Tie-2/CD202b Polyklonaler Antikörper
Tie-2/CD202b Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 19157-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
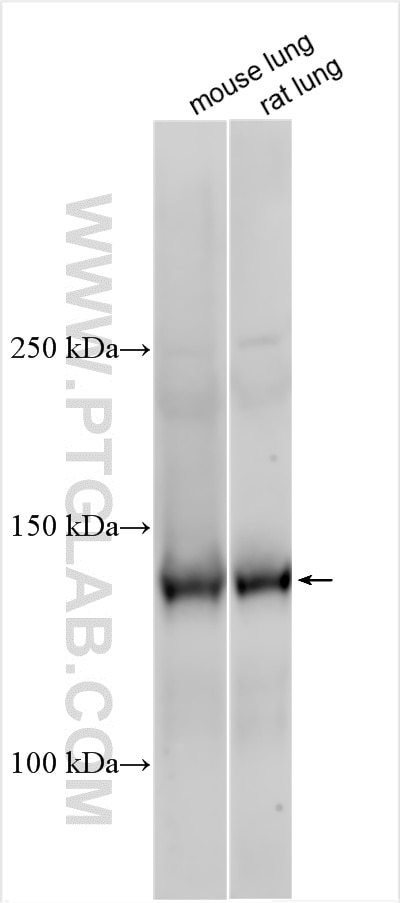
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Mauslungengewebe, Mauslebergewebe, Rattenlungengewebe |
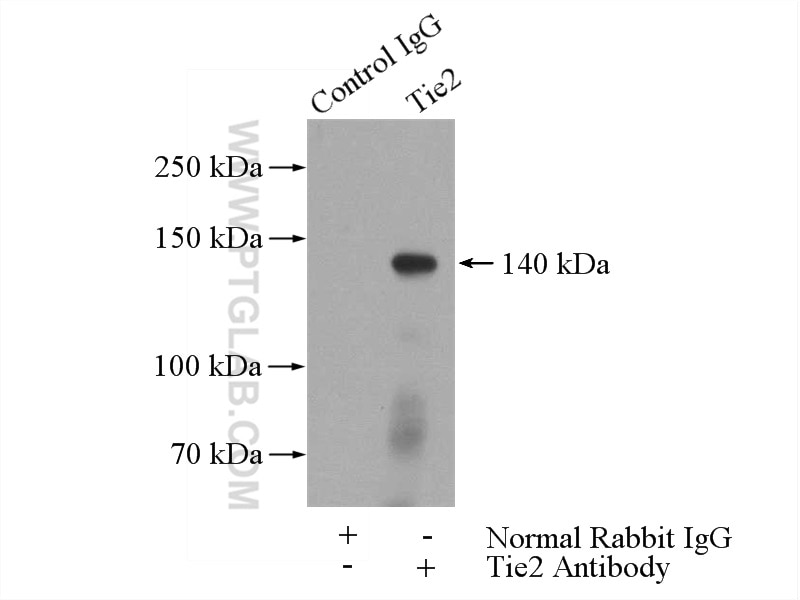
| Erfolgreiche IP | Mauslungengewebe |
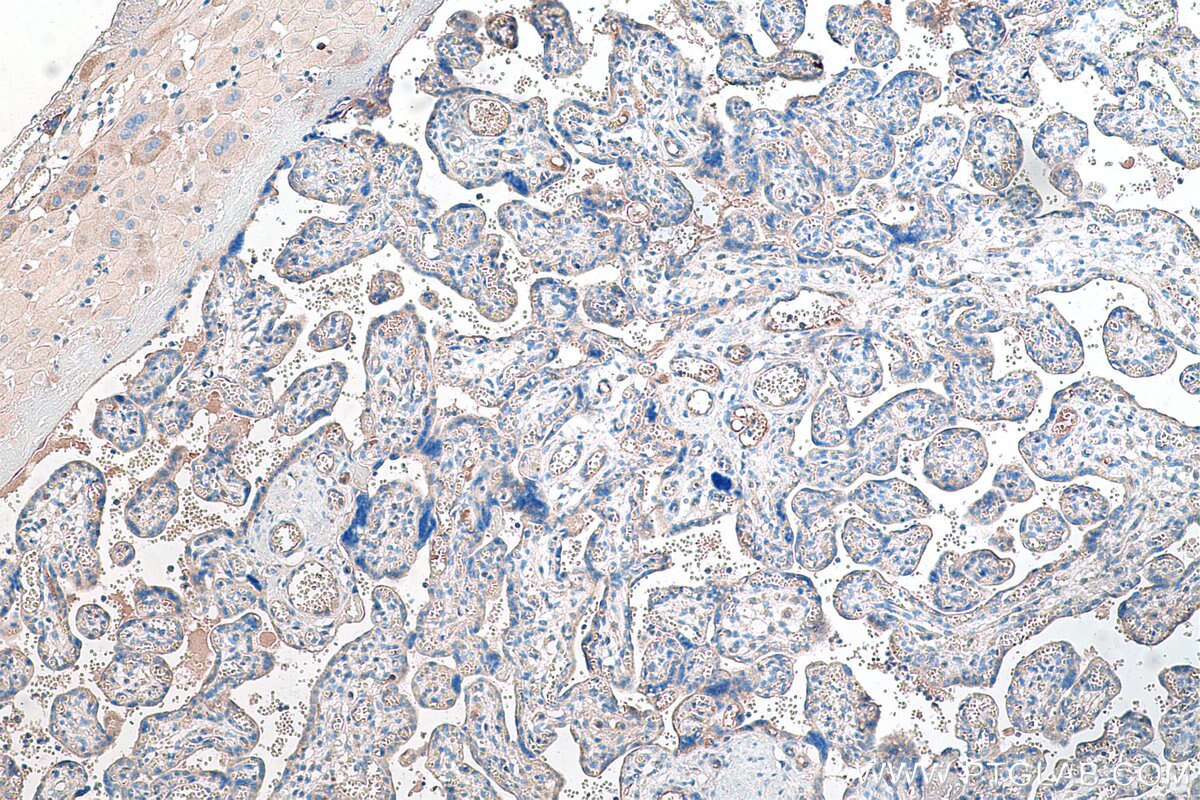
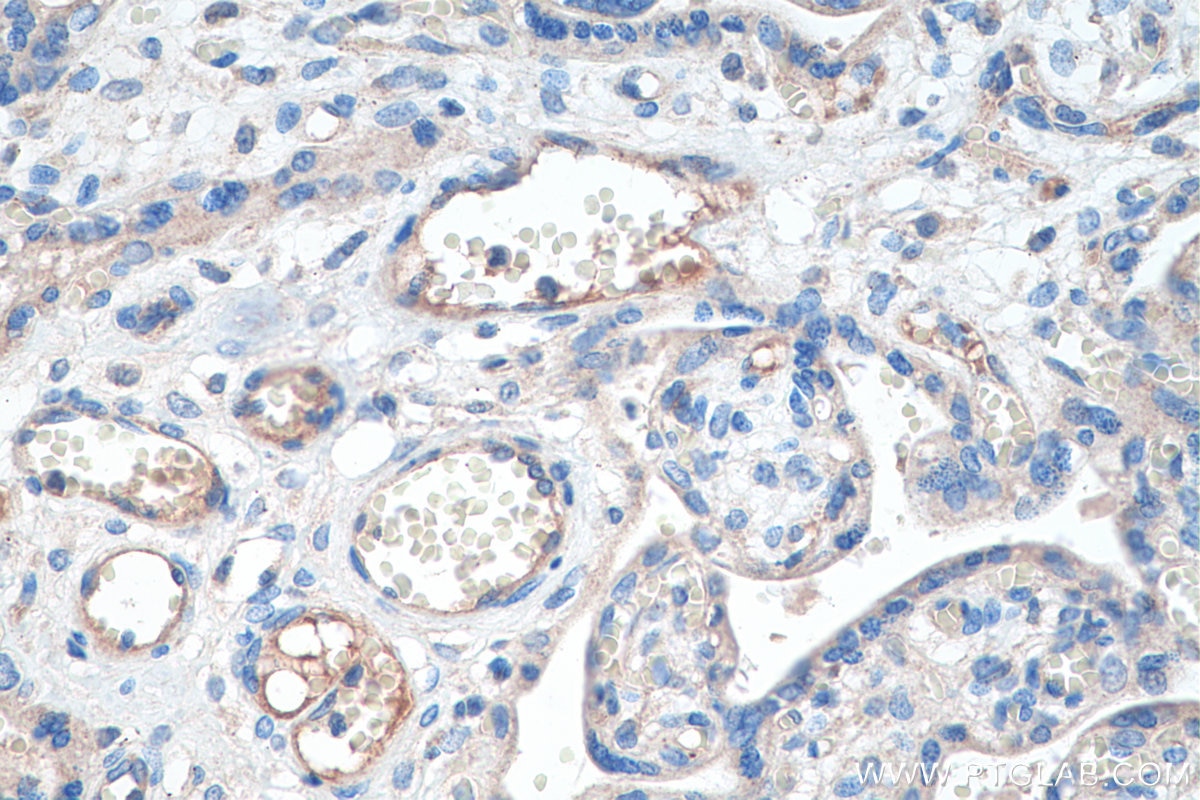
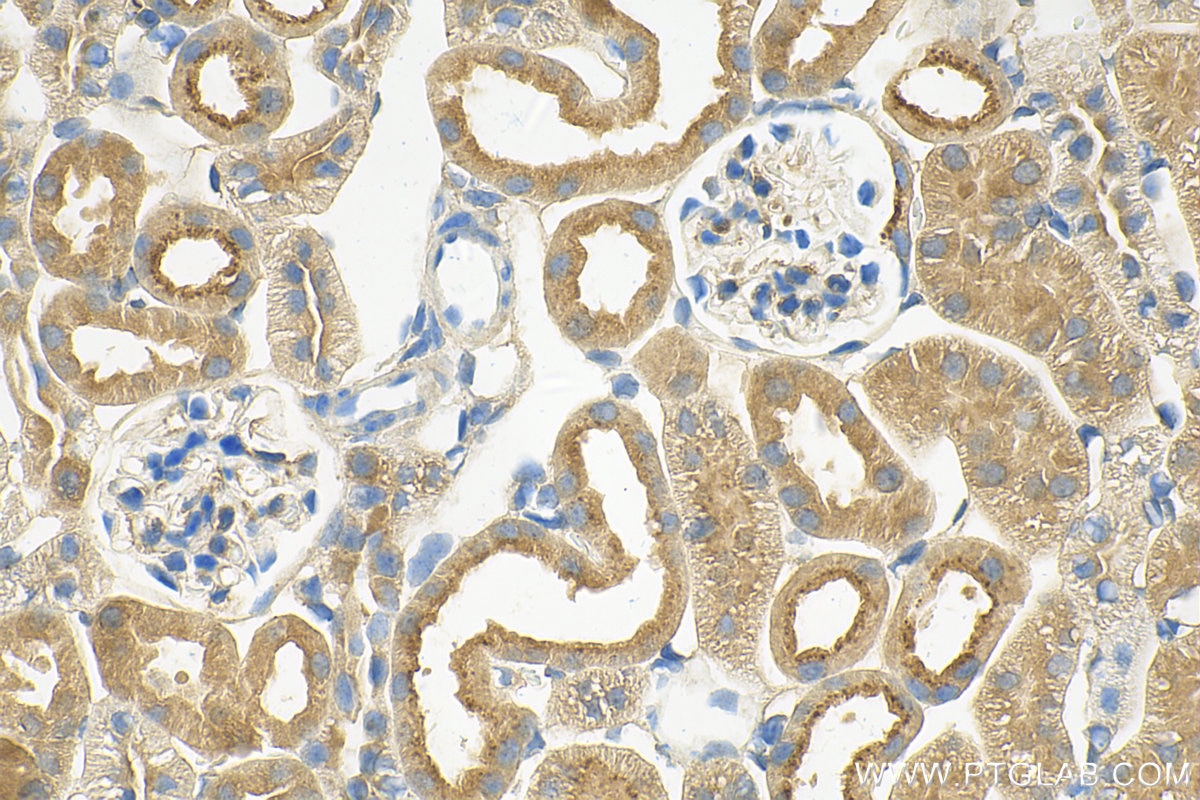
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Plazenta-Gewebe, Mausnierengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 19 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 5 publications below |
Produktinformation
19157-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA Tie-2/CD202b und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Tie-2/CD202b fusion protein Ag13523 |
| Vollständiger Name | TEK tyrosine kinase, endothelial |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 1124 aa, 126 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 140 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC035514 |
| Gene symbol | Tie2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7010 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Tie2 (also known as TEK) is a tyrosine-protein kinase expressed almost exclusively on endothelial cells. It contains two immunoglobulin-like domains, three epidermal growth factor (EGF)--like domains and three fibronectin type III repeats. Tie2 acts as a cell-surface receptor for ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and ANGPT4 and regulates angiogenesis, endothelial cell survival, proliferation, migration, adhesion and cell spreading, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, but also maintenance of vascular quiescence. Mutations in the gene Tie2 are associated with inherited venous malformations of the skin and mucous membranes. Human Tie2 has a calculated molecular weight of 126 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of Tie2 is approximately 140-160 kDa.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Tie-2/CD202b antibody 19157-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Tie-2/CD202b antibody 19157-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IP protocol for Tie-2/CD202b antibody 19157-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Ther Adv Med Oncol Development and external validation of a composite immune-clinical prognostic model associated with EGFR mutation in East-Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma. | ||
Mol Cancer Ther JQ1 induces DNA damage and apoptosis, and inhibits tumor growth in a patient-derived xenograft model of cholangiocarcinoma. | ||
Front Cell Dev Biol Inhibiting Heat Shock Protein 90 Protects Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Stem/Progenitor Cells From Compression-Induced Necroptosis and Apoptosis. | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther Human endometrium-derived stem cell improves cardiac function after myocardial ischemic injury by enhancing angiogenesis and myocardial metabolism. | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther MicroRNA-9 modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) repair severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) via inducing angiogenesis in rats. | ||
J Mol Cell Cardiol BMP9 attenuates occurrence of venous malformation by maintaining endothelial quiescence and strengthening vessel walls via SMAD1/5/ID1/α-SMA pathway. |