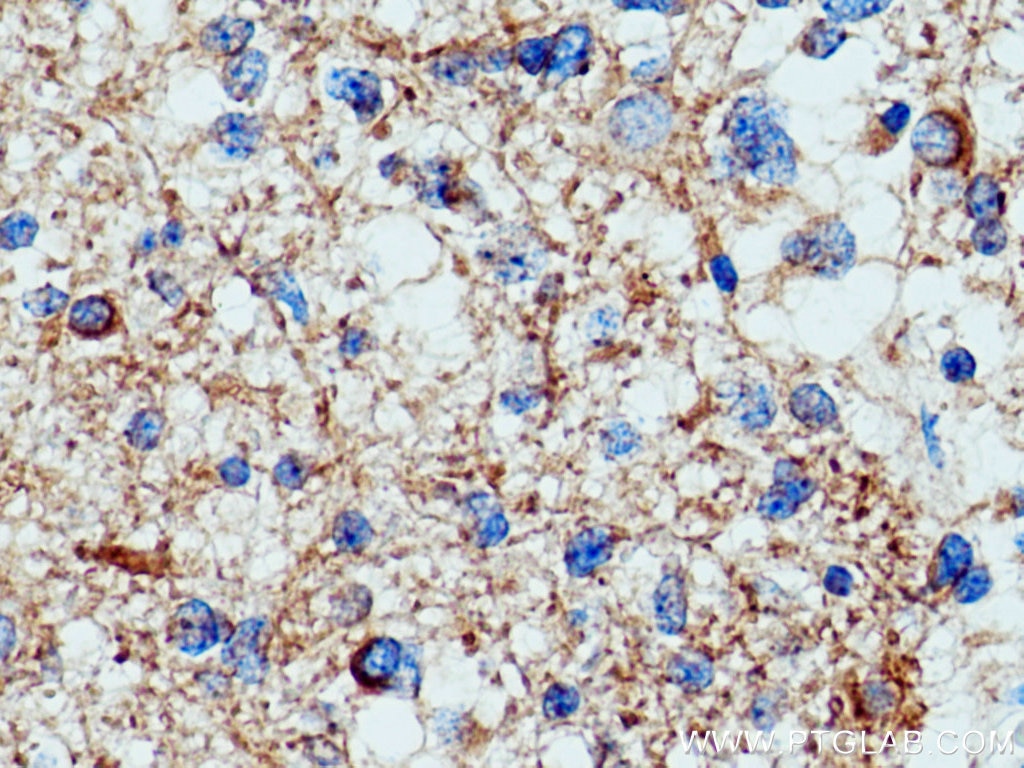
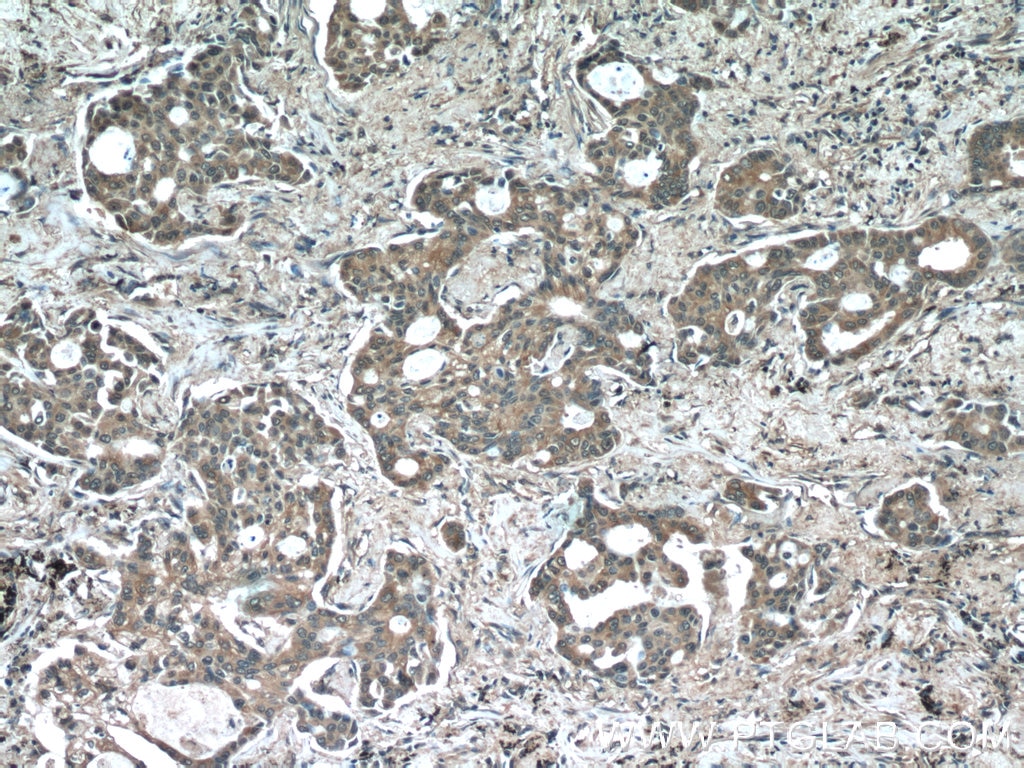
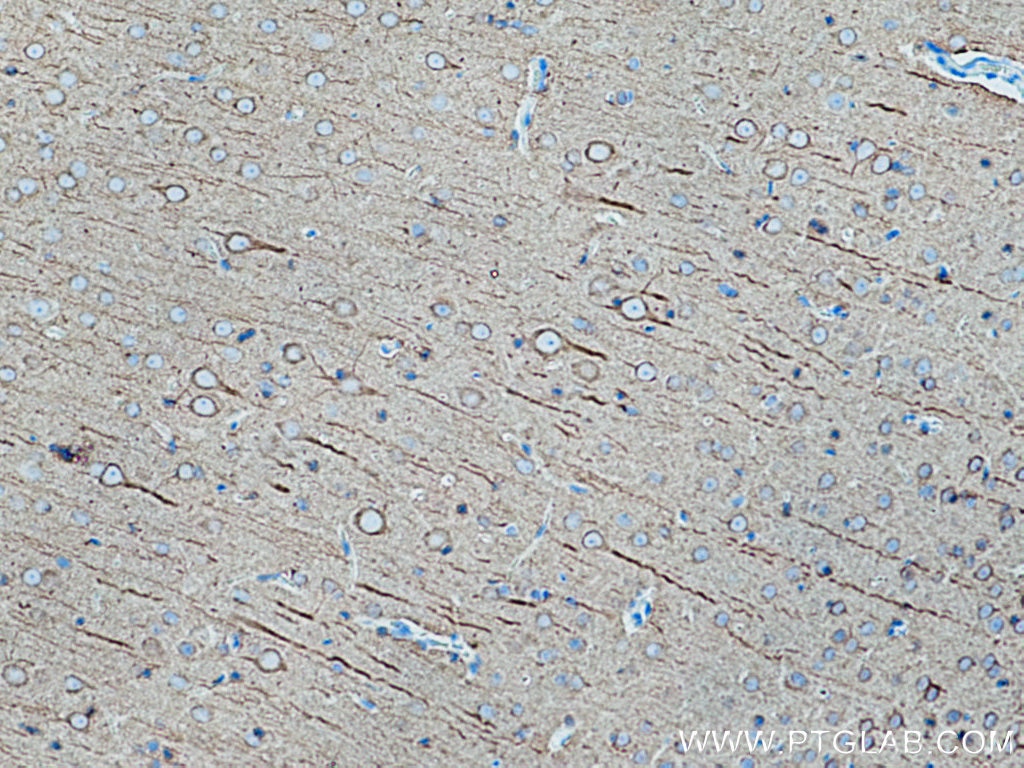
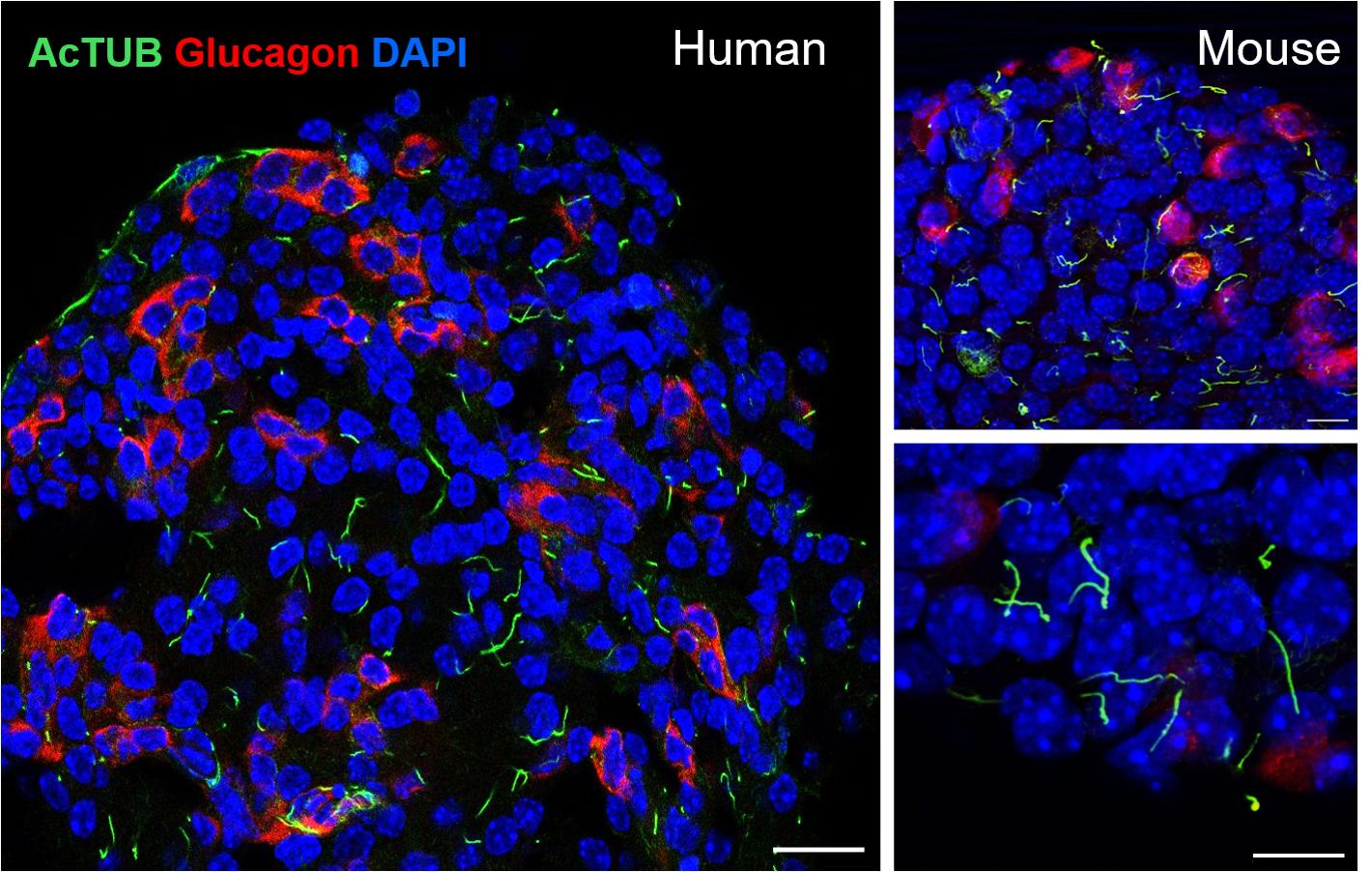
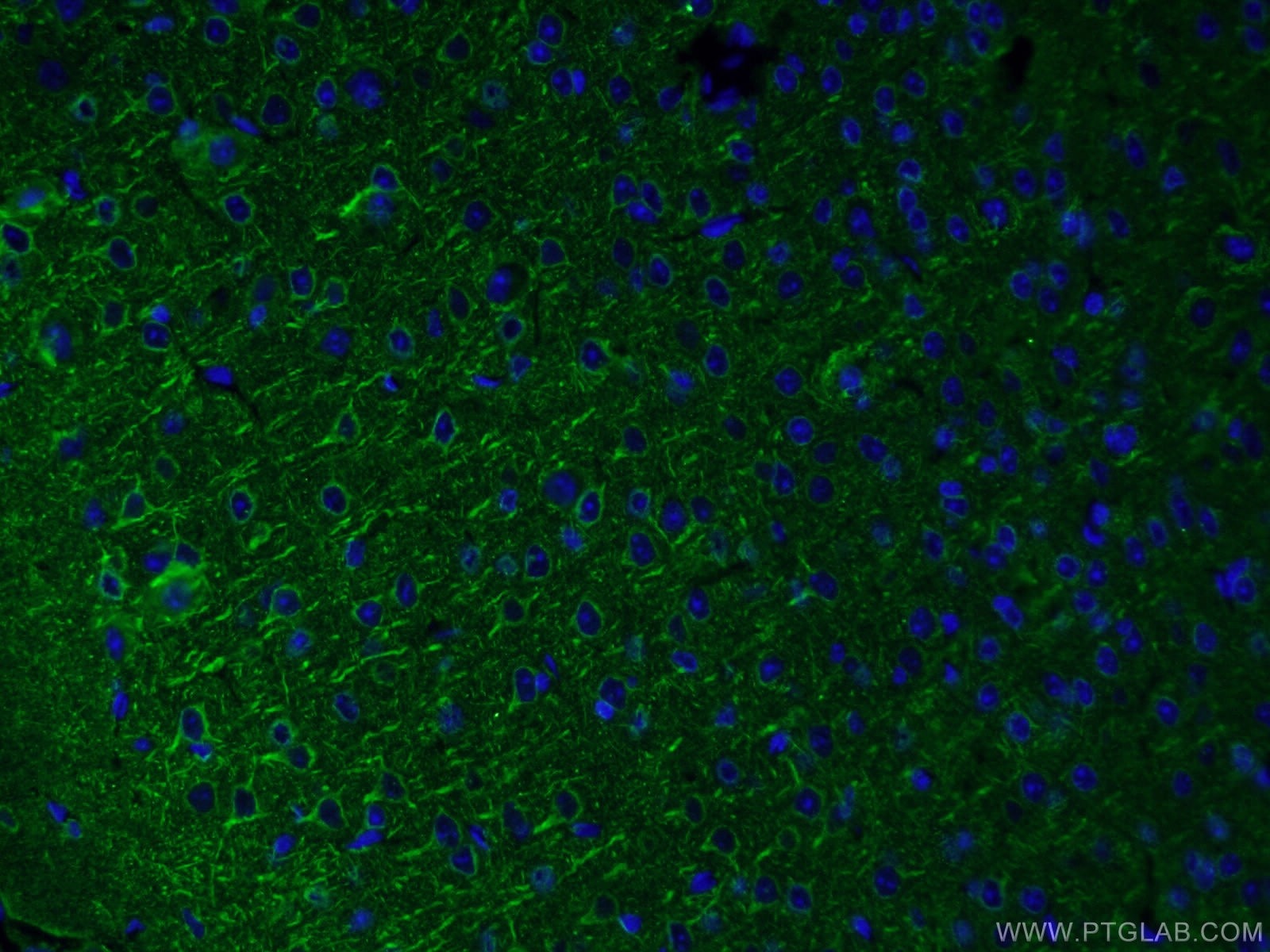
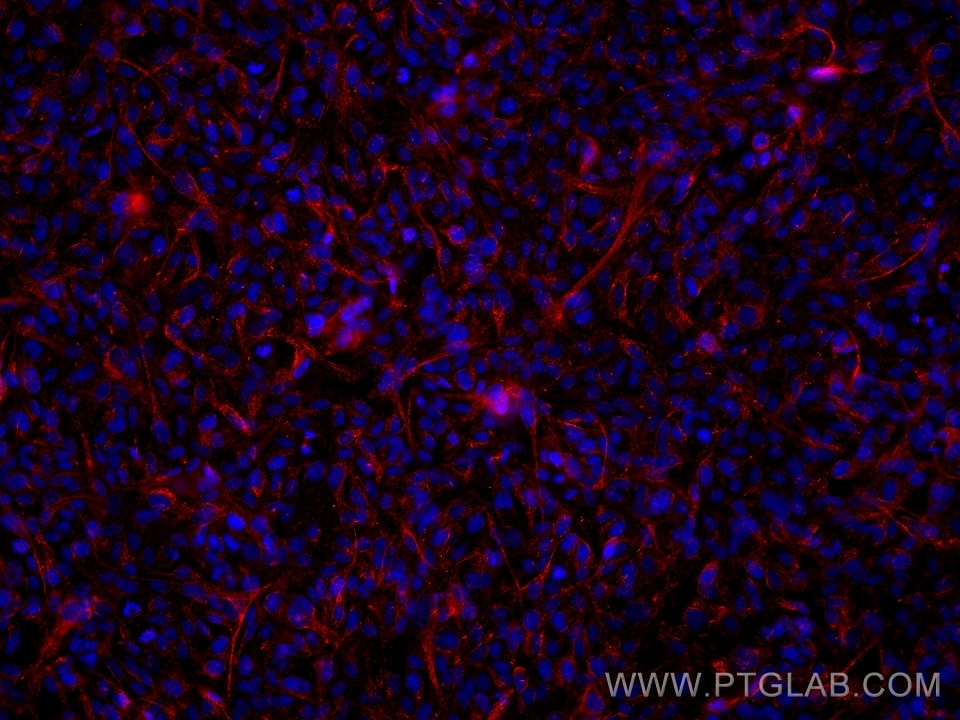
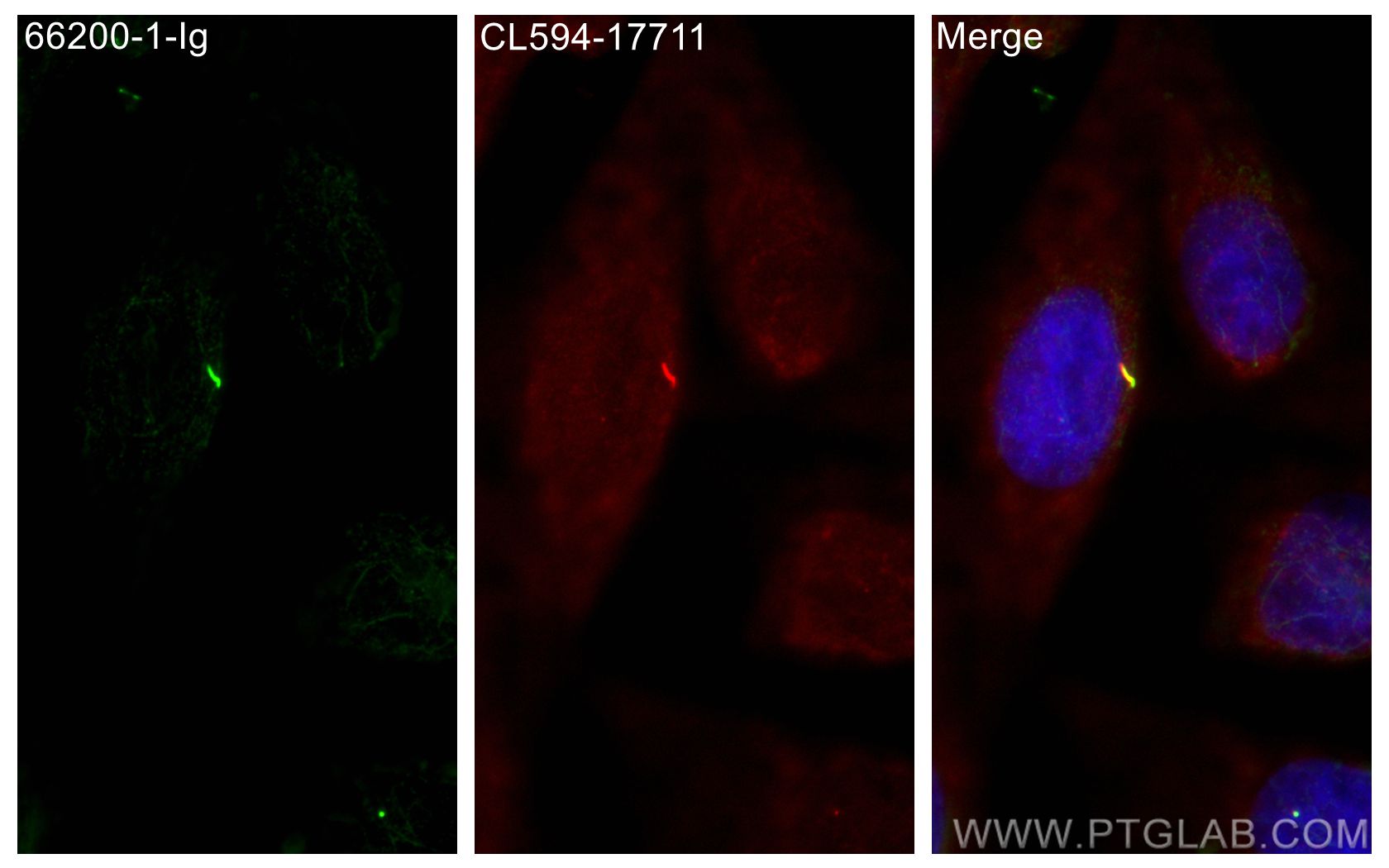
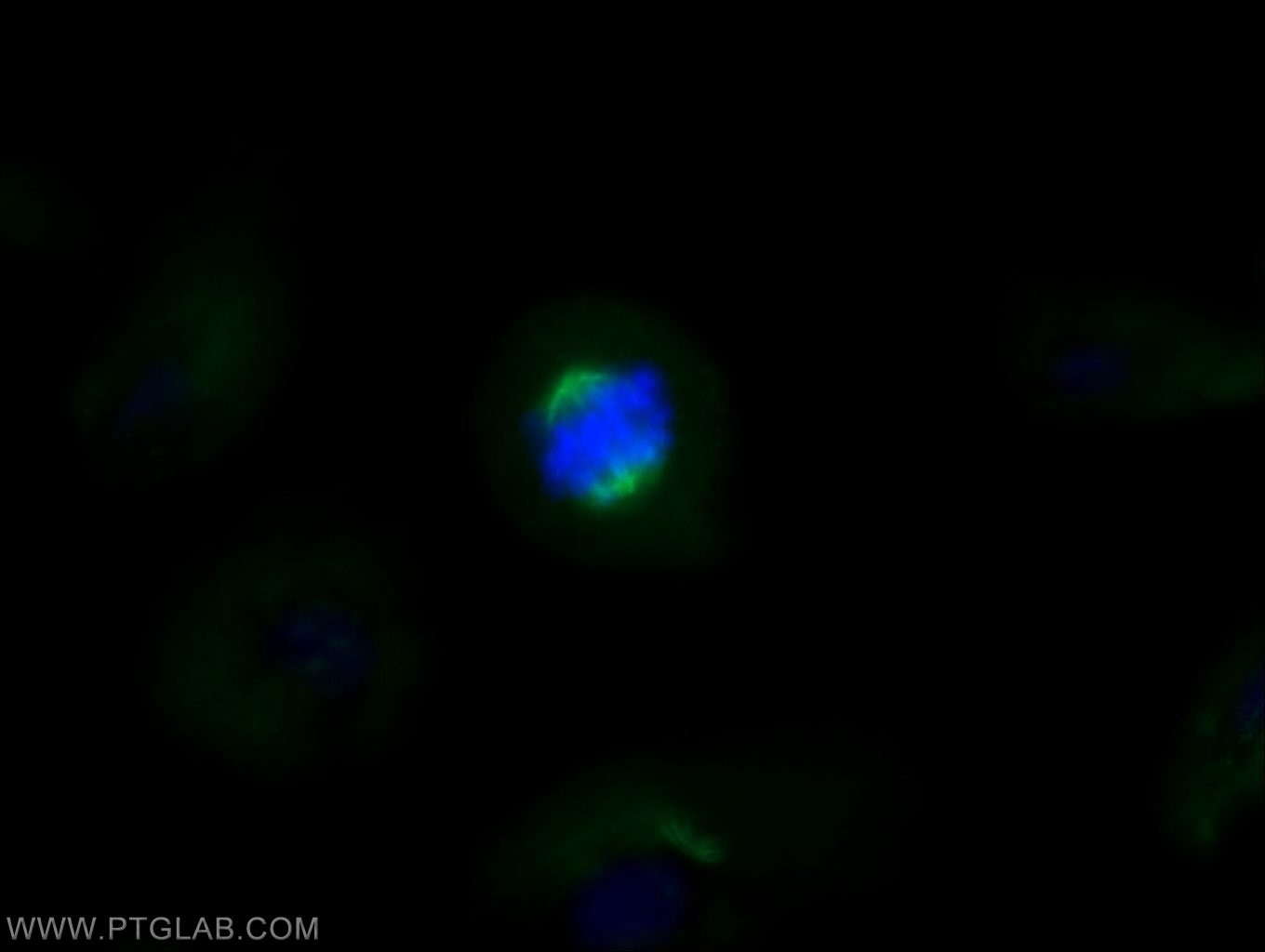
Acetyl-Tubulin (Lys40) Monoklonaler Antikörper
Acetyl-Tubulin (Lys40) Monoklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
Hausschwein, human, Hund, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
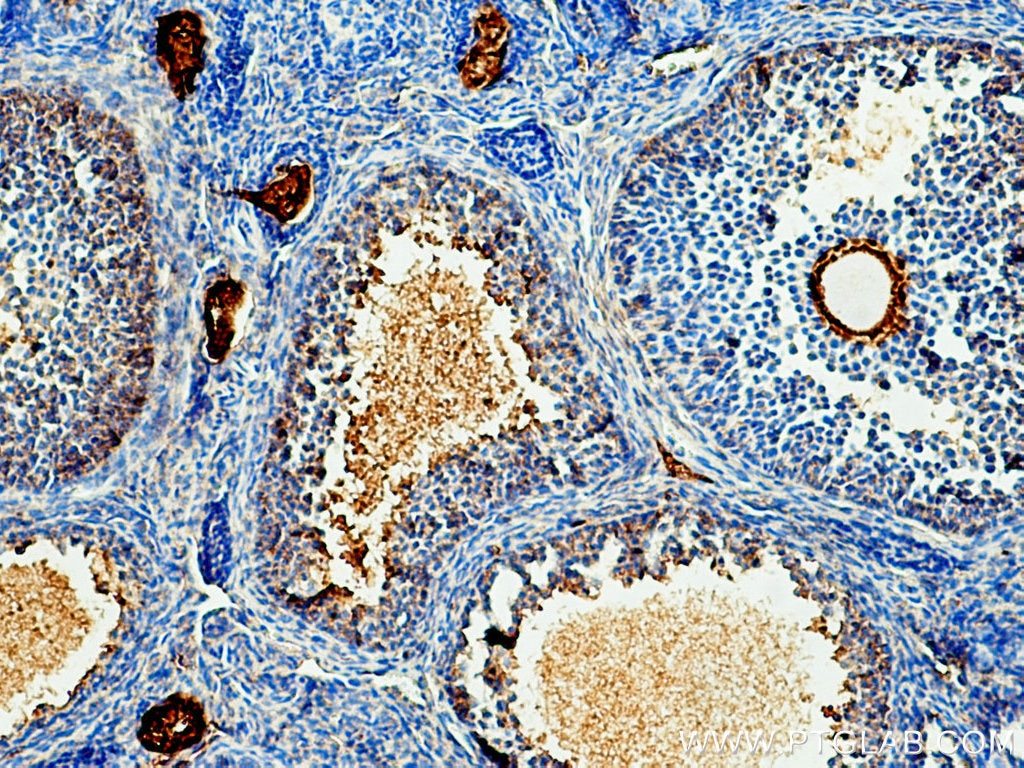
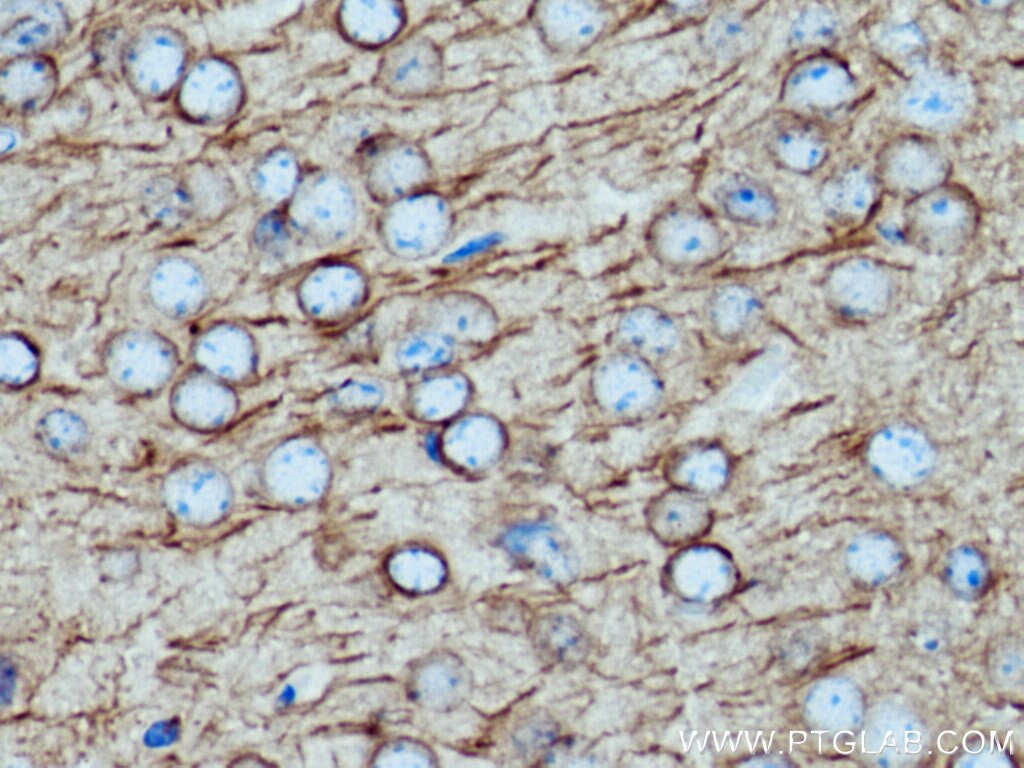
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA, Indirect ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
7E5H8
Kat-Nr. : 66200-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
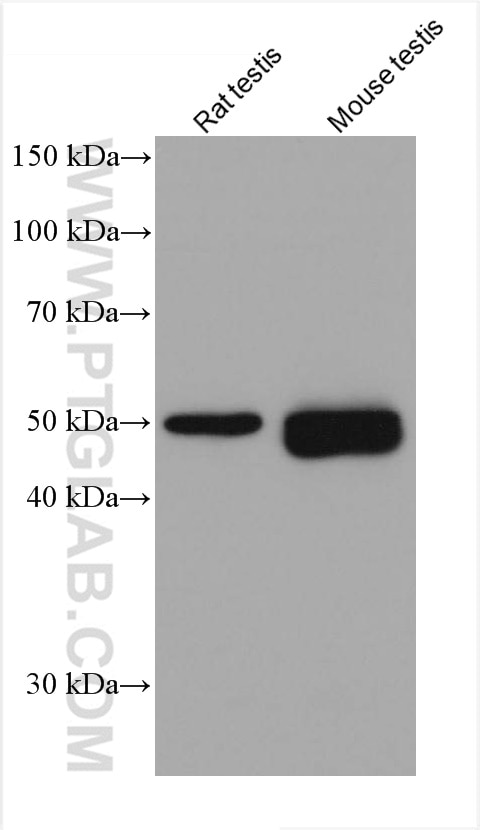
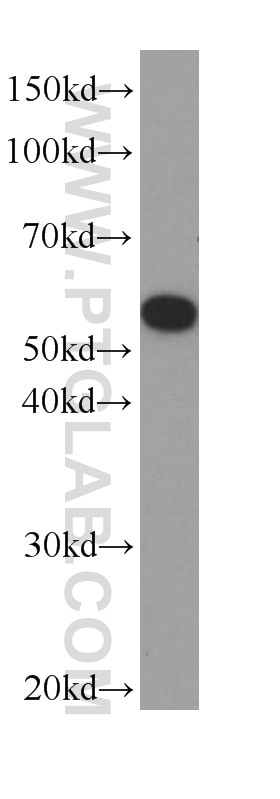
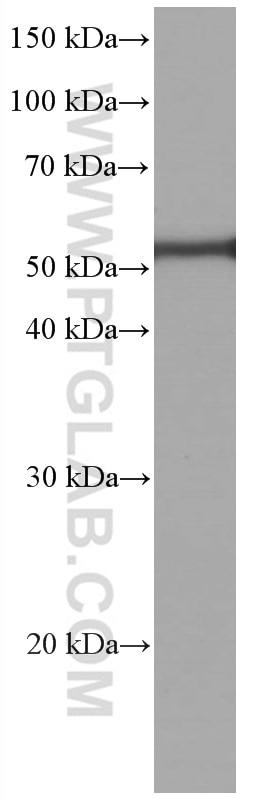
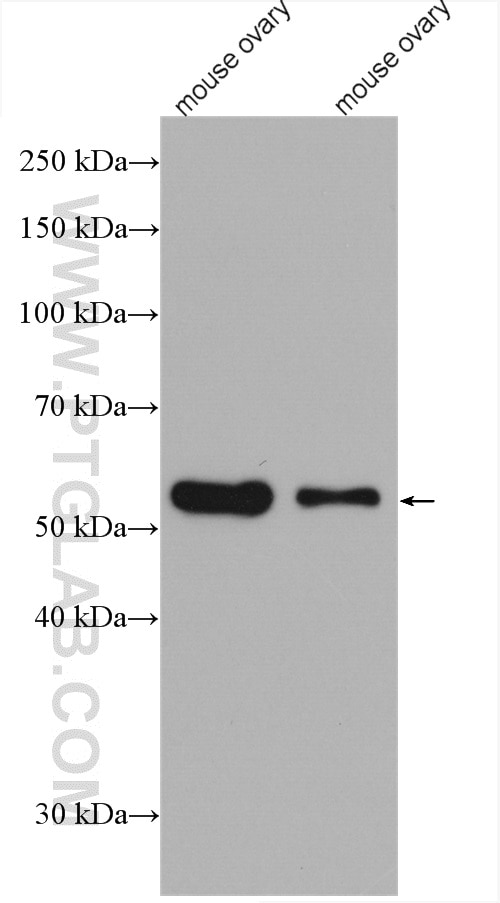
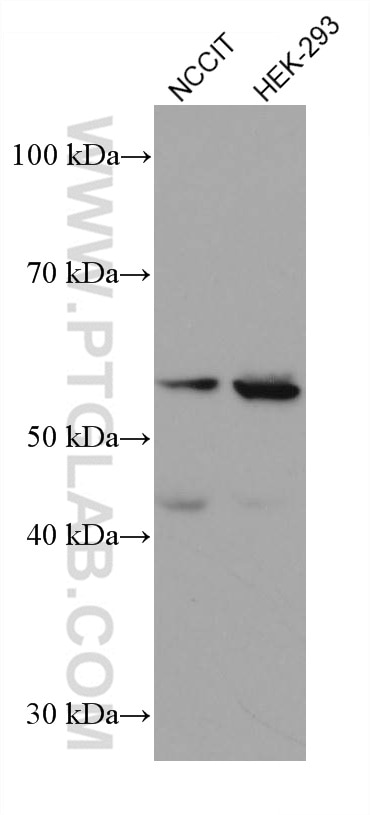
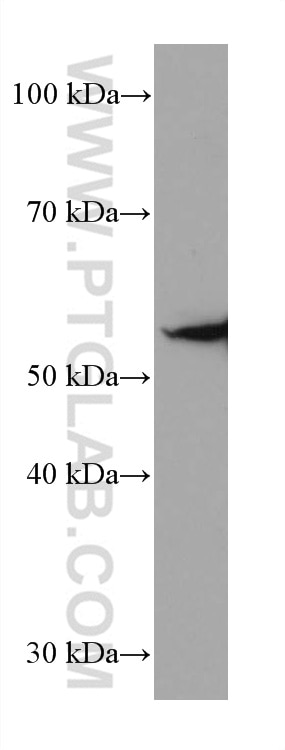
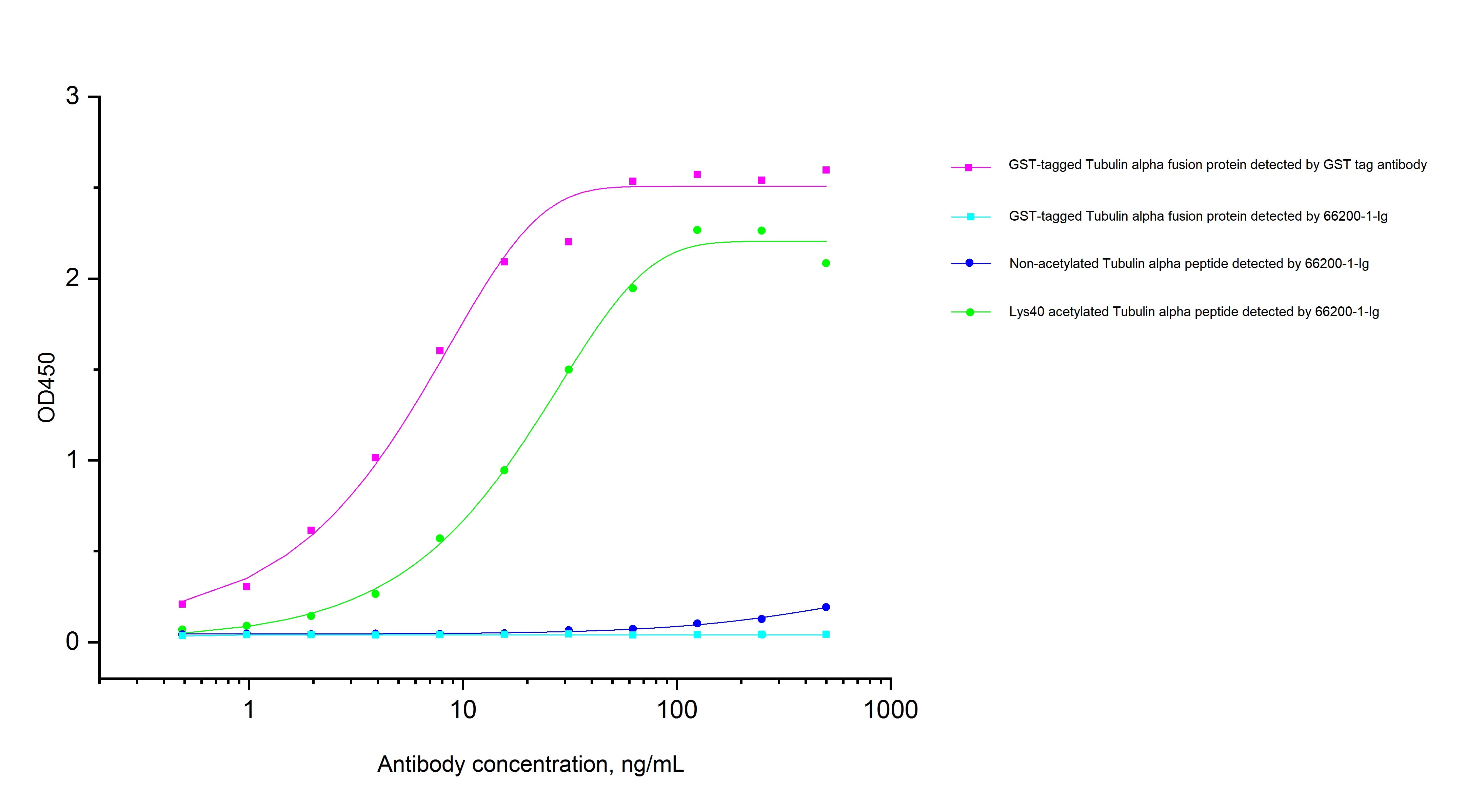
66200-1-PBS bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA, Indirect ELISA Acetyl-Tubulin (Lys40) und zeigt Reaktivität mit Hausschwein, human, Hund, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | Hausschwein, human, Hund, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | tubulin, alpha 1a |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 52 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_006009 |
| Gene symbol | Alpha Tubulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7846 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
What is the molecular weight of acetyl-α-tubulin?
The molecular weight of acetylated tubulin is 52 kD.
Where does the acetylation of Lys 40 occur?
This acetylation occurs inside the microtubule lumen by the α-tubulin acetyltransferase 1 (αTAT1) (PMID: 29207274).
How can acetylation be reversed?
Acetylation of Lys 40 can be reversed by deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), which is mostly cytoplasmic that also deacetylates Hsp90, and sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), which also mainly cytoplasmic and uses NAD as a coenzyme. Unlike HDAC6, SIRT uses both polymerized and soluble tubulin as substrates. Deacetylases are believed to be more active on soluble tubulin, while acetylases function preferentially on stable polymers (PMIDs: 29207274, 30079247, 19185337).
What is the function of acetylation?
Acetylation is a conserved post-translational modification of alpha tubulin at Lys 40 during tubulin assembly, and it correlates to increased microtubule stability and intracellular transport (PMIDs: 29207274, 30079247, 20940043).
Is acetylation of α-tubulin strictly associated with stable microtubules?
Not necessarily, as acetylation can have other effects on microtubule subpopulations (PMID 20940043).
Is ac-tubulin found only in cilia?
Acetylated-α-tubulin is located in cytoplasmic tubulin as well as in cilia; therefore, it is not strictly region-specific (PMID: 30079247).
What are the cellular effects of tubulin acetylation?
Microtubule acetylation seems to provide a critical role in neuronal development and function, and while its effect on cancer cells remains unclear, it has been shown that decreased acetylated α-tubulin impairs neuronal cell line migration. The post-translational modification may also help regulate organelle-independent signalling throughout the cell, supporting the notion of a microtubule network serving as a coordinator of cellular signaling (PMIDs: 29207274, 25503560, 20940043, 19185337).