RBP4 Rekombinanter Antikörper
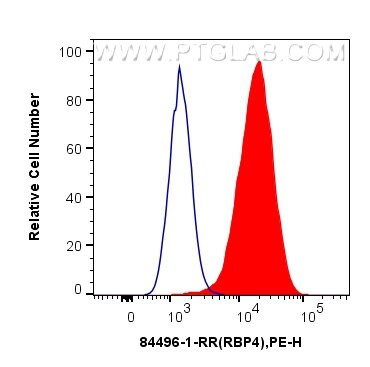
RBP4 Rekombinant Antikörper für WB, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA, Sample test
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA, Sample test
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
241944B3
Kat-Nr. : 84496-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
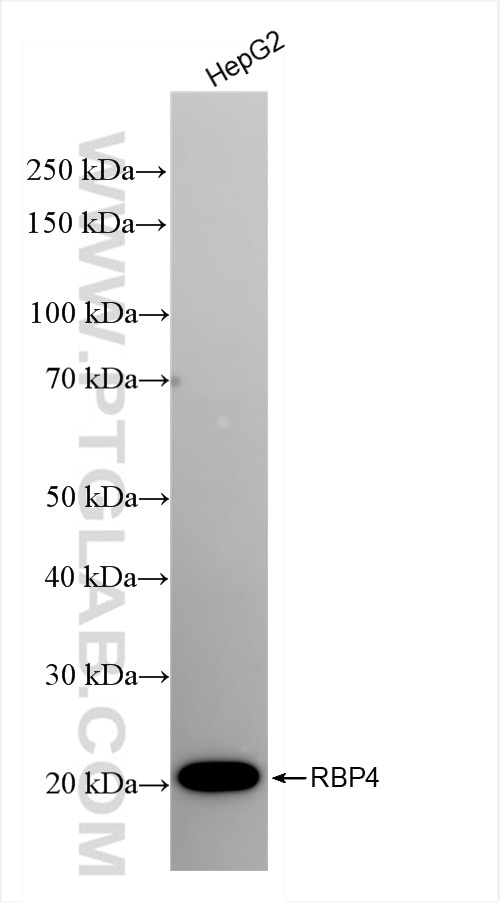
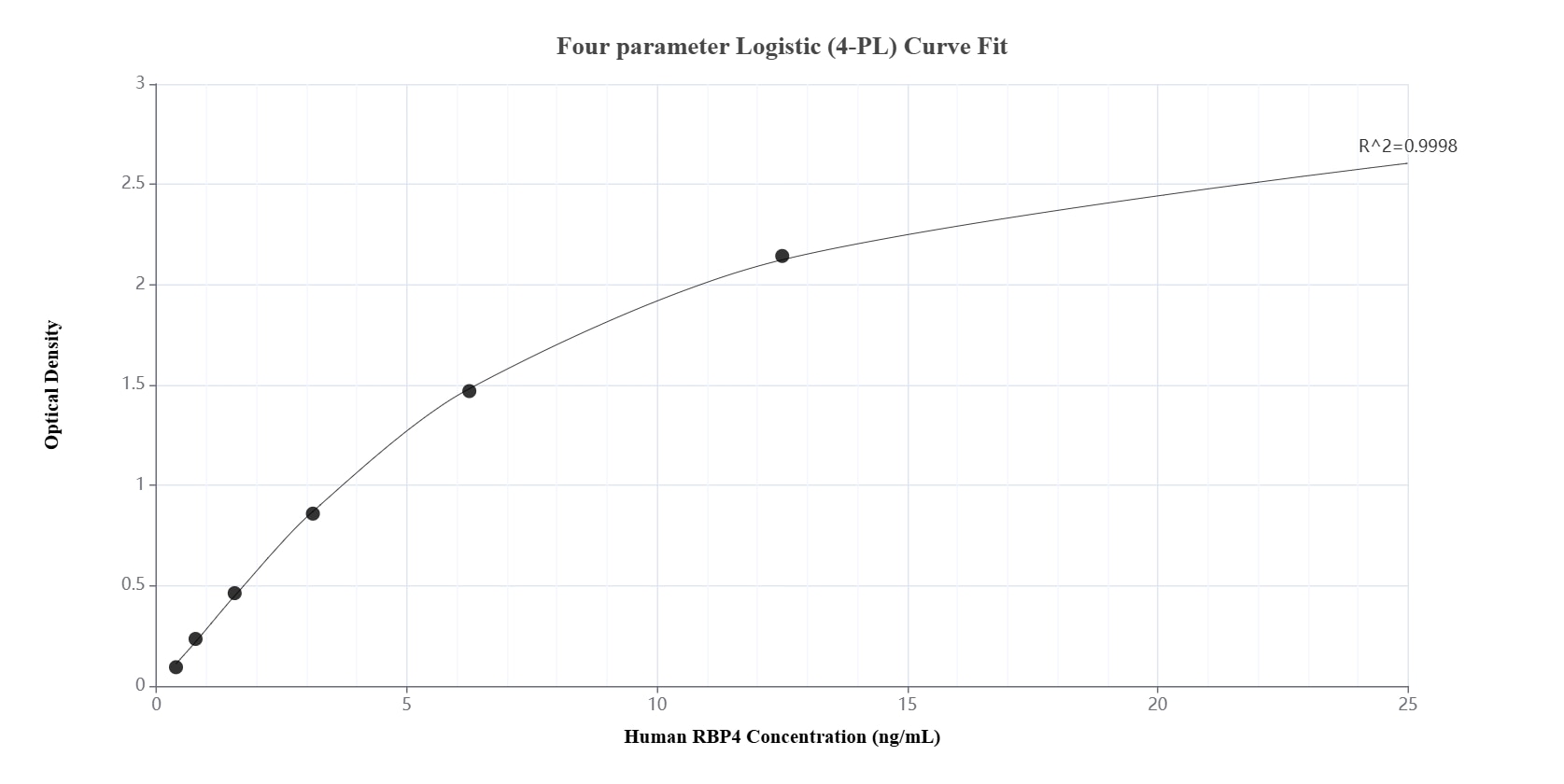
84496-1-PBS bindet in WB, FC (Intra), Cytometric bead array, Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA, Sample test RBP4 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Rekombinant |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | RBP4 fusion protein Eg31642 |
| Vollständiger Name | retinol binding protein 4, plasma |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 201 aa, 23 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 20-21 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC020633 |
| Gene symbol | RBP4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5950 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
RBP4 (retinol-binding protein 4) is a carrier protein that transports vitamin A (retinol) from the liver to the peripheral tissues. Synthesized primarily by hepatocytes and adipocytes as a 21 kDa non-glycosylated protein, RBP4 is secreted into the circulation as a retinol-RBP4 complex. In plasma the RBP4-retinol complex is bound to transthyretin (TRR), which prevents prevent kidney filtration. Two truncated forms of RBP4, RBP4-L (truncated at Leu-183) and RBP4-LL (truncated at Leu-182 and Leu-183), exist by proteolytic process. RBP4-L and RBP4-LL, which do not bind TTR, are normally excreted into the urine but accumulate in the serum during renal failure. Urinary RBP4 has been reported as marker for glomerular disease. RBP4 also was identified as an adipokine that elevated in some INS-resistant states. Measurement of serum RBP4 could be used to assess the risk of INS resistance, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. (18752671, 16034410)