- Featured Product
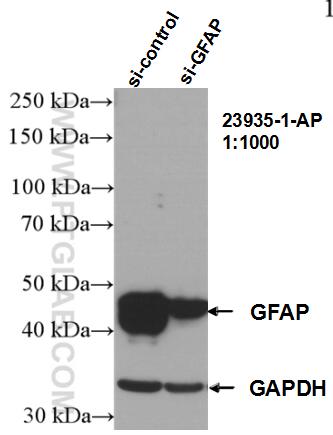
- KD/KO Validated
GFAP Polyklonaler Antikörper
GFAP Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF-P, IF-Fro, IP, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
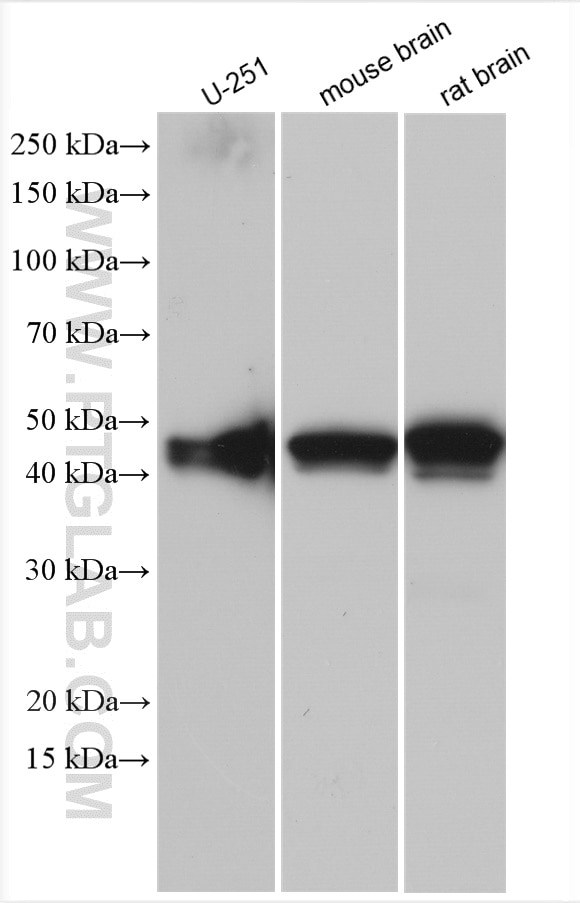
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
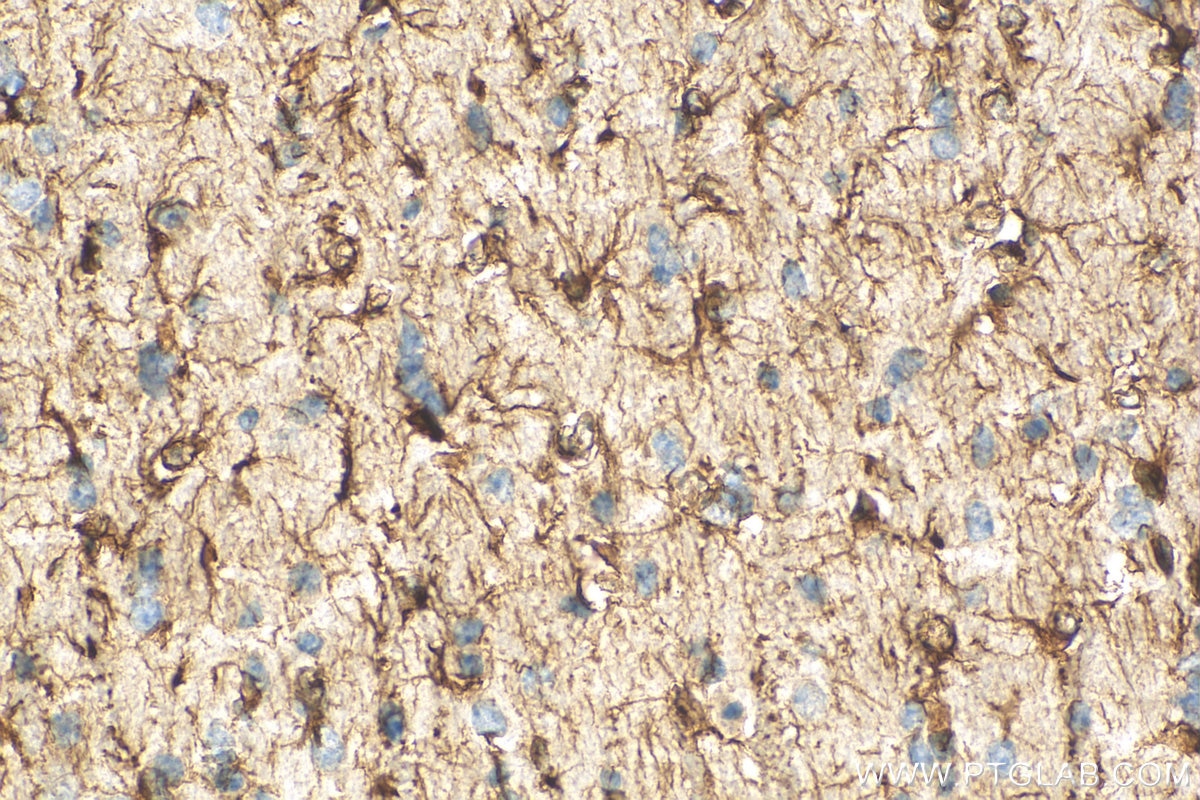
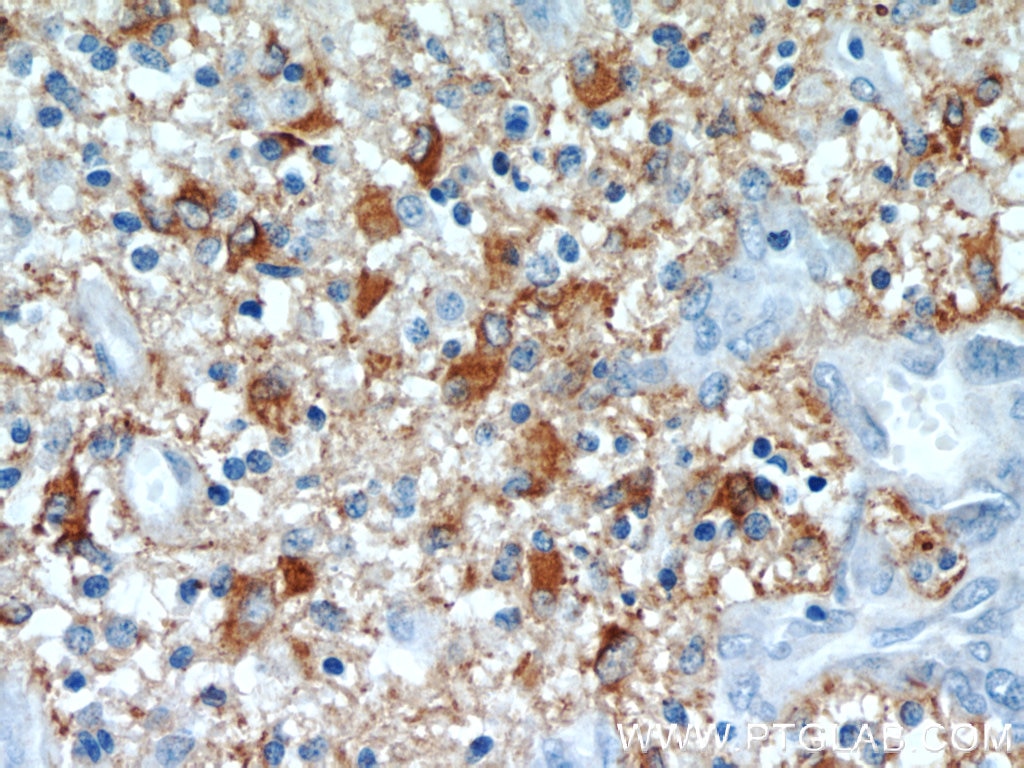
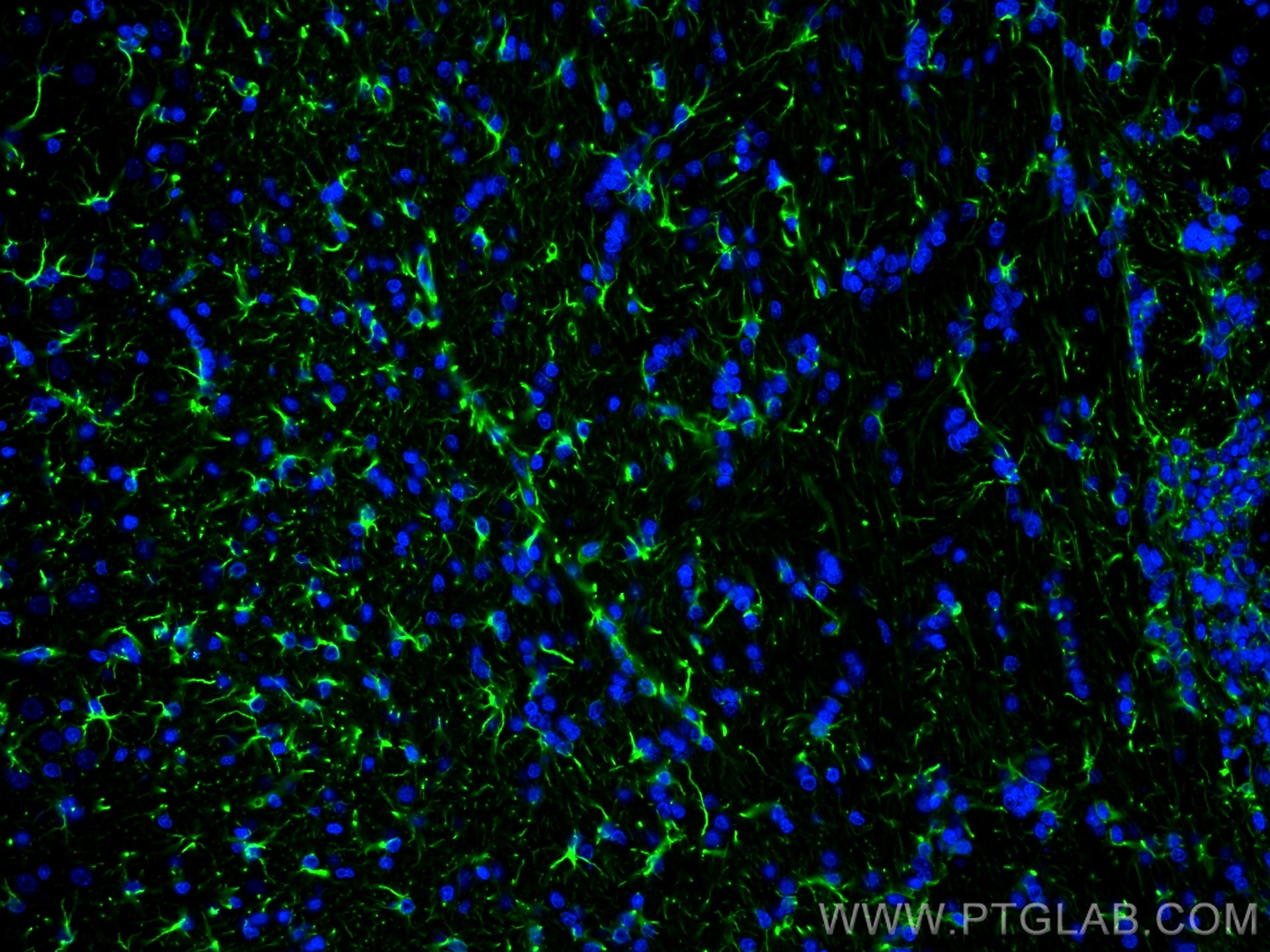
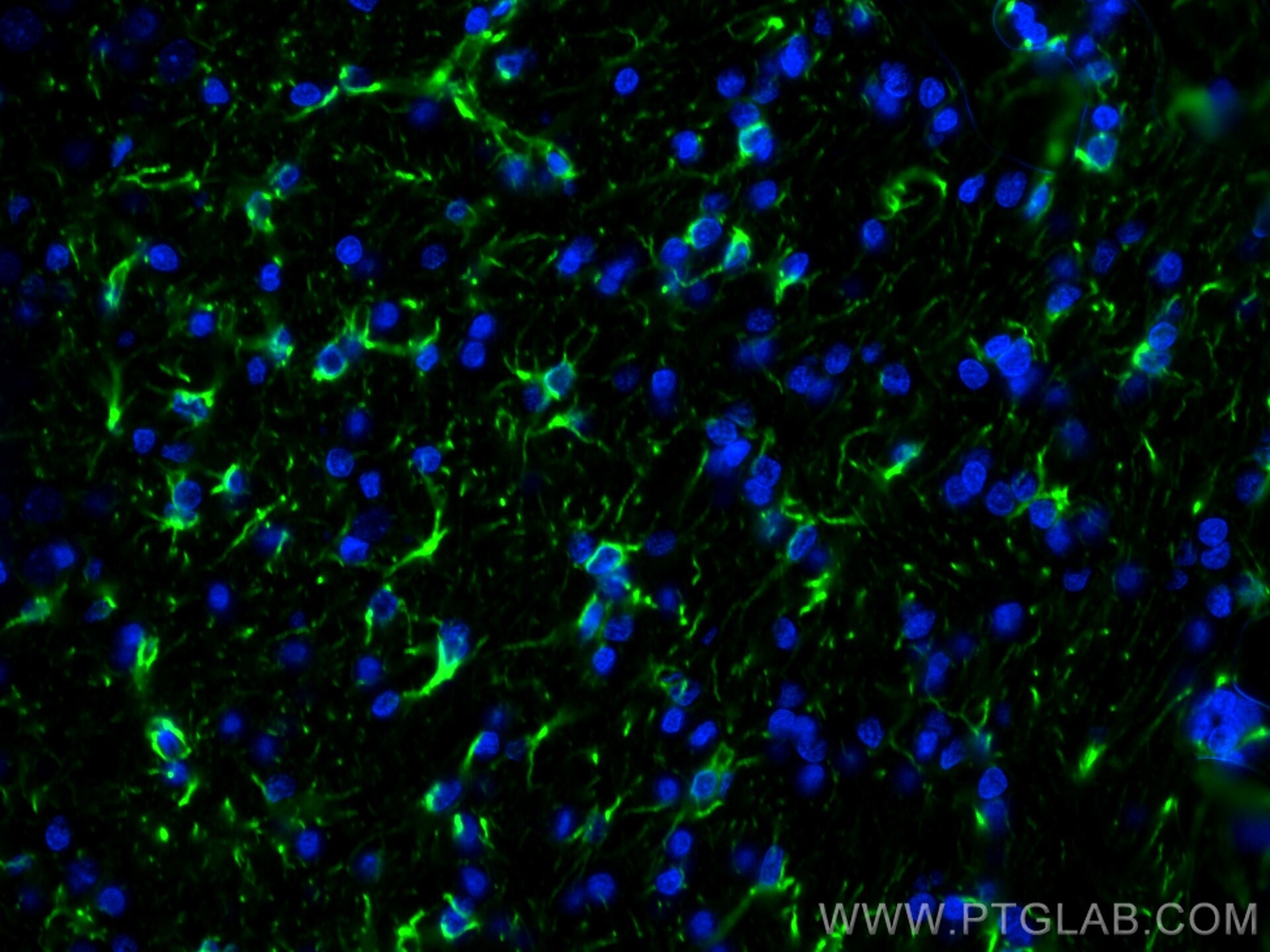
WB, IHC, IF-P, IF-Fro, IP, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 23935-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
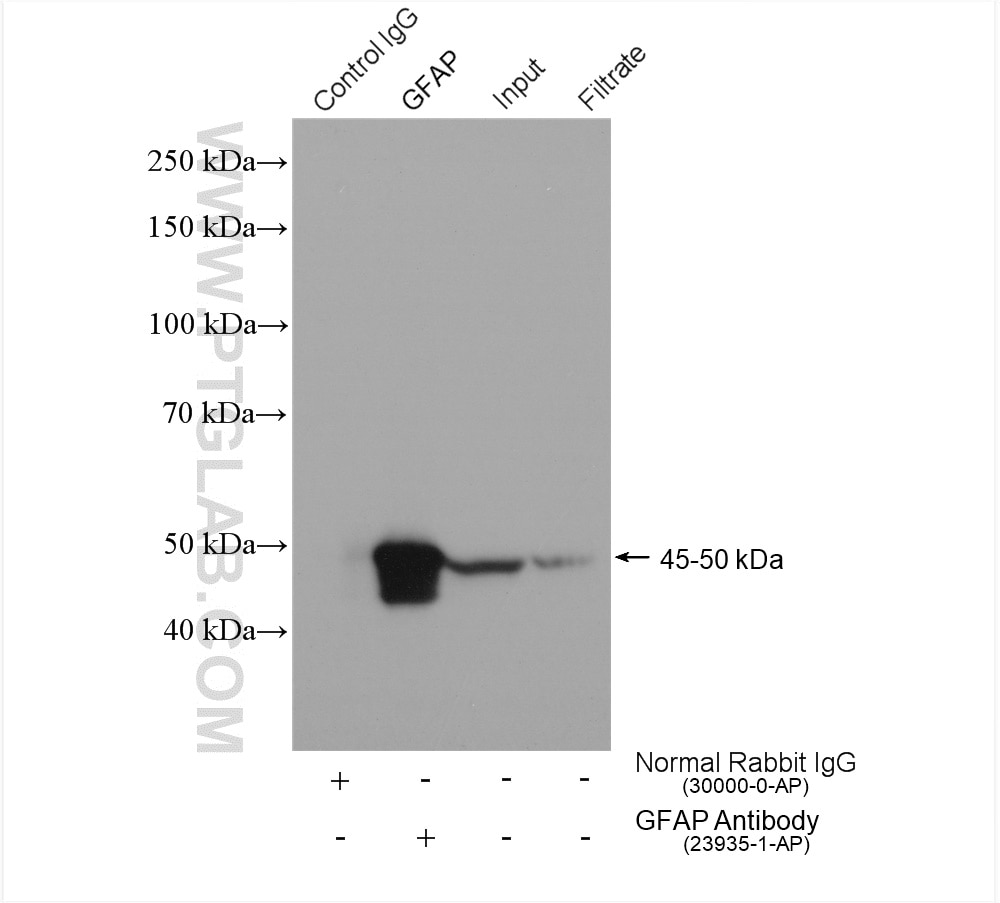
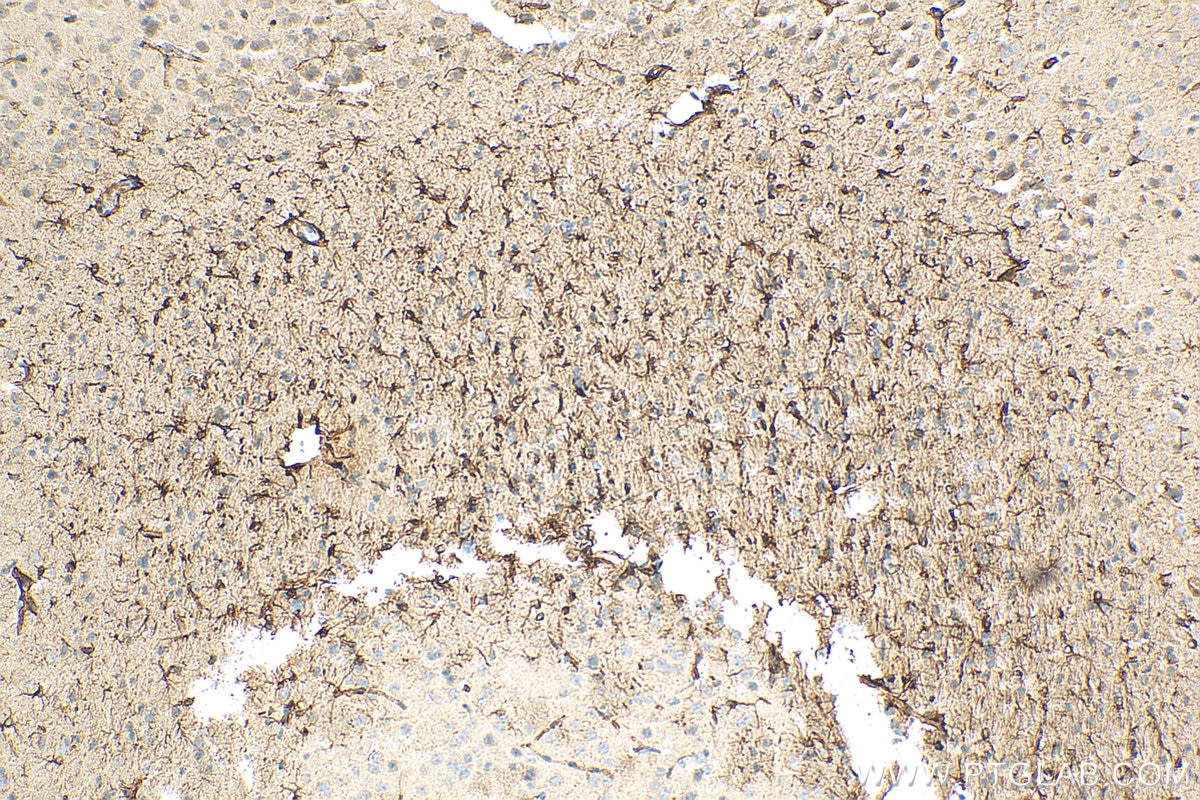
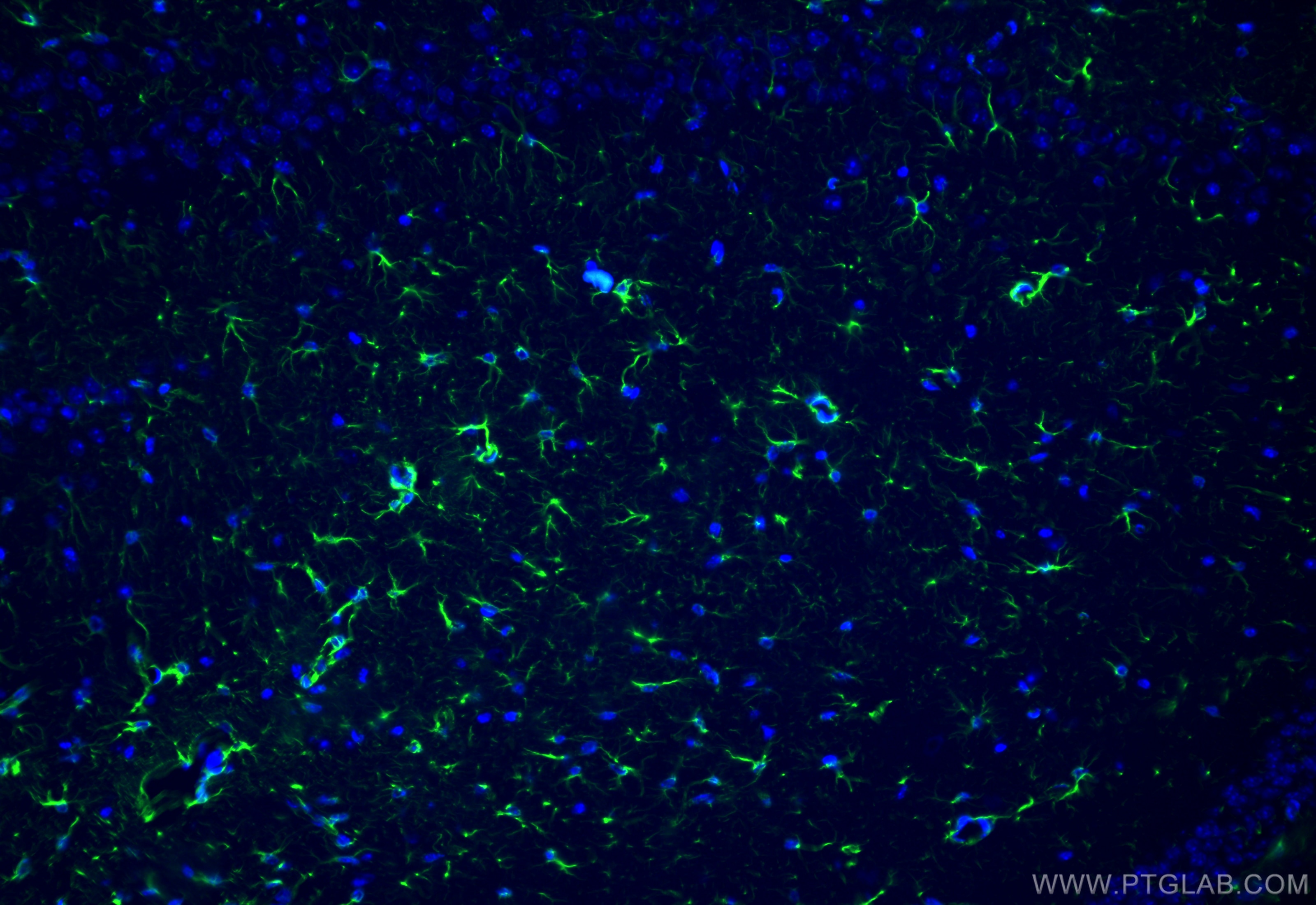
23935-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF-P, IF-Fro, IP, Indirect ELISA GFAP und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | GFAP fusion protein Ag20853 |
| Vollständiger Name | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 432 aa, 50 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 45-50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC013596 |
| Gene symbol | GFAP |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2670 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Function
GFAP (Glial fibrillary acidic protein) is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein specific to the central nervous system (CNS). GFAP is one of the main components of the intermediate filament network in astrocytes and has been proposed as playing a role in cell migration, cell motility, maintaining mechanical strength, and in mitosis.
Tissue specificity
GFAP is expressed in central nervous system cells, predominantly in astrocytes. GFAP is commonly used as an astrocyte marker. However, GFAP is also present in peripheral glia and in non-CNS cells, including fibroblasts, chondrocytes, lymphocytes, and liver stellate cells (PMID: 21219963).
Involvement in disease
Mutations in GFAP lead to Alexander disease (OMIM: 203450), an autosomal dominant CNS disorder. The mutations present in affected individuals are thought to be gain-of-function.
Upregulation of GFAP is a hallmark of reactive astrocytes, in which GFAP is present in hypertrophic cellular processes. Reactive astrogliosis is present in many neurological disorders, such as stroke, various neurodegenerative diseases (including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease), and neurotrauma.
Isoforms
Astrocytes express 10 different isoforms of GFAP that differ in the rod and tail domains (PMID: 25726916), which means that they differ in molecular size. Isoform expression varies during the development and across different subtypes of astrocytes. Not all isoforms are upregulated in reactive astrocytes.
Post-translational modifications
Intermediate filament proteins are regulated by phosphorylation. Six phosphorylation sites have been identified in GFAP protein, at least some of which are reported to control filament assembly (PMID: 21219963).
Cellular localization
GFAP localizes to intermediate filaments and stains well in astrocyte cellular processes.