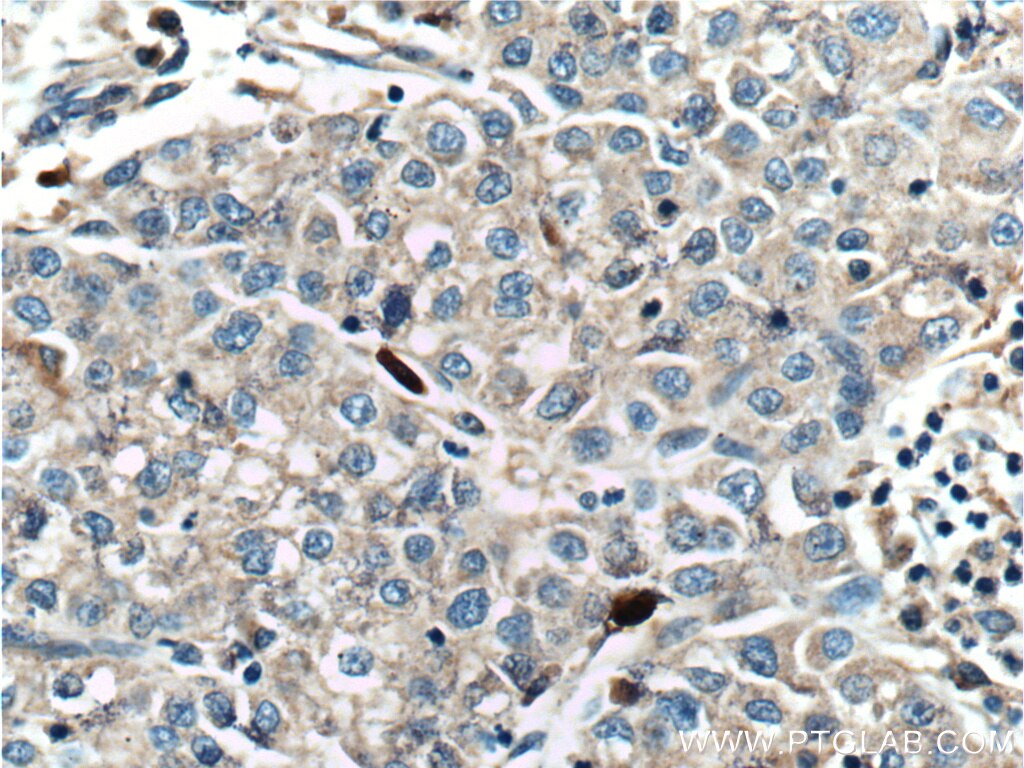
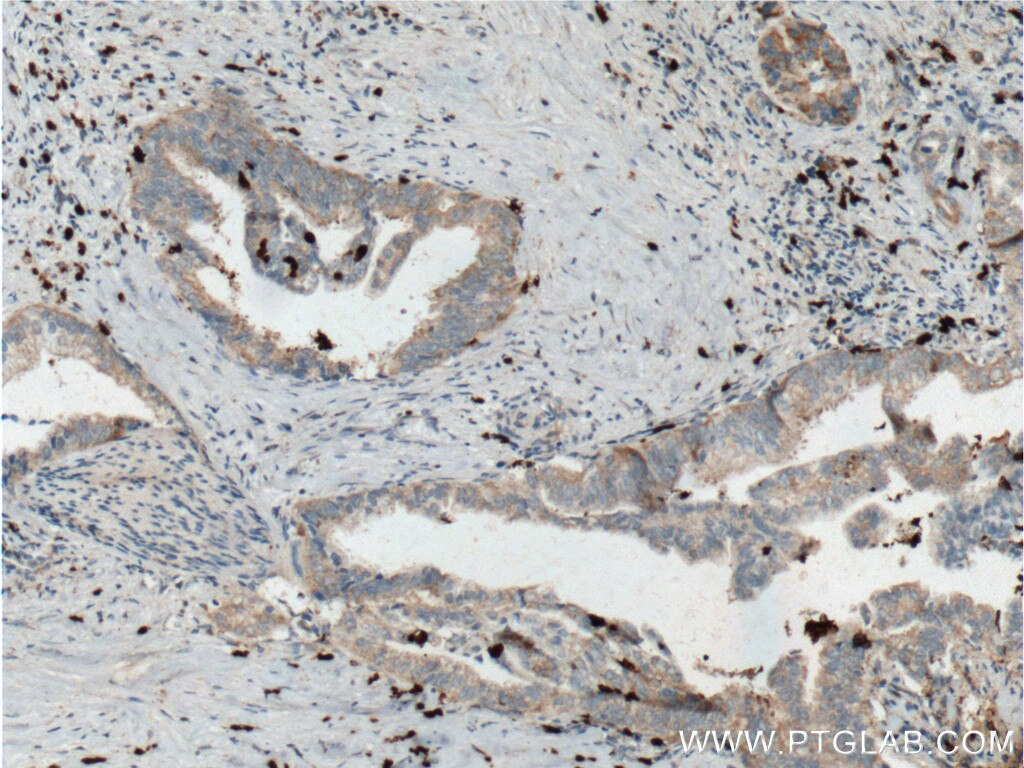
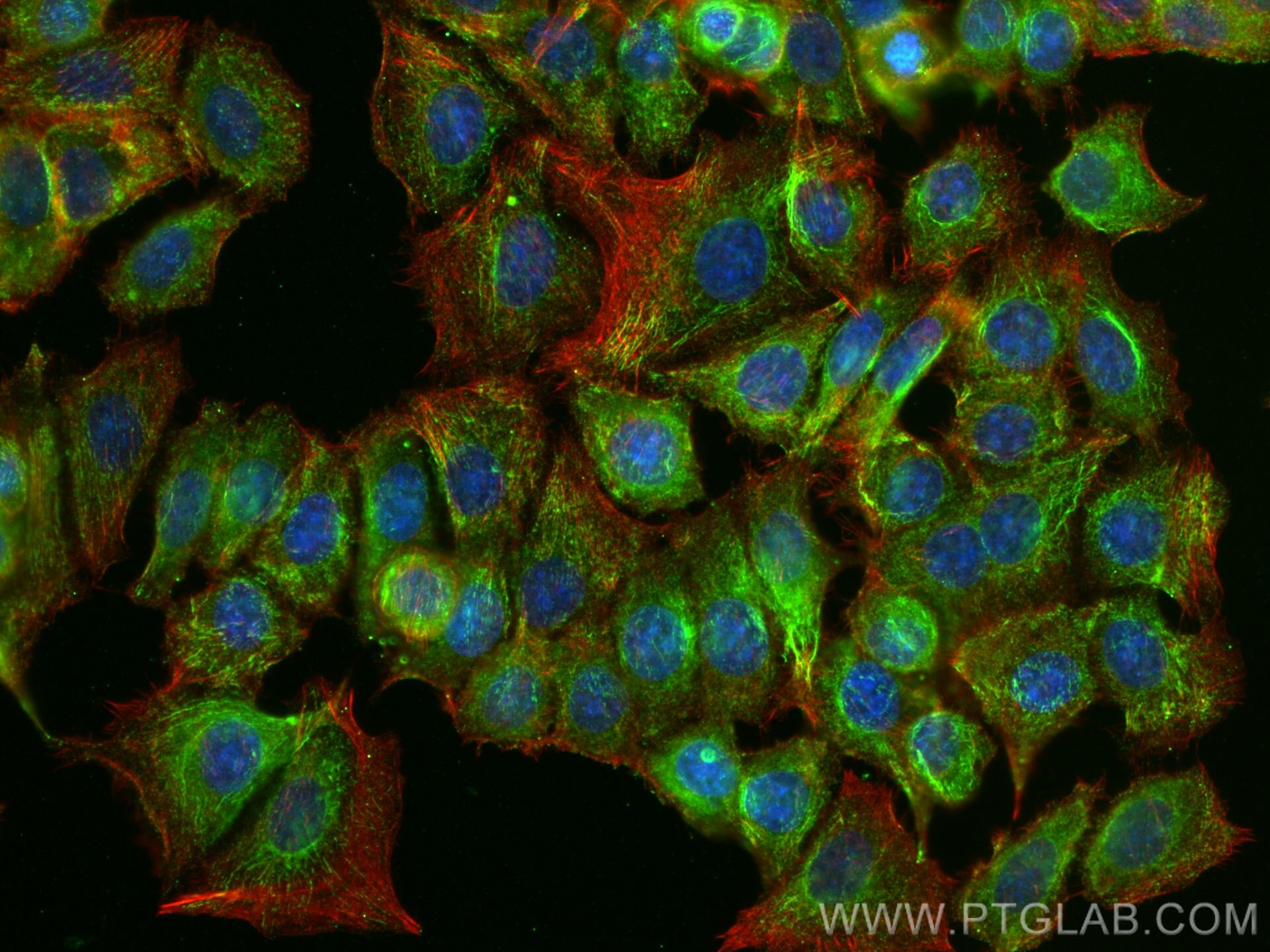
SMYD3 Monoklonaler Antikörper
SMYD3 Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
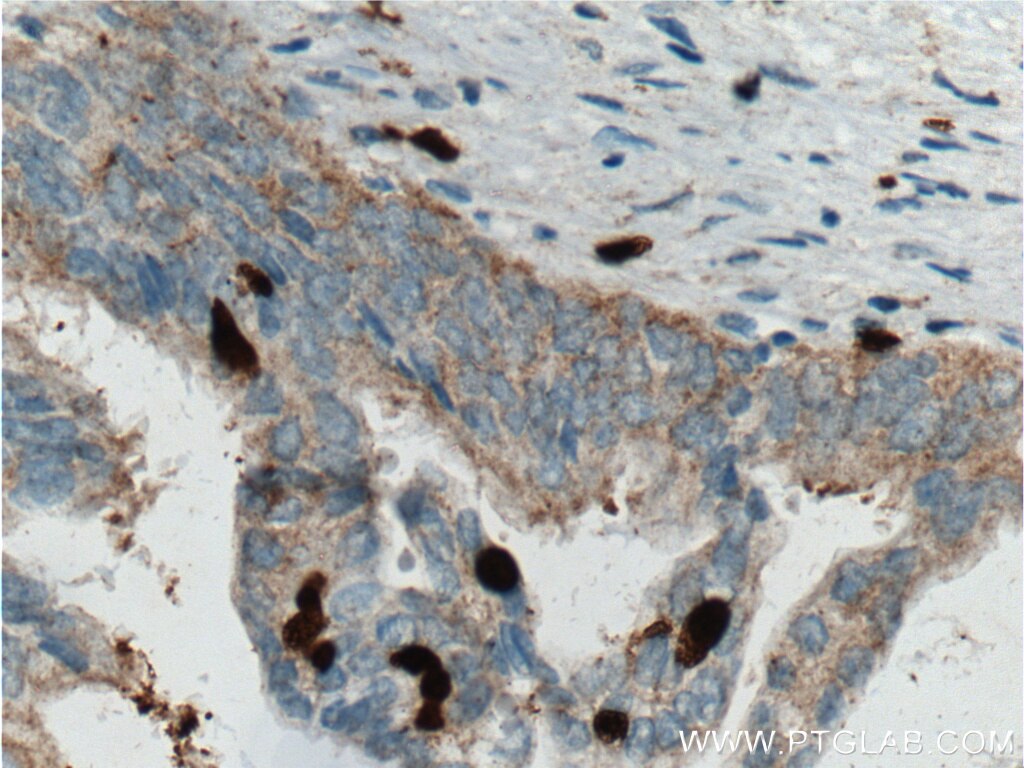
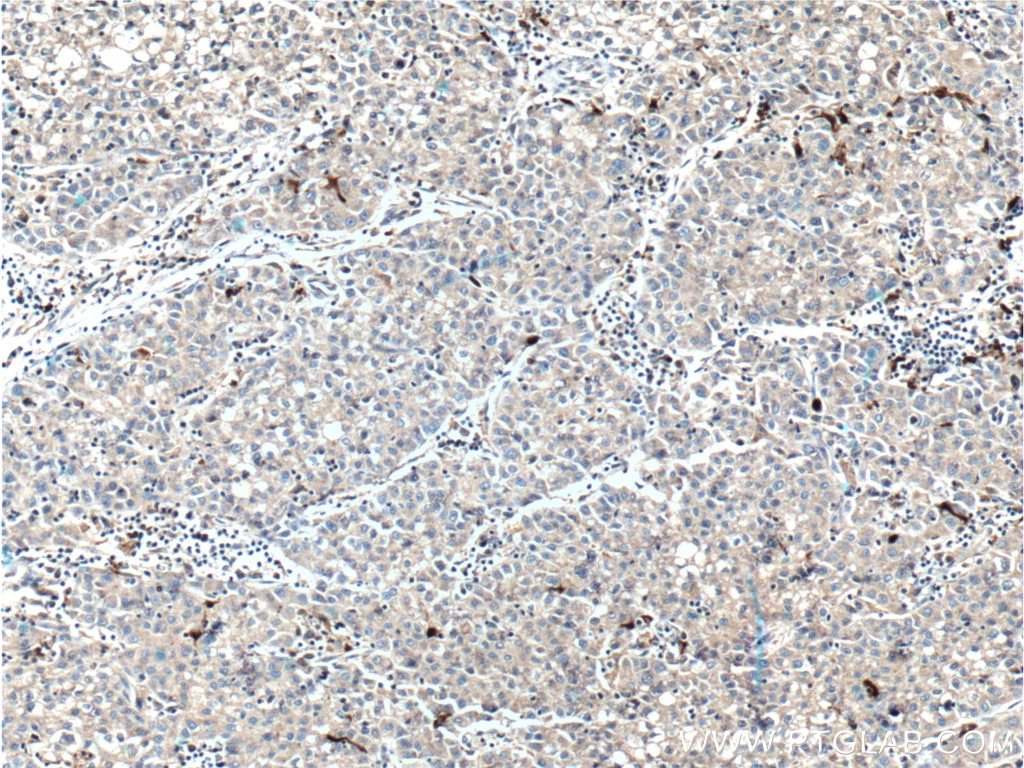
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1B5C10
Kat-Nr. : 66330-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
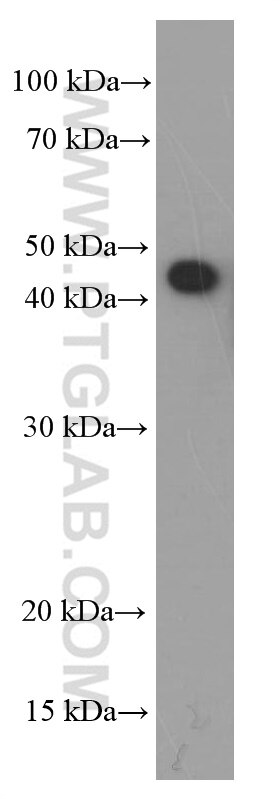
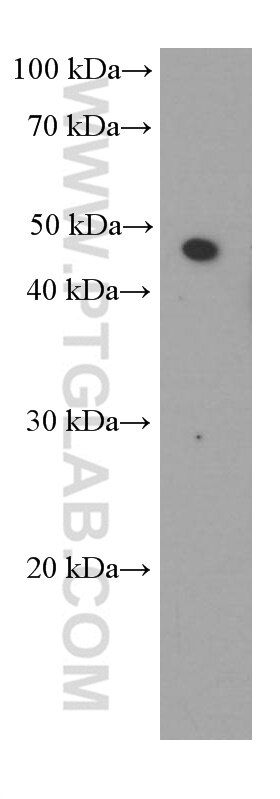
66330-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA SMYD3 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | SMYD3 fusion protein Ag2624 |
| Vollständiger Name | SET and MYND domain containing 3 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 428aa,49 kDa; 369aa,42 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 49 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC031010 |
| Gene symbol | SMYD3 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 64754 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
SMYD3,also name as ZMYND1 and ZNFN3A1, belongs to the histone-lysine methyltransferase family.It is a histone methyltransferase that plays an important role in transcriptional regulation in human carcinogenesis. It can specifically methylate histone H3 at lysine 4 and activate the transcription of a set of downstream genes, including several oncogenes (e.g., N-myc, CrkL, Wnt10b, RIZ and hTERT) and genes involved in the control of cell cycle.(PMID: 20957523). It plays an important role in transcriptional activation as a member of an RNA polymerase complex. SMYD3 is frequently overexpressed in different types of cancer cells. It functions as a coactivator of Era and potentiates Era activity in response to ligand. SMYD3 as a new coactivator for ER-mediated transcription, providing a possible link between SMYD3 overexpression and breast cancer. (PMID: 19509295) The common variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism in SMYD3 is a susceptibility factor for some types of human cancer(PMID:16155568). Mainly cytoplasmic when cells are arrested at G0/G1, accumulates in the nucleus at S phase and G2/M(Uniprot).