- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
Vimentin Polyklonaler Antikörper
Vimentin Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 22031-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
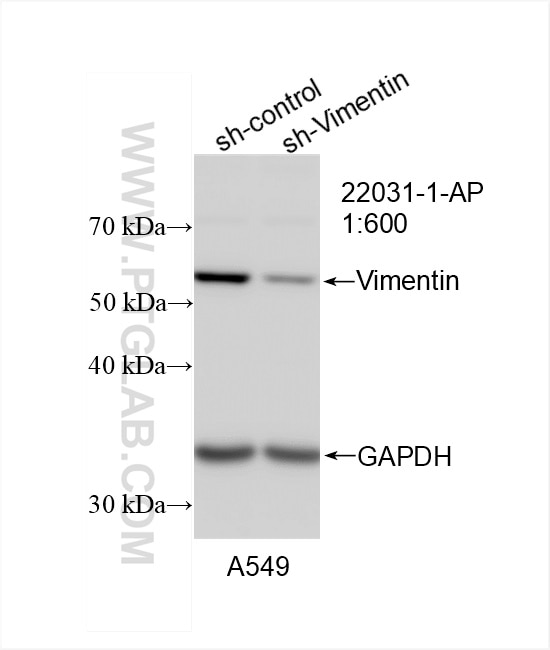
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HEK-293-Zellen, A549-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, Mausherzgewebe |
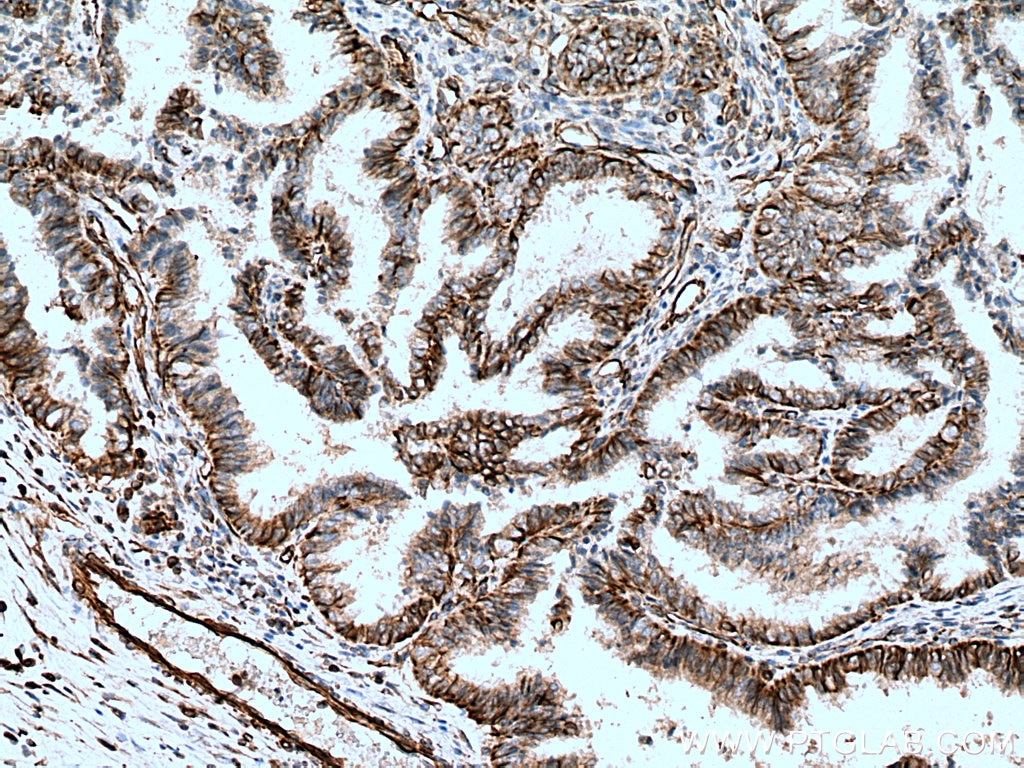
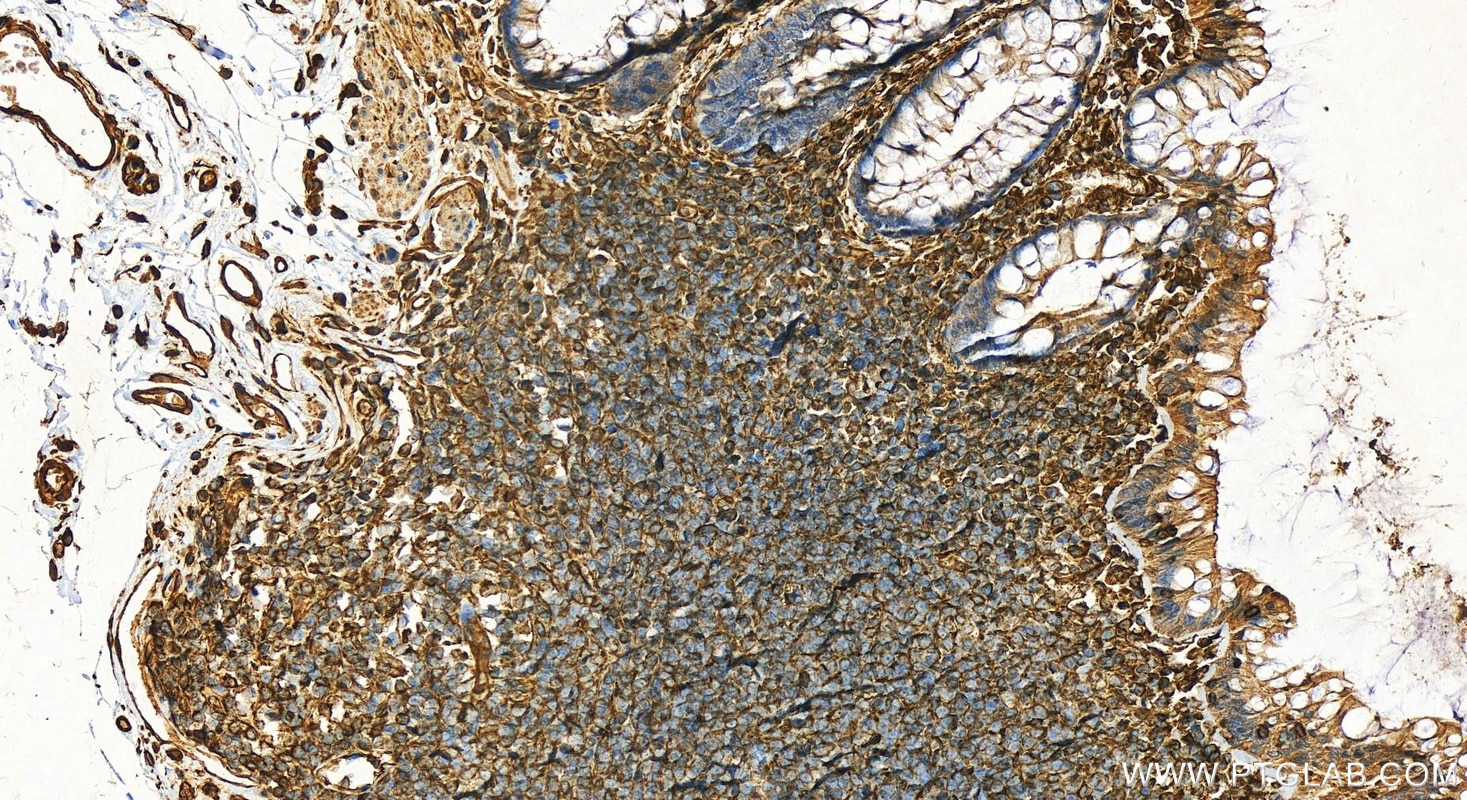
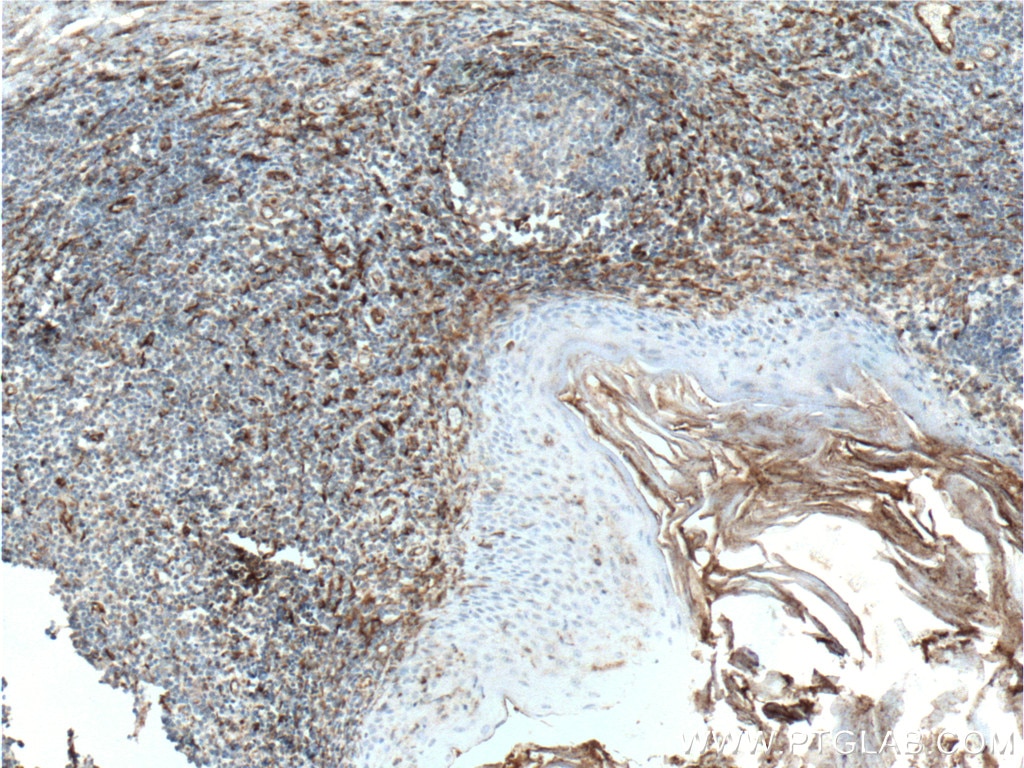
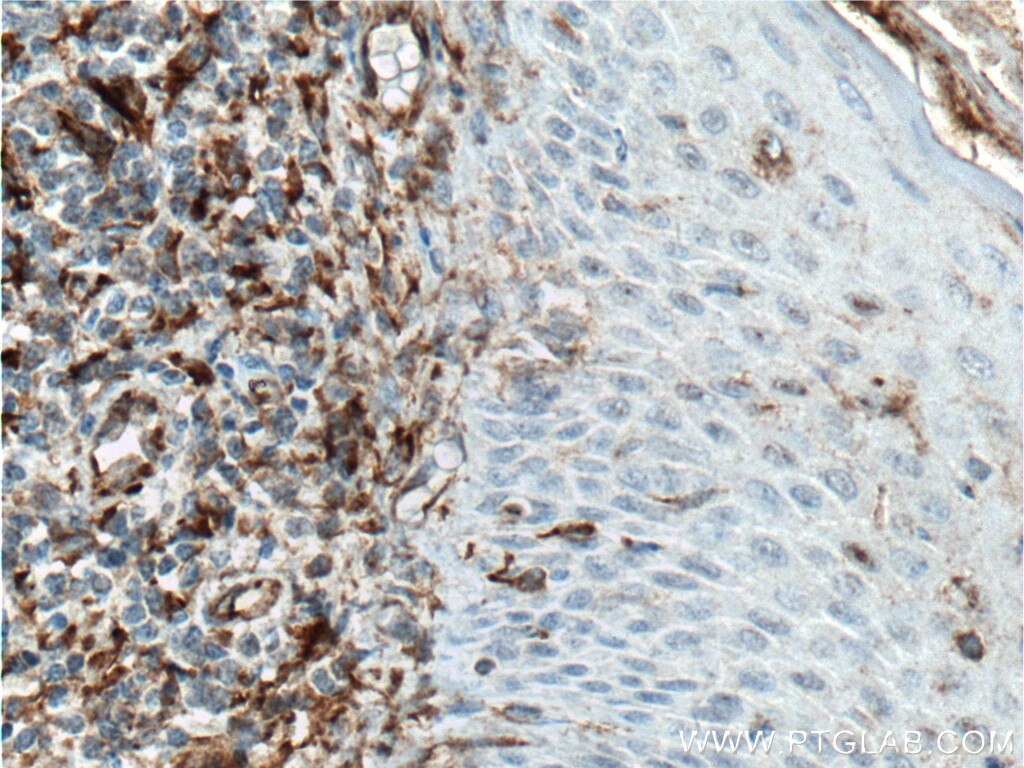
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Ovarialkarzinomgewebe, humanes Tonsillitisgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
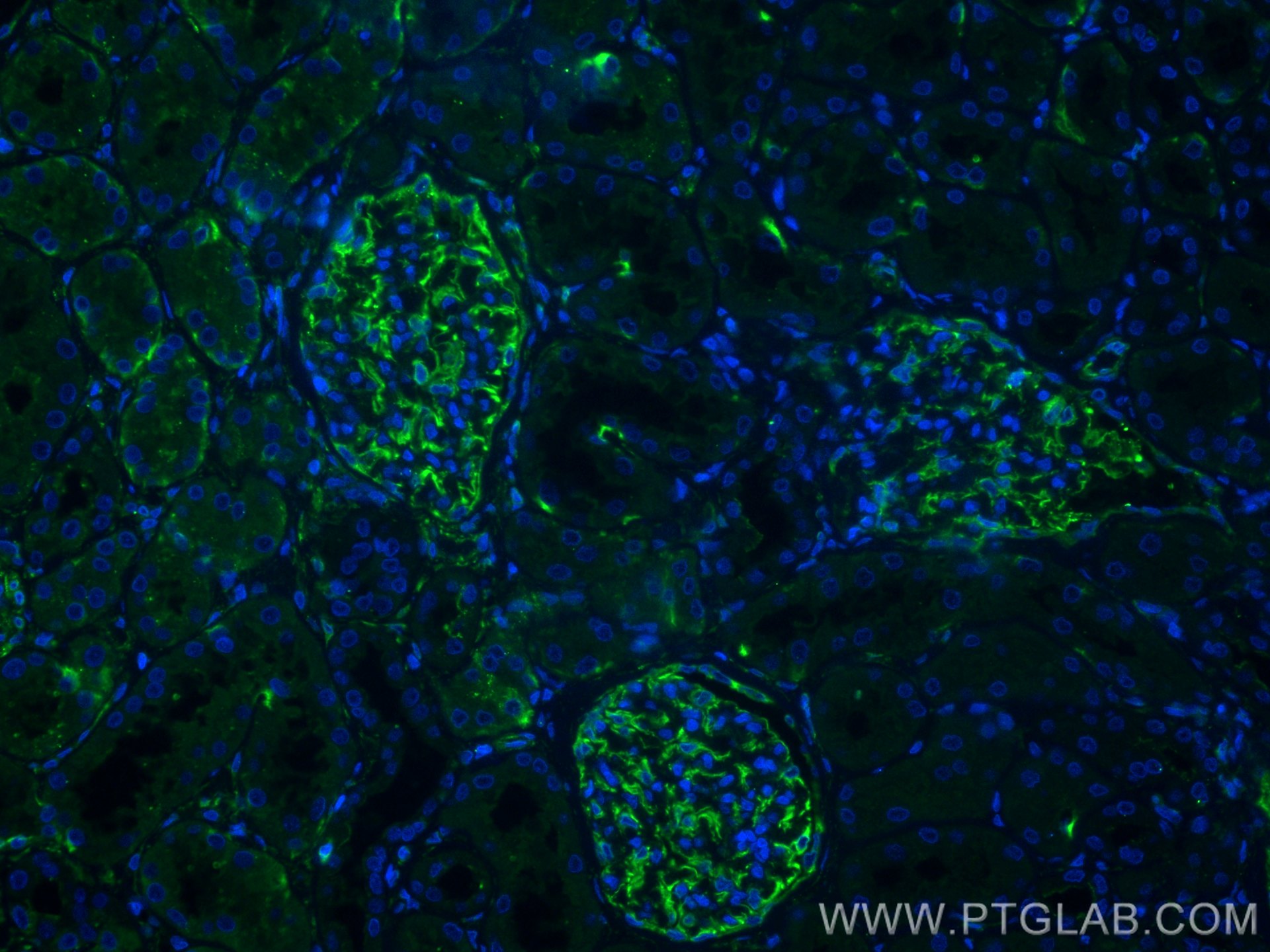
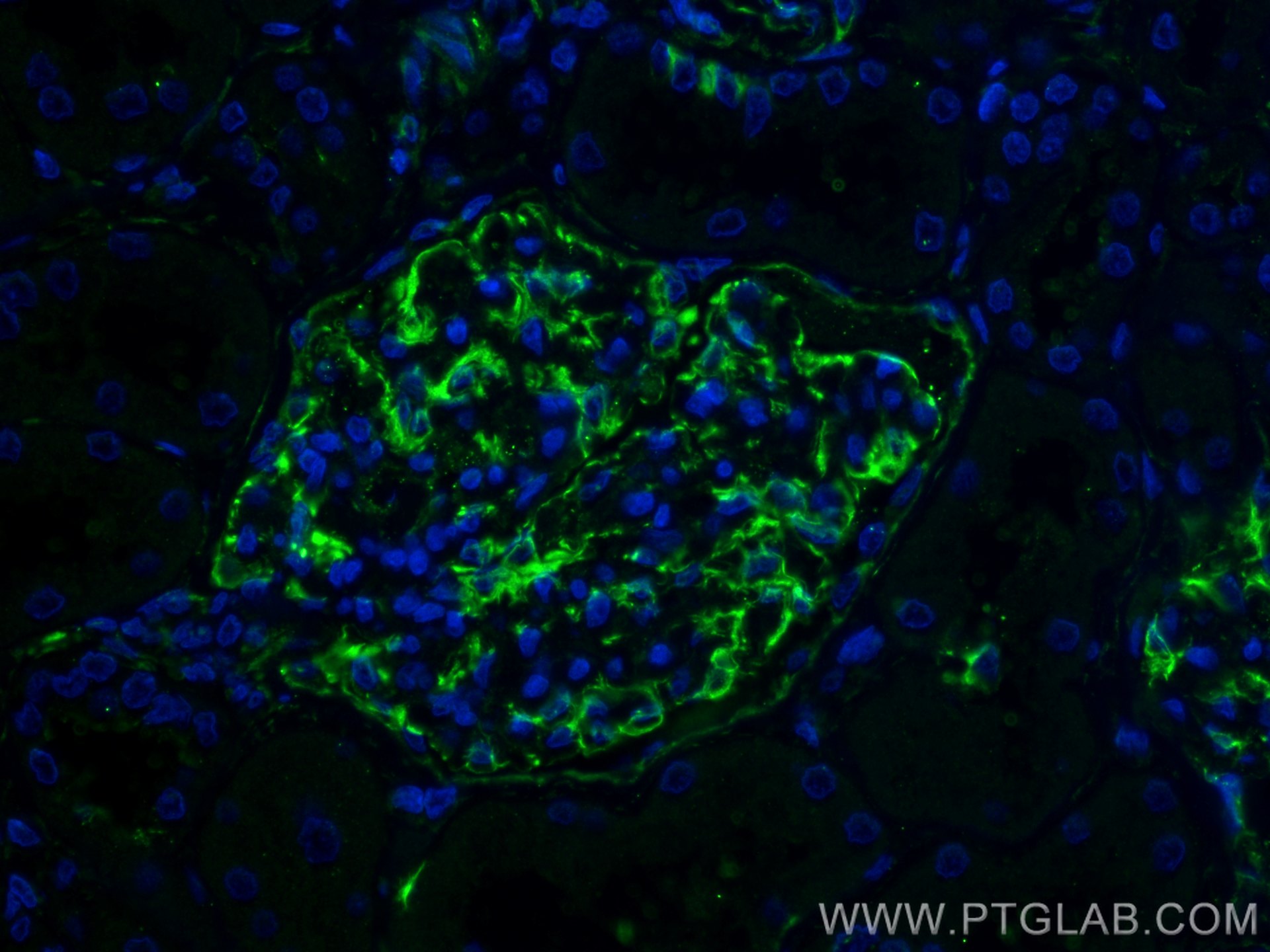
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF-P | humanes Nierengewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 18 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 8 publications below |
Produktinformation
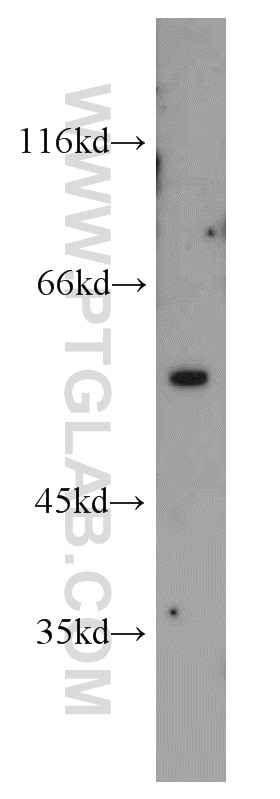
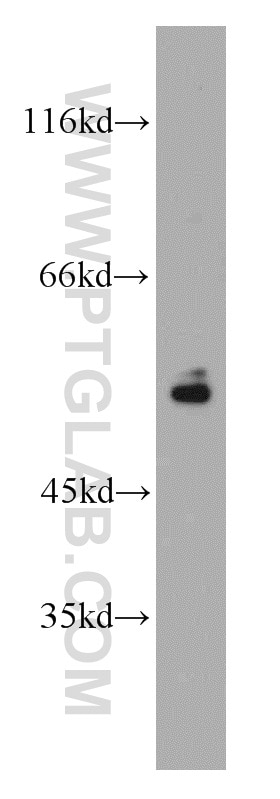
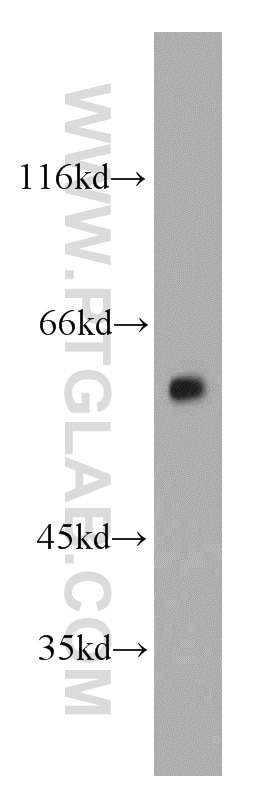
22031-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA Vimentin und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Vimentin fusion protein Ag16898 |
| Vollständiger Name | vimentin |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 466 aa, 54 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 57 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC000163 |
| Gene symbol | VIM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7431 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Vimentin, also named as VIM, belongs to the intermediate filament family. Vimentin is class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is important for stabilizing the architecture of the cytoplasm. Monocyte-derived macrophages secrete vimentin into the extracellular space in vitro. Secretion of vimentin was enhanced by the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFA; 191160) and inhibited by the antiinflammatory cytokine IL10 (124092), suggesting that vimentin is involved in the immune response. Vimentin has specialized functions that contribute to specific dynamic cellular processes. As a phosphoprotein, 55-60 kDa of vimentin proteins can be observed due to the different phosphorylation level. Isoforms of vimentin (49 kDa and 60 kDa) had also been reported. (PMID: 8640945, 22728585).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Vimentin antibody 22031-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Vimentin antibody 22031-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for Vimentin antibody 22031-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Death Dis ZNF652 exerts a tumor suppressor role in lung cancer by transcriptionally downregulating cyclin D3 | ||
J Transl Med Single-cell and spatial transcriptome profiling reveal CTHRC1+ fibroblasts promote EMT through WNT5A signaling in colorectal cancer | ||
Tissue Eng Part C Methods Pretreatment with Inflammatory Factors Altered the Secretome of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells | ||
Clin Respir J SIRT3 Inhibits Cell Proliferation of Nonsmall Cell Lung Carcinoma by Inducing ROS Production | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis A novel Cdc42-YAP-fibronectin signaling axis regulates ameloblast differentiation during early enamel formation | ||
Breast Cancer Res SMYD4 promotes MYH9 ubiquitination through lysine monomethylation modification to inhibit breast cancer progression |