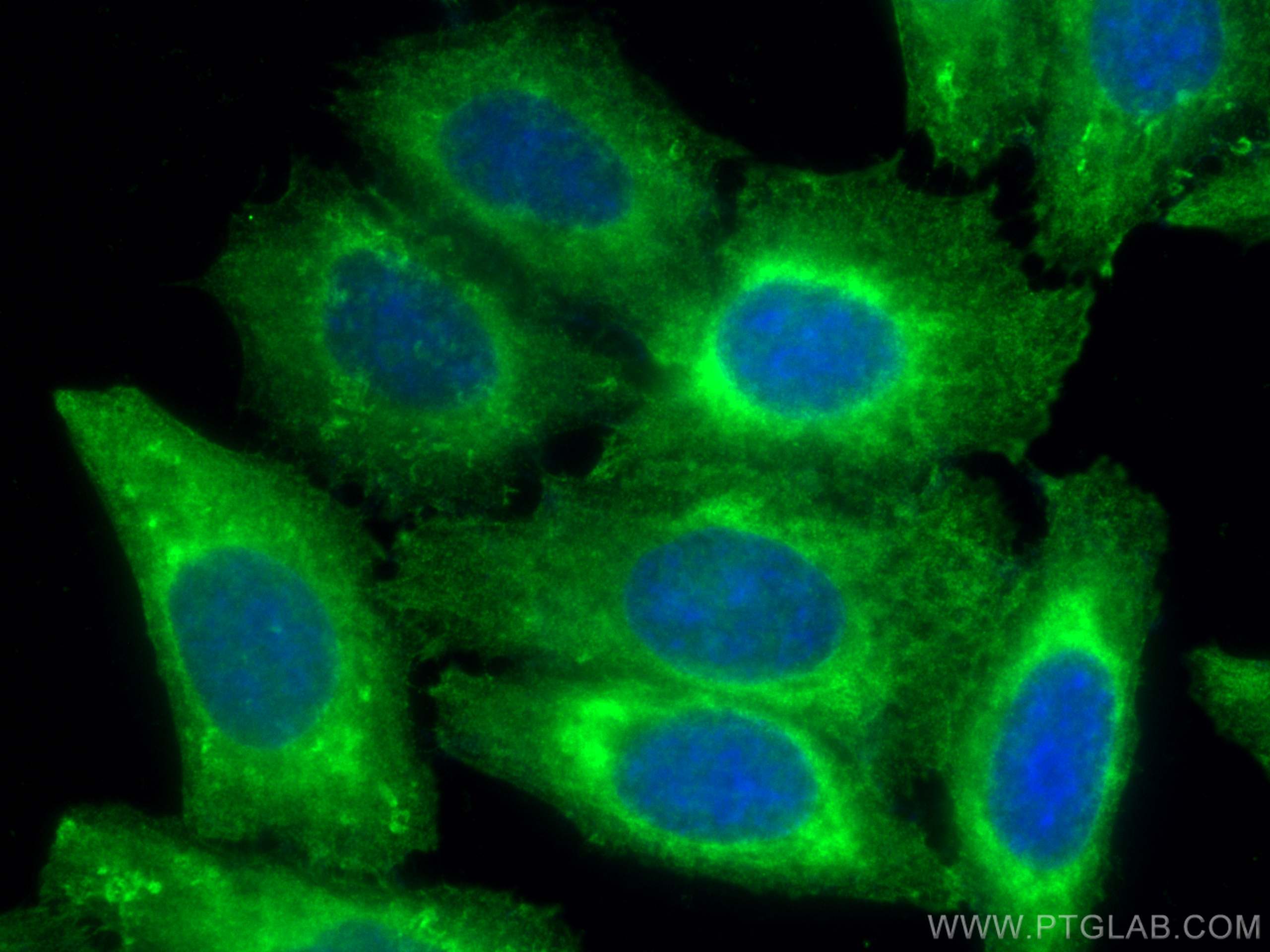
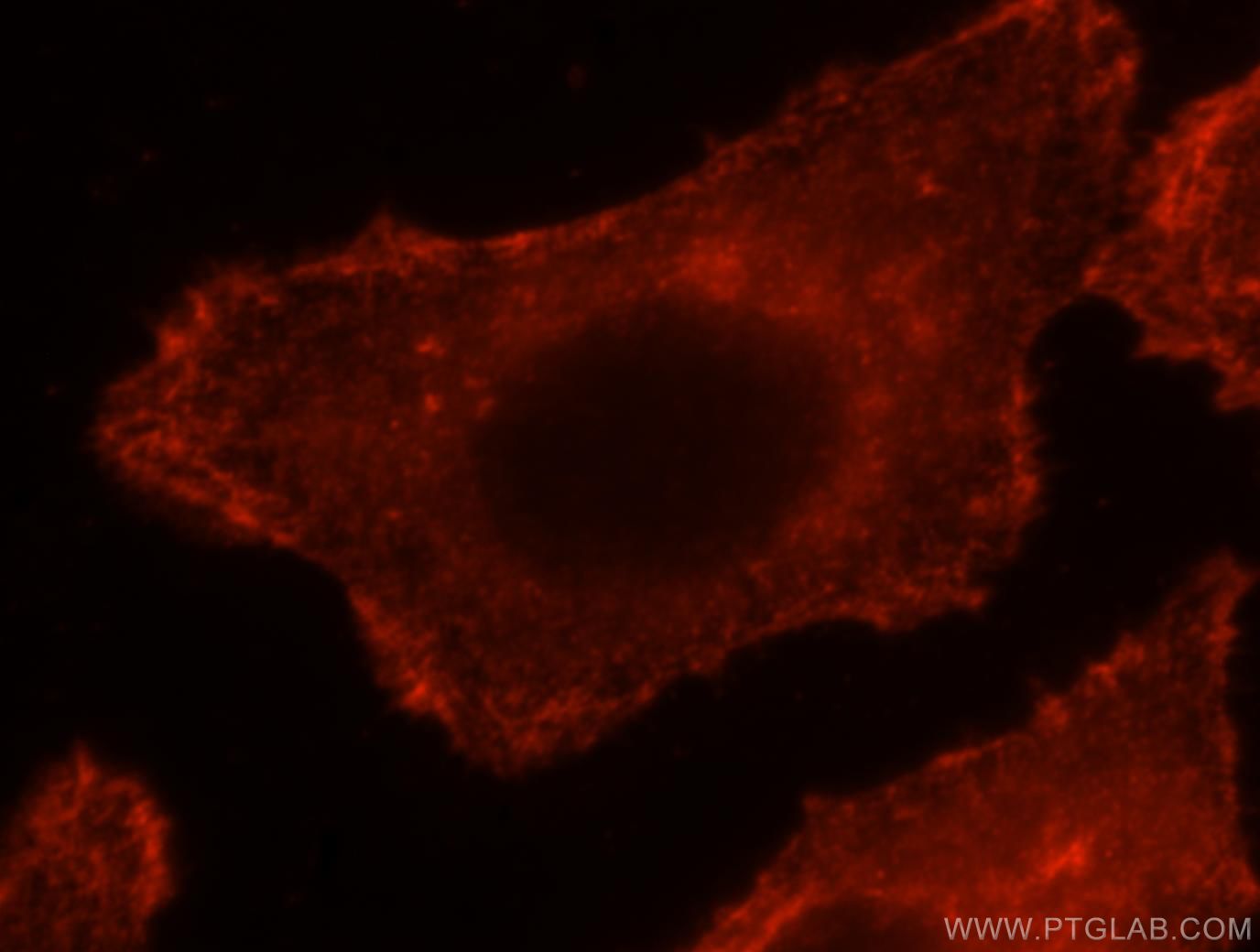
- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
EPLIN Polyklonaler Antikörper
EPLIN Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 16639-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
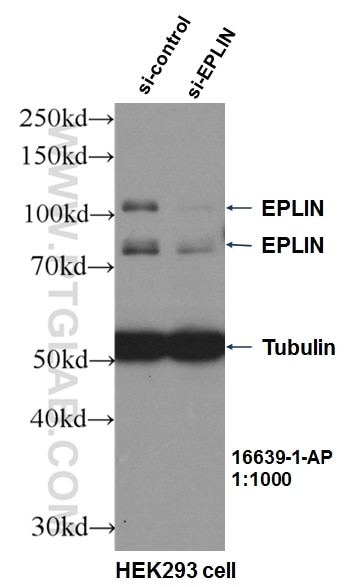
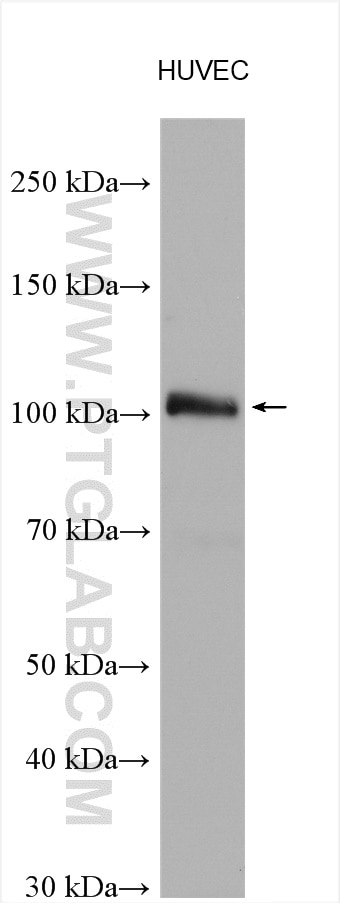
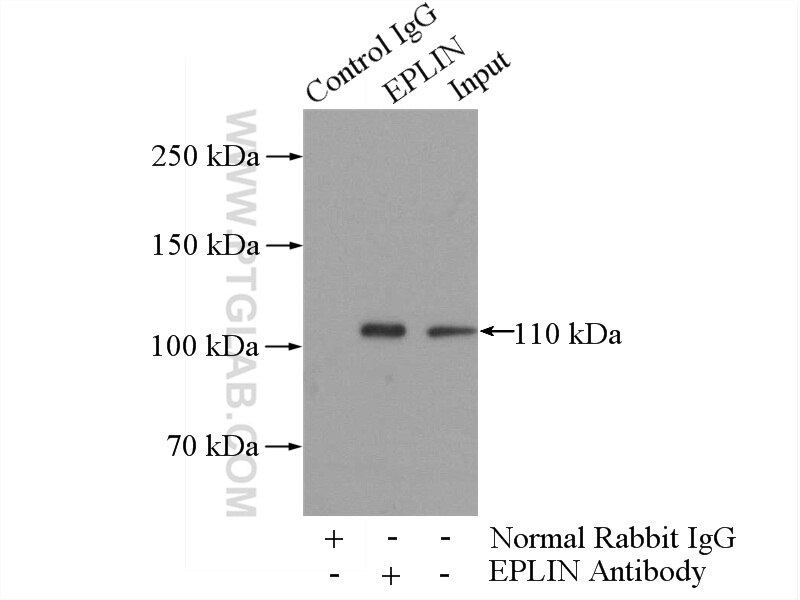
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HUVEC-Zellen, HEK-293-Zellen, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe |
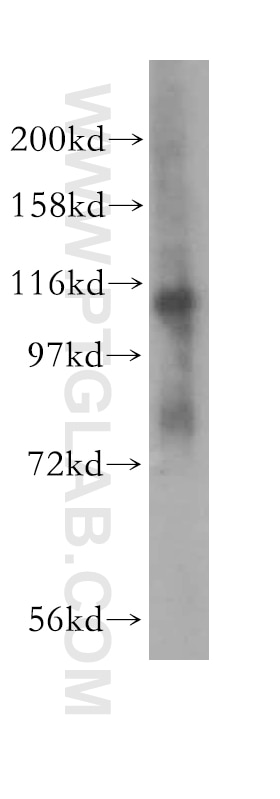
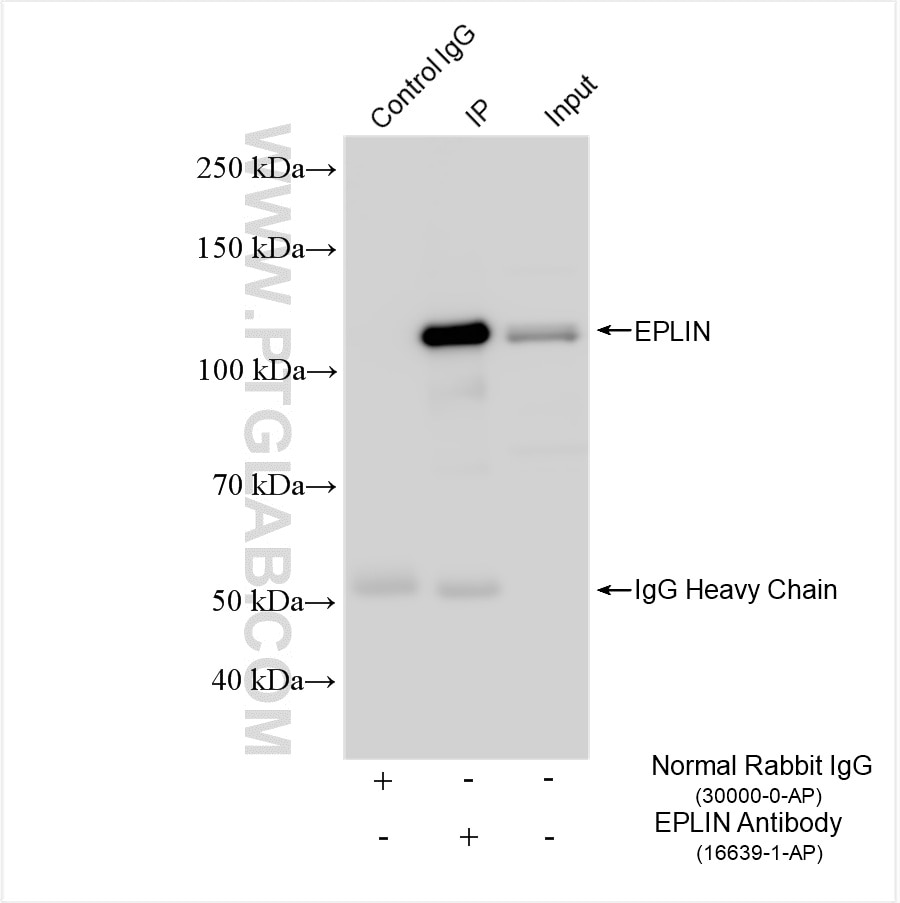
| Erfolgreiche IP | HepG2-Zellen, Mauslebergewebe |
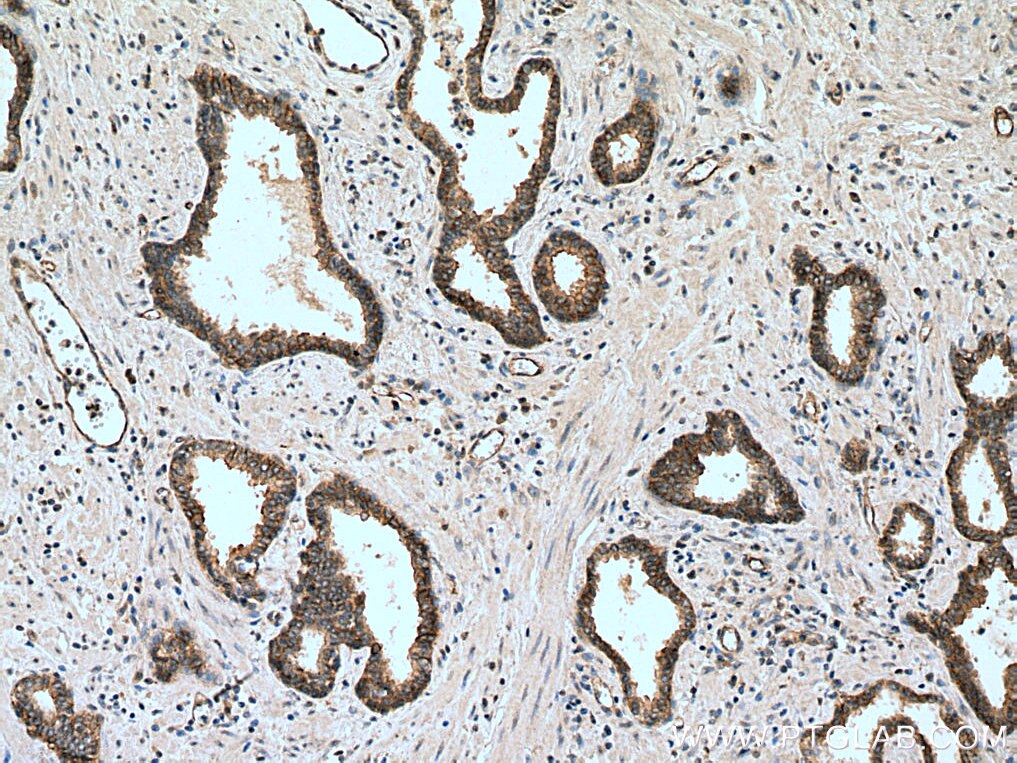
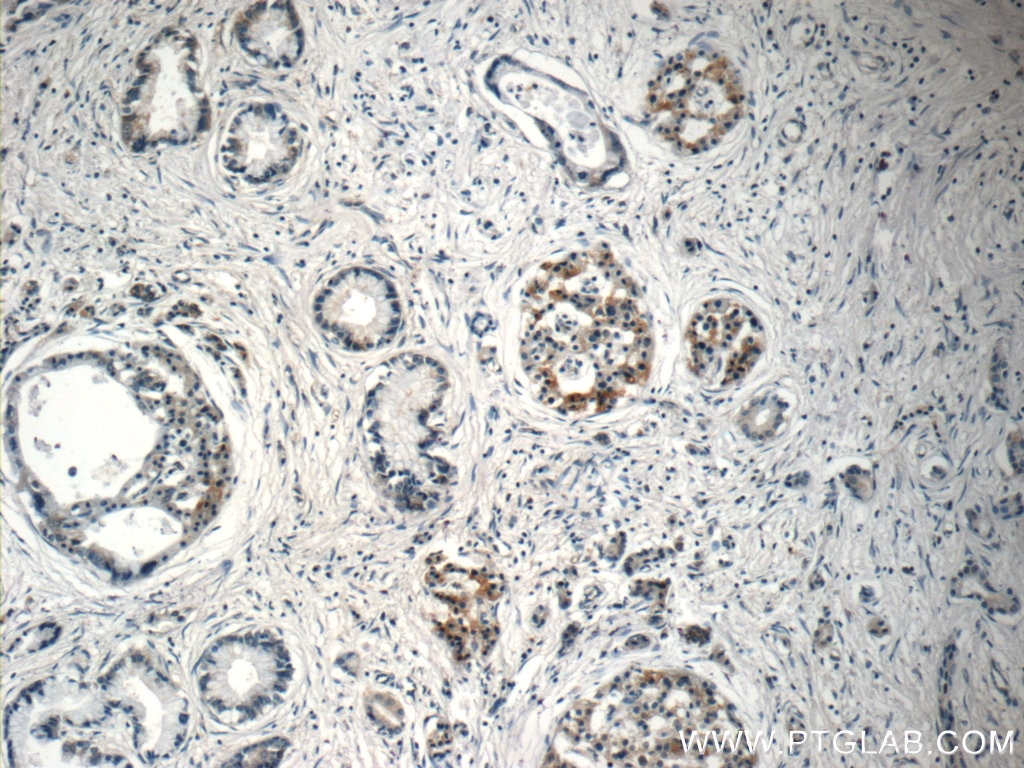
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Prostatakarzinomgewebe, humanes Pankreaskarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
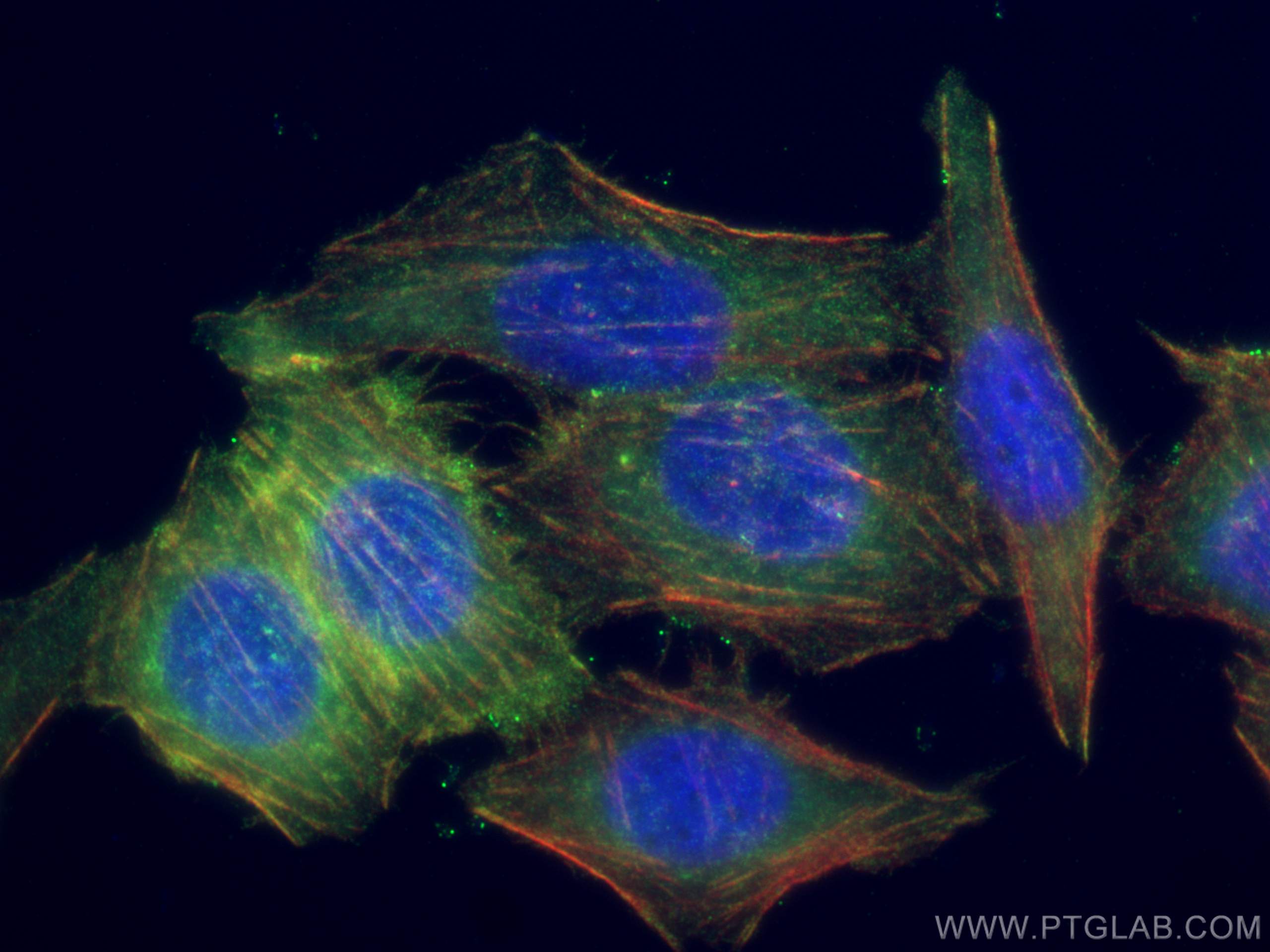
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | PC-3-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 4 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
16639-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA EPLIN und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | EPLIN fusion protein Ag9994 |
| Vollständiger Name | LIM domain and actin binding 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 85 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 90 kDa, 110 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC001247 |
| Gene symbol | EPLIN |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 51474 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
EPLIN is a cytoskeletal protein that is preferentially expressed in epithelial cells and is implicated in regulation of cytoskeletal dynamics and cytokinesis. In human, there are two known isoforms, EPLIN-a and -b, generated by alternative promoter usage from a single gene. The 110 kDa EPLIN-β isoform represents the full-length protein and the 90 kDa EPLIN-α isoform lacks the amino-terminal 160 amino acids. EPLIN-a expression is often down-regulated in cancerous cells and tissues. (PMID: 10806352, 31644899)
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for EPLIN antibody 16639-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for EPLIN antibody 16639-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for EPLIN antibody 16639-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for EPLIN antibody 16639-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Exp Mol Med The deubiquitinating enzyme STAMBP is a newly discovered driver of triple-negative breast cancer progression that maintains RAI14 protein stability | ||
J Cell Biol Rab40-Cullin5 complex regulates EPLIN and actin cytoskeleton dynamics during cell migration. | ||
Acta Histochem Cytochem EPLINβ Is Involved in the Assembly of Cadherin-catenin Complexes in Osteoblasts and Affects Bone Formation. | ||
Proteomics A proteomic signature and potential pharmacological opportunities in the adaptive resistance to MEK and PI3K kinase inhibition in pancreatic cancer cells | ||
Exp Cell Res Nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation of SQSTM1/p62 protein enhances ESCC cell migration and invasion by stabilizing EPLIN expression
| ||
Cell Biol Toxicol M6A modification-mediated LIMA1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through the wnt-βcatenin/Hippo pathway |