Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT Polyklonaler Antikörper
Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 17034-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
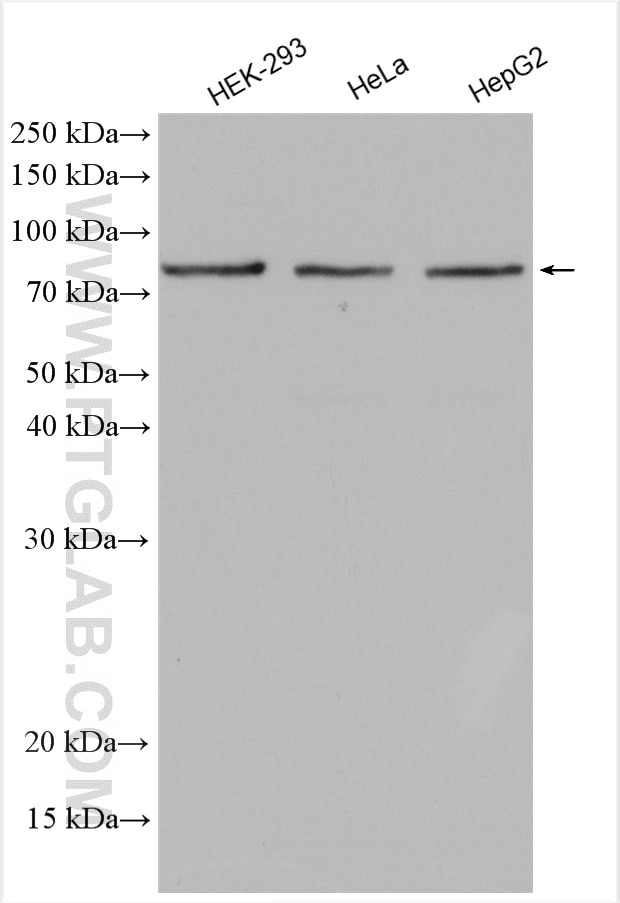
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HEK-293-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen |
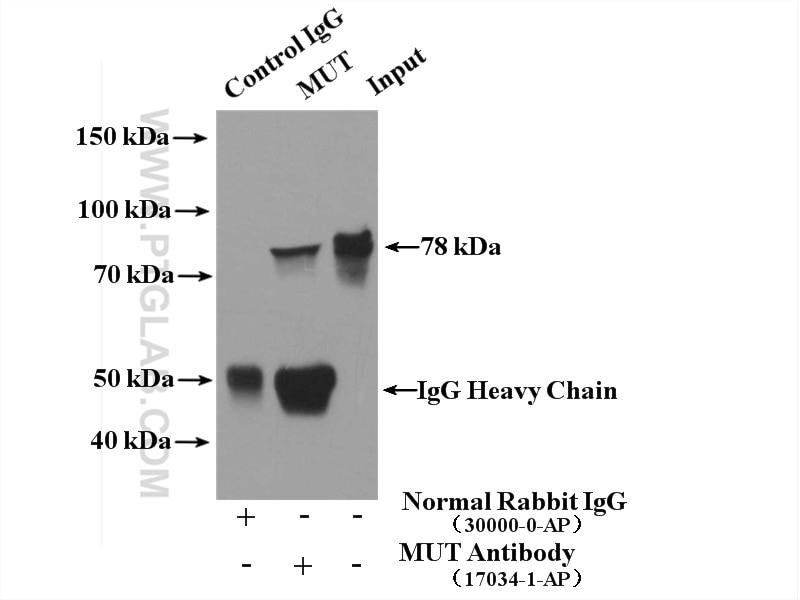
| Erfolgreiche IP | HepG2-Zellen |
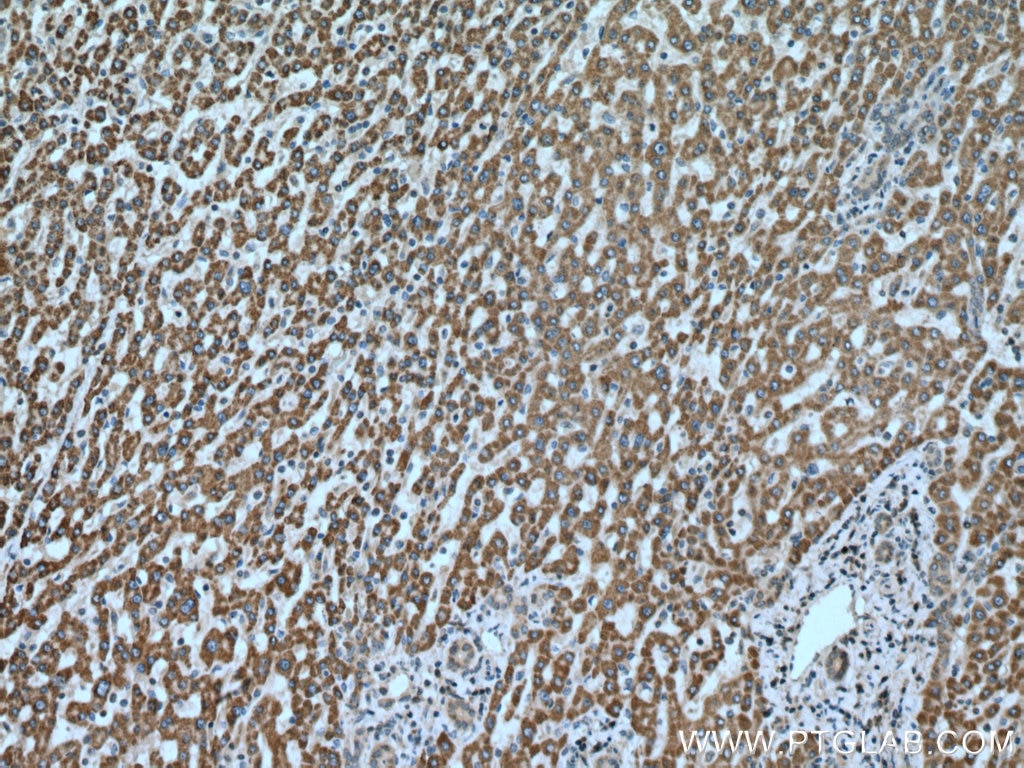
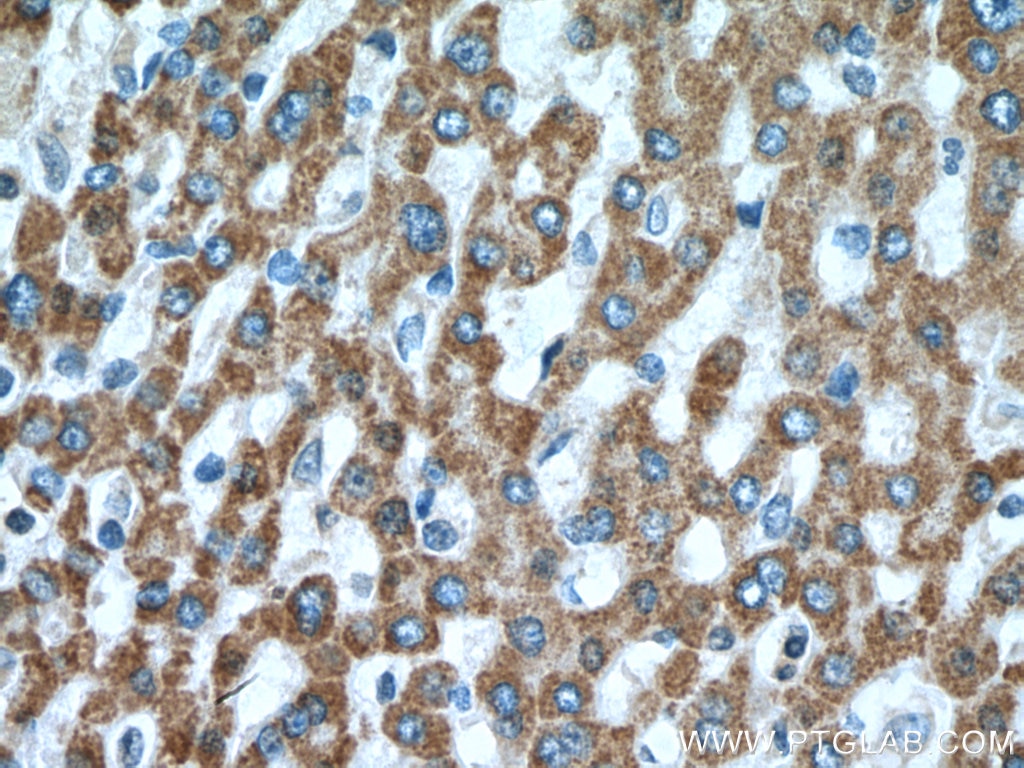
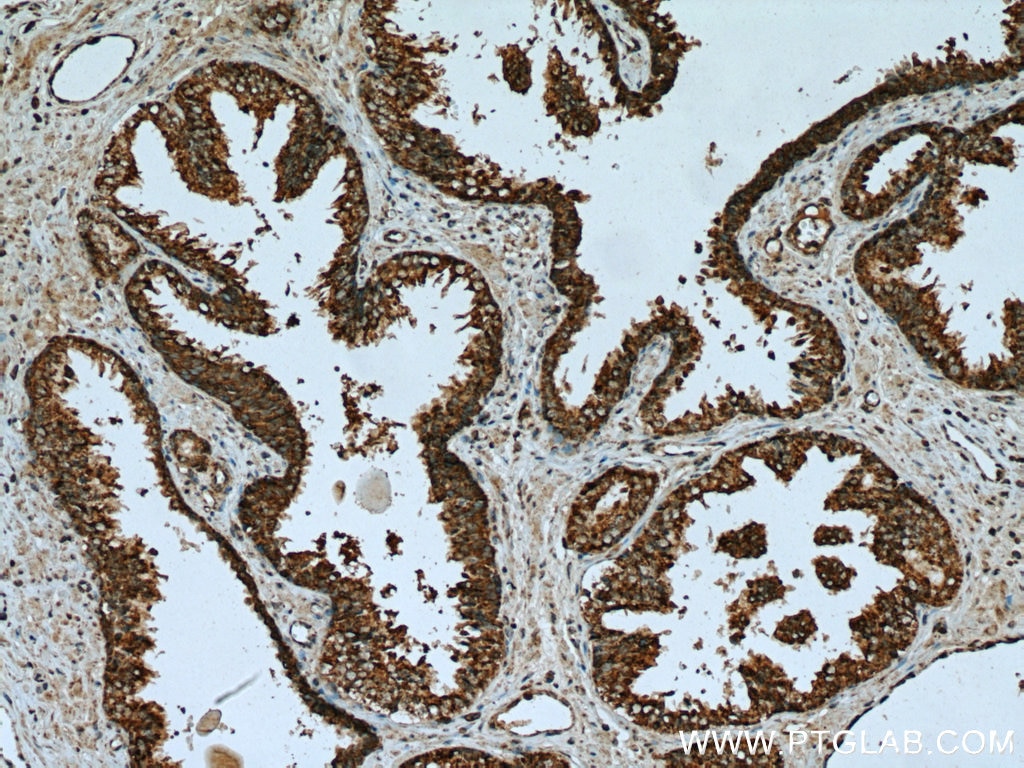
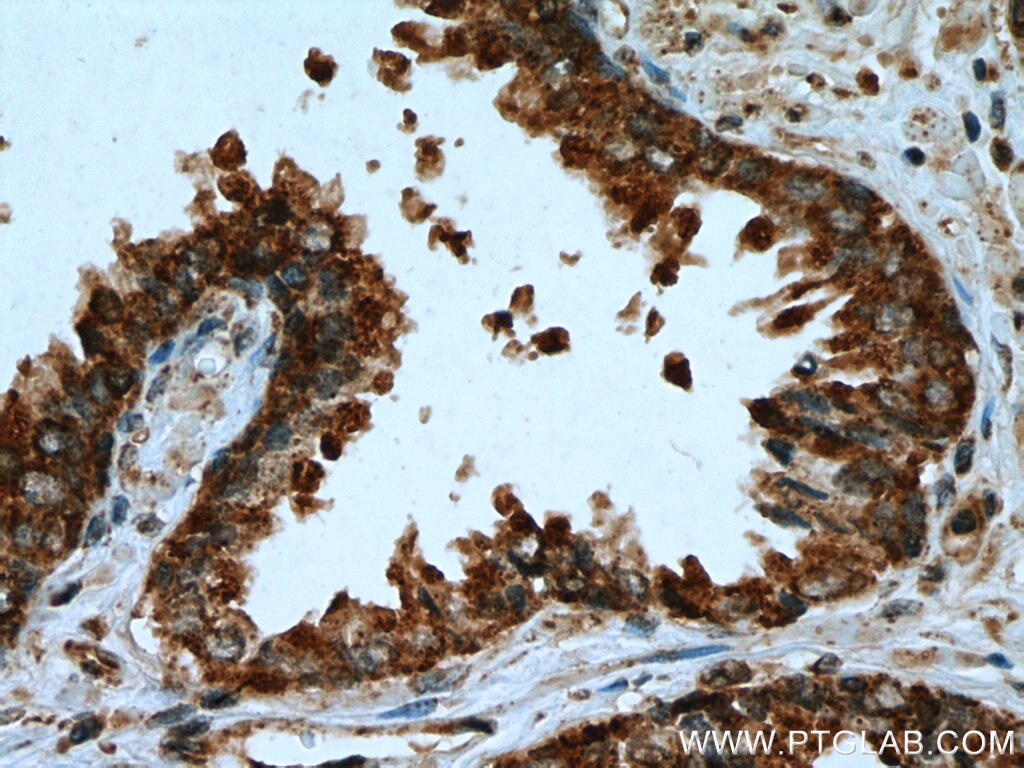
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Leberkarzinomgewebe, humanes Prostatakarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:12000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 4 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
Produktinformation
17034-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IP, ELISA Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT fusion protein Ag10523 |
| Vollständiger Name | methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 750 aa, 83 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 78 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC016282 |
| Gene symbol | MUT |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4594 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase (MUT) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of certain amino acids and fatty acids (PMID: 15647267). Mutations in the MUT gene can lead to methylmalonic acidemia, a metabolic disorder characterized by the accumulation of toxic compounds such as methylmalonyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA (PMID: 30428564), resulting in life-threatening metabolic acidosis, respiratory distress, neurological impairment, hyperammonemia, and ketosis (PMID: 32679819). MUT is essential for maintaining normal metabolic processes and its dysfunction can have significant health implications, highlighting its importance in both basic metabolism and clinical medicine (PMID: 23041189).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT antibody 17034-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT antibody 17034-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IP protocol for Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT antibody 17034-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Hepatology Promoterless, Nuclease-Free Genome Editing Confers a Growth Advantage for Corrected Hepatocytes in Mice With Methylmalonic Acidemia. | ||
Cells Inactivity of Peptidase ClpP Causes Primary Accumulation of Mitochondrial Disaggregase ClpX with Its Interacting Nucleoid Proteins, and of mtDNA. | ||
PLoS One Novel AAV-mediated genome editing therapy improves health and survival in a mouse model of methylmalonic acidemia | ||
EMBO Mol Med A coordinated multiorgan metabolic response contributes to human mitochondrial myopathy | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis ACSS3 regulates the metabolic homeostasis of epithelial cells and alleviates pulmonary fibrosis | ||
Am J Pathol Aging-associated Metabolite Methylmalonic Acid Increases Susceptibility to Pulmonary Fibrosis
|