CD43 Monoklonaler Antikörper
CD43 Monoklonal Antikörper für Single Cell (Intra)
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2b
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
Single Cell (Intra)
Konjugation
5CFLX Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
2A11D6
Kat-Nr. : G66224-1-5C
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in Single Cell (Intra) | 10x Genomics Gene Expression Flex with Feature Barcodes and Multiplexing product |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| SINGLE CELL (INTRA) | SINGLE CELL (INTRA) : <0.5ug/test |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
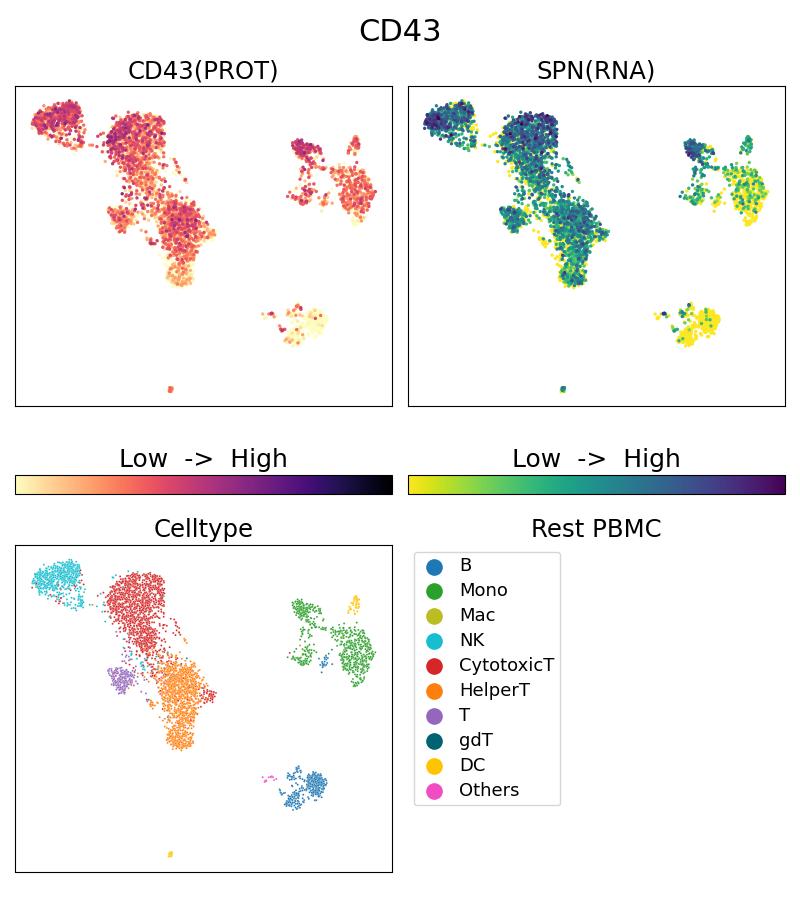
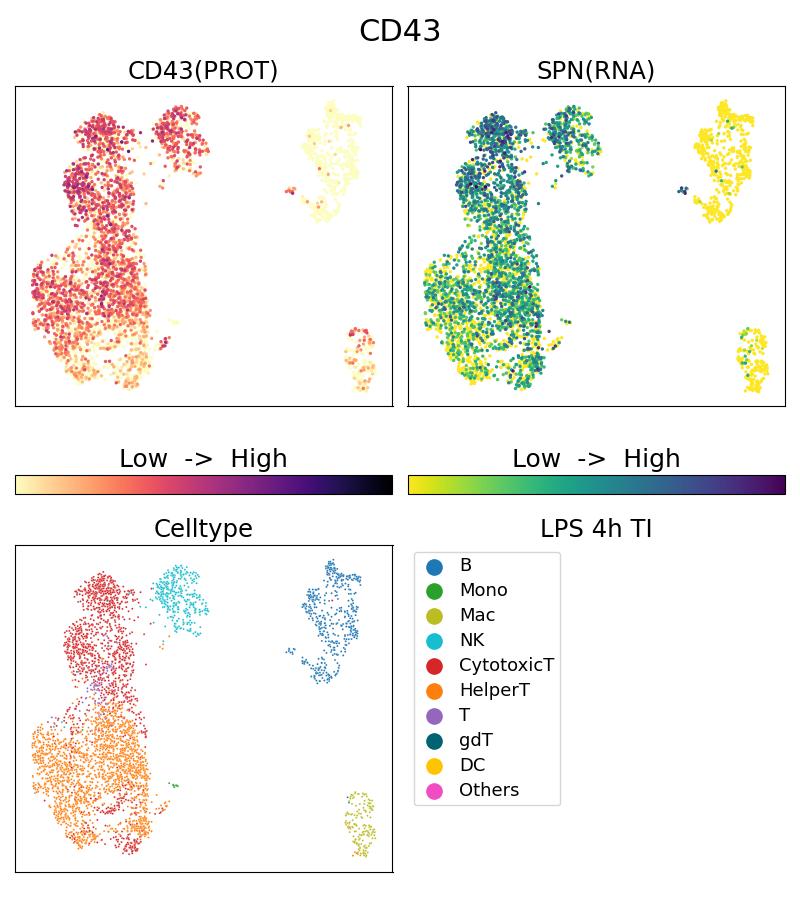
G66224-1-5C bindet in Single Cell (Intra) CD43 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2b |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CD43 fusion protein Ag23595 |
| Vollständiger Name | sialophorin |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 400 aa, 43 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC012350 |
| Gene symbol | CD43 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6693 |
| Konjugation | 5CFLX Fluorescent Dye |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 1mM EDTA and 0.09% sodium azide |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | 2-8°C Stable for one year after shipment. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
CD43, also named leukosialin, sialophorin, galactoglycoprotein, leukocyte sialoglycoprotein, SPN, and is a mucin-like type I transmembrane protein. In humans, it is expressed in haematopoietic cells, including T lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, natural killer cells, platelets, and haematopoietic stem cells, with the exception of mature erythrocytes and B cell subpopulations. The unglycosylated form of CD43 migrates on SDS-PAGE with a molecular weight of 54 kDa (PMID: 2943740), whereas CD43 from different haematopoietic cell lines displays increased molecular weights since it is glycosylated with O-linked chains that differ in core structure and sialylation.