- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
KEAP1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
KEAP1 Polyklonal Antikörper für IF-P
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
IF-P
Konjugation
CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye
Kat-Nr. : CL594-10503
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
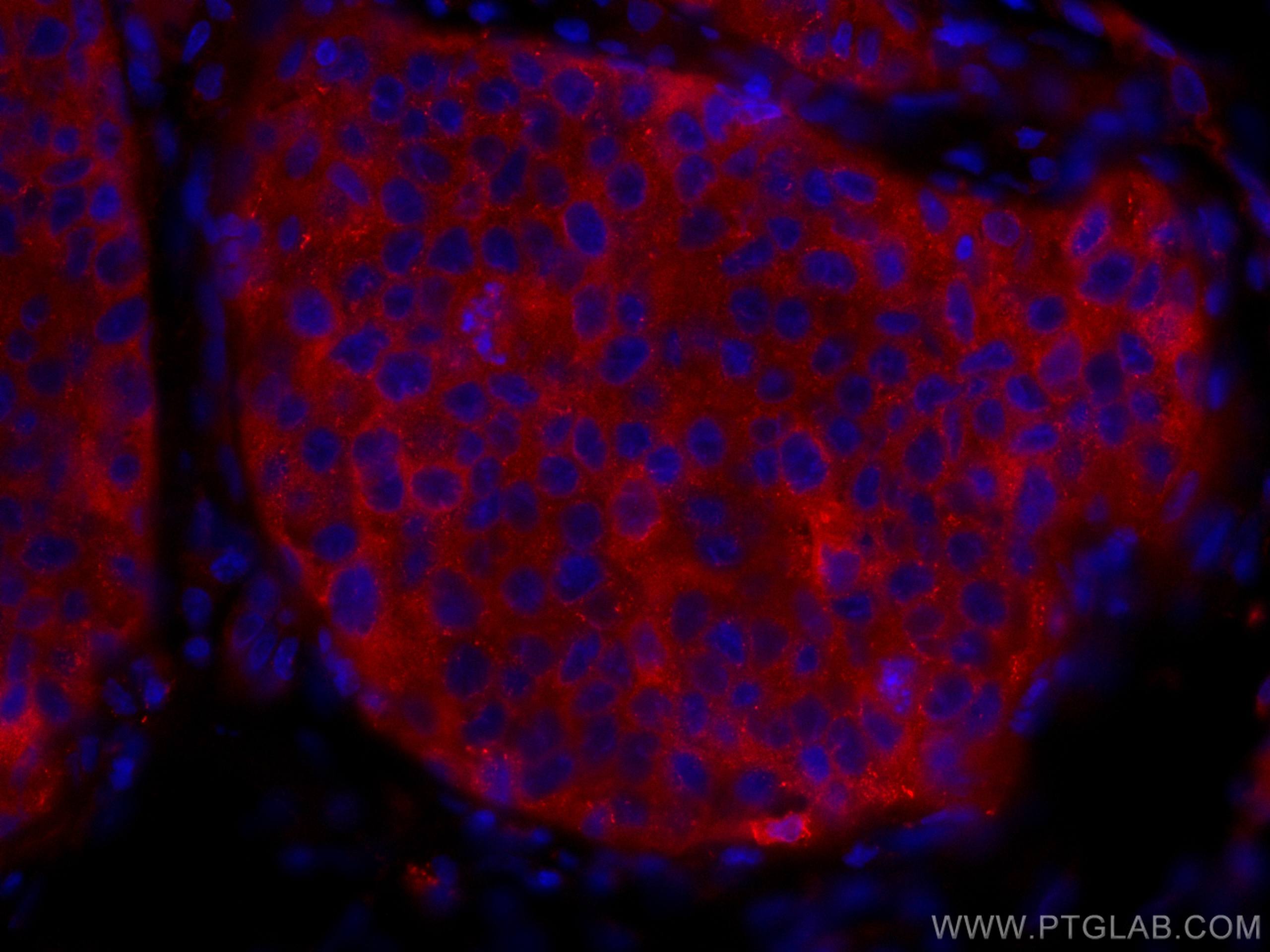
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF-P | humanes Mammakarzinomgewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
CL594-10503 bindet in IF-P KEAP1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | KEAP1 fusion protein Ag0779 |
| Vollständiger Name | kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 624 aa, 70 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 70 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC002930 |
| Gene symbol | KEAP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9817 |
| Konjugation | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Vor Licht schützen. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr stabil. Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) is a negative regulator of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a transcription factor governing the antioxidant response.
What is the molecular weight of KEAP1 protein? Are there any isoforms of KEAP1?
The molecular weight of KEAP1 protein is 70 kDa. The KEAP1 gene gives rise only to protein isoforms, but mutations of KEAP1 protein have been found in various cancer types.
What is the subcellular localization of KEAP1?
KEAP1 resides in the cytoplasm, where it binds to Nrf2, targeting it for degradation and preventing translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus.
How does KEAP1 control Nrf2 levels? Is KEAP1 post-translationally modified?
KEAP1 is rich in reactive cysteine residues, whose thiol groups play a role in binding to CUL3 and the polyubiquitination of Nrf2, which leads to degradation of Nrf2 via the proteasome system. During oxidative stress, electrophiles and reactive oxygen species (ROS) modify the KEAP1 thiol groups, reducing the affinity of KEAP1 to CUL3 and the stabilization of Nrf2. Nrf2 then translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to the antioxidant responsive elements (AREs) and induces the expression of antioxidant proteins (PMID: 16354693).
How to measure oxidative stress using KEAP1 and Nrf2 proteins as a readout
Under basal conditions (unstressed cells), a detectable KEAP1 protein level is observed. Oxidative stress modifies KEAP1 protein activity by increasing the Nrf2 protein levels. This can be measured, for example, using western blotting (PMID: 27697860). KEAP1 protein levels are not altered by oxidative stress.
What is the role of the KEAP1-Nrf2 pathway in health and disease?
The KEAP-Nrf2 pathway plays a vital role in redox homeostasis and cryoprotection. Inhibition of KEAP1 activity leads to the activation of Nrf2 and increase the response to oxidative stress and anti-inflammatory effects (PMID: 29717933). The activation of Nrf2 can be beneficial in the case of metabolic diseases, such as diabetes, as well as neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. However, the increased activation of Nrf2 is also known to promote tumor growth and metastasis. Mutations in both KEAP1 and Nrf2 were found in various solid tumor types.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL594 KEAP1 antibody CL594-10503 | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |