HLA-G Monoklonaler Antikörper
HLA-G Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2b
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1E5A10
Kat-Nr. : 66447-1-Ig
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
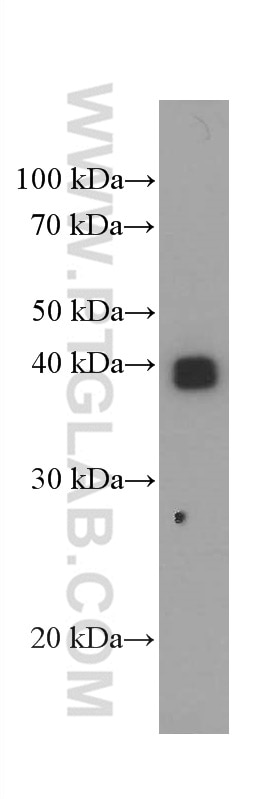
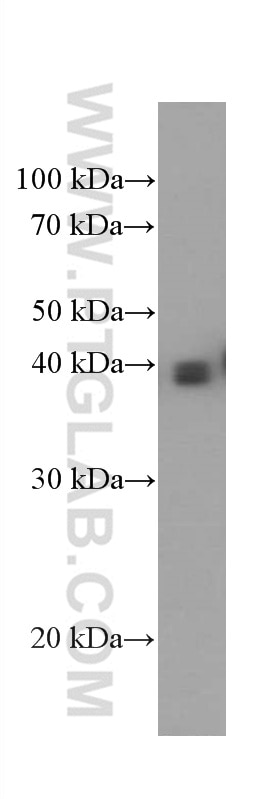
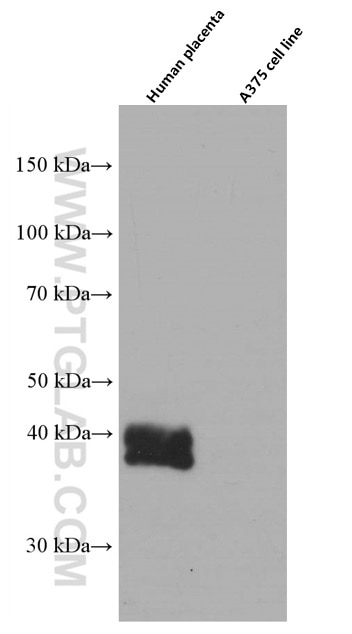
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | humanes Plazenta-Gewebe |
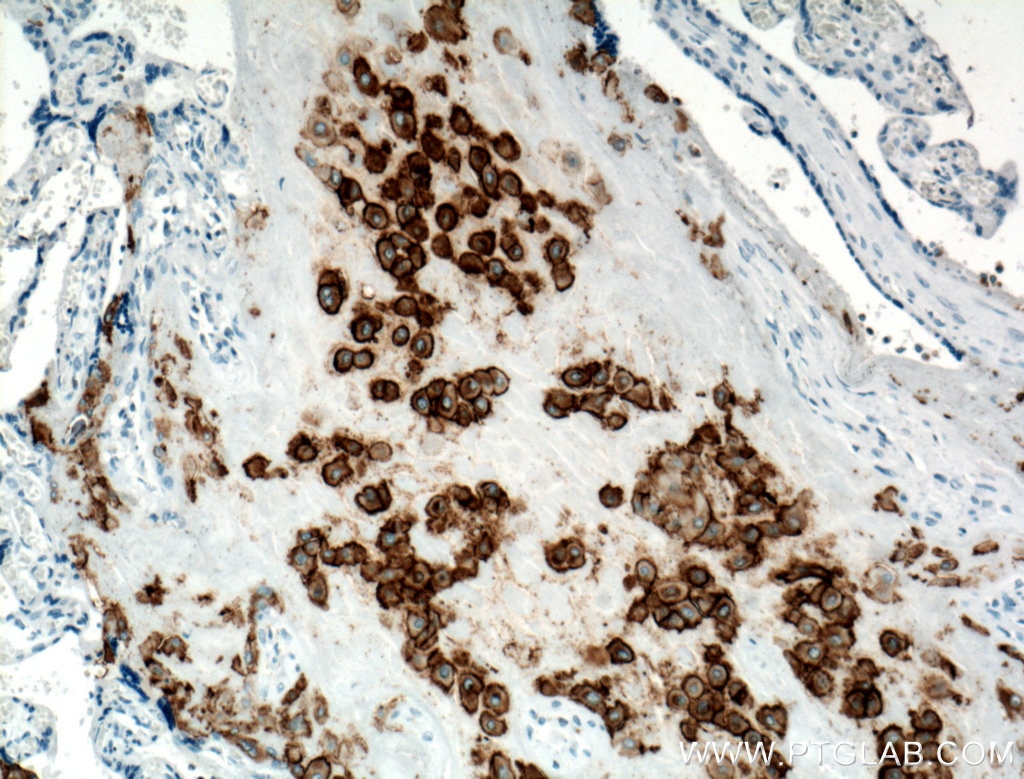
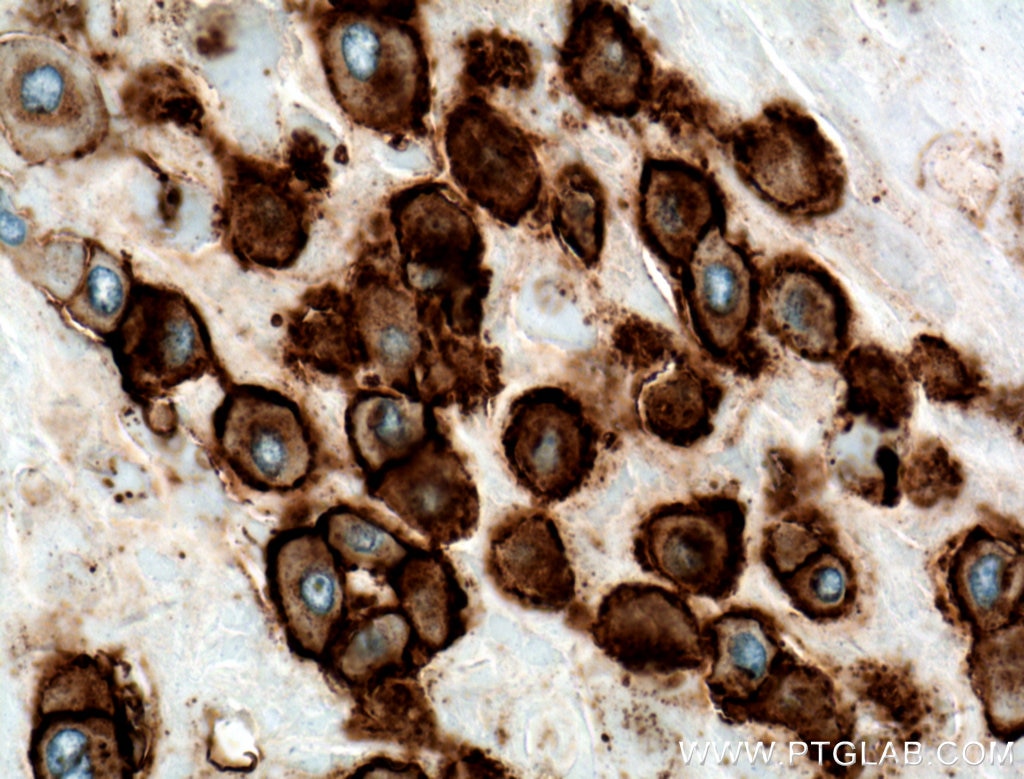
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Plazenta-Gewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:20000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 14 publications below |
| IF | See 21 publications below |
Produktinformation
66447-1-Ig bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA HLA-G und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2b |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | HLA-G fusion protein Ag10839 |
| Vollständiger Name | major histocompatibility complex, class I, G |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 338 aa, 38 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 33-45 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC021708 |
| Gene symbol | HLA-G |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3135 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, also referred to as human leukocyte antigens (HLA), are encoded by genes located on the short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3). HLA-G is a non-classical MHC class I molecule with multiple immunoregulatory properties. HLA-G exhibits a restricted pattern of expression that includes placental extravillous trophoblasts at the maternal-fetal interface, where it abolishes maternal immune cell activity against fetus and establishes immune tolerance. Aberrant expression of HLA-G has been found in a variety of human neoplastic diseases. It plays an important role in the escape of tumor cells from immunosurveillance.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for HLA-G antibody 66447-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for HLA-G antibody 66447-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Aging Cell Advanced Maternal Age-associated SIRT1 Deficiency Compromises Trophoblast Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through an Increase in Vimentin Acetylation. | ||
Oxid Med Cell Longev Deletion of ACLY Disrupts Histone Acetylation and IL-10 Secretion in Trophoblasts, Which Inhibits M2 Polarization of Macrophages: A Possible Role in Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion. | ||
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids miR21 modulates the Hippo signaling pathway via interference with PP2A Bβ to inhibit trophoblast invasion and cause preeclampsia | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res Suppression of GATA3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and simultaneous cellular senescence in human extravillous trophoblasts | ||
FASEB J Cyclin G2 upregulation impairs migration, invasion, and network formation through RNF123/Dvl2/JNK signaling in the trophoblast cell line HTR8/SVneo, a possible role in preeclampsia. | ||
Cell Signal Hypermethylation and low expression of FOXM1 predisposes women to unexplained recurrent miscarriage by impairing trophoblast stem cell proliferation |