ING4 Monoklonaler Antikörper
ING4 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
Hausschwein, human, Kaninchen, Ratte
Anwendung
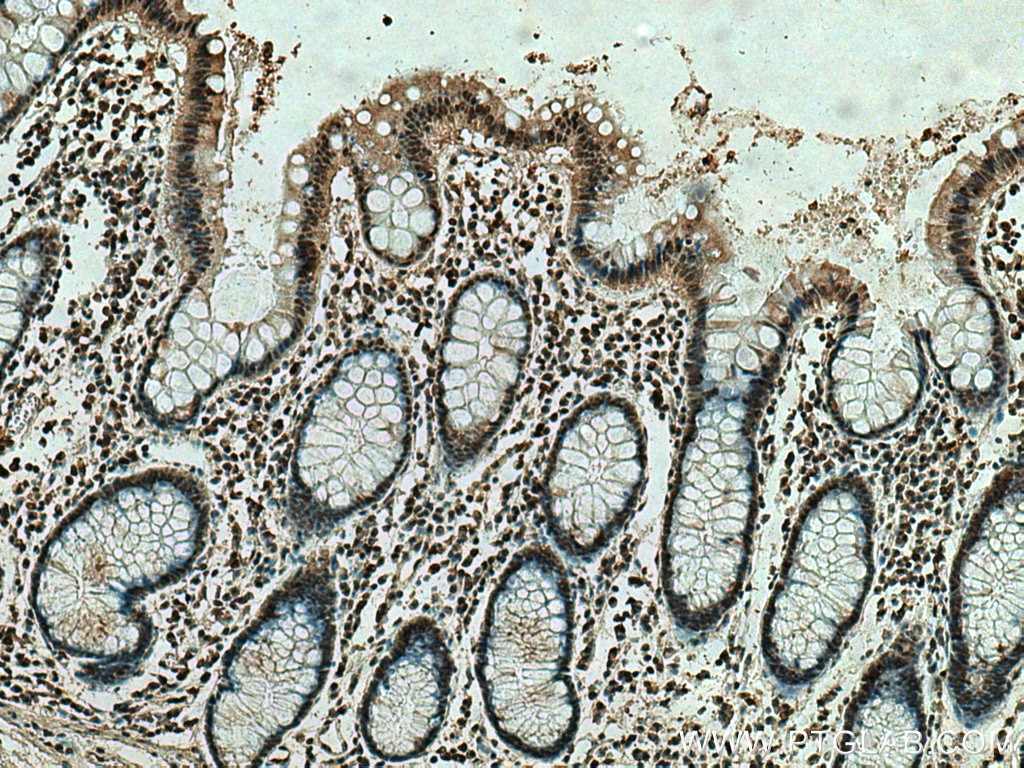
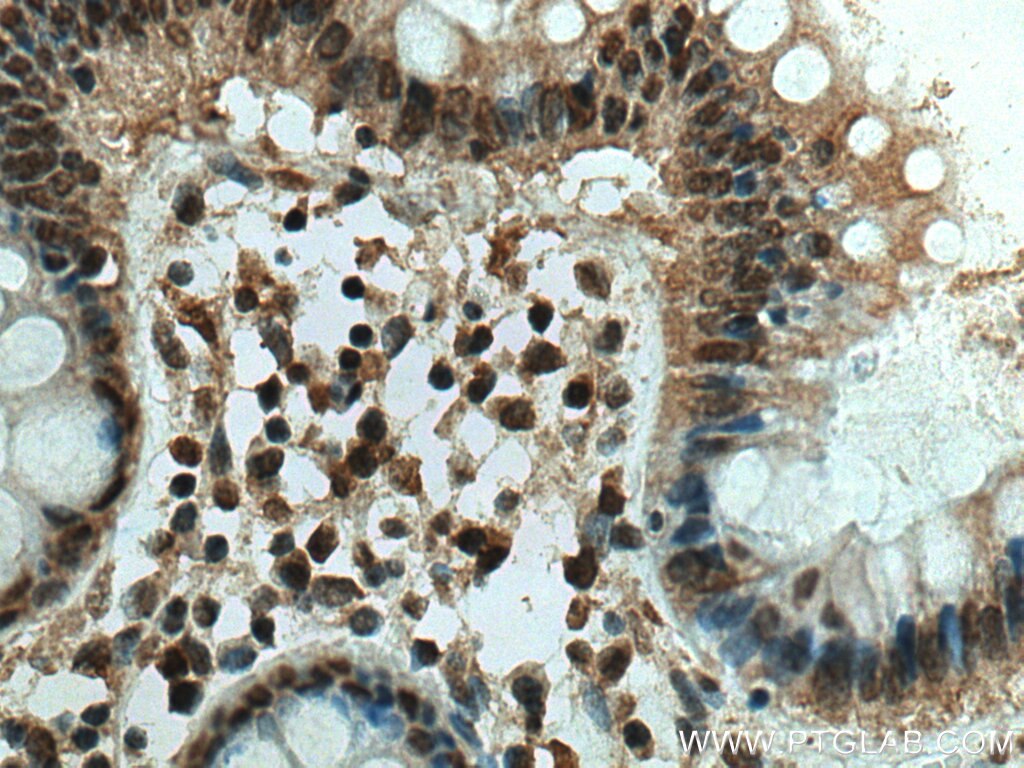
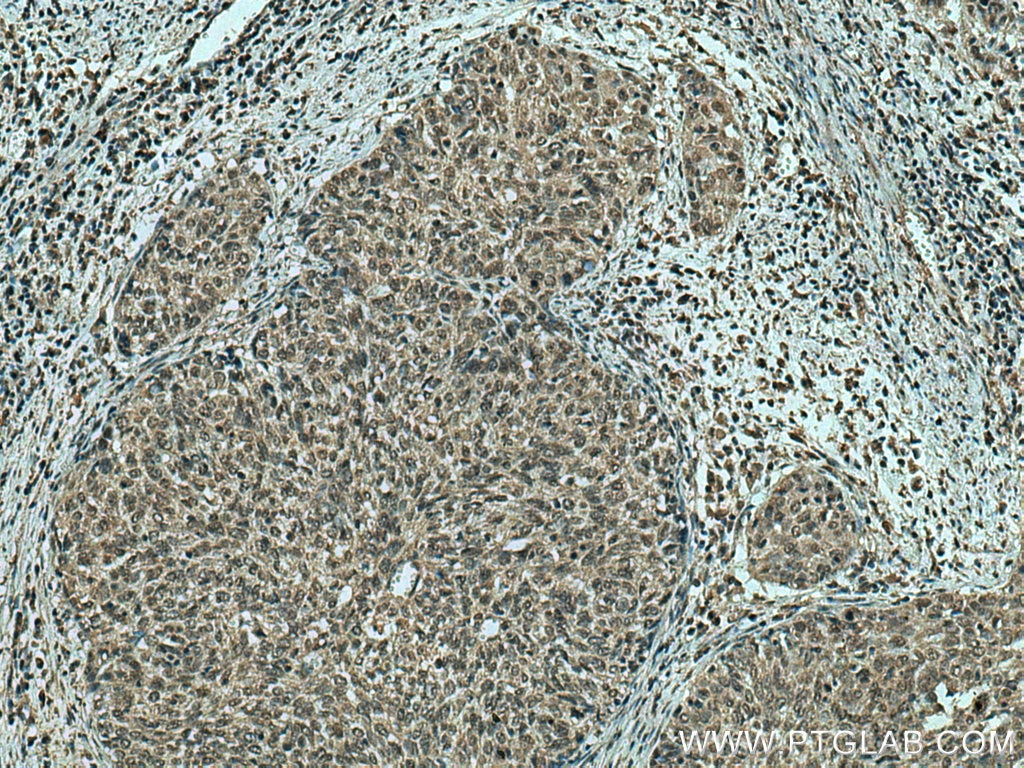
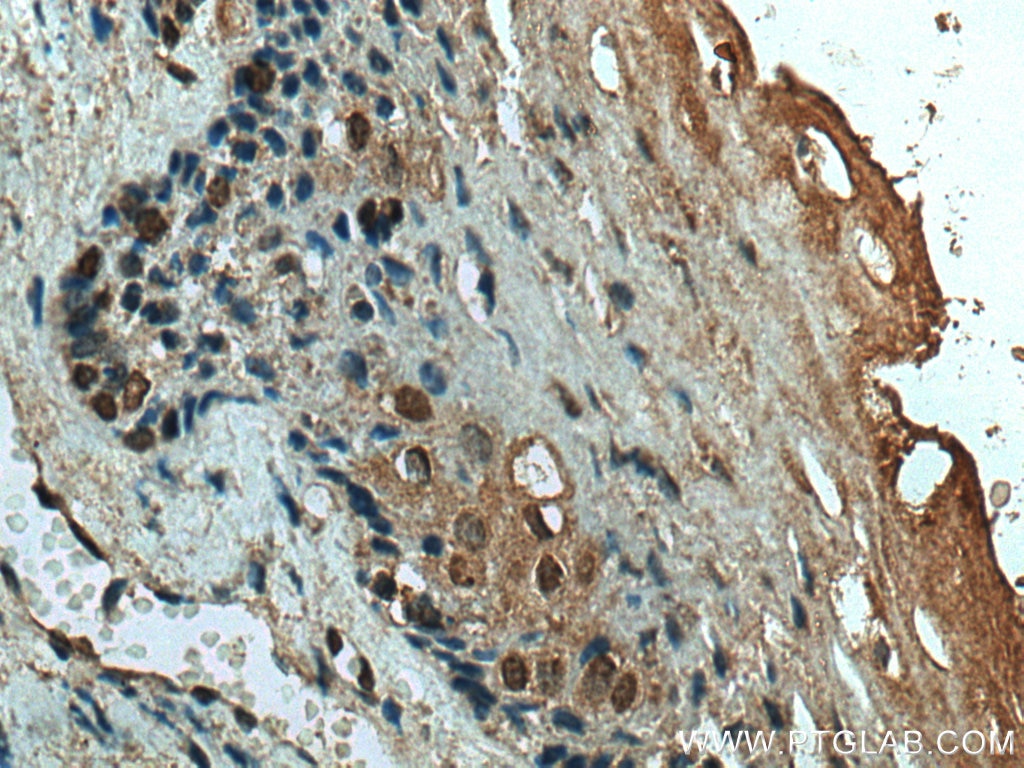
WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1A12A3
Kat-Nr. : 67754-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
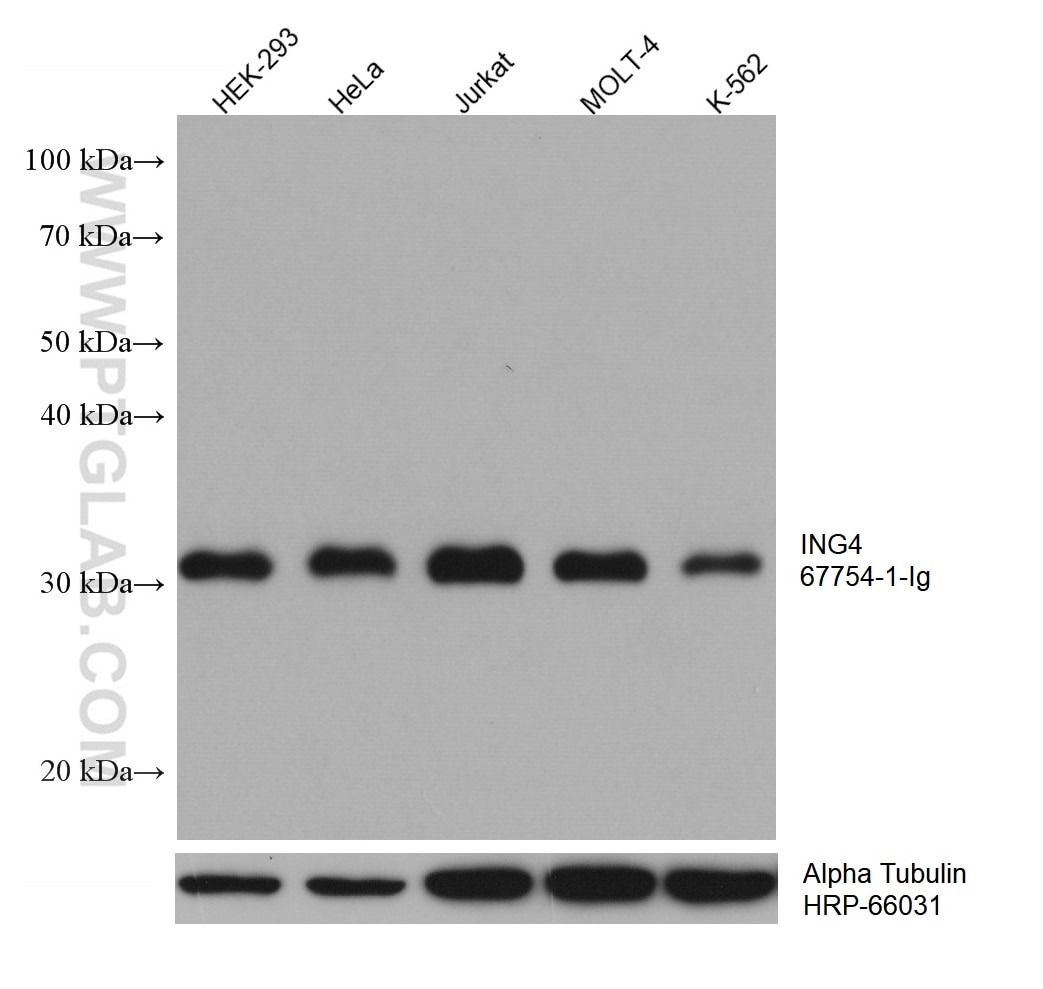
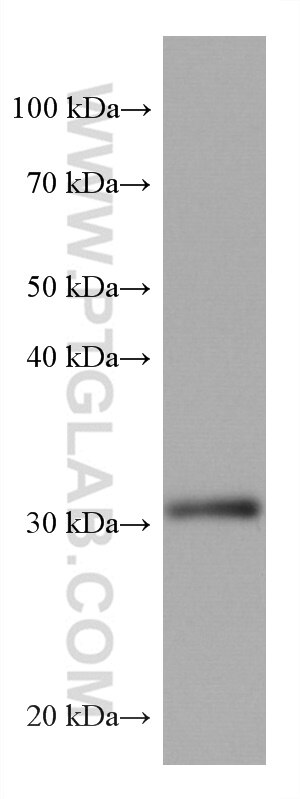
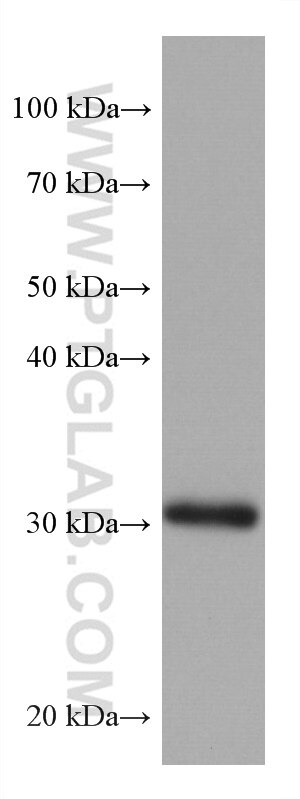
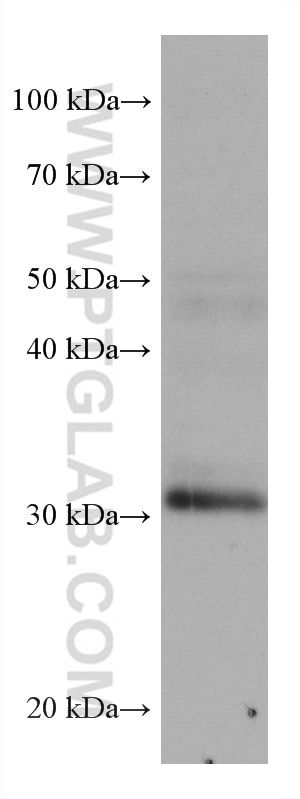
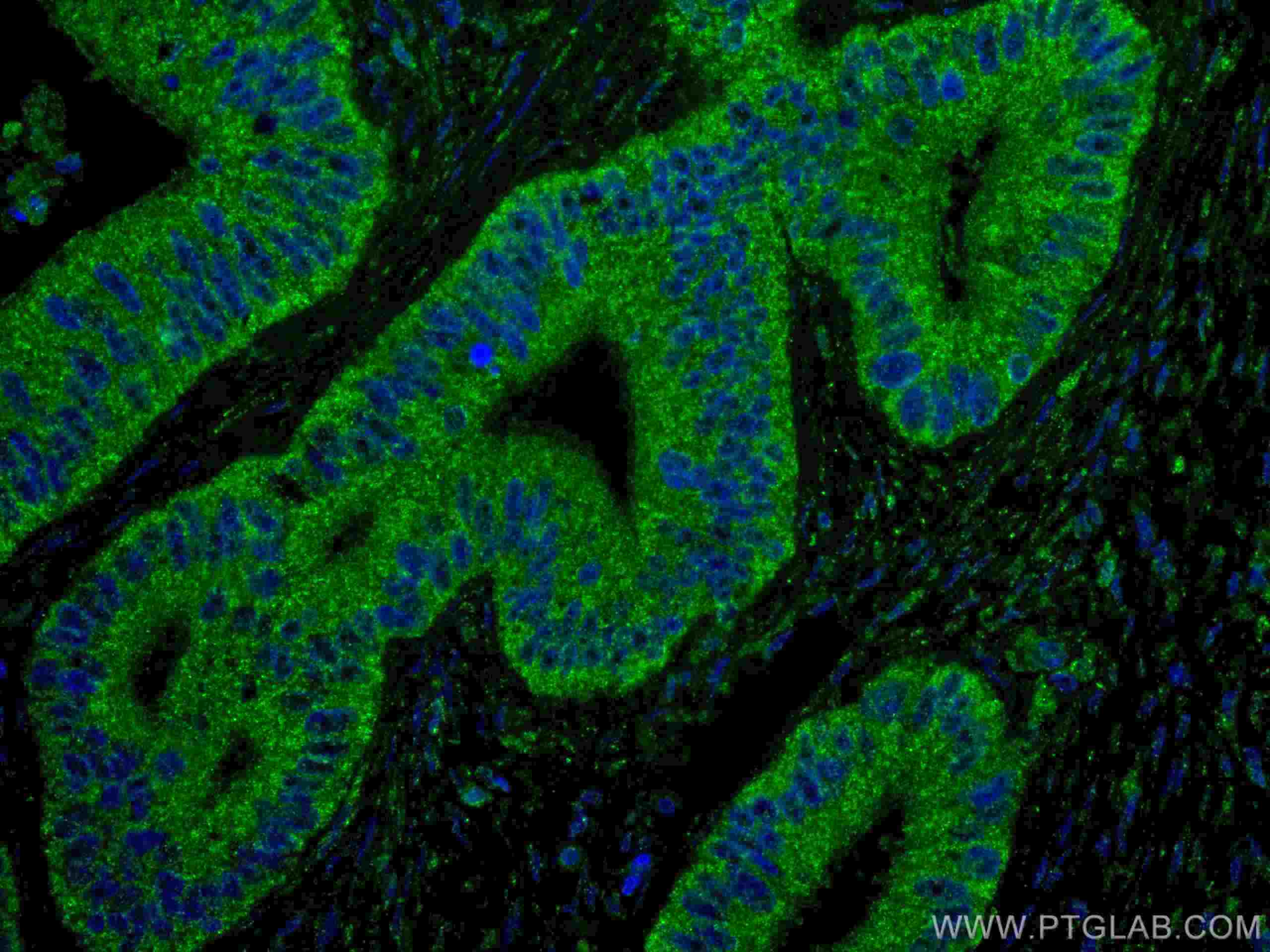
67754-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA ING4 und zeigt Reaktivität mit Hausschwein, human, Kaninchen, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | Hausschwein, human, Kaninchen, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | ING4 fusion protein Ag4610 |
| Vollständiger Name | inhibitor of growth family, member 4 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 29 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 29 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC007781 |
| Gene symbol | ING4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 51147 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
ING4, also named as p29ING4, belongs to the ING family. It is a component of the HBO1 complex which has a histone H4-specific acetyltransferase activity, a reduced activity toward histone H3 and is responsible for the bulk of histone H4 acetylation in vivo. It may inhibit tumor progression by modulating the transcriptional output of signaling pathways which regulate cell proliferation. ING4 can suppress brain tumor angiogenesis through transcriptional repression of RELA/NFKB3 target genes when complexed with RELA. It may also specifically suppress loss of contact inhibition elicited by activated oncogenes such as MYC. Represses hypoxia inducible factor's (HIF) activity by interacting with HIF prolyl hydroxylase 2 (EGLN1). ING4 is a tumor suppressor gene that interacts with NFkB and represses its transcriptional activity. Several lines of evidence suggest that the tumor suppressor gene ING4, NFkB and its target genes matrix metalloproteases MMP-2, MMP-9 and u-PA are critically involved in tumor invasion.