- Featured Product
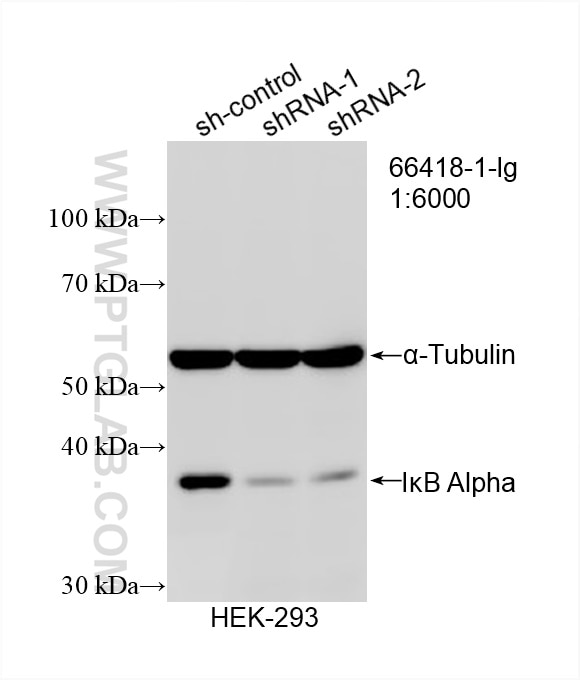
- KD/KO Validated
IkB Alpha Monoklonaler Antikörper
IkB Alpha Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
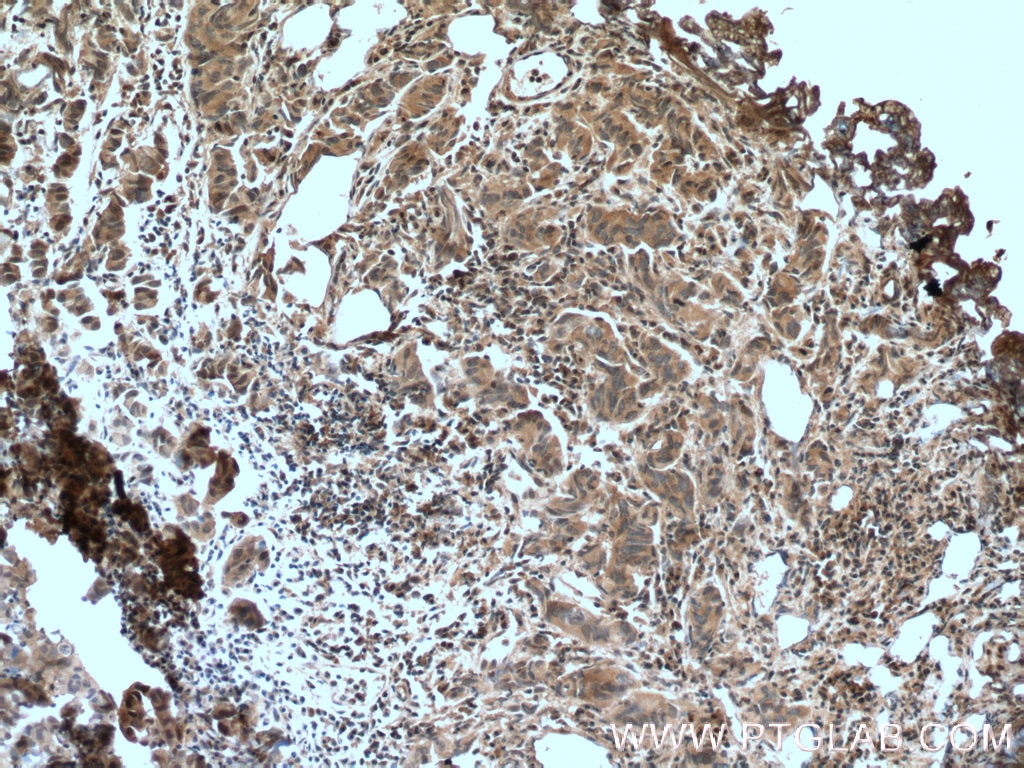
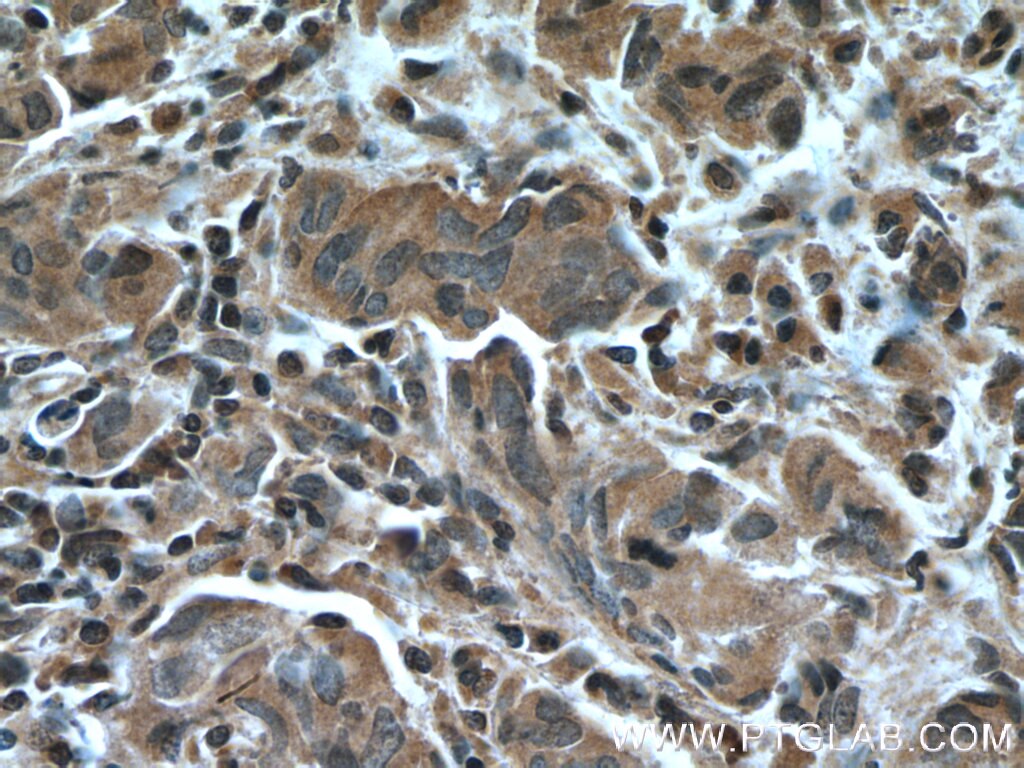
WB, IHC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
2G6H7
Kat-Nr. : 66418-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
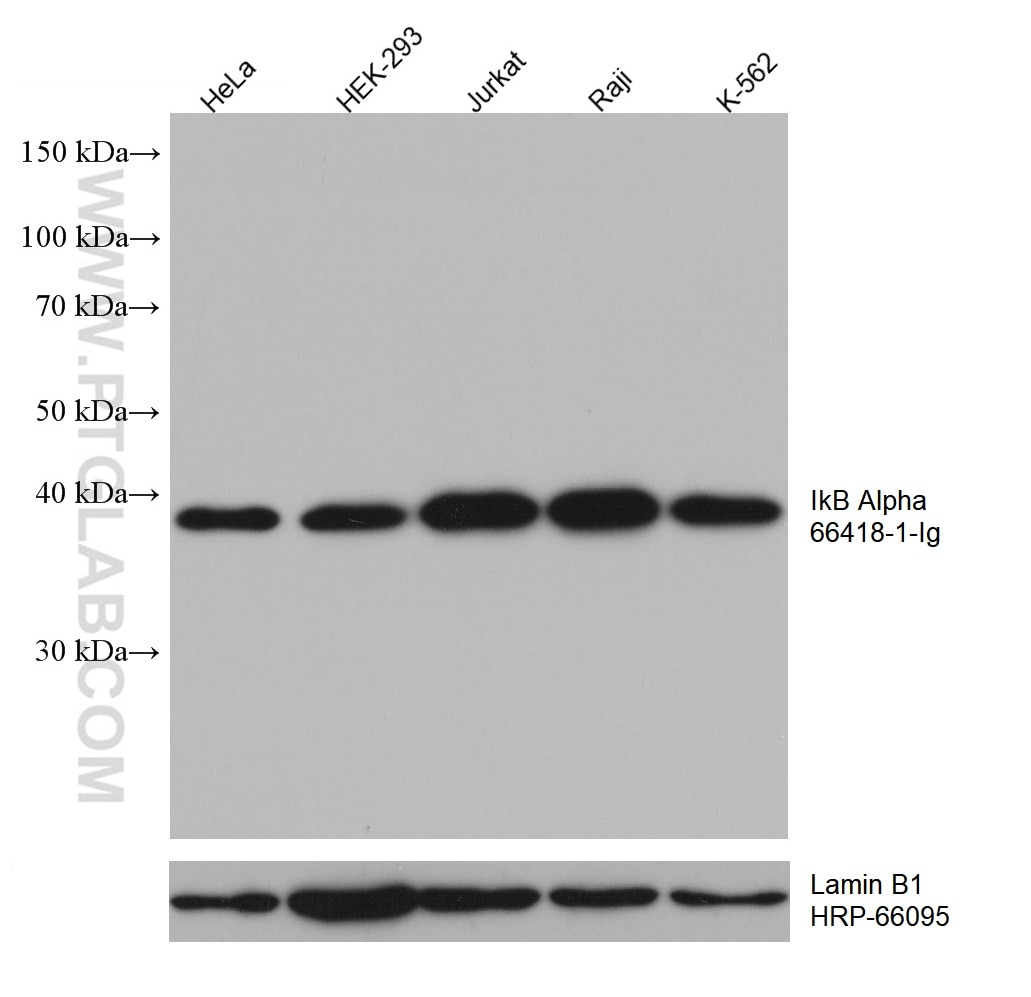
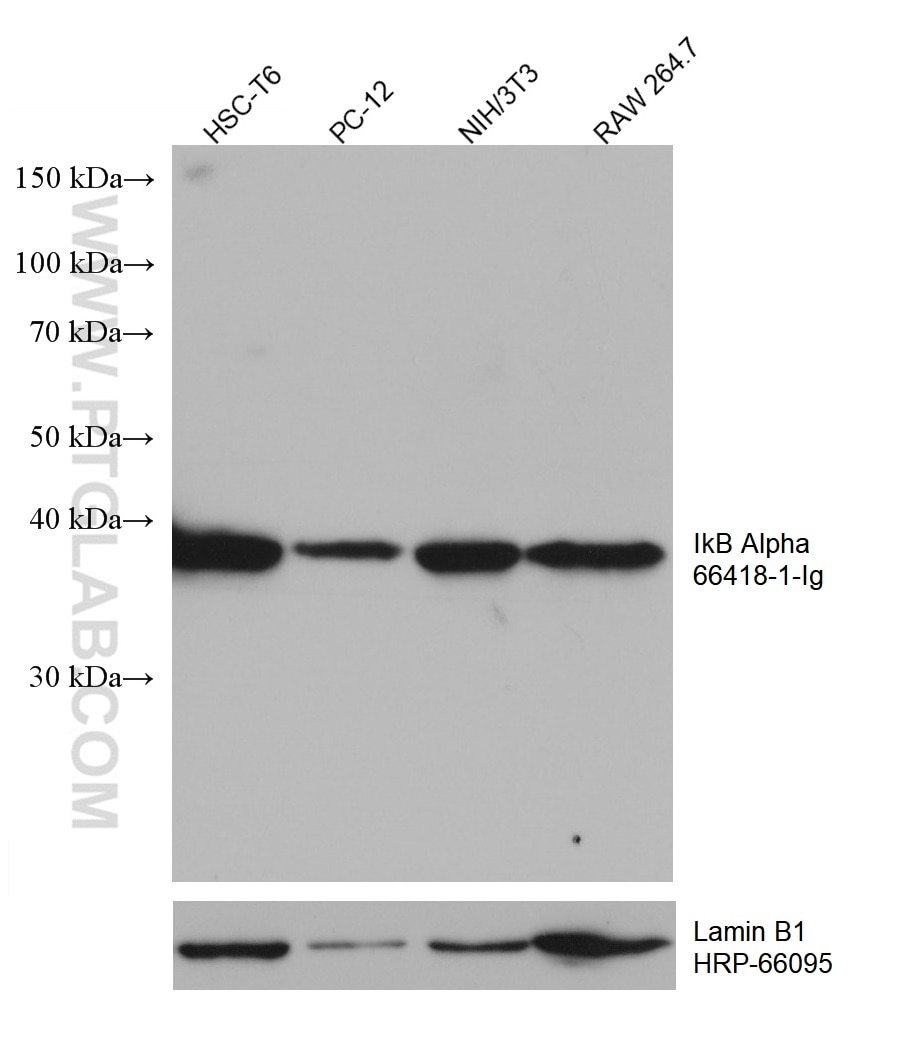
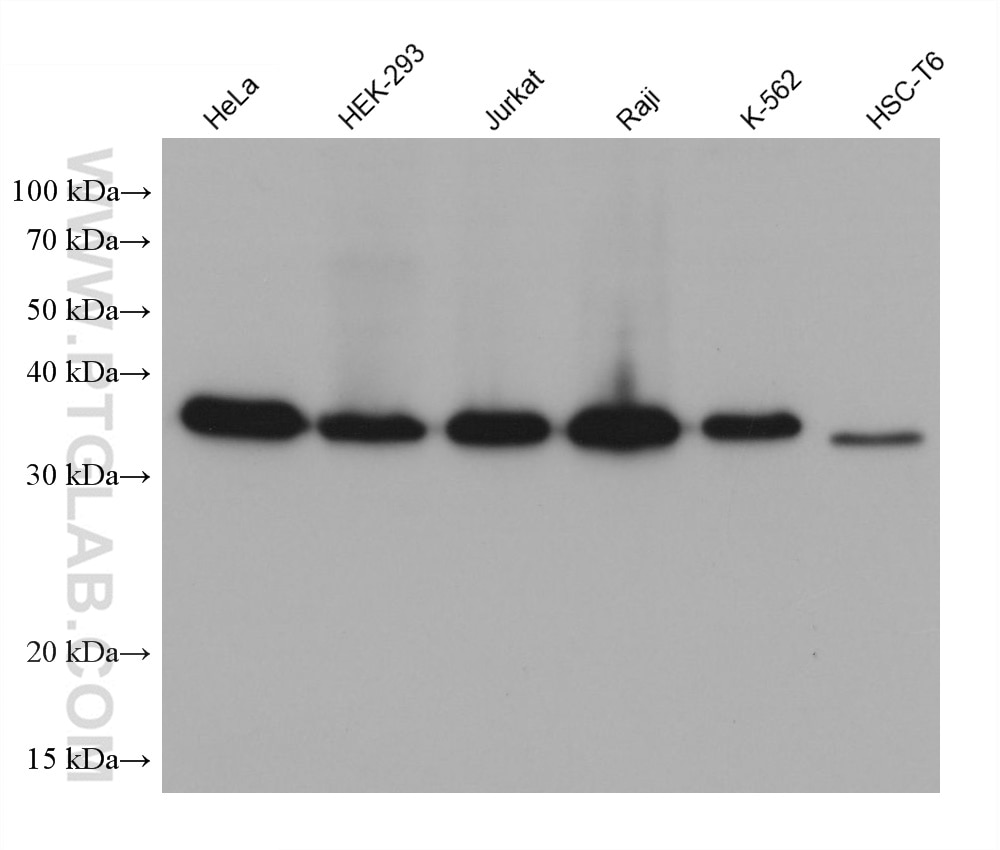
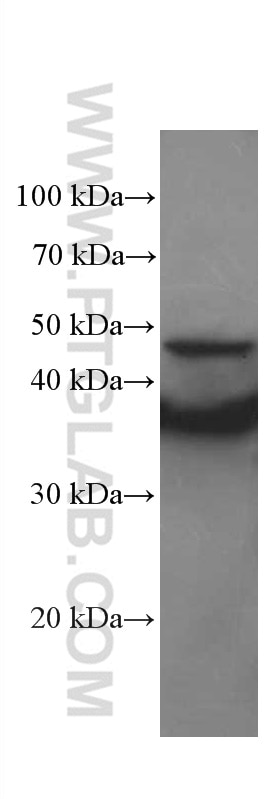
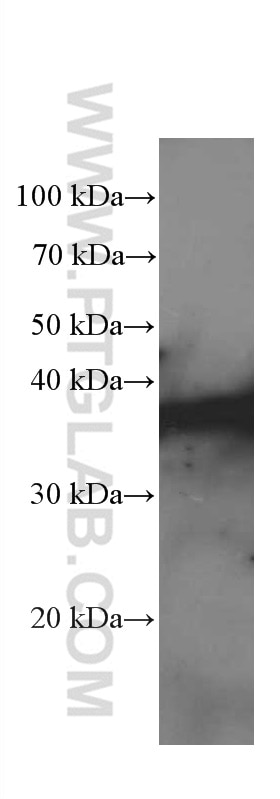
66418-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA IkB Alpha und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | IkB Alpha fusion protein Ag22040 |
| Vollständiger Name | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 36 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 36 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC004983 |
| Gene symbol | IkB Alpha |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4792 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (NFKBIA, synonyms: IKBA, MAD-3, NFKBI). NFKB1 or NFKB2 is bound to REL, RELA , or RELB to form the NFKB complex. The NFKB complex is inhibited by I-kappa-B proteins (NFKBIA or NFKBIB), which inactivate NF-kappa-B by trapping it in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of serine residues on the I-kappa-B proteins by kinases (IKBKA, or IKBKB) marks them for destruction via the ubiquitination pathway, thereby allowing activation of the NF-kappa-B complex. Activated NFKB complex translocates into the nucleus and binds DNA at kappa-B-binding motifs such as 5-prime GGGRNNYYCC 3-prime or 5-prime HGGARNYYCC 3-prime.