SCAMP5 Rekombinanter Antikörper
SCAMP5 Rekombinant Antikörper für WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
243122F5
Kat-Nr. : 85669-2-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
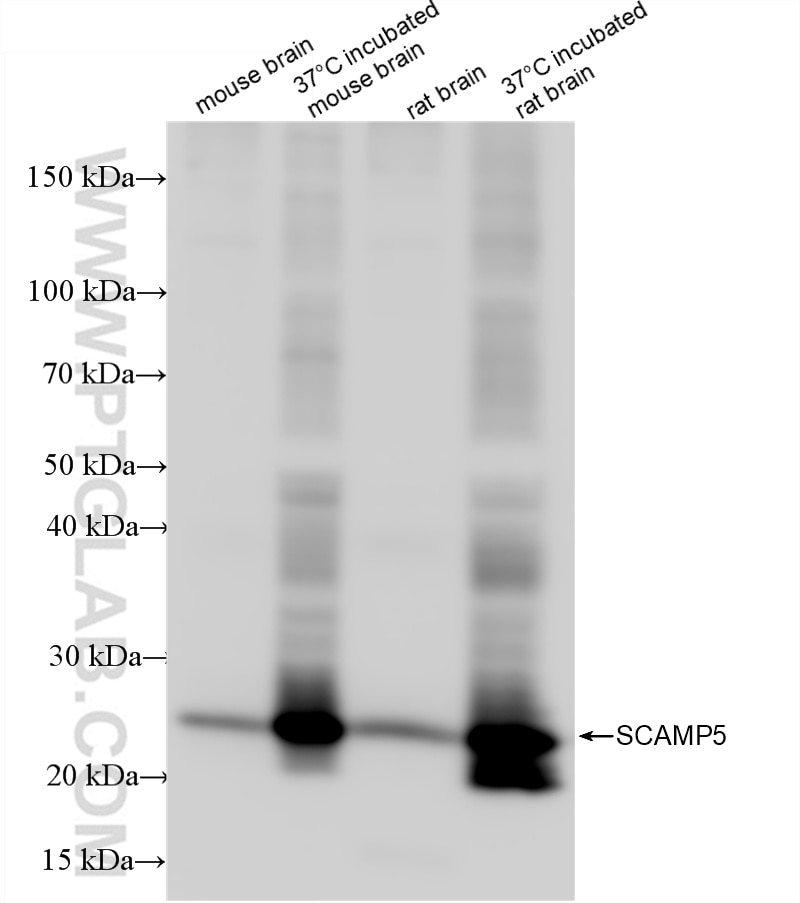
85669-2-PBS bindet in WB, Cytometric bead array, Indirect ELISA SCAMP5 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Rekombinant |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | SCAMP5 fusion protein Ag31837 |
| Vollständiger Name | secretory carrier membrane protein 5 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 26 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 26 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC024700 |
| Gene symbol | SCAMP5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 192683 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Secretory carrier-associated membrane protein 5 (SCAMP5) belongs to the to the SCAMP family. Secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs) constitute a group of membrane transport proteins in plants, insects and mammals. The mammalian genome contains five types of SCAMP genes, namely, SCAMP1-SCAMP5. (PMID:36217917, PMID:19234194). SCAMPs participate in the vesicle cycling fusion of vesicles and cell membranes and play roles in regulating exocytosis and endocytosis, activating synaptic function and transmitting nerve signals. Among these proteins, SCAMP5 is highly expressed in the brain and has direct or indirect effects on the function of the central nervous system (PMID:36217917). SCAMP5 regulates membrane transport, controls the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles and is related to secretion carrier and membrane function. In addition, SCAMP5 plays a major role in the normal maintenance of the physiological functions of nerve cells (PMID:36217917, PMID:33663553). For optimal WB detection of this membrane protein, we recommend to avoid boiling the sample after lysis.