- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
GFAP Polyklonaler Antikörper
GFAP Polyklonal Antikörper für IF-P
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
IF-P
Konjugation
CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye
Kat-Nr. : CL488-16825
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
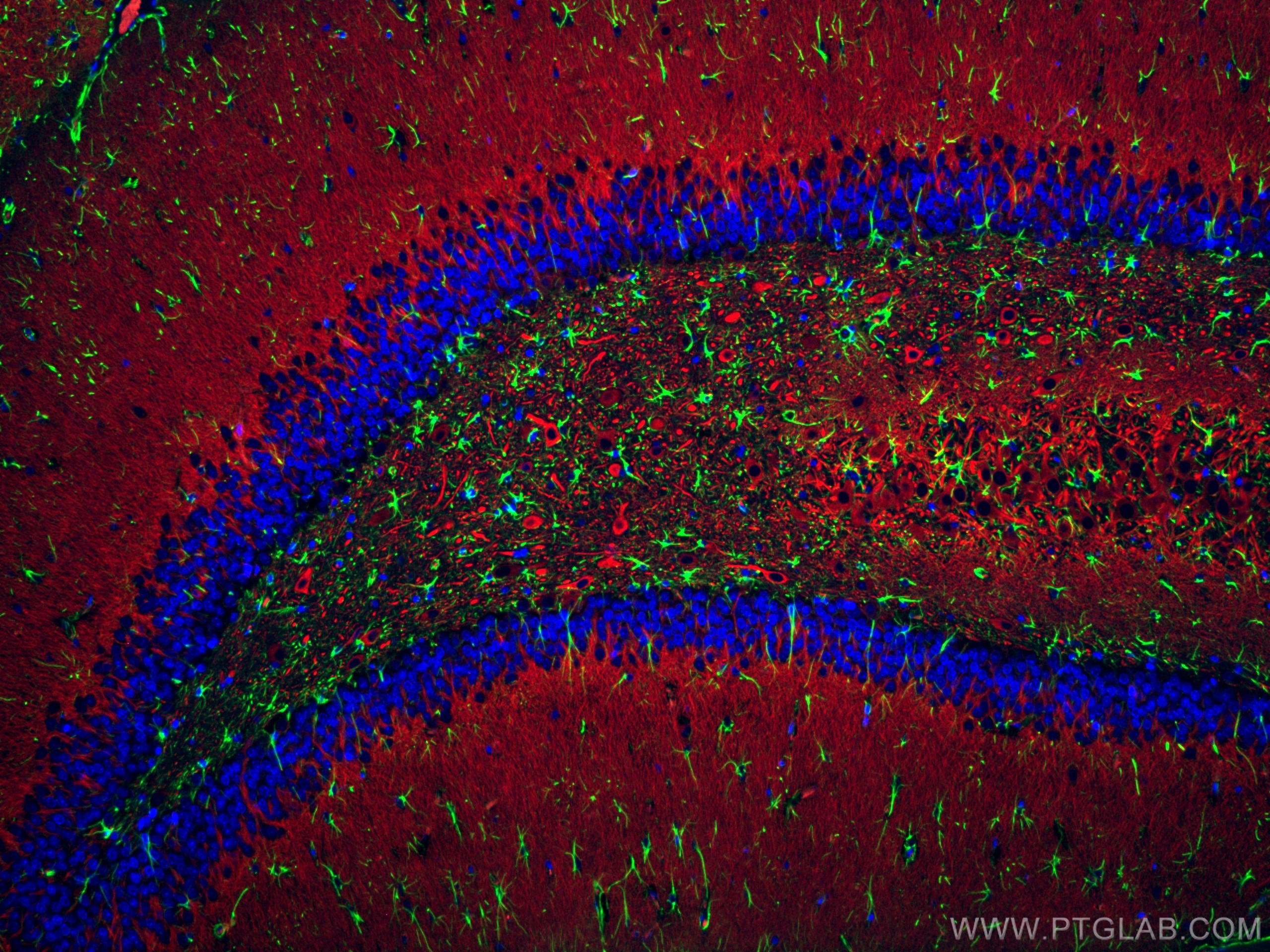
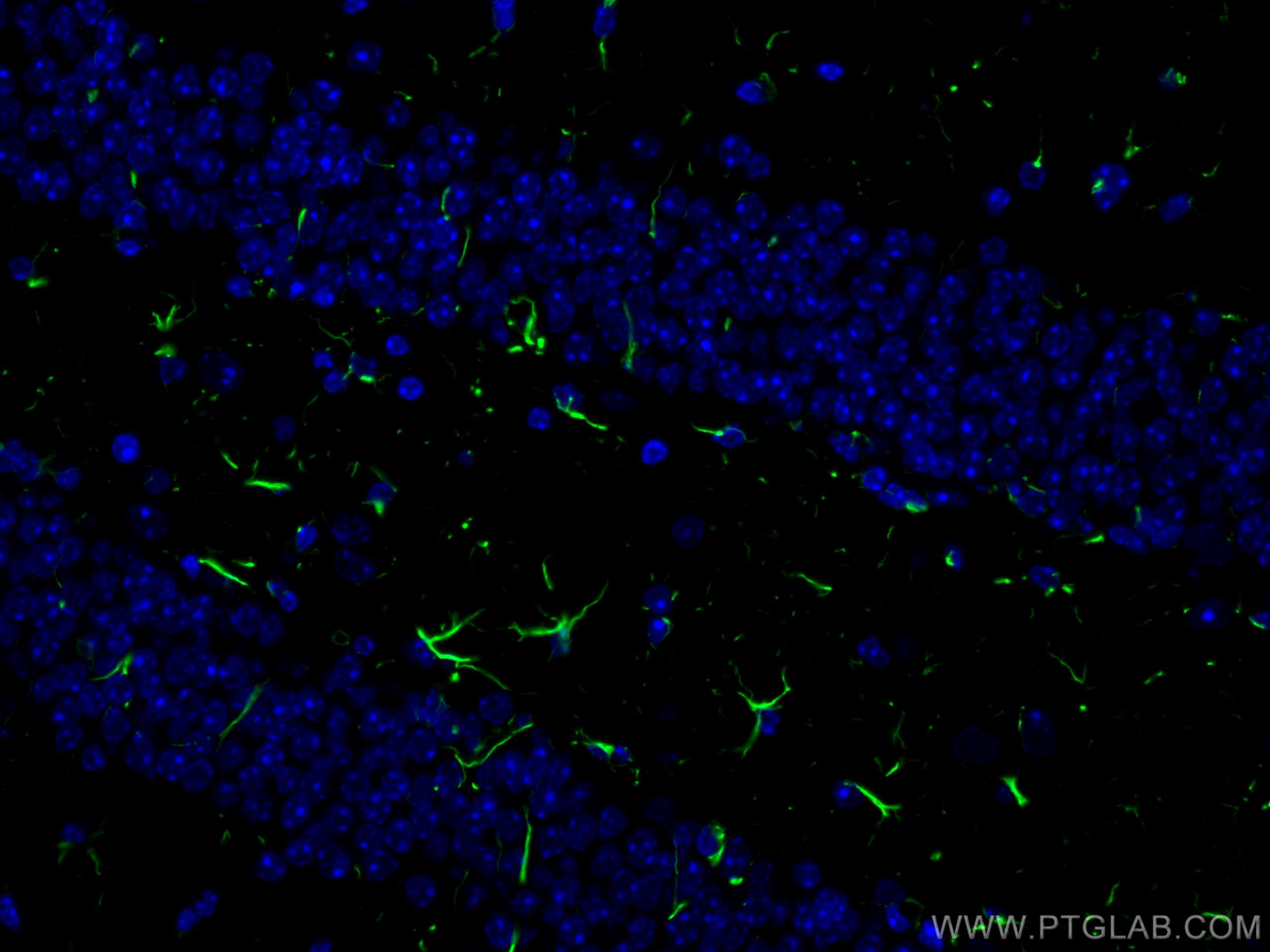
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF-P | Rattenhirngewebe, Maushirngewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| IF | See 6 publications below |
Produktinformation
CL488-16825 bindet in IF-P GFAP und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | GFAP fusion protein Ag10423 |
| Vollständiger Name | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 432 aa, 50 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 45-50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC013596 |
| Gene symbol | GFAP |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2670 |
| Konjugation | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Vor Licht schützen. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr stabil. Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Function
GFAP (Glial fibrillary acidic protein) is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein specific to the central nervous system (CNS). GFAP is one of the main components of the intermediate filament network in astrocytes and has been proposed as playing a role in cell migration, cell motility, maintaining mechanical strength, and in mitosis.Tissue specificity
GFAP is expressed in central nervous system cells, predominantly in astrocytes. GFAP is commonly used as an astrocyte marker. However, GFAP is also present in peripheral glia and in non-CNS cells, including fibroblasts, chondrocytes, lymphocytes, and liver stellate cells (PMID: 21219963).Involvement in disease
- Mutations in GFAP lead to Alexander disease (OMIM: 203450), an autosomal dominant CNS disorder. The mutations present in affected individuals are thought to be gain-of-function.
- Upregulation of GFAP is a hallmark of reactive astrocytes, in which GFAP is present in hypertrophic cellular processes. Reactive astrogliosis is present in many neurological disorders, such as stroke, various neurodegenerative diseases (including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease), and neurotrauma.
Isoforms
Astrocytes express 10 different isoforms of GFAP that differ in the rod and tail domains (PMID: 25726916), which means that they differ in molecular size. Isoform expression varies during the development and across different subtypes of astrocytes. Not all isoforms are upregulated in reactive astrocytes.Post-translational modifications
Intermediate filament proteins are regulated by phosphorylation. Six phosphorylation sites have been identified in GFAP protein, at least some of which are reported to control filament assembly (PMID: 21219963).Cellular localization
GFAP localizes to intermediate filaments and stains well in astrocyte cellular processes.Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 GFAP antibody CL488-16825 | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Glia Mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 is an essential regulator in cell cycle progression of optic nerve head astrocytes | ||
Biomolecules Interplay between Energy Supply and Glutamate Toxicity in the Primary Cortical Culture | ||
Neuropharmacology Neuromolecular and behavioral effects of Cannabidiol on depressive-associated behaviors and neuropathic pain conditions in mice | ||
Biol Trace Elem Res The Role of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Arsenic-Induced Neurotoxicity: Insights from the Crosstalk Between Astrocytes and Neurons | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Tungsten-based polyoxometalate nanoclusters as ferroptosis inhibitors modulating S100A8/A9-mediated iron metabolism pathway for managing intracerebral haemorrhage | ||
J Integr Neurosci FKBP51 is Involved in Epileptic Seizure by Regulating PSD95 in a PTZ-Induced Epileptic Mouse Model |