- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
TNFSF11/RANKL Monoklonaler Antikörper
TNFSF11/RANKL Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IF/ICC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IF/ICC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
3F2E1
Kat-Nr. : 66610-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
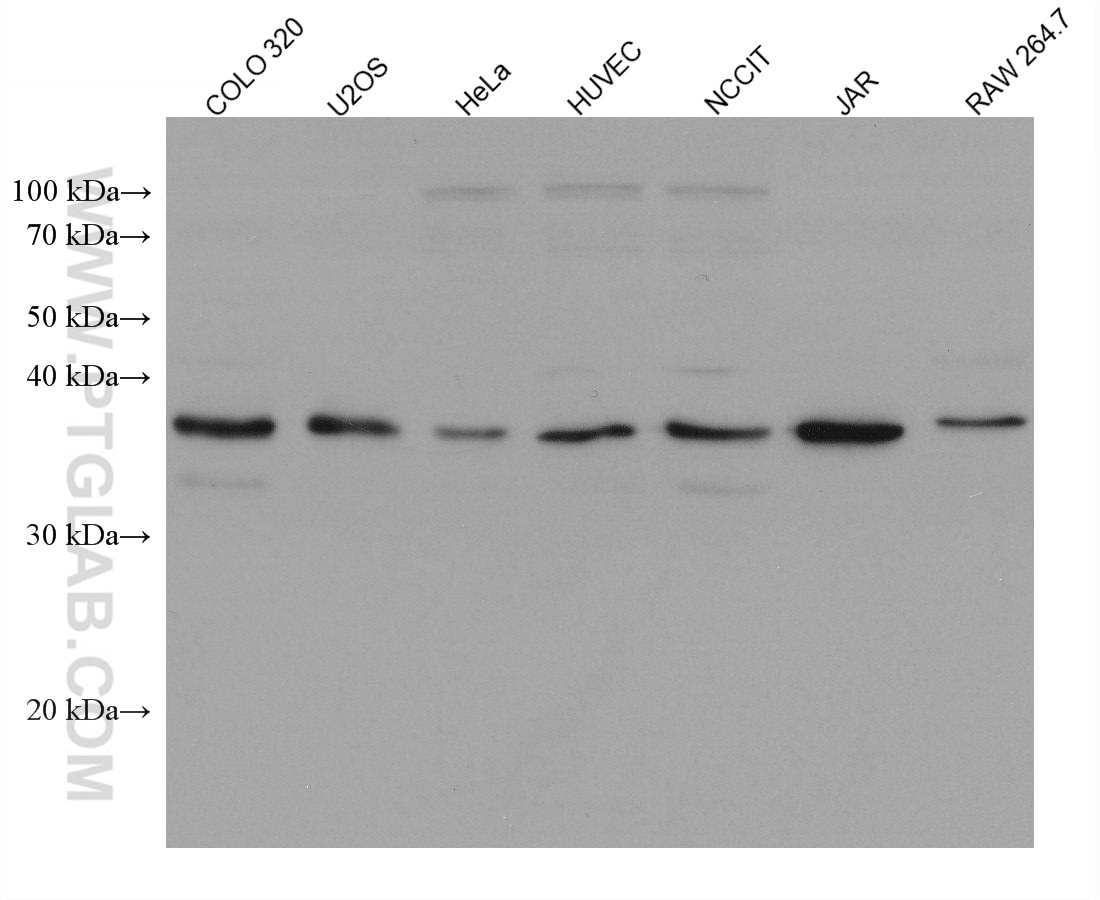
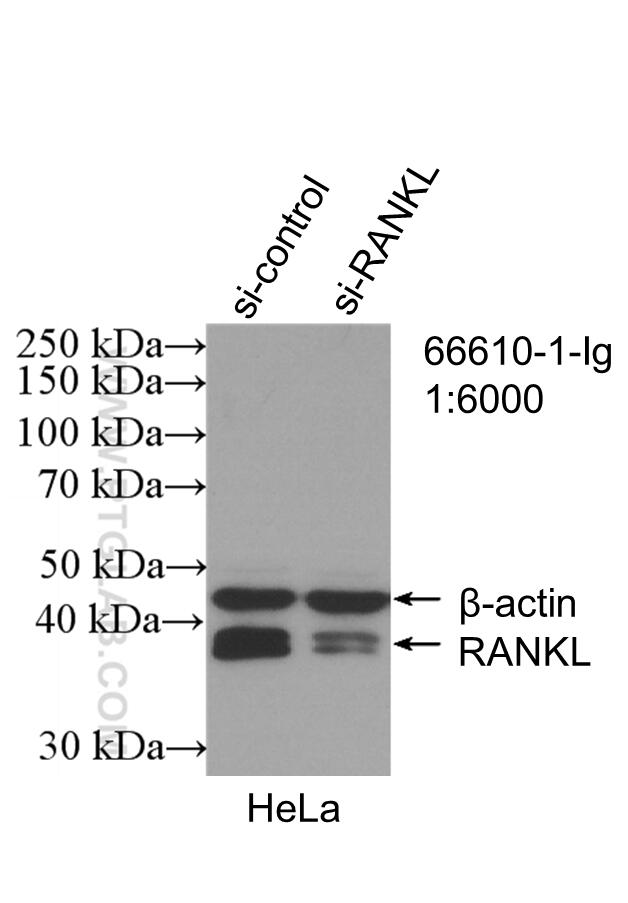
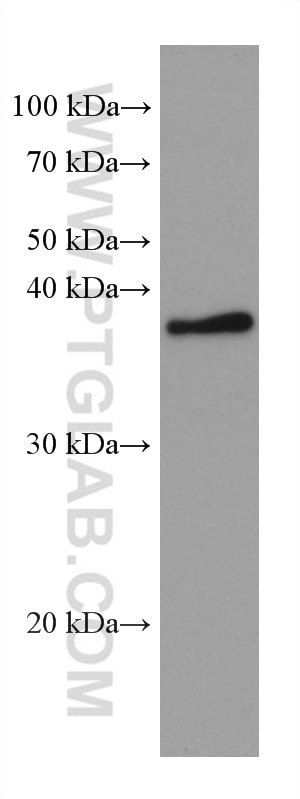
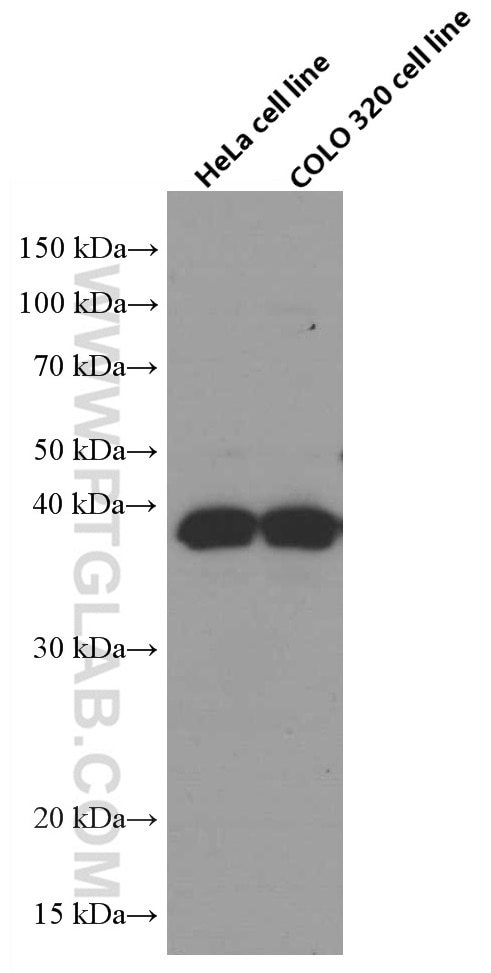
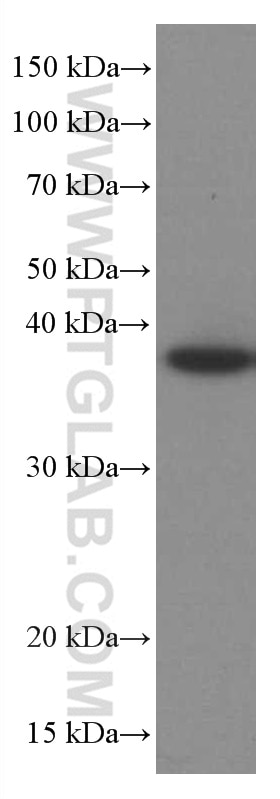
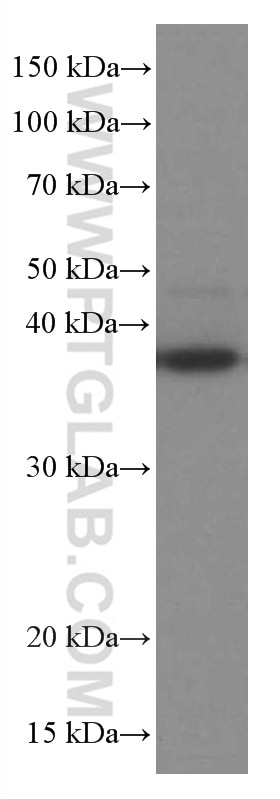
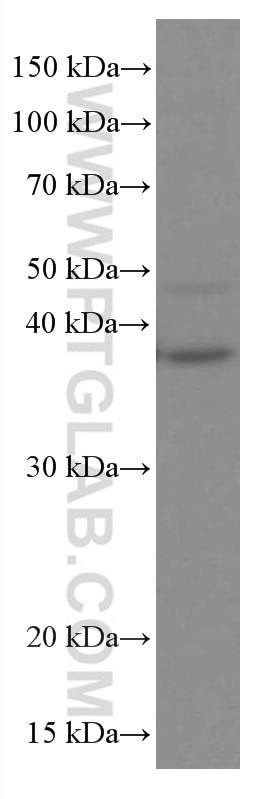
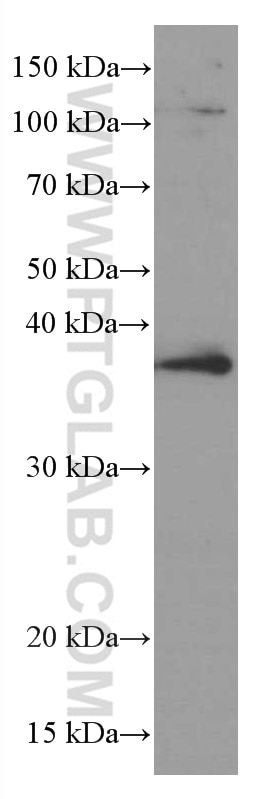
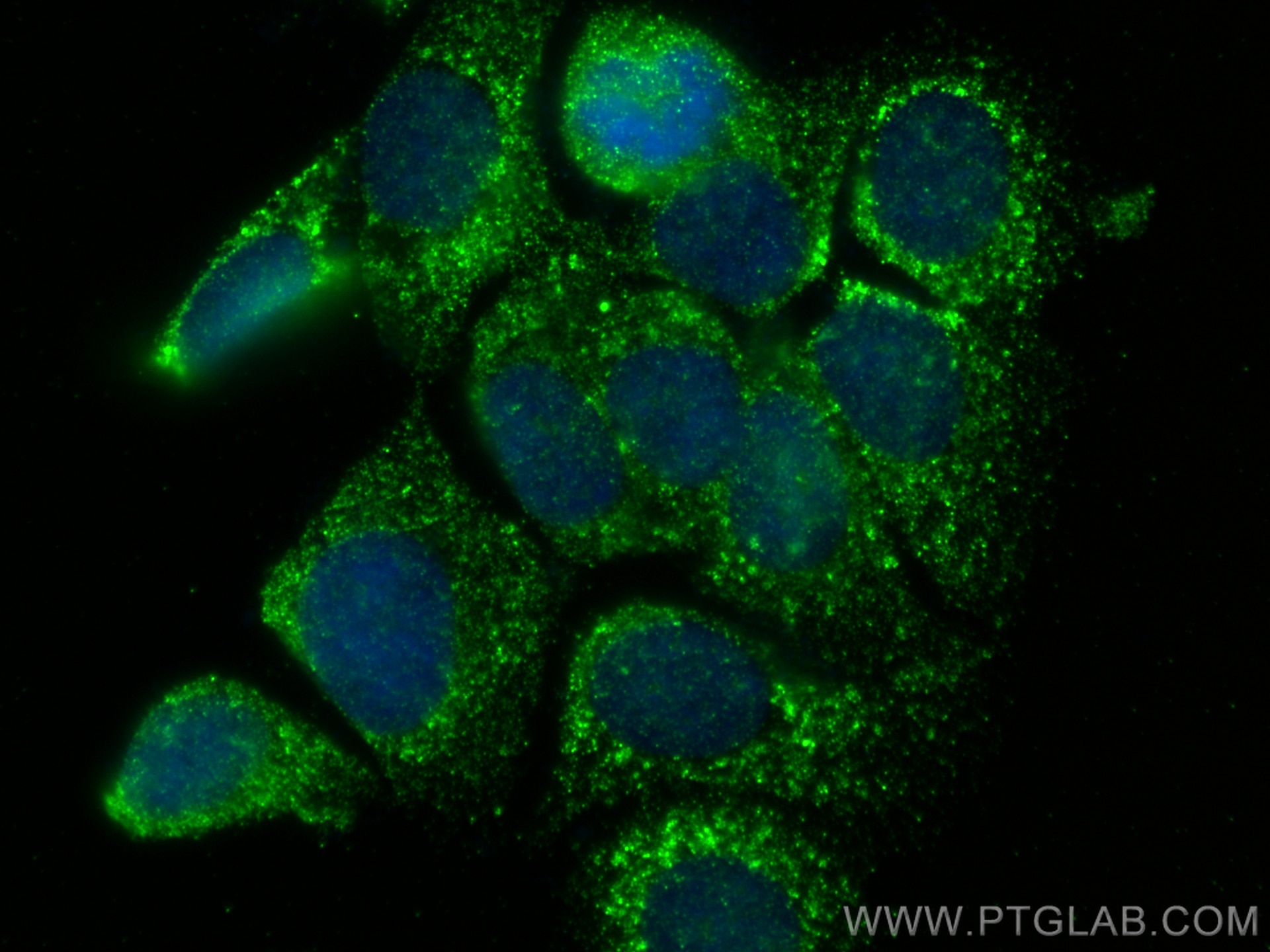
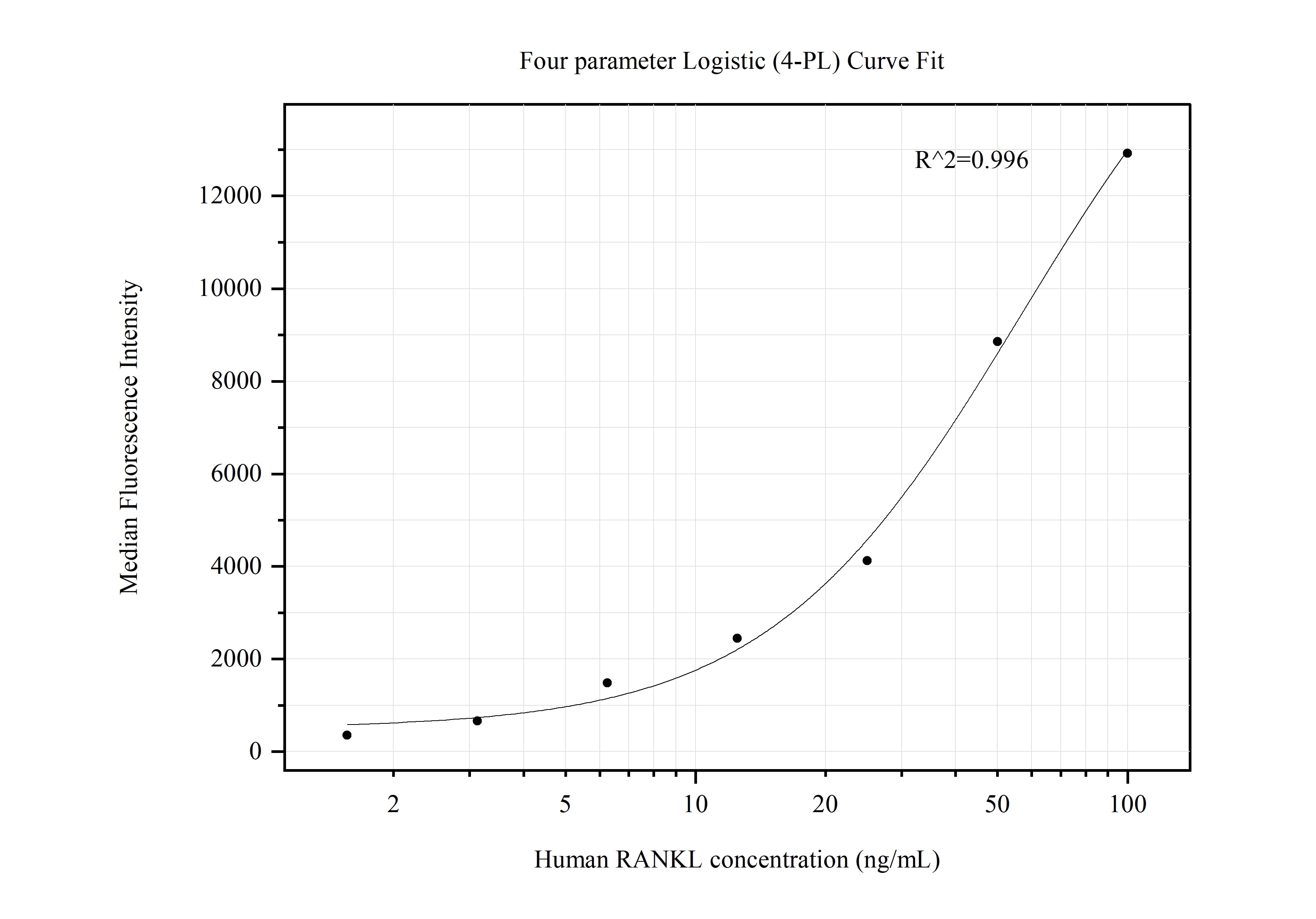
66610-1-PBS bindet in WB, IF/ICC, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA TNFSF11/RANKL und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | TNFSF11/RANKL fusion protein Ag19975 |
| Vollständiger Name | tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 317 aa, 35 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 35-38 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC074890 |
| Gene symbol | RANKL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8600 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
TNFSF11 also known as RANKL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. RANKL is a polypeptide of 217 amino acids that exerts its biological activity both in a transmembrane form of about 40-45 kDa and in soluble one of 31 kDa (PMID: 15308315). The membrane-bound RANKL (mRANKL) is cleaved into a sRANKL by the metalloprotease-disintegrin TNF-alpha convertase (TACE) or a related metalloprotease (MP). RANKL induces osteoclast formation through its receptor, RANK, which transduces signals by recruiting adaptor molecules, such as the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of proteins. RANKL was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. RANKL was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis.