PSMG1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
PSMG1 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10335-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
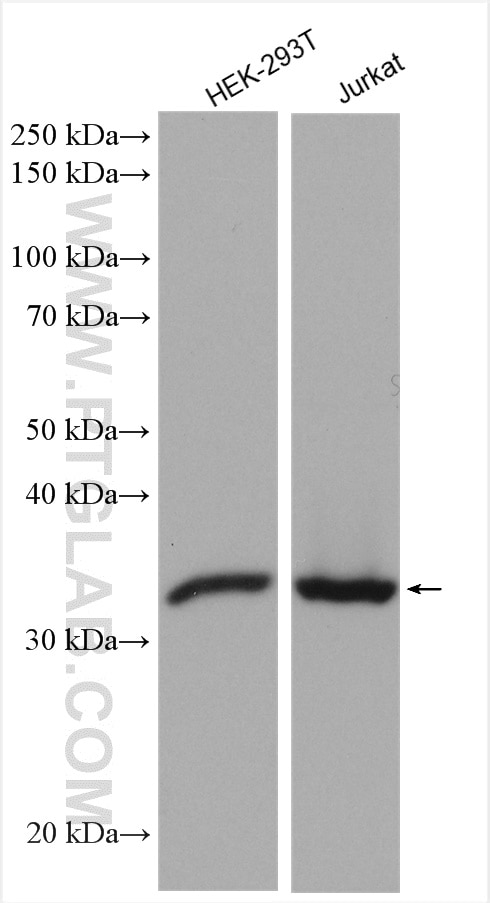
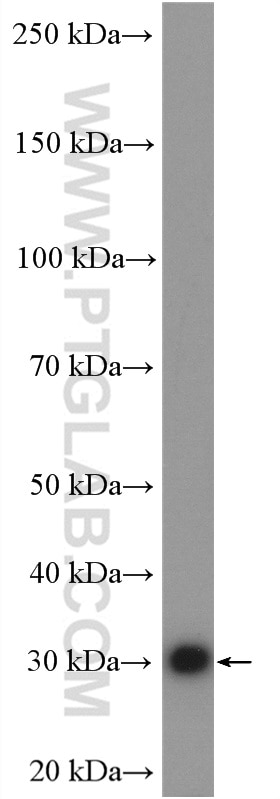
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HEK-293T-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen, Jurkat-Zellen |
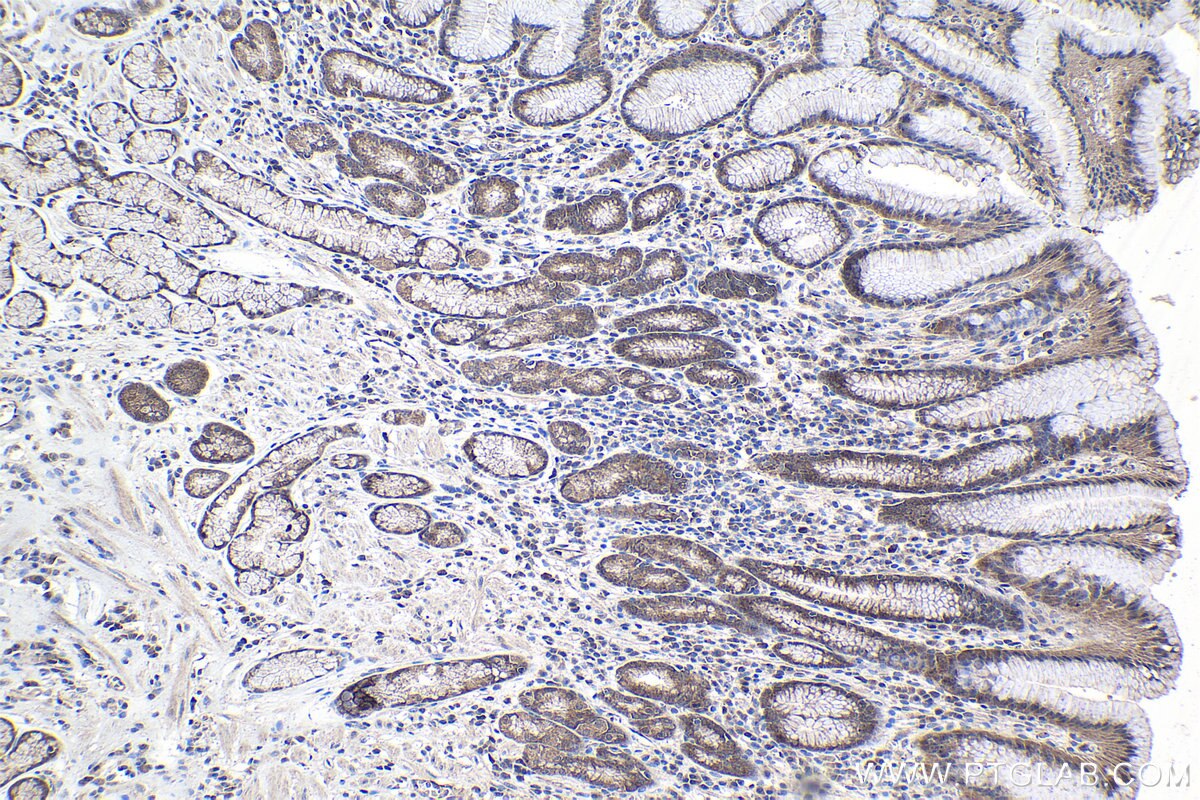
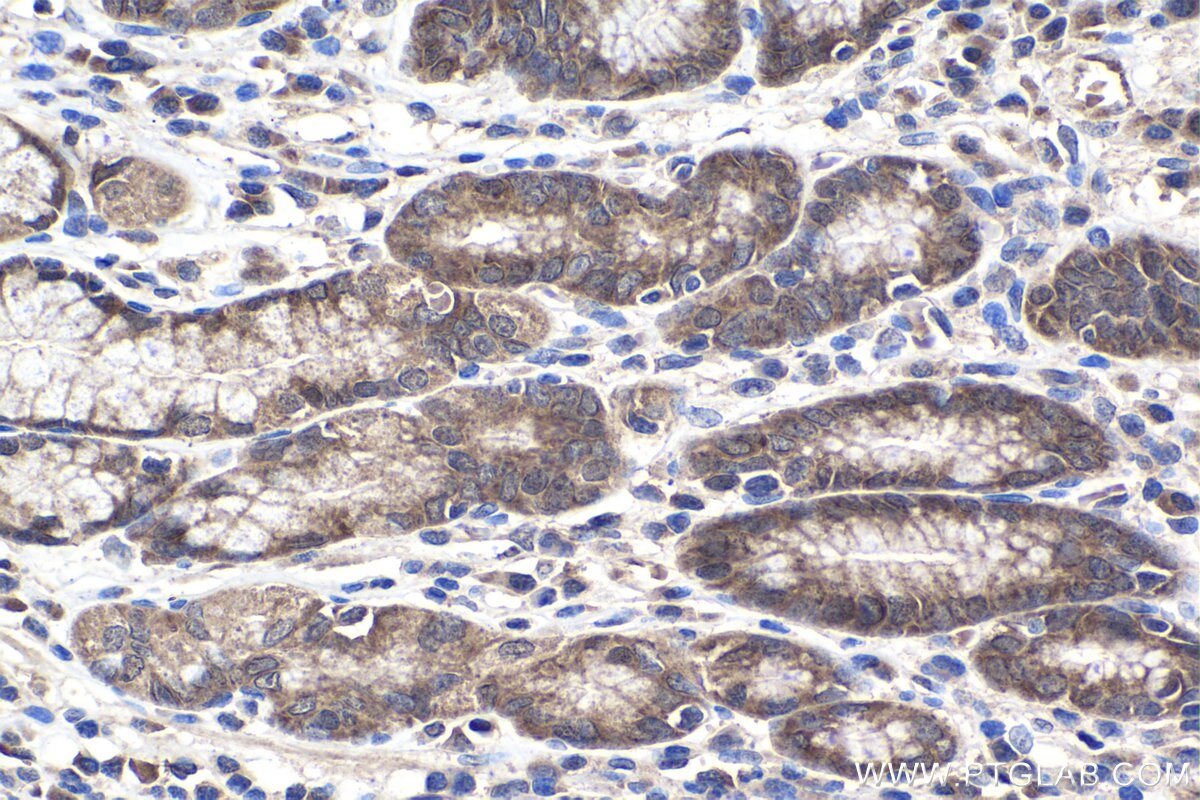
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Magenkrebsgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
10335-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, ELISA PSMG1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | PSMG1 fusion protein Ag0303 |
| Vollständiger Name | proteasome (prosome, macropain) assembly chaperone 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 288 aa, 33 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 30-33 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC003619 |
| Gene symbol | PSMG1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8624 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PSMG1 antibody 10335-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for PSMG1 antibody 10335-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Stem Cell Res Ther Melatonin induces the rejuvenation of long-term ex vivo expanded periodontal ligament stem cells by modulating the autophagic process. | ||
Oncol Rep Association of p53/p21 expression and cigarette smoking with tumor progression and poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. | ||
iScience Elabela inhibits TRAF1/NF-κB induced oxidative DNA damage to promote diabetic foot ulcer wound healing |