TNFSF11/RANKL Polyklonaler Antikörper
TNFSF11/RANKL Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human und mehr (2)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 23408-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
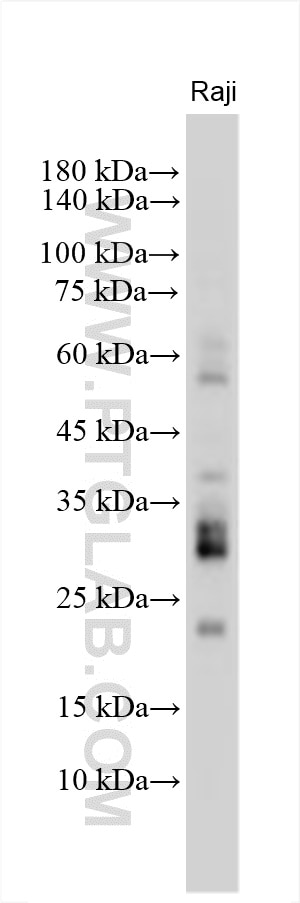
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Raji-Zellen |
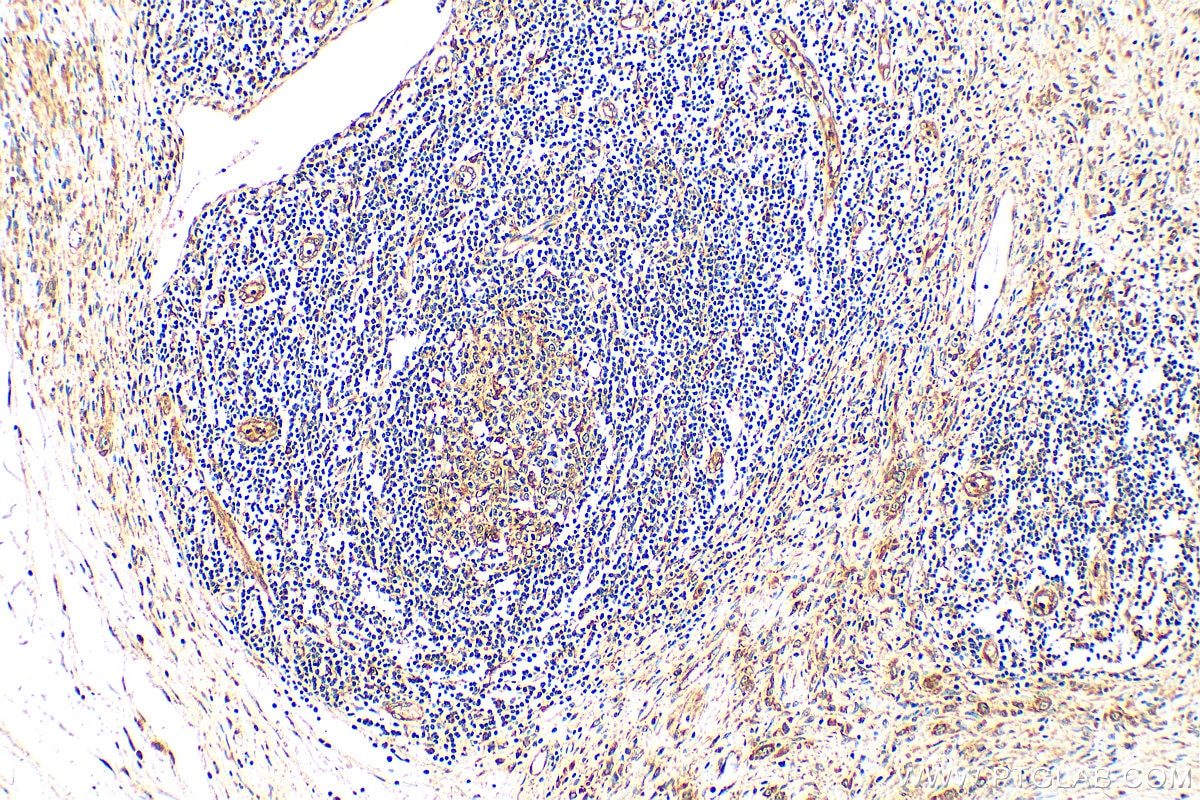
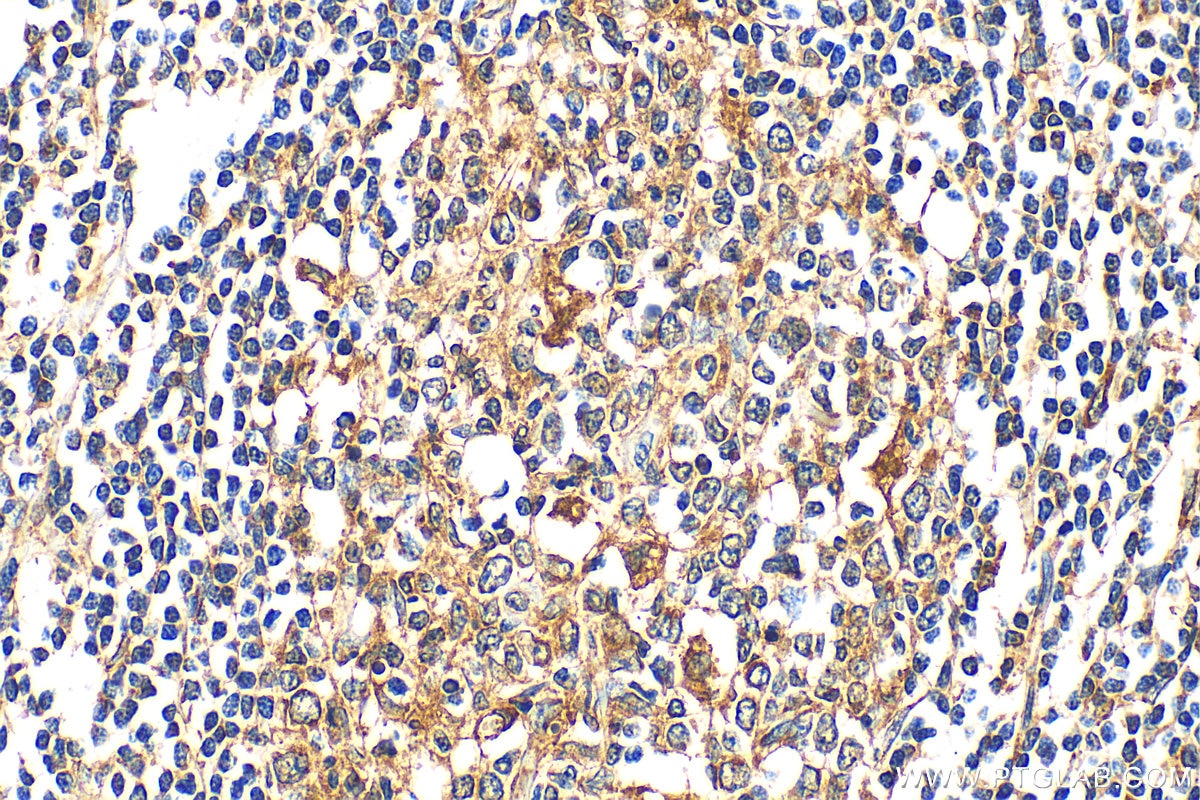
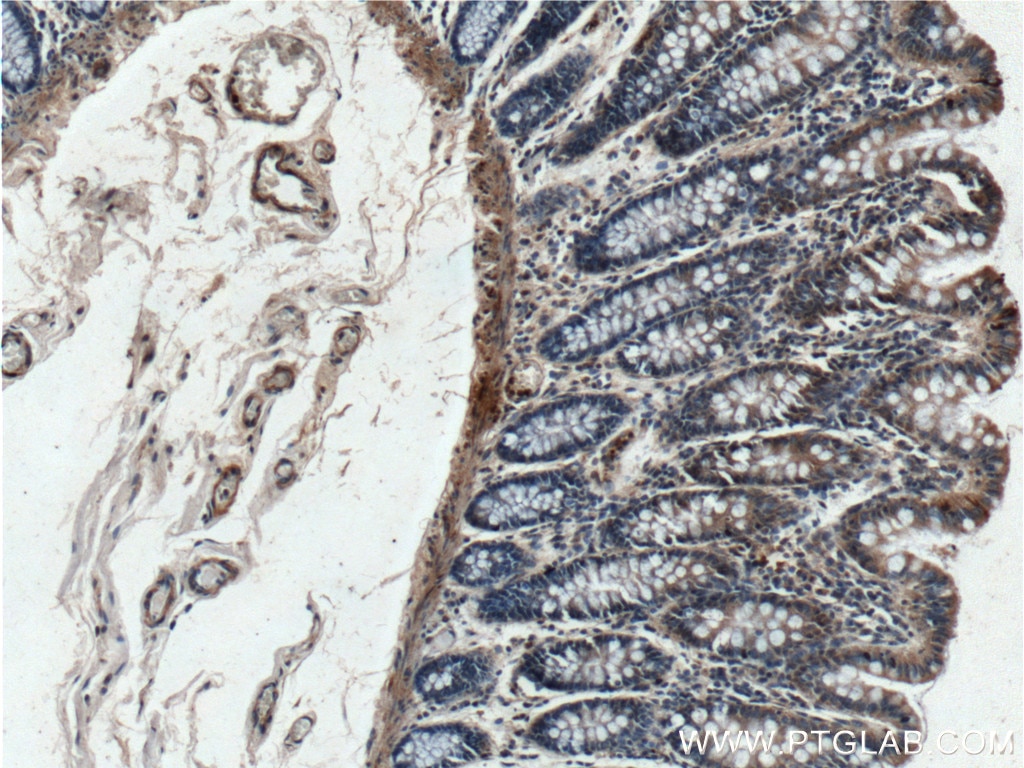
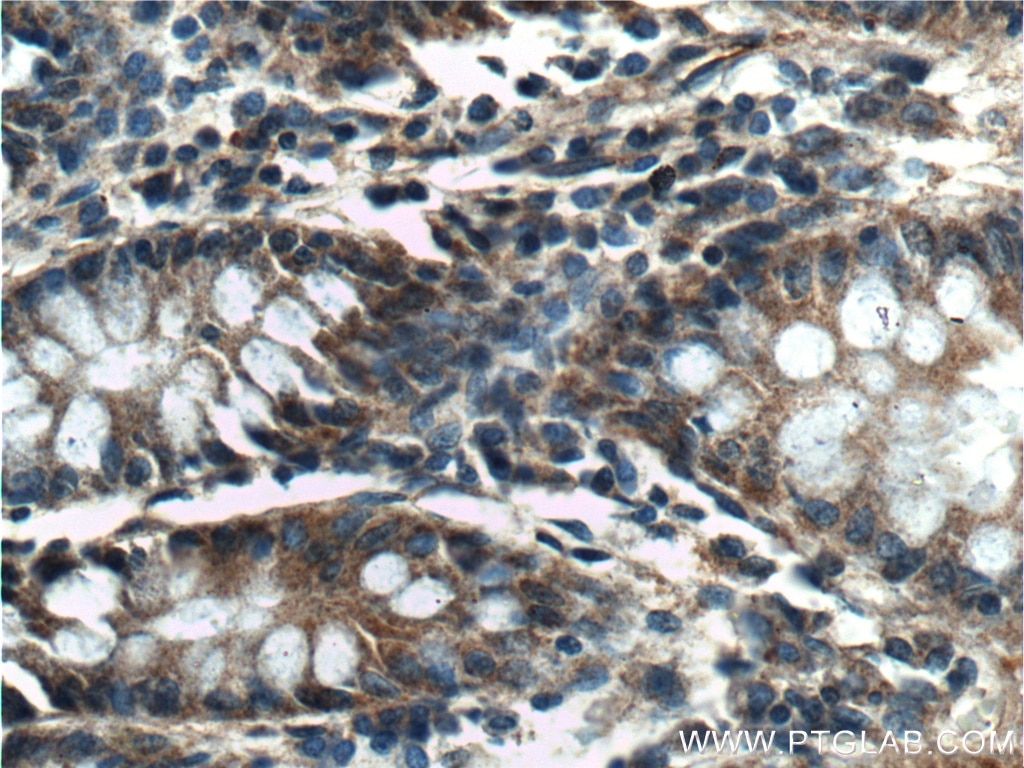
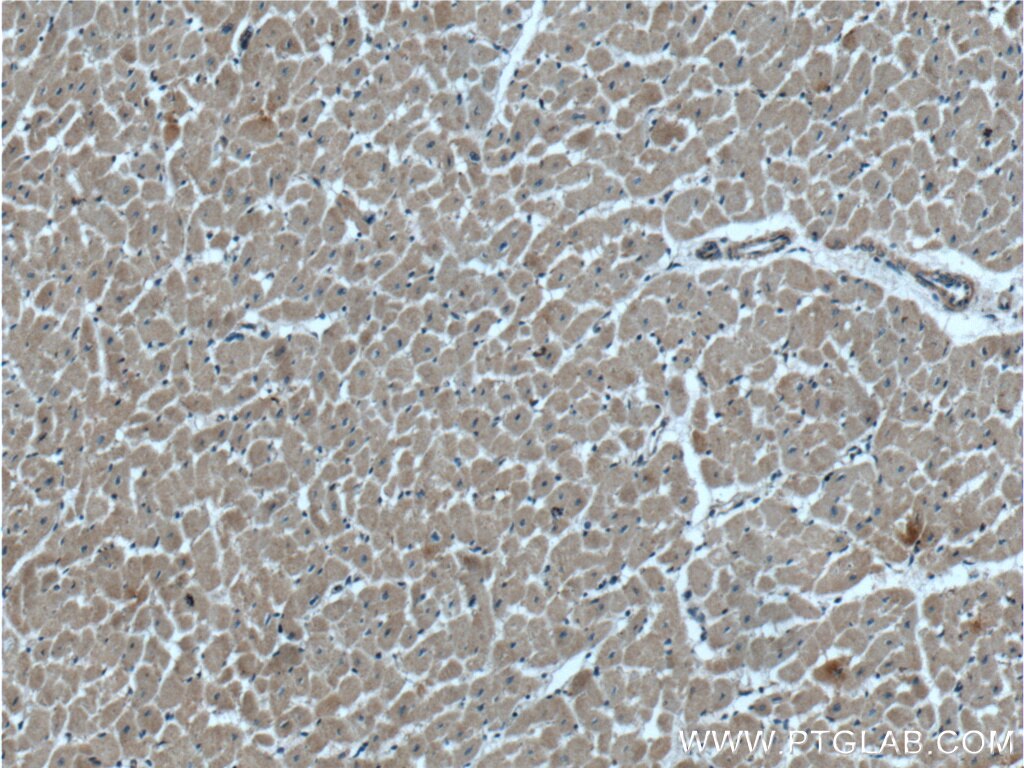
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Magenkrebsgewebe, humanes Kolongewebe, humanes Herzgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 48 publications below |
| IHC | See 25 publications below |
| IF | See 10 publications below |
Produktinformation
23408-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA TNFSF11/RANKL und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | TNFSF11/RANKL fusion protein Ag19975 |
| Vollständiger Name | tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 317 aa, 35 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 20-30 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC074890 |
| Gene symbol | RANKL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8600 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
TNFSF11 also known as RANKL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. RANKL is a polypeptide of 217 amino acids that exerts its biological activity both in a transmembrane form of about 40-45 kDa and in soluble one of 31 kDa (PMID: 15308315). The membrane-bound RANKL (mRANKL) is cleaved into a sRANKL by the metalloprotease-disintegrin TNF-alpha convertase (TACE) or a related metalloprotease (MP). RANKL induces osteoclast formation through its receptor, RANK, which transduces signals by recruiting adaptor molecules, such as the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of proteins. RANKL was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. RANKL was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for TNFSF11/RANKL antibody 23408-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for TNFSF11/RANKL antibody 23408-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Extracell Vesicles Exosomes derived from osteogenic tumor activate osteoclast differentiation and concurrently inhibit osteogenesis by transferring COL1A1-targeting miRNA-92a-1-5p. | ||
Aging Cell Pyrroloquinoline quinone alleviates natural aging-related osteoporosis via a novel MCM3-Keap1-Nrf2 axis-mediated stress response and Fbn1 upregulation | ||
J Control Release Sialic acid-modified chitosan oligosaccharide-based biphasic calcium phosphate promote synergetic bone formation in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. | ||
Antioxid Redox Signal Titanium Particles Activate Osteocytic Connexin 43 to Induce Oxidative Stress and Osteoclastogenesis Through the JAK-STAT Pathway | ||
Aging (Albany NY) Increased expression of osteopontin in subchondral bone promotes bone turnover and remodeling, and accelerates the progression of OA in a mouse model. |