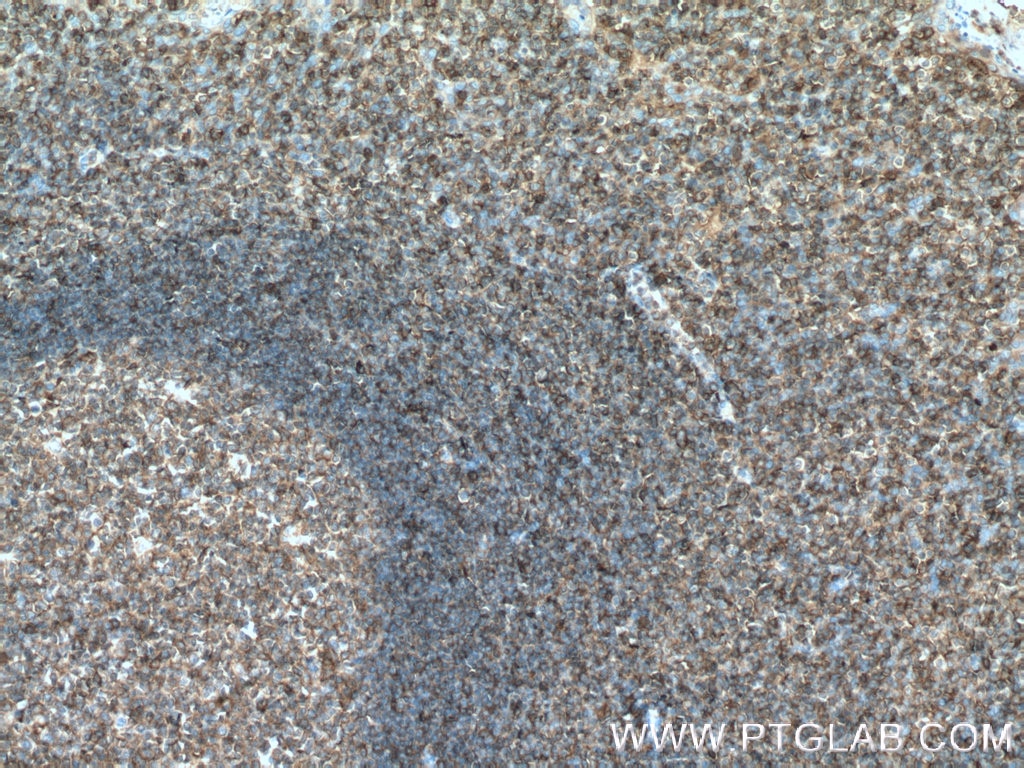
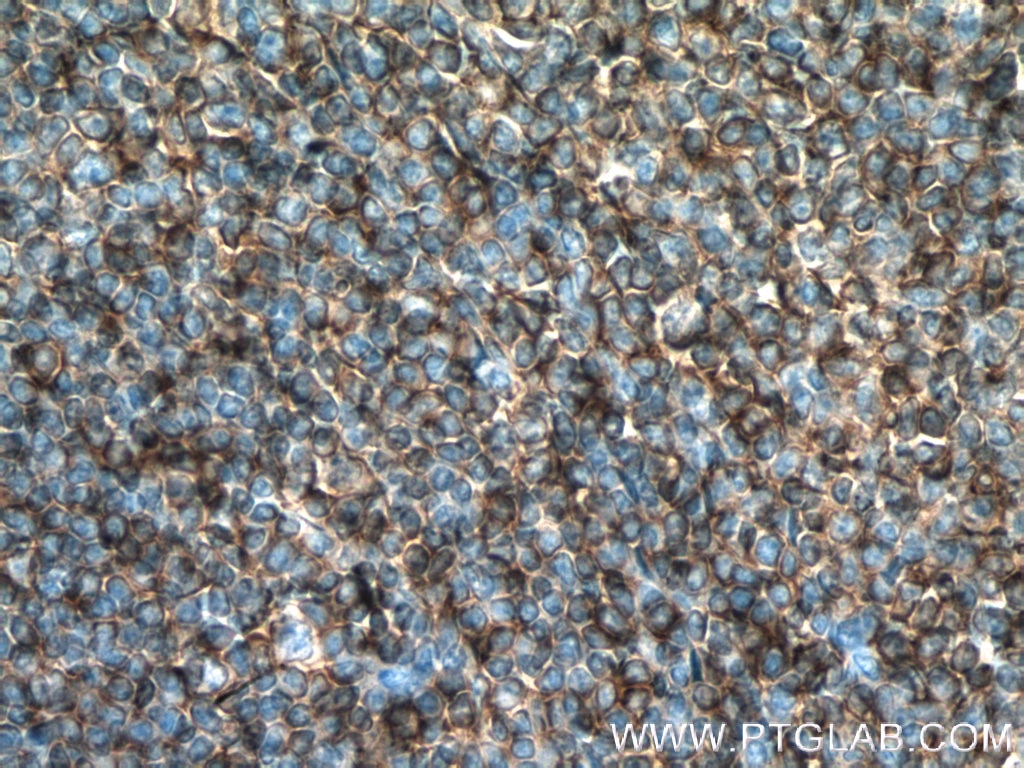
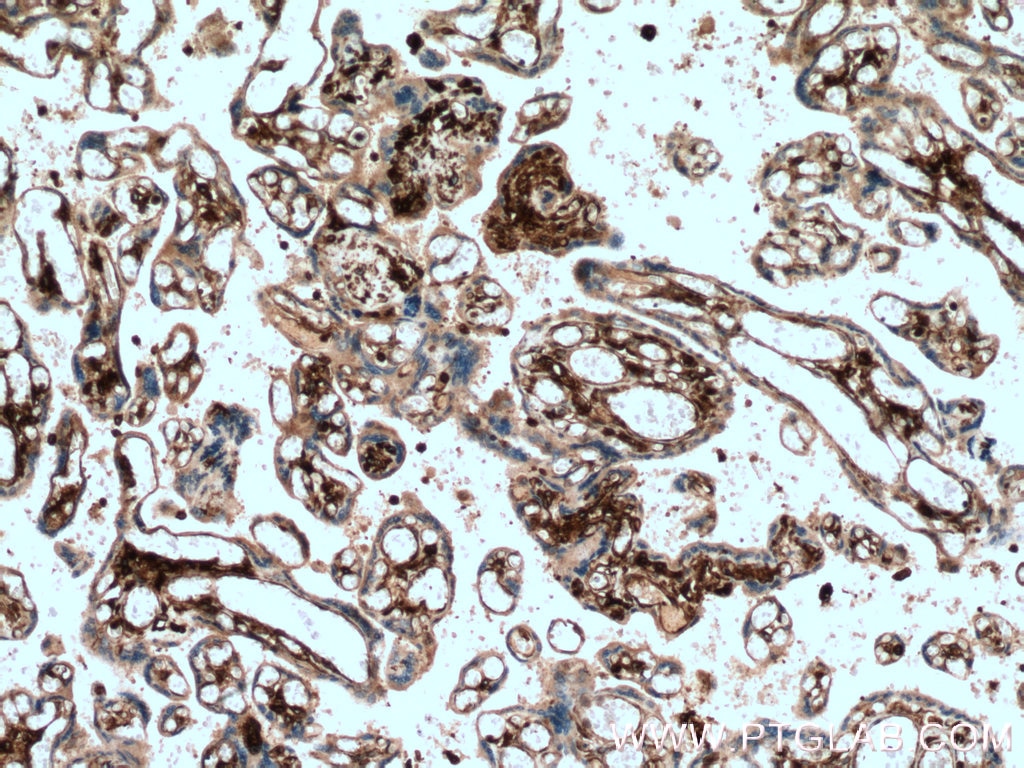
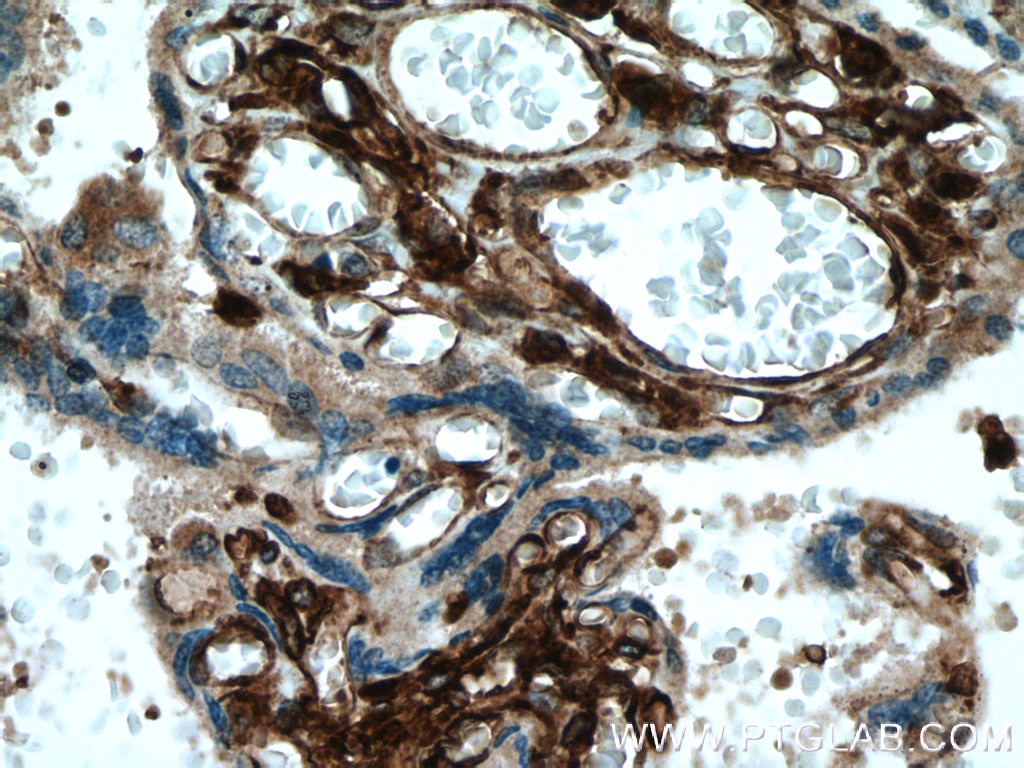
HLA-E Monoklonaler Antikörper
HLA-E Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2a
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1A4G3
Kat-Nr. : 66530-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
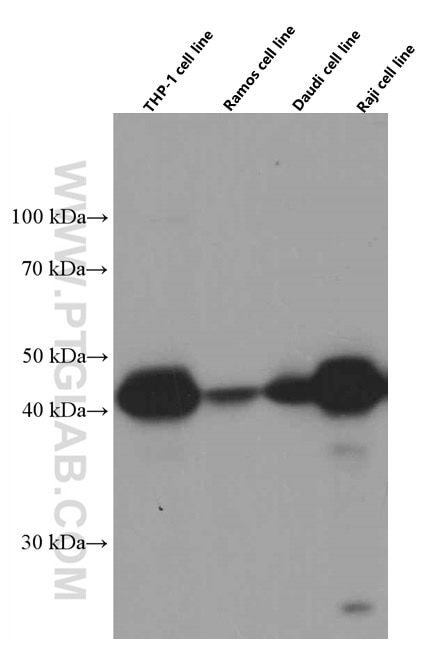
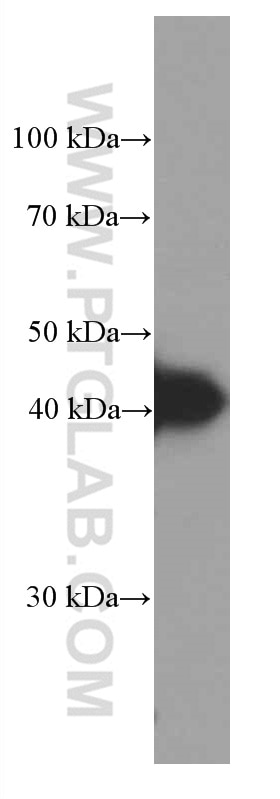
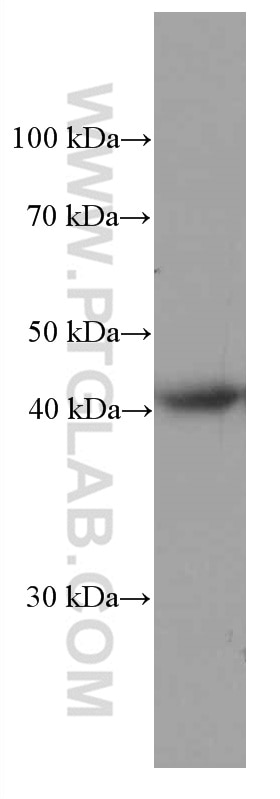
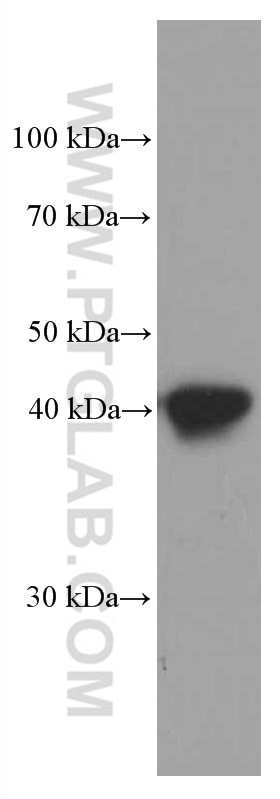
66530-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA HLA-E und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2a |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | HLA-E fusion protein Ag6724 |
| Vollständiger Name | major histocompatibility complex, class I, E |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 40 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 40 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC002578 |
| Gene symbol | HLA-E |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3133 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, also referred to as human leukocyte antigens (HLA), are encoded by genes located on the short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3). There are two classes of HLA antigens: class I and class II. This class I molecules are membrane glycoproteins composed of a heavy (alpha) chain which is encoded by a HLA class I gene, and β2-microglobulin light (beta) chain. The most extensively characterized members of the HLA class I gene family are the genes encoding the major transplantation antigenes, HLA-A, B and C. HLA-E is a non-classical MHC class I molecule. HLA-E is frequently overexpressed in tumor diseases, transplants and virus-infected cells and represents an immunomodulatory molecule by binding to the receptors CD94/NKG2A, -B and -C on NK and T cells. Due to its immune suppressive features HLA-E expression might represent an important mechanism of tumors to escape immune surveillance.(PMID: 667938; 3375250; 2249951; 27589686)