- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) Polyklonaler Antikörper
PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 28076-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
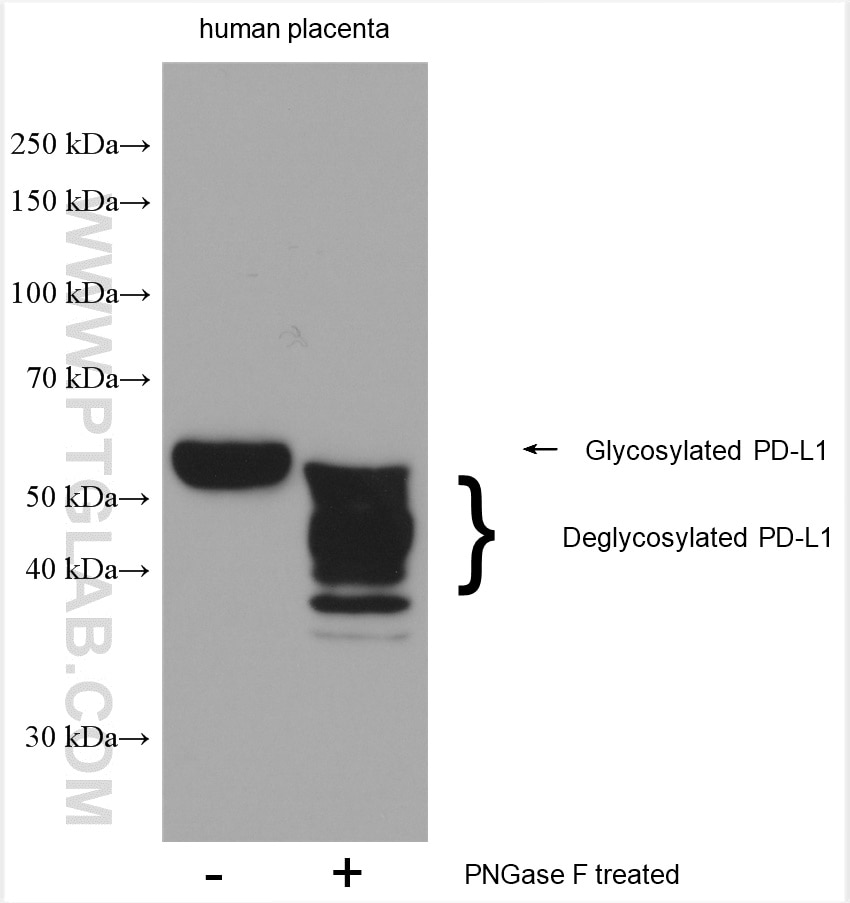
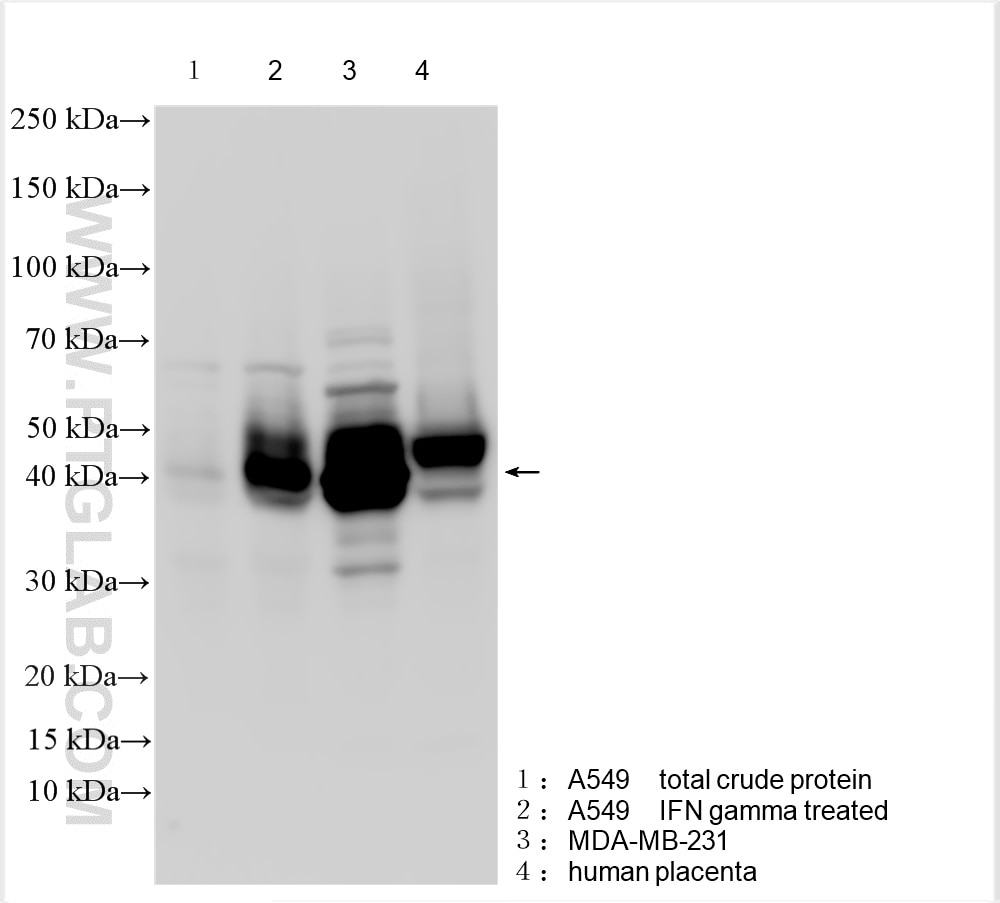
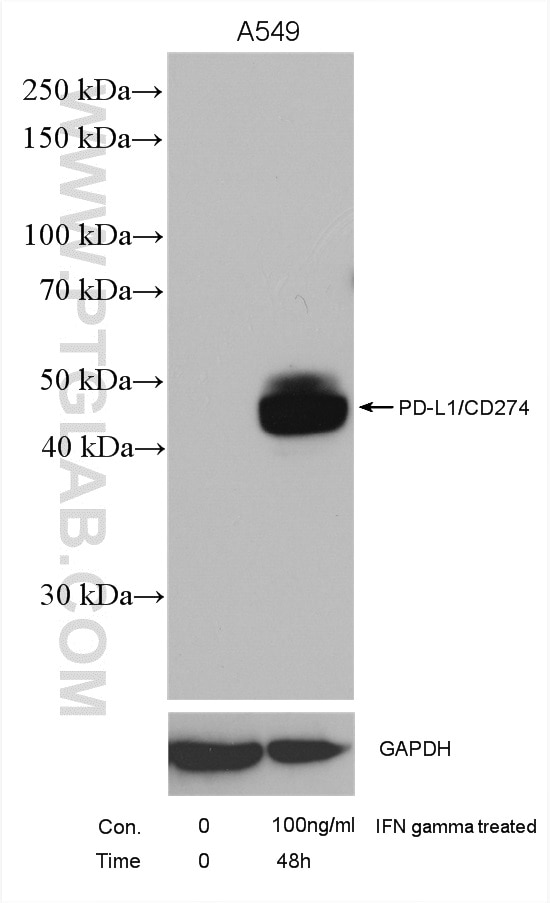
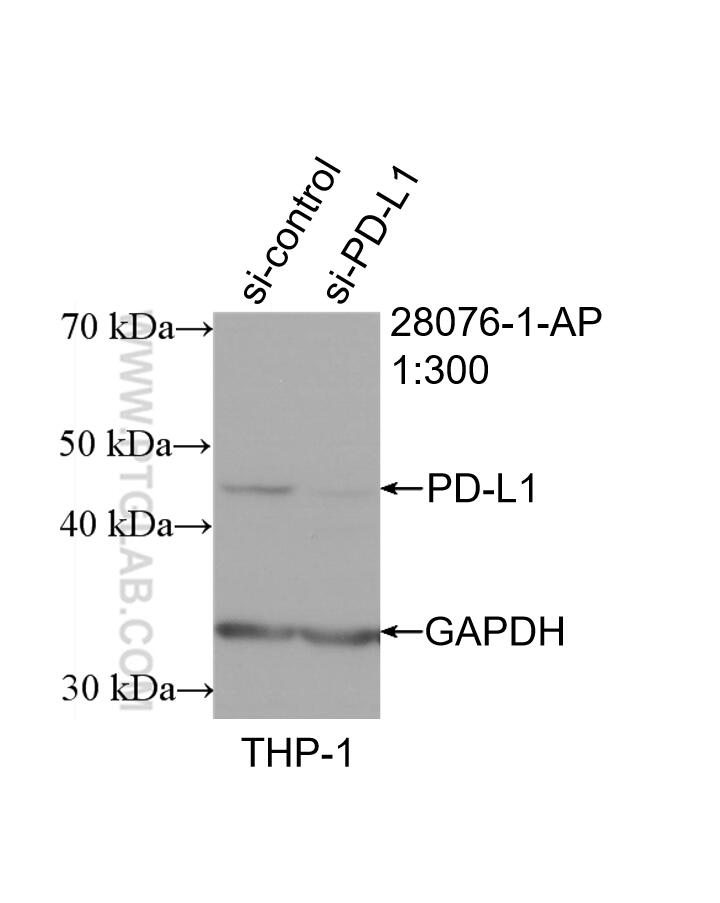
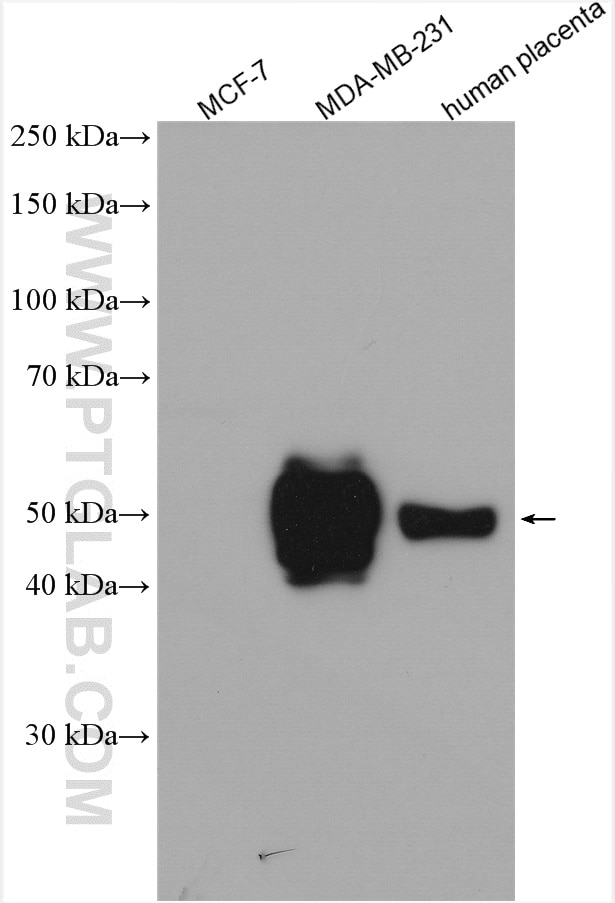
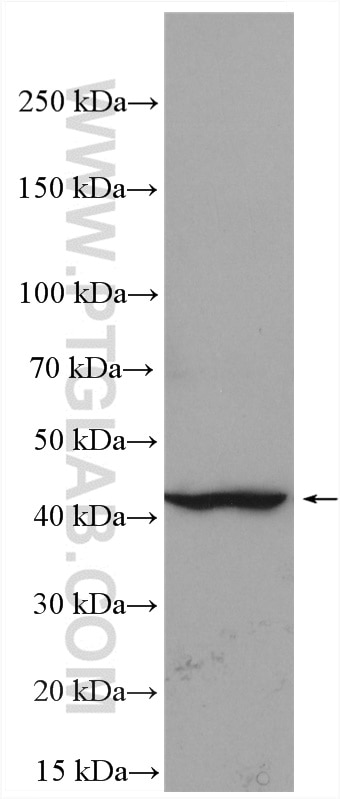
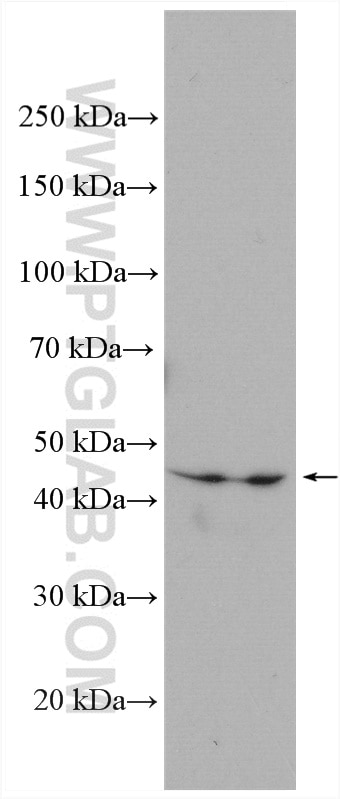
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | mit IFN-gamma behandelte A549-Zellen, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe, MDA-MB-231-Zellen, Mausherzgewebe, Rattenherzgewebe, THP-1-Zellen |
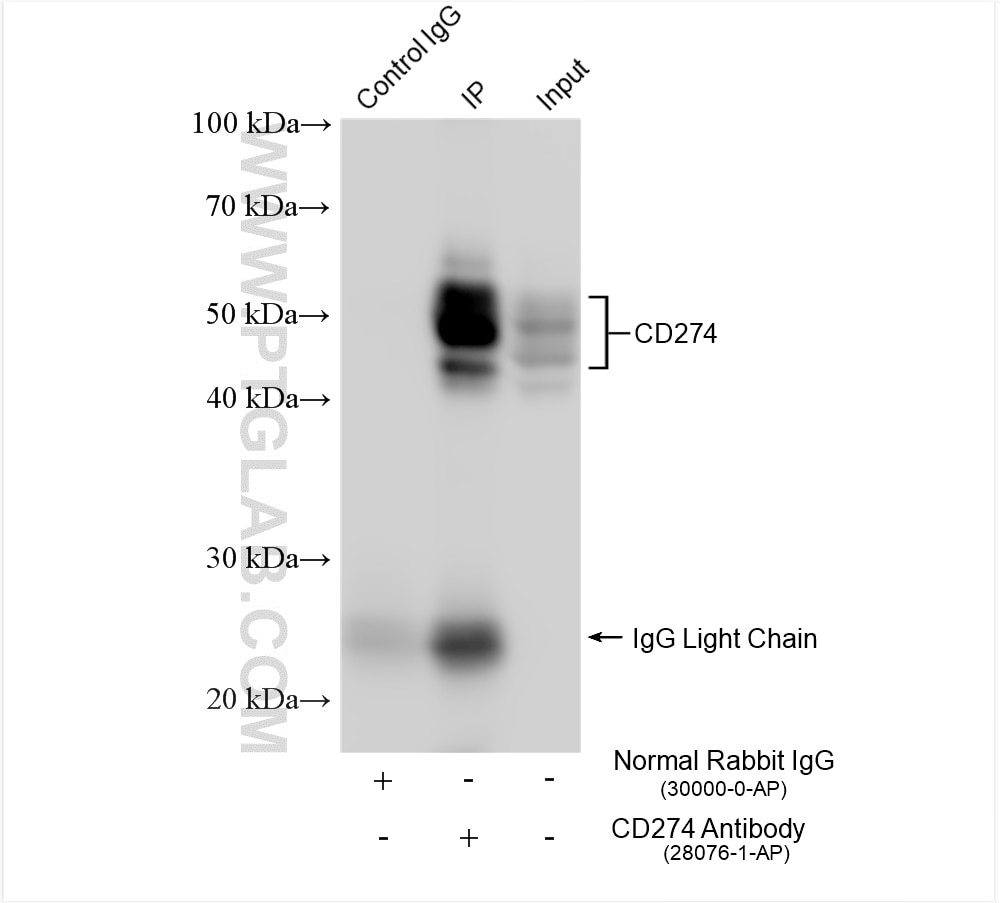
| Erfolgreiche IP | MDA-MB-231-Zellen |
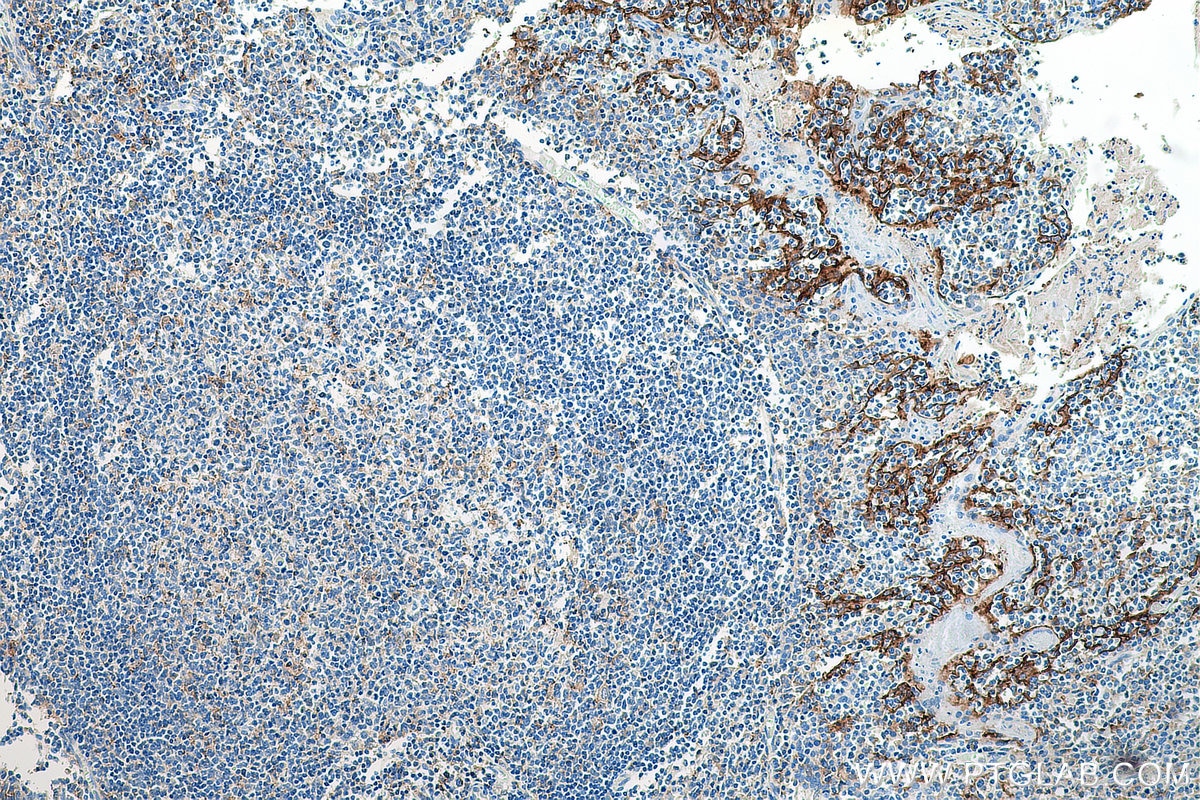
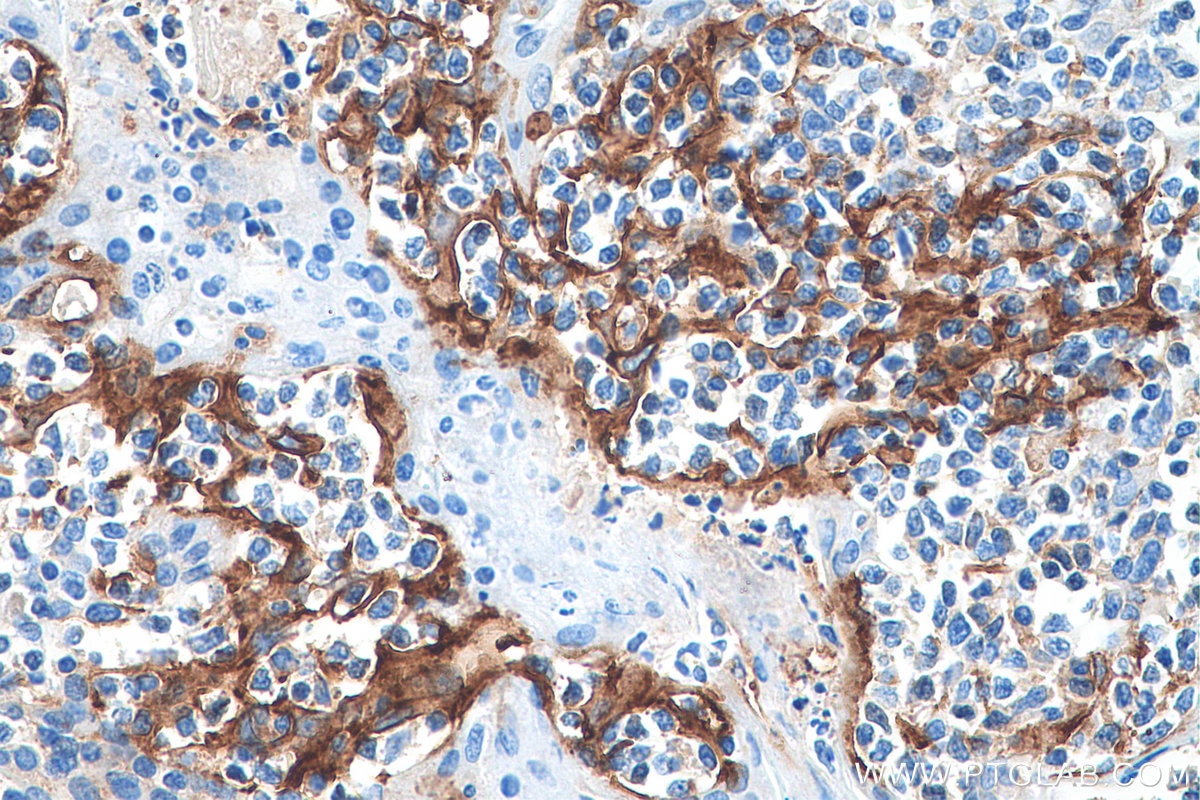
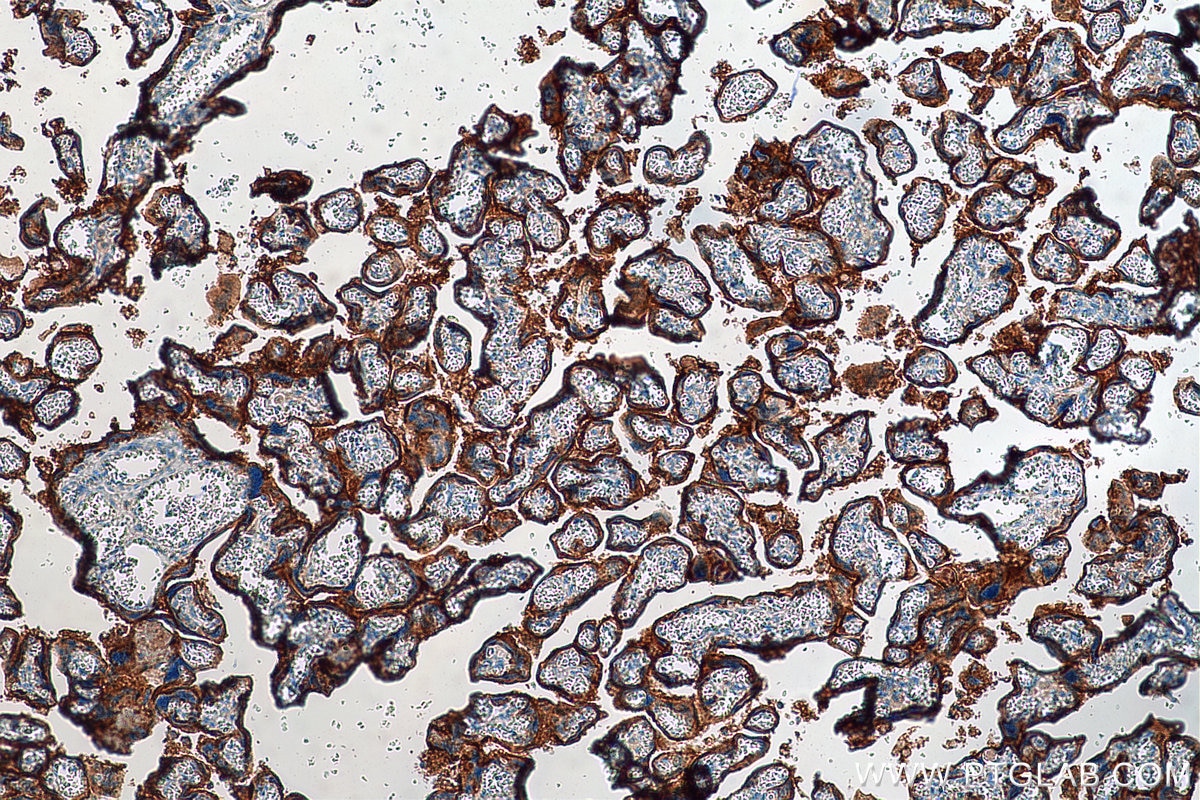
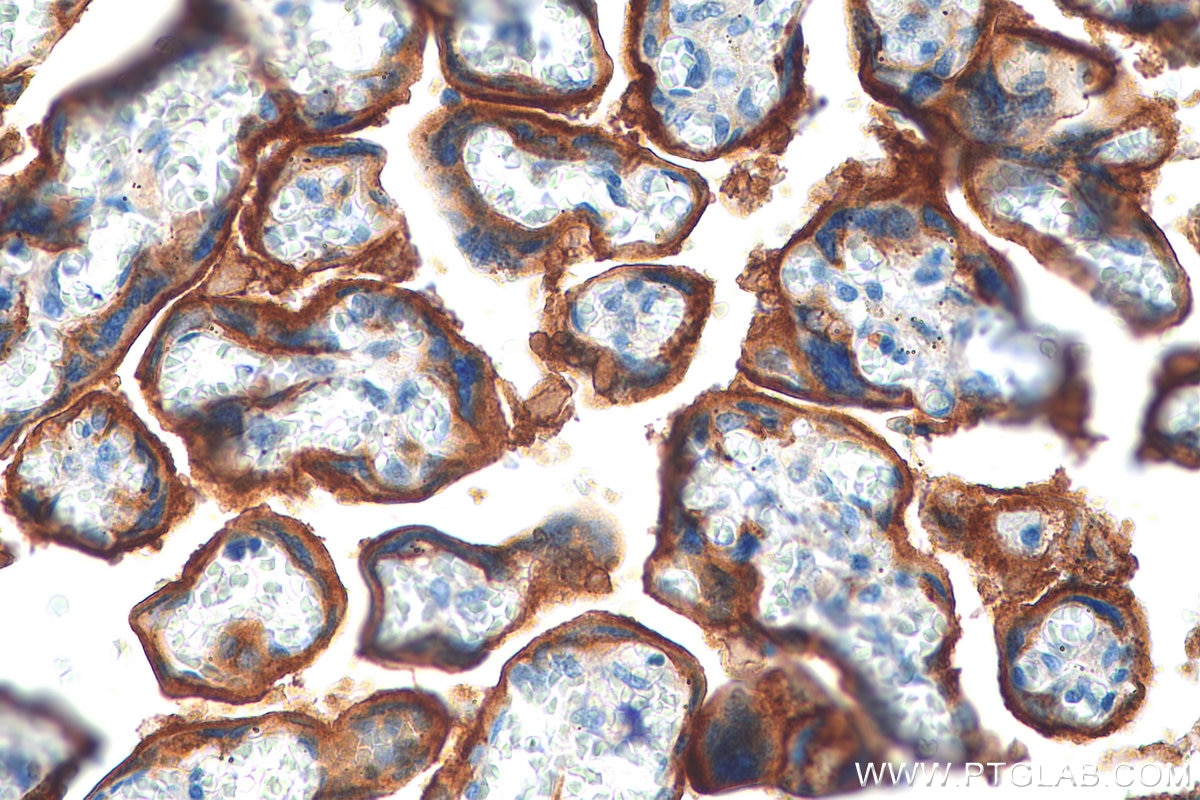
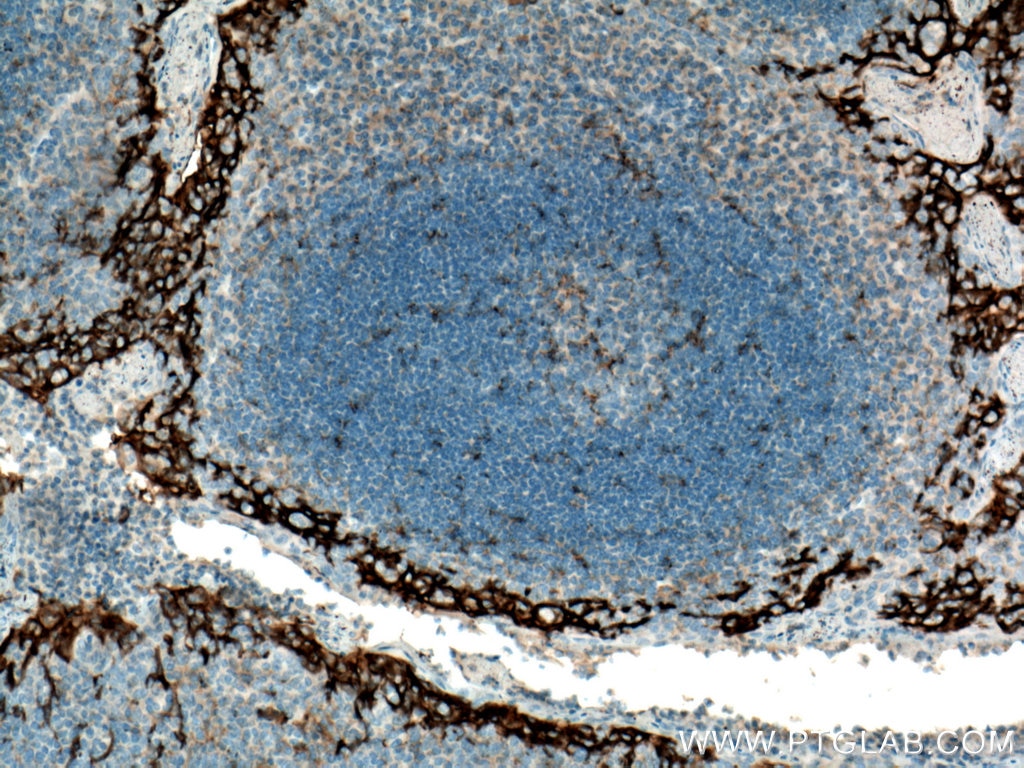
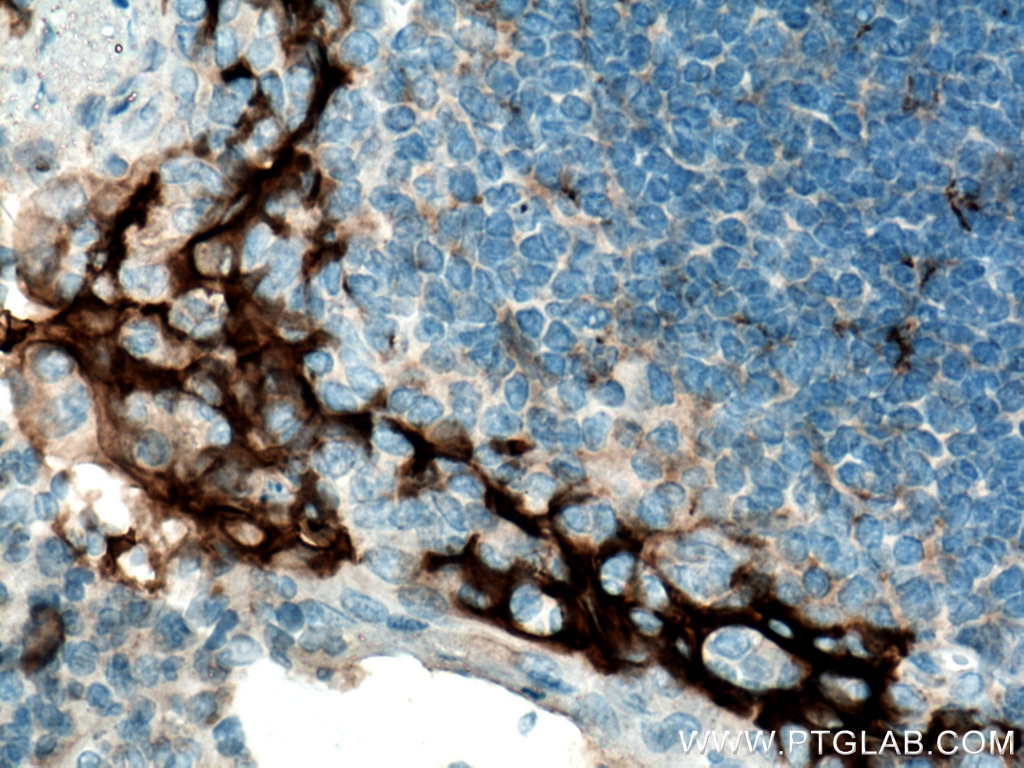
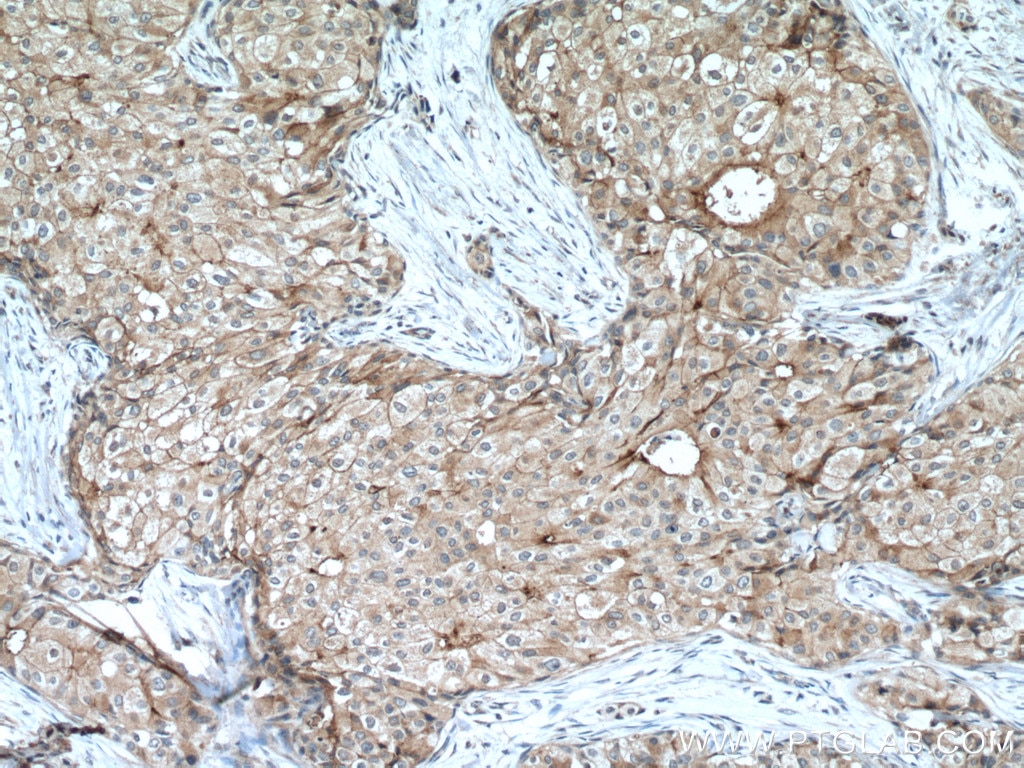
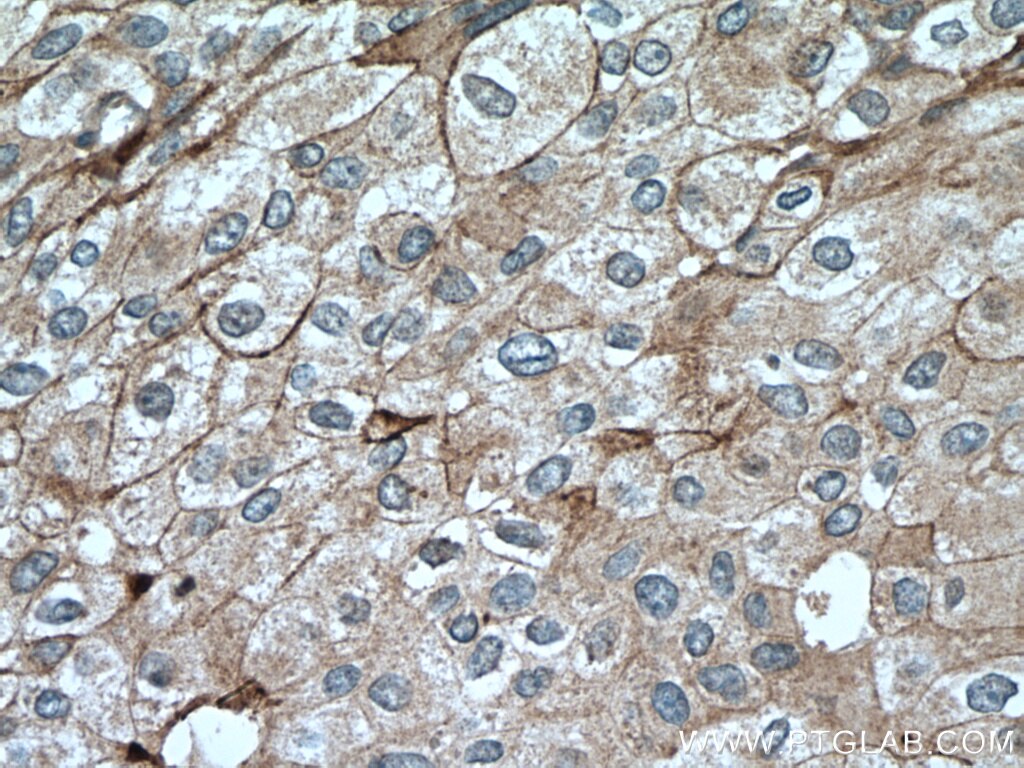
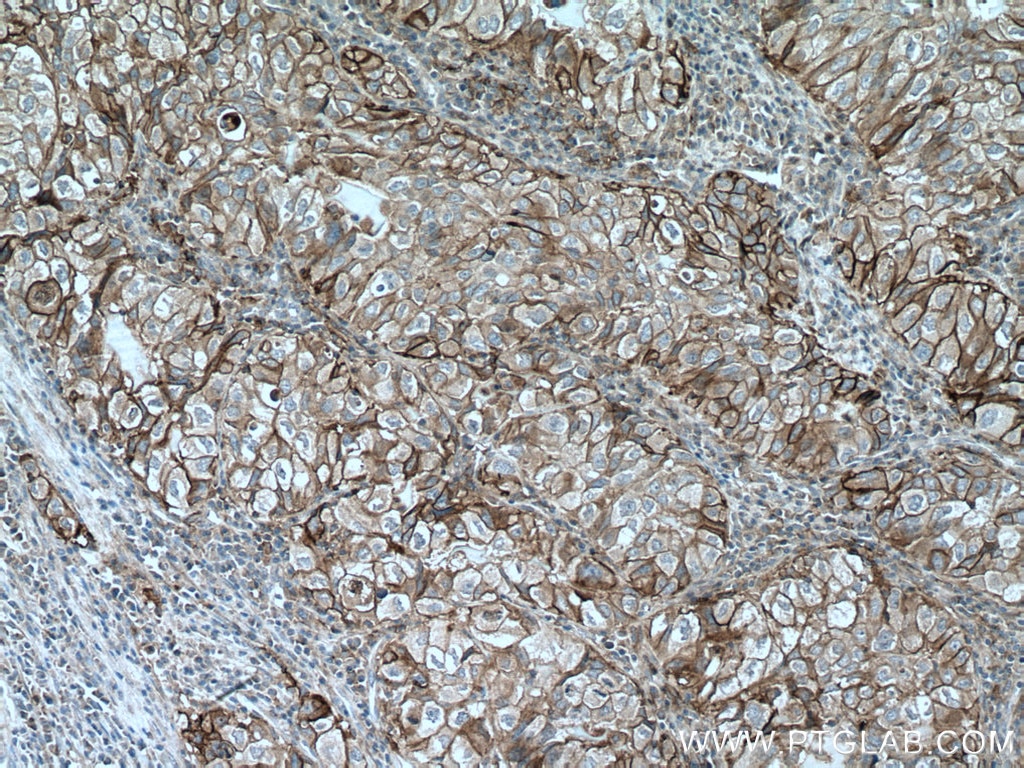
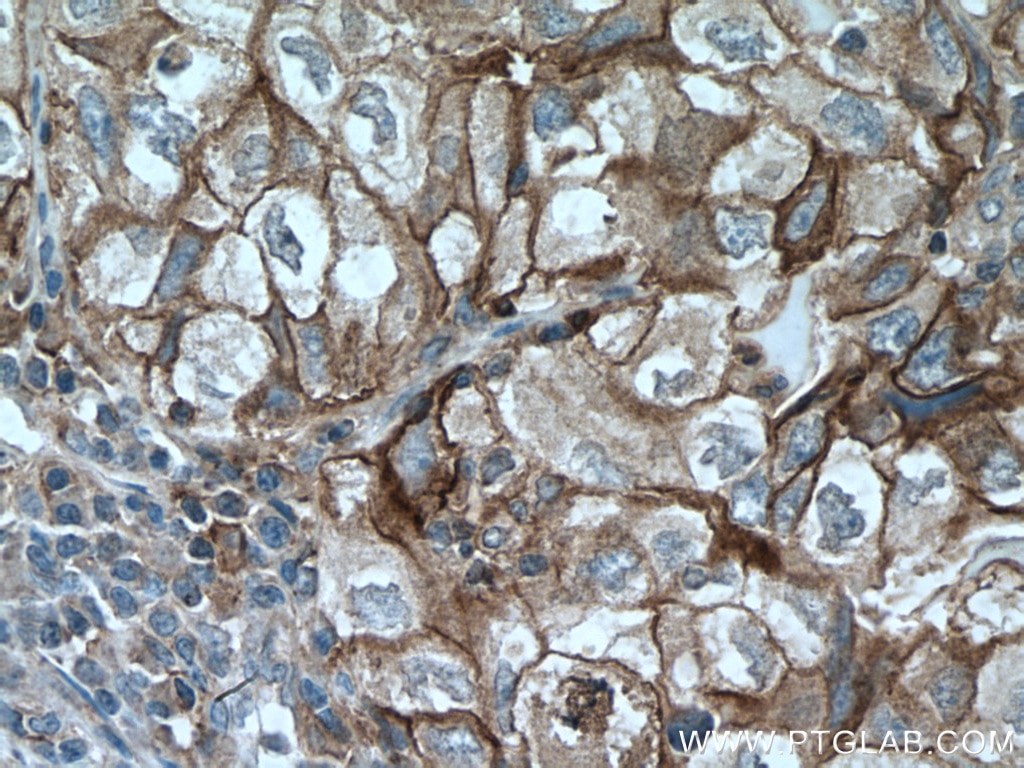
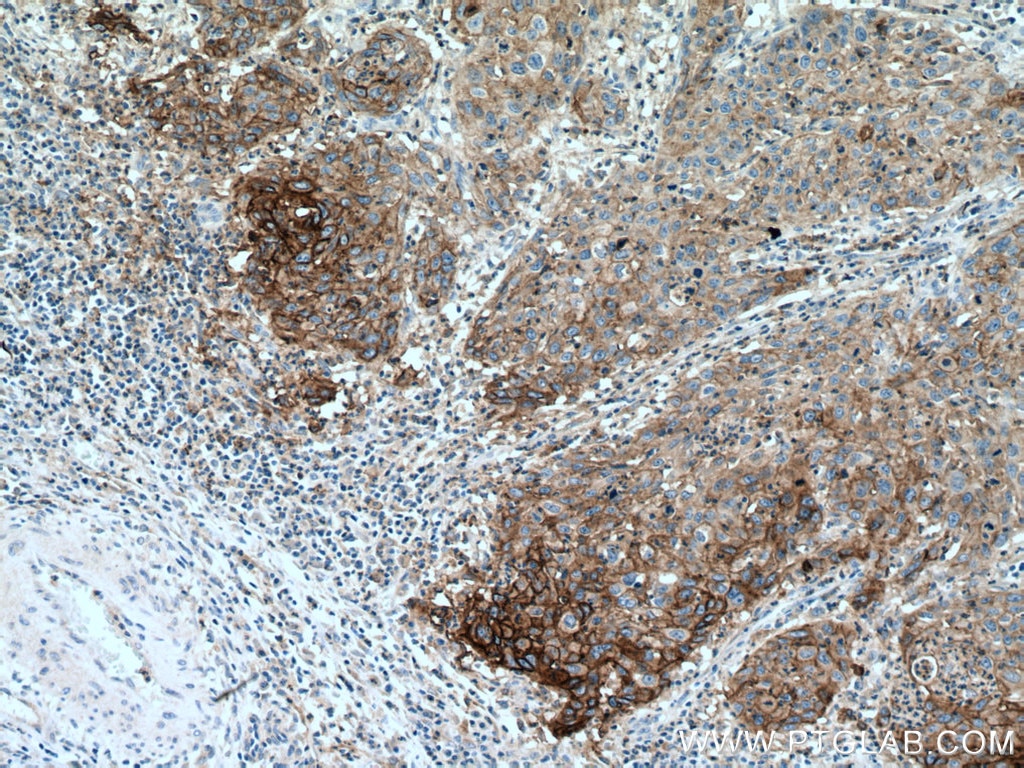
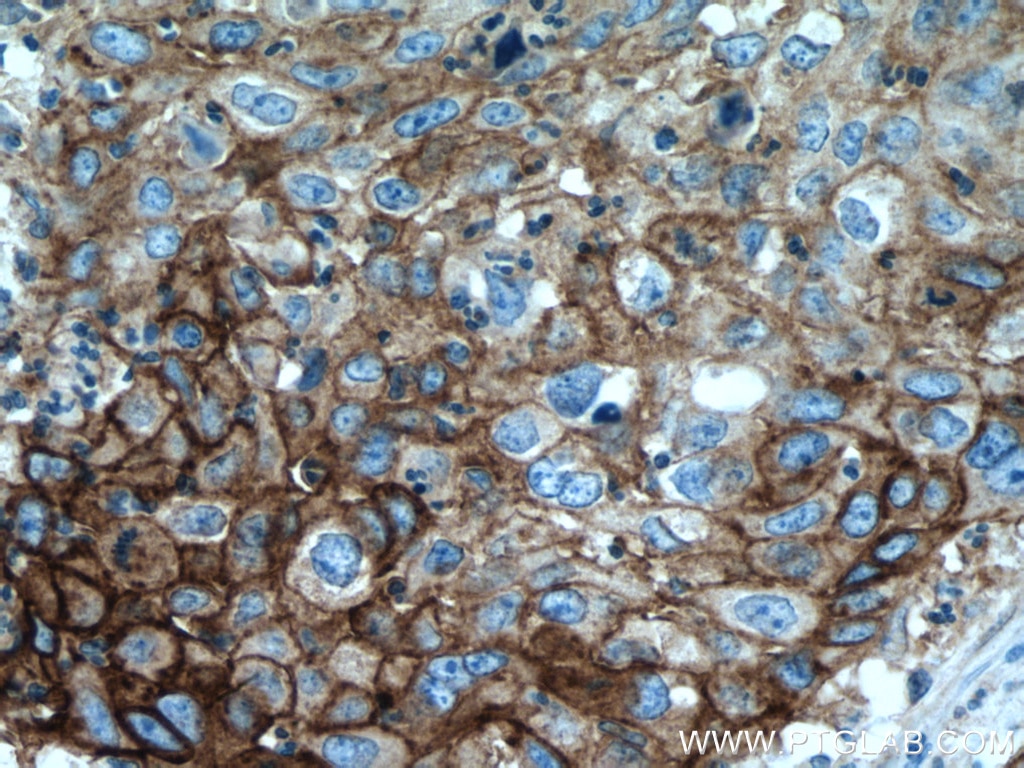
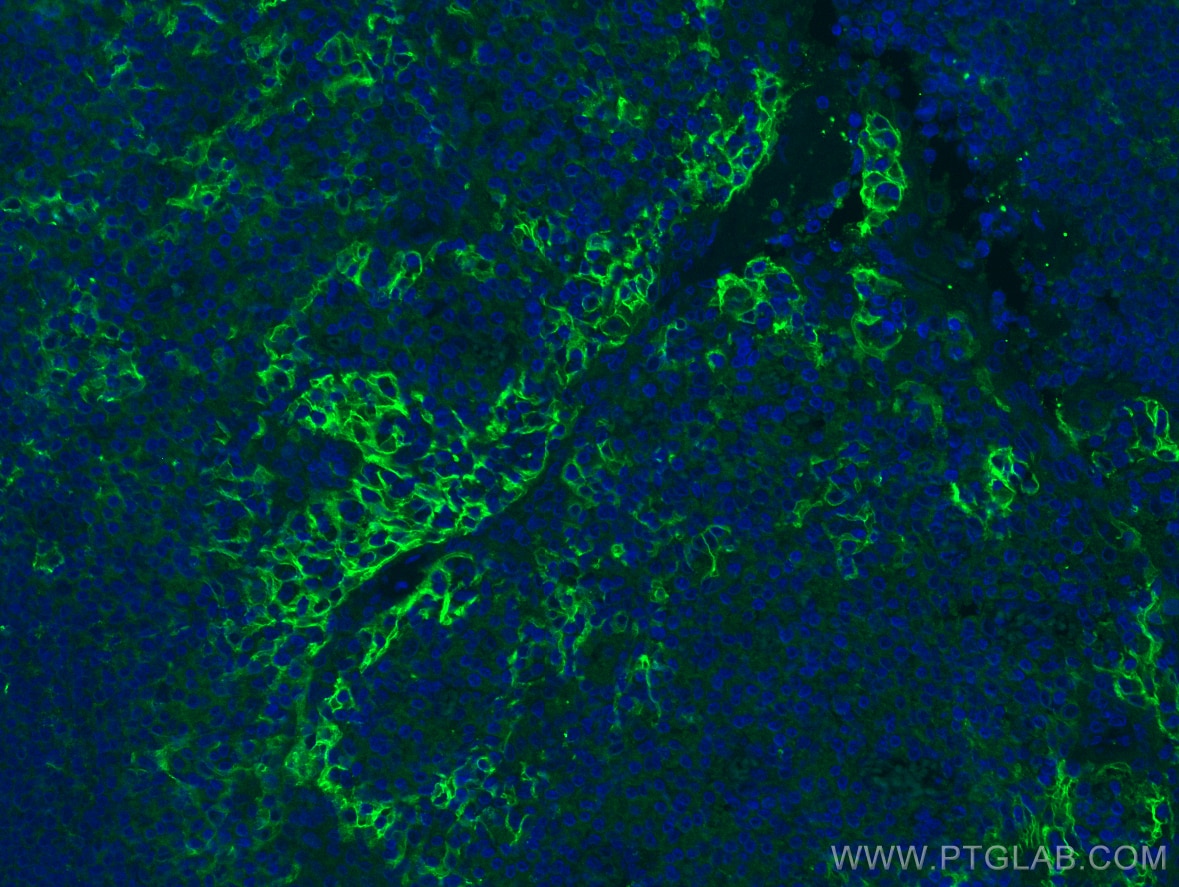
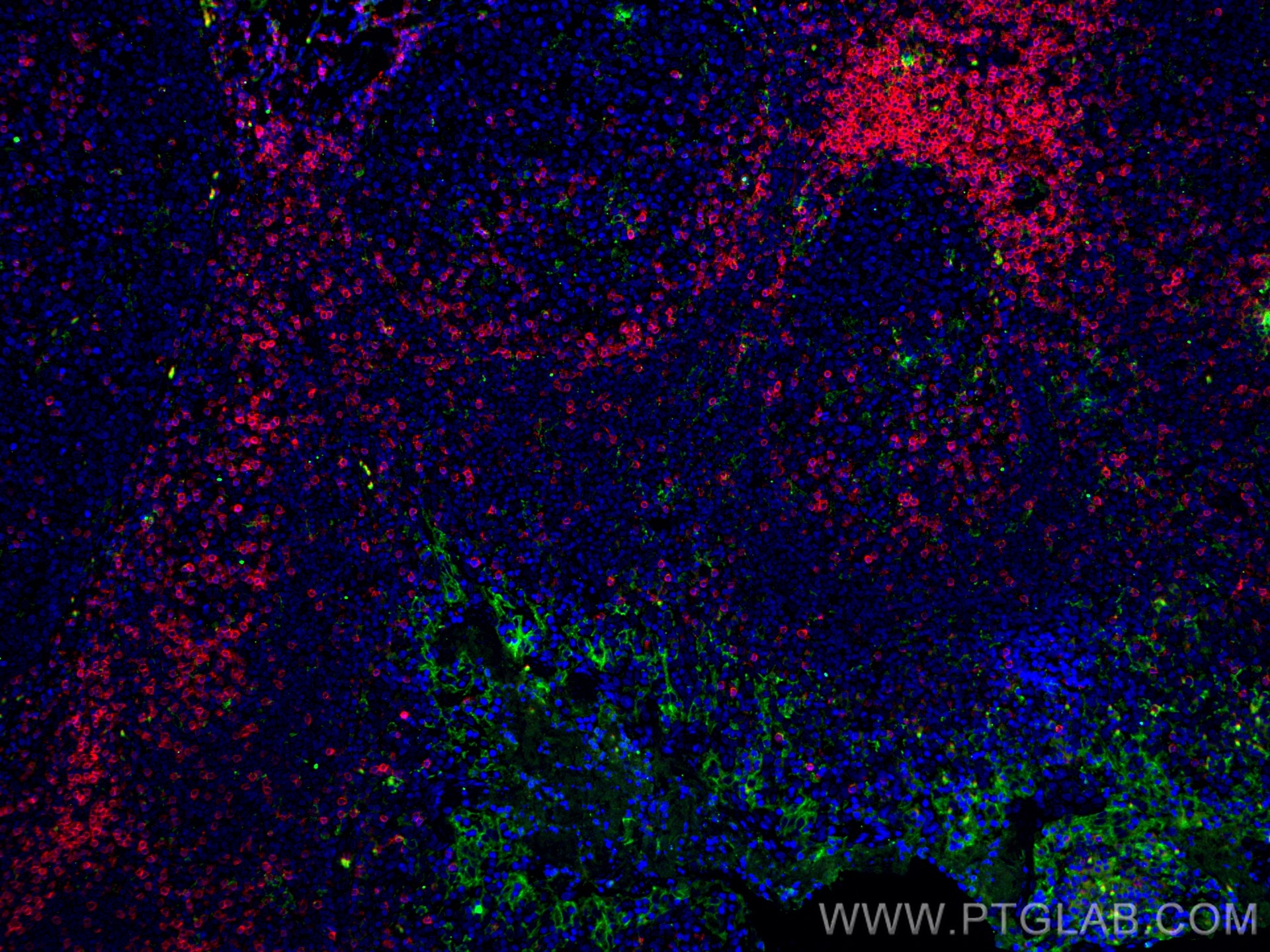
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Tonsillitisgewebe, humanes Mammakarzinomgewebe, humanes Zervixkarzinomgewebe, humanes Lungenkarzinomgewebe, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
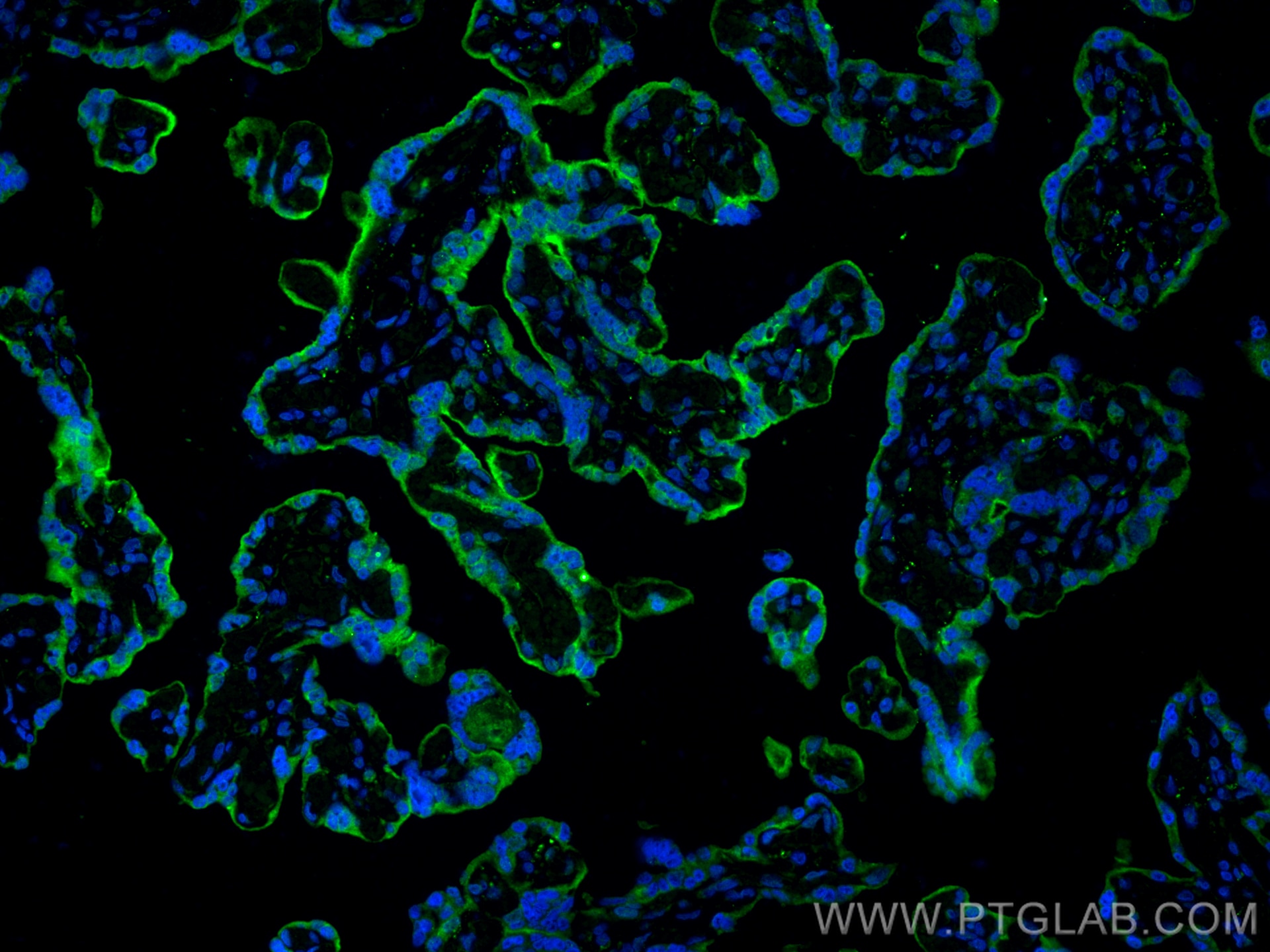
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF-P | humanes Tonsillitisgewebe, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
28076-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) fusion protein Ag27557 |
| Vollständiger Name | CD274 molecule |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 290 aa, 33 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 45-50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC074984 |
| Gene symbol | PD-L1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 29126 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
PD-L1, also known as CD274 or B7H1, stands for programmed cell death ligand 1. It is a type I transmembrane protein that is thought to repress immune responses by binding to its receptor (PD1), thus inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. It contains V-like and C-like immunoglobulin domains. PD-L1 expression is regulated by various cytokines, such as TNF-α or LPS (ISSN: 1848-7718). Increased expression of this protein in certain types of cancers, e.g., renal cell carcinoma or colon cancer, correlates with poor prognosis.
What is the molecular weight of PD-L1?
Depending on the isoform, the calculated molecular weight of the protein varies between 20 and 33 kDa (176-290 aa).
What are the isoforms of PD-L1?
According to NCBI, three different isoforms have been identified. There are significant differences in the untranslated and protein coding regions.
What is the subcellular localization and tissue specificity of PD-L1?
It is predicted to localize in the plasma membrane of various cell types, with a particularly high expression in placental trophoblast and subsets of immune cells. High levels of PD-L1 protein have also been detected in lung and colon tissues.
What is the function of PD-L1 in immune responses?
PD-L1 is critical for the induction and maintenance of immune self-tolerance during infection or inflammation in normal tissues. The interaction of PD-L1 and its receptors is responsible for preventing auto-immune phenotypes and balancing the overall immune response in situations such as pregnancy or tissue allografts. The interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 or B7.1 starts an inhibitory signaling cascade, which results in the decreased proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells and increased survival of regulatory T-cells (PMID: 15240681).
How can PD-L1's implication in cancer be used as a drug target?
In certain tumors, high expression of PD-L1 serves as a stop-sign to inhibit the recognition of cancer cells by T-cells (PMID: 23087408). The interaction between PD-L1 and its receptors (PD1 and B7.1) is a mechanism for the tumor to evade the host immune response (PMID: 29357948). Several mAbs have been developed to target that interaction and thus prevent the inactivation of cytotoxic T-cells by the tumor (PMIDs: 23890059, 18173375).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for PD-L1/CD274 (C-terminal) antibody 28076-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Cancer Targeting PERP promotes anti-tumor immunity in HNSCC by regulating tumor immune microenvironment and metabolic homeostasis | ||
Cell Metab Dual impacts of serine/glycine-free diet in enhancing antitumor immunity and promoting evasion via PD-L1 lactylation | ||
ACS Cent Sci Allosteric Regulation of IGF2BP1 as a Novel Strategy for the Activation of Tumor Immune Microenvironment | ||
Nat Commun A protease-cleavable liposome for co-delivery of anti-PD-L1 and doxorubicin for colon cancer therapy in mice | ||
Cell Rep Med Benzosceptrin C induces lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 and promotes antitumor immunity by targeting DHHC3 | ||
Sci Adv Inhibition of ACLY overcomes cancer immunotherapy resistance via polyunsaturated fatty acids peroxidation and cGAS-STING activation |