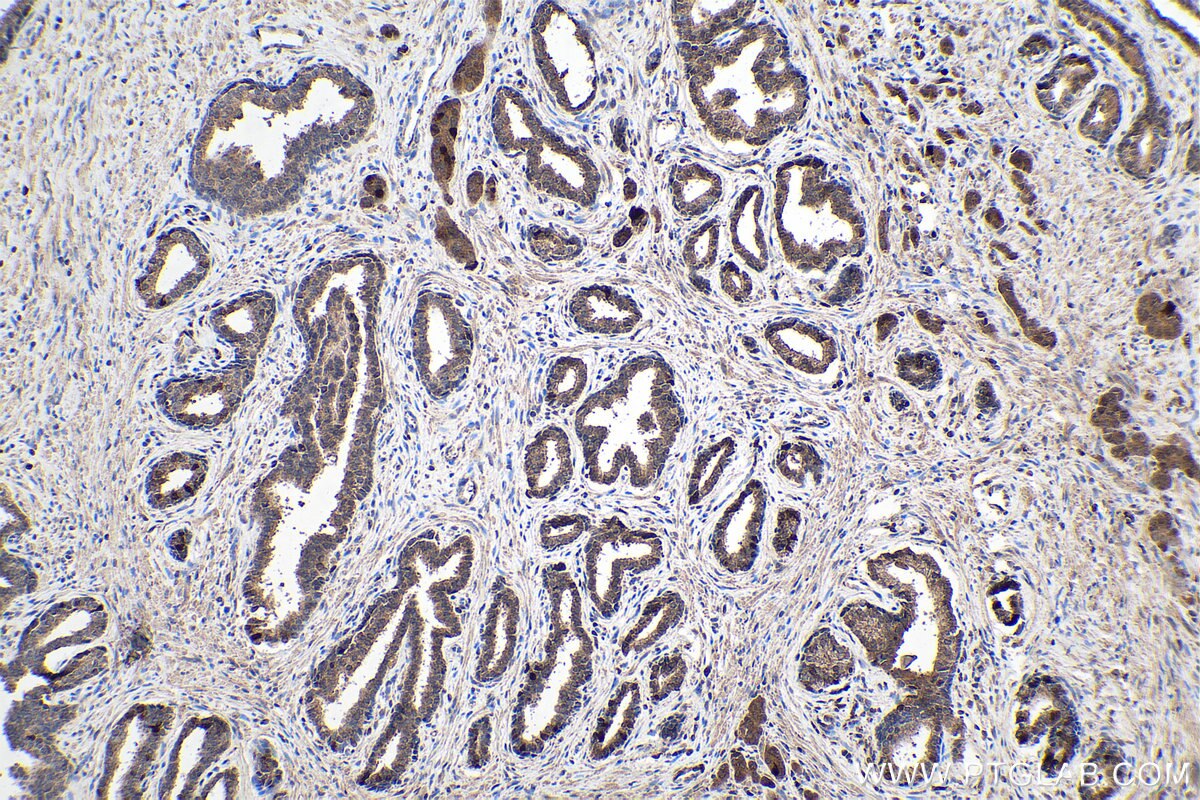
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Mammakarzinomgewebe, humanes Prostatakarzinomgewebe, braunes Mausfettgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
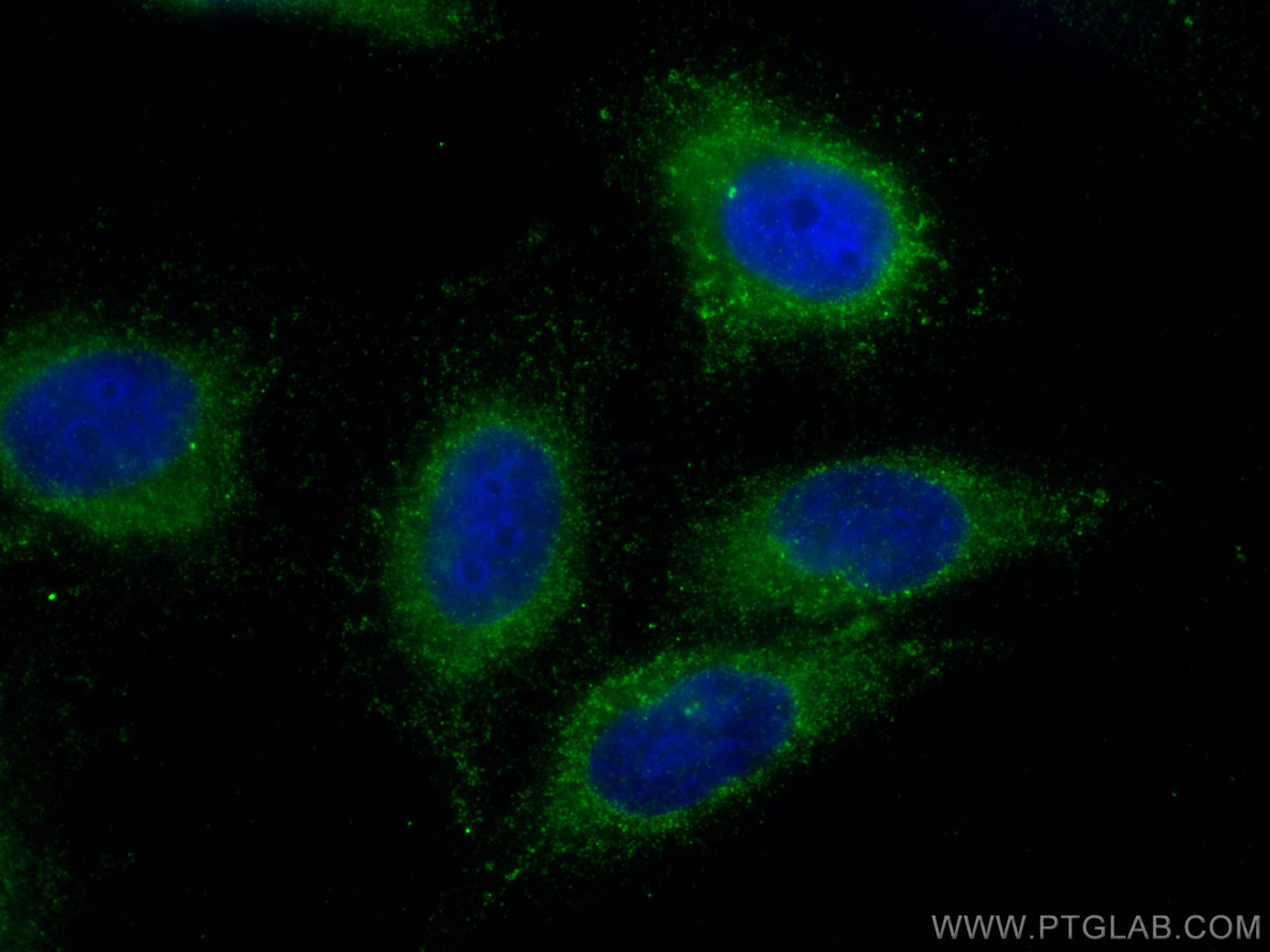
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HepG2-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:16000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:4000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
66299-1-Ig bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA FABP5 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | FABP5 fusion protein Ag3005 |
| Vollständiger Name | fatty acid binding protein 5 (psoriasis-associated) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 135 aa, 15 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 15 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC019385 |
| Gene symbol | FABP5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2171 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
FABP5, also named as PA-FABP and E-FABP, belongs to the calycin superfamily and Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family. It is high specificity for fatty acids. FABP5 is highest affinity for C18 chain length. It may be involved in keratinocyte differentiation. FABP5 is a fatty acid-binding protein and is expressed in epidermis and endothelial cells of the microvasculature of different organs. FABP5 has also been identified as a tumor-associated antigen, which is highly expressed in various cancers. FABP5 was detected in the sera of HNSCC patients with early stage cancer. Antibodies specific for FABP5 were significantly increased in a substantial amount in patients, suggesting that FABP5 may be a potential diagnostic biomarker for HNSCC. FABP5 may serve as a biomarker for HNSCC.(PMID:19602232)
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for FABP5 antibody 66299-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for FABP5 antibody 66299-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for FABP5 antibody 66299-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Carcinogenesis Serum fatty acid-binding protein 5 is a significant factor in hepatocellular carcinoma progression independent of tissue expression level.
| ||
Med Mol Morphol Expression of fatty-acid-binding protein 5 in intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the possibility of different energy metabolisms in anatomical location. | ||
J Allergy Clin Immunol Melatonin treatment increases skin microbiota-derived propionic acid to alleviate atopic dermatitis | ||
Free Radic Biol Med Oxidative stress-induced decreased expression of FABP5 leads to mitochondrial damage and survival disorder of decidual stromal cells in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion |