Polyglutamine Monoklonaler Antikörper
Polyglutamine Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2b, kappa
Getestete Reaktivität
n/a
Anwendung
WB, ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
MW1
Kat-Nr. : 65239-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
65239-1-PBS bindet in WB, ELISA, Indirect ELISA Polyglutamine und zeigt Reaktivität mit n/a
| Getestete Reaktivität | n/a |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2b, kappa |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Rekombinantes Protein |
| Vollständiger Name | Polyglutamine |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | N/A |
| Gene symbol | |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
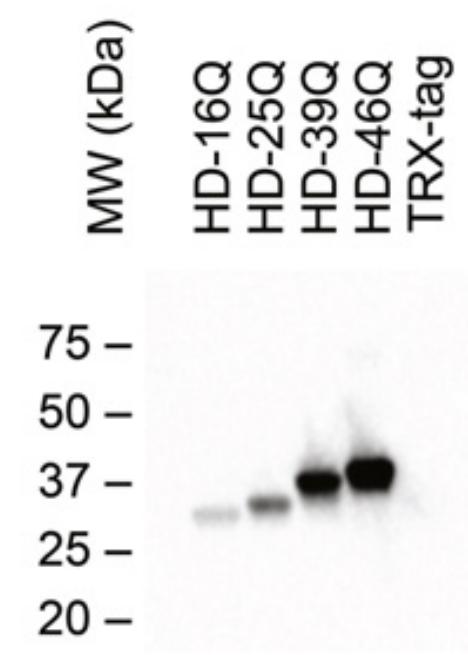
Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the expansion of a polyglutamine (polyQ) repeat in the N-terminal portion of huntingtin protein to a length above 35-40 units (PMID: 26047735; 19507258). The mutational expansion of polyglutamine above a critical length causes a toxic gain of function in huntingtin and results in neuronal death. In the course of the disease, expanded huntingtin is proteolyzed, becomes abnormally folded, and accumulates in oligomers, fibrils, and microscopic inclusions (PMID: 25336039). The anti-polyglutamine (polyQ) antibody MW1 specifically binds the polyQ domain of huntingtin exon 1. On western blot, the MW1 clone strongly prefers to bind to the expanded polyQ repeat form of Htt, displaying no detectable binding to normal huntingtin (PMID: 11719267).