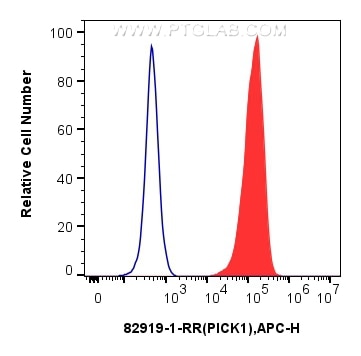
- Featured Product
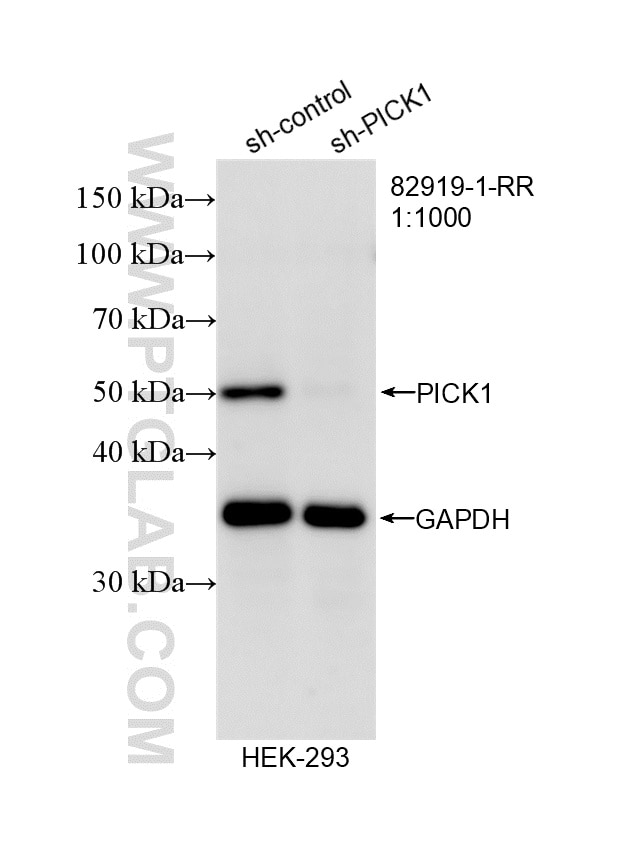
- KD/KO Validated
PICK1 Rekombinanter Antikörper
PICK1 Rekombinant Antikörper für WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
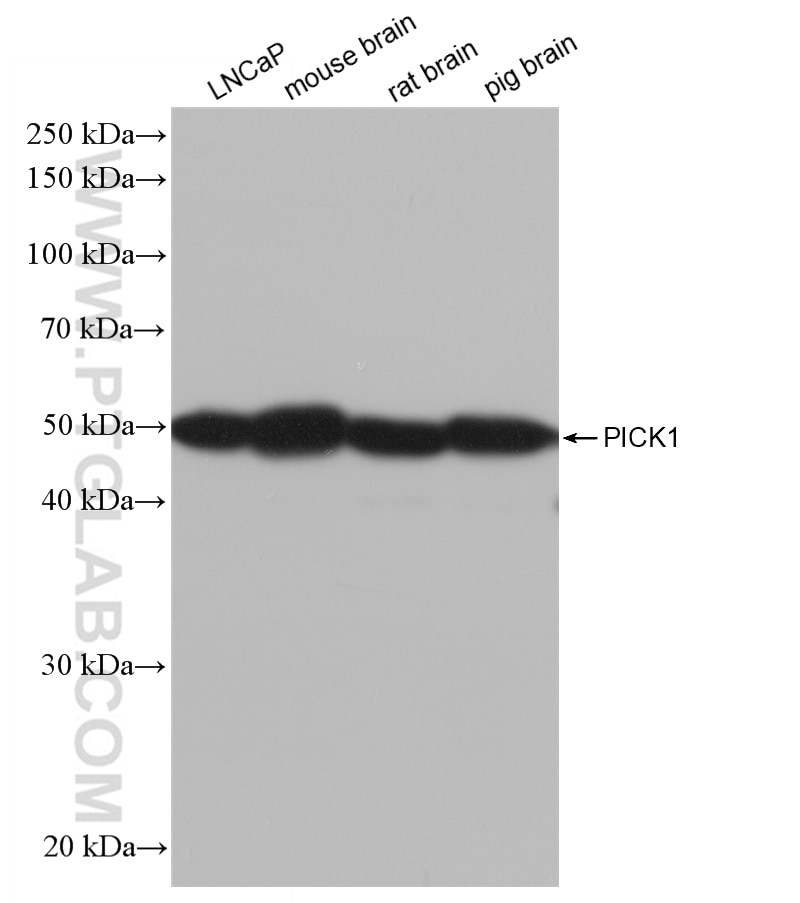
Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
230185B8
Kat-Nr. : 82919-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
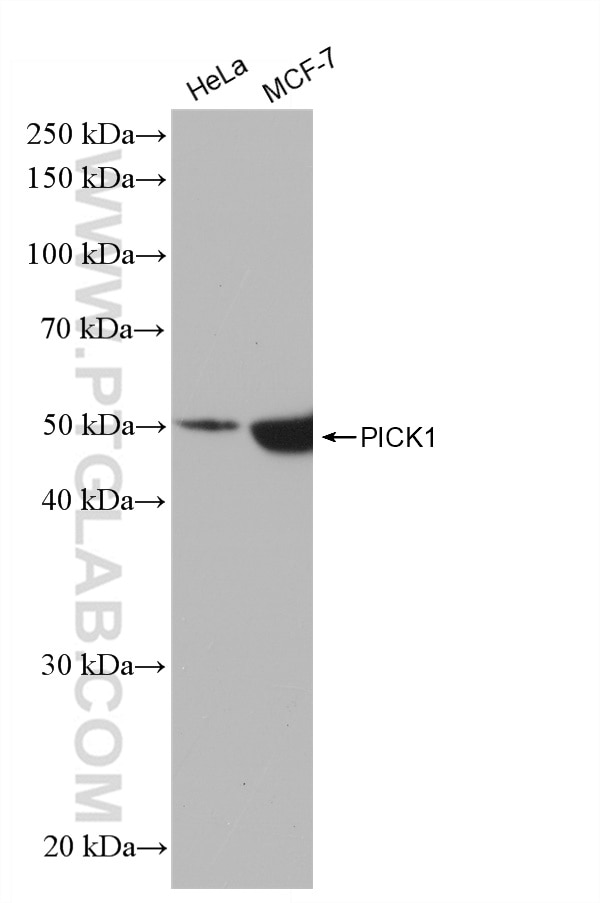
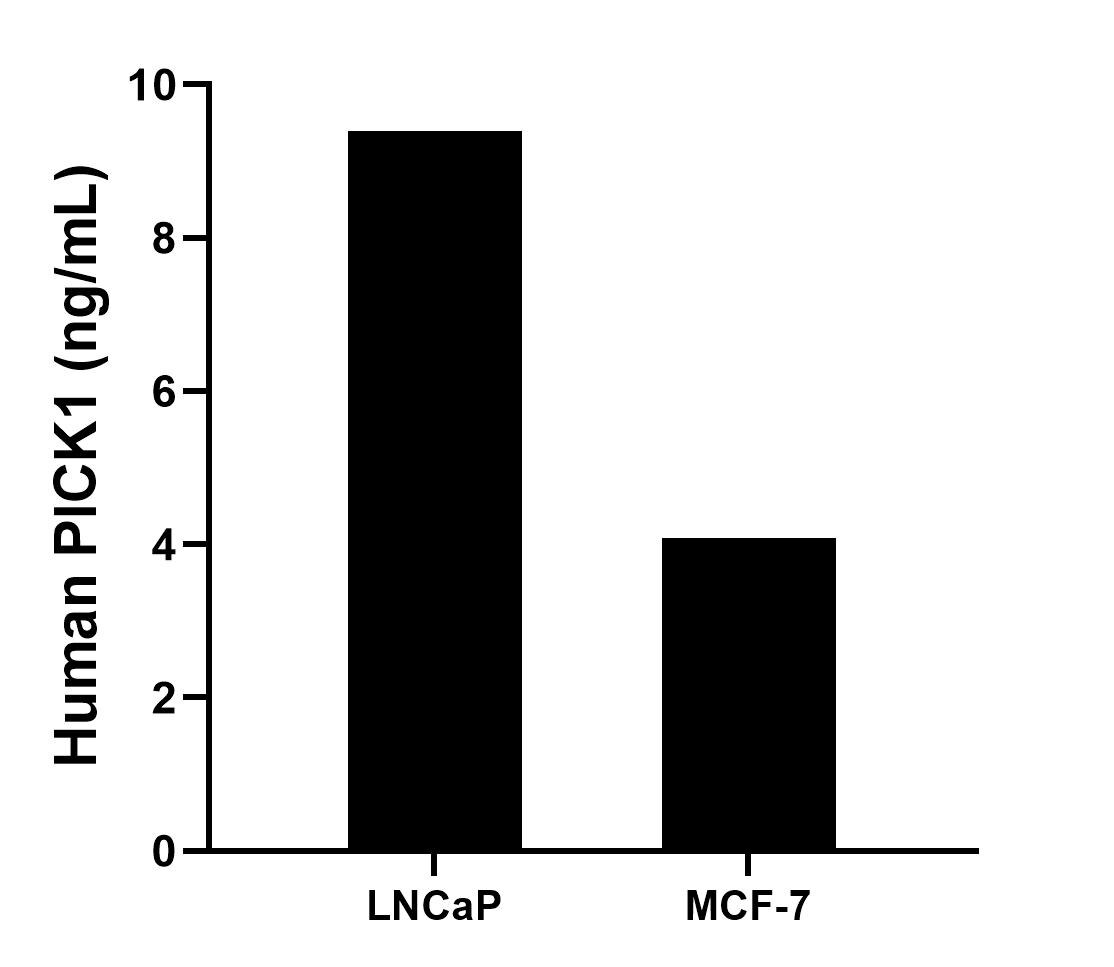
82919-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA PICK1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Rekombinant |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | PICK1 fusion protein Ag1443 |
| Vollständiger Name | protein interacting with PRKCA 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 47 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC017561 |
| Gene symbol | PICK1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9463 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) was first cloned as a PKC-binding partner through yeast two hybrid system. PICK1 acts as a critical regulator of membrane receptors' subcellular trafficking to modulate neural processes such as learning and memory, and is widely expressed in brain, testis, heart, lung, liver, kidney and muscle. It probably binds to and organize the subcellular localization of a variety of membrane proteins containing some PDZ recognition sequence, for instance, PICK1 is a critical mediator of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) trafficking in neural synapses. PICK1 expression on D-serine release and glutamate transport in astrocytes suggests a potential implication of PICK1 in the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). PICK1 may also participate in breast cancer development through inhibition of TGF-β signaling.