- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
c-MYC Polyklonaler Antikörper
c-MYC Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
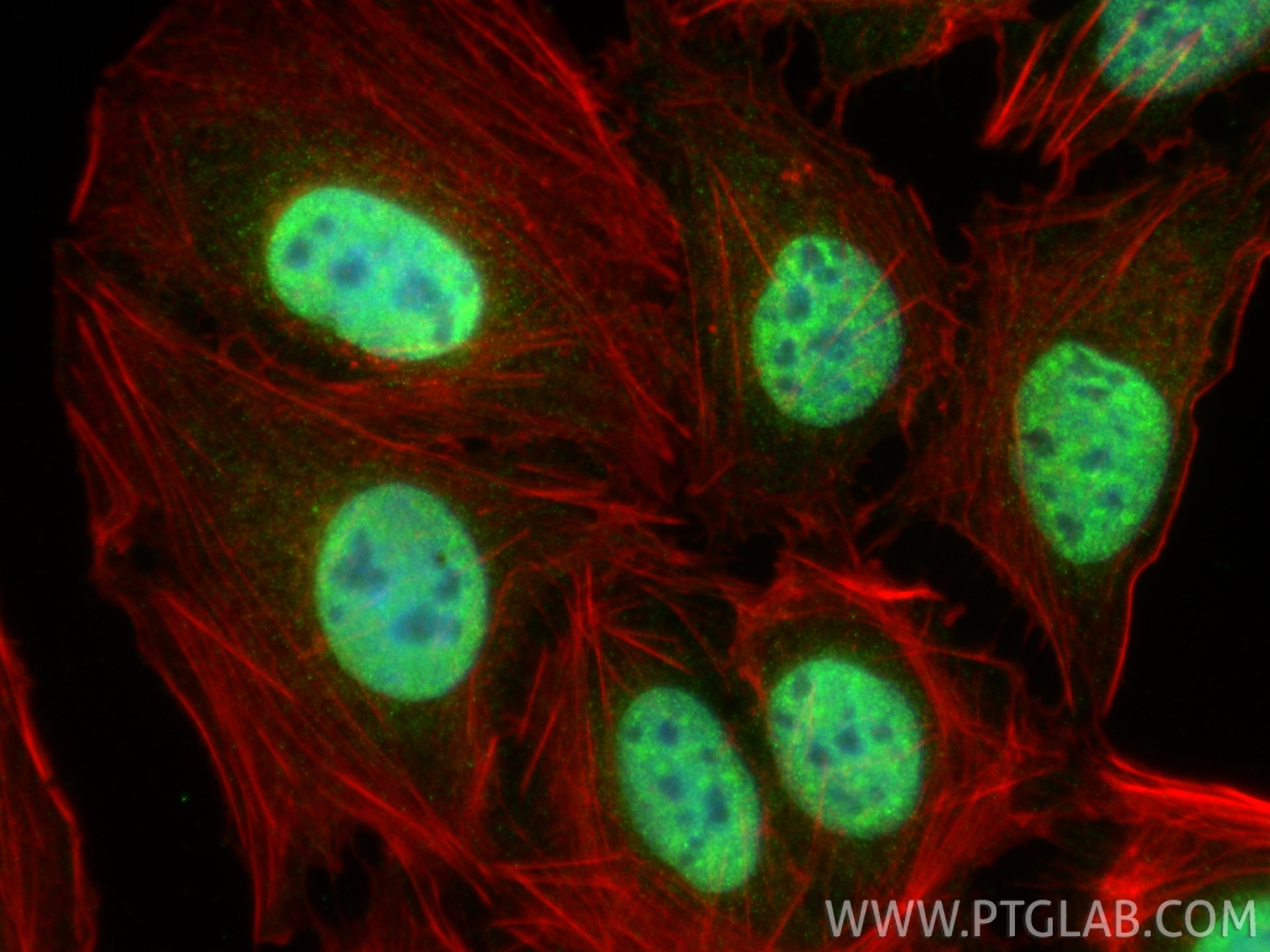
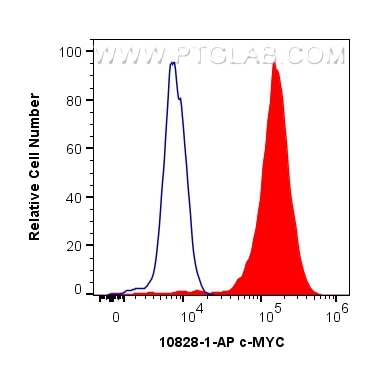
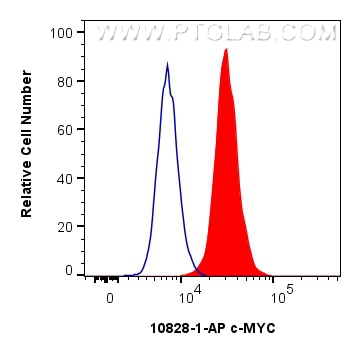
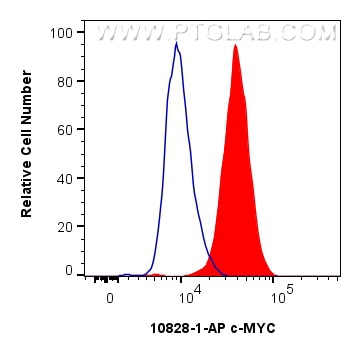
WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10828-1-PBS
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Produktinformation
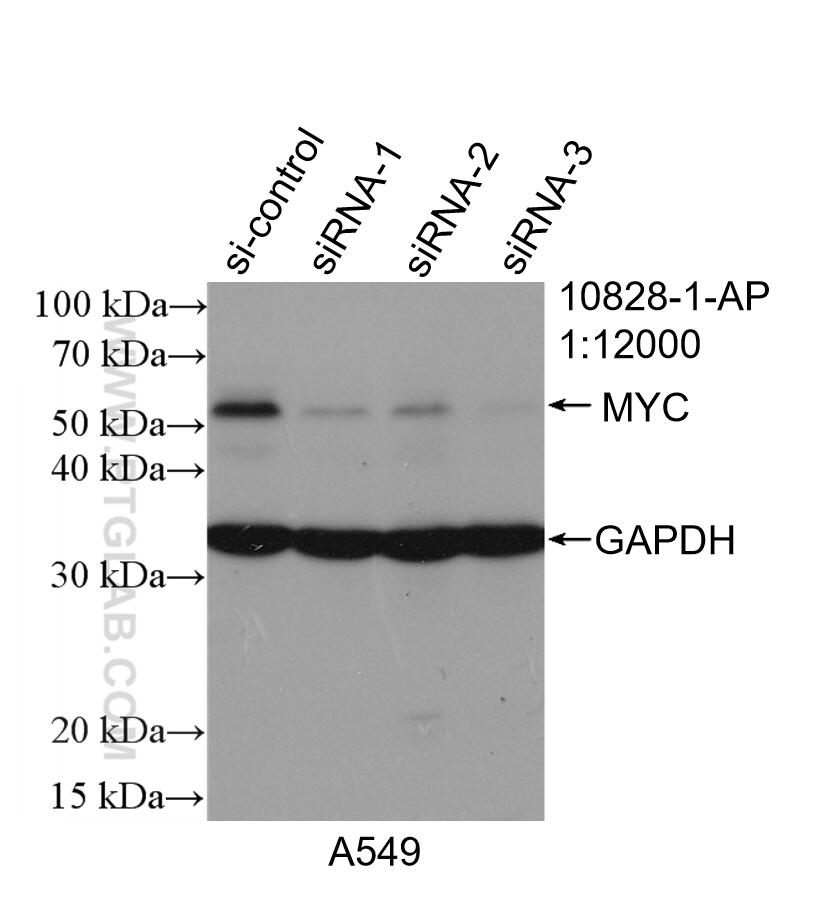
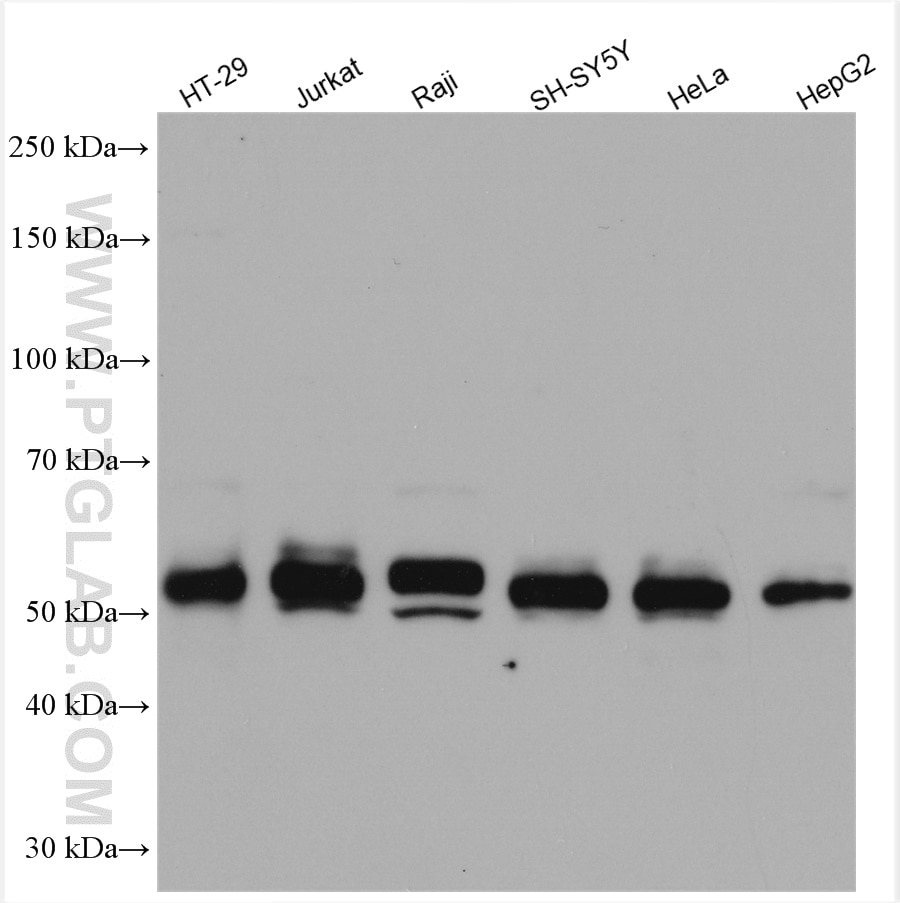
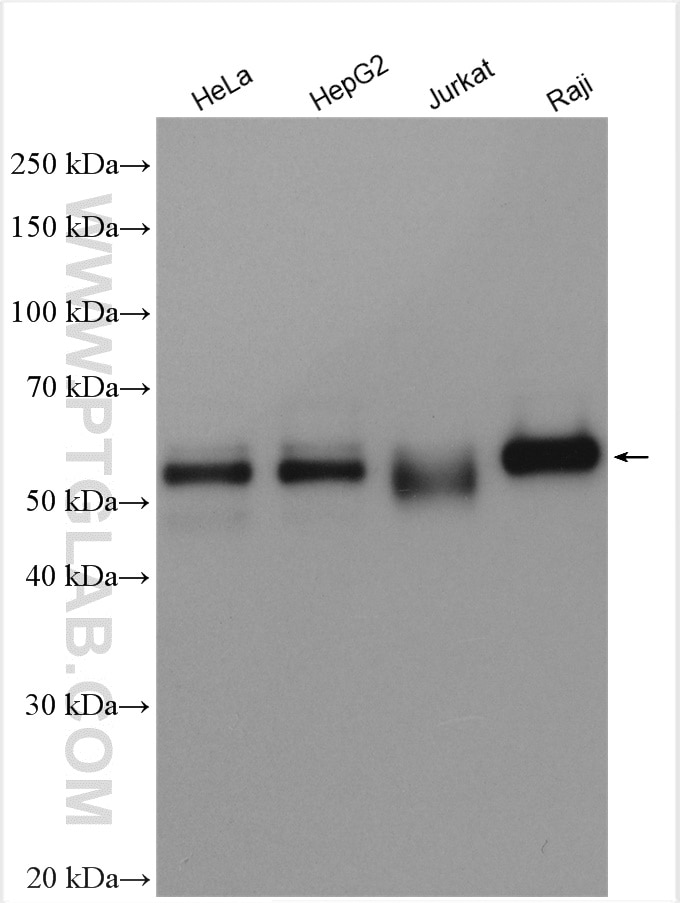
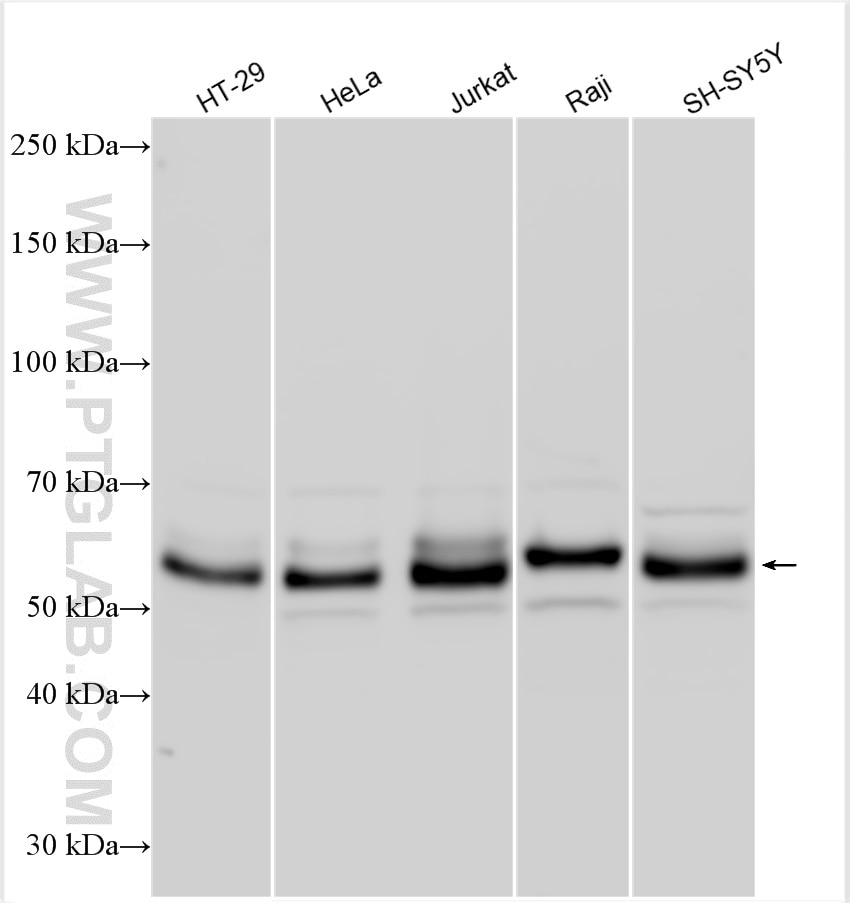
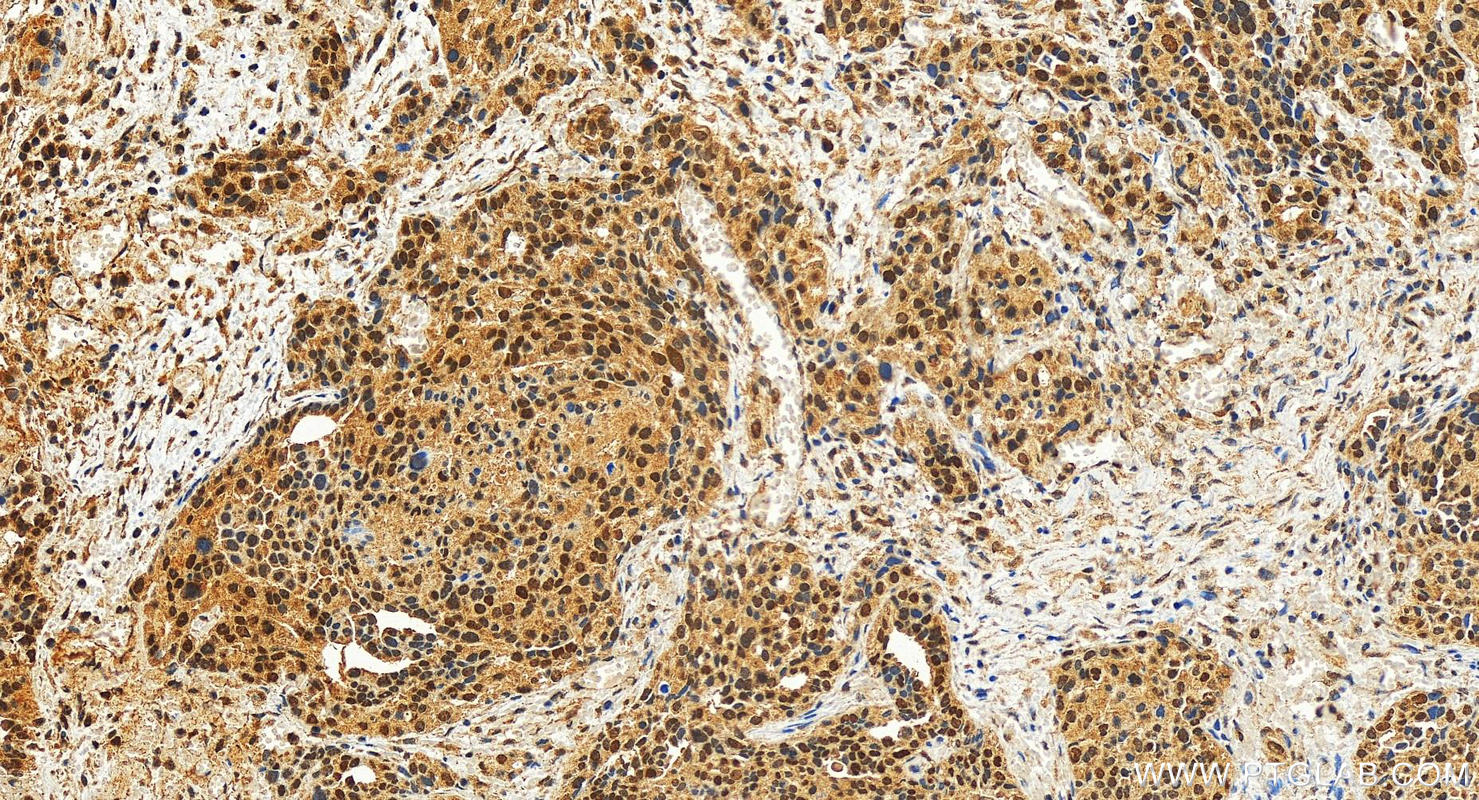
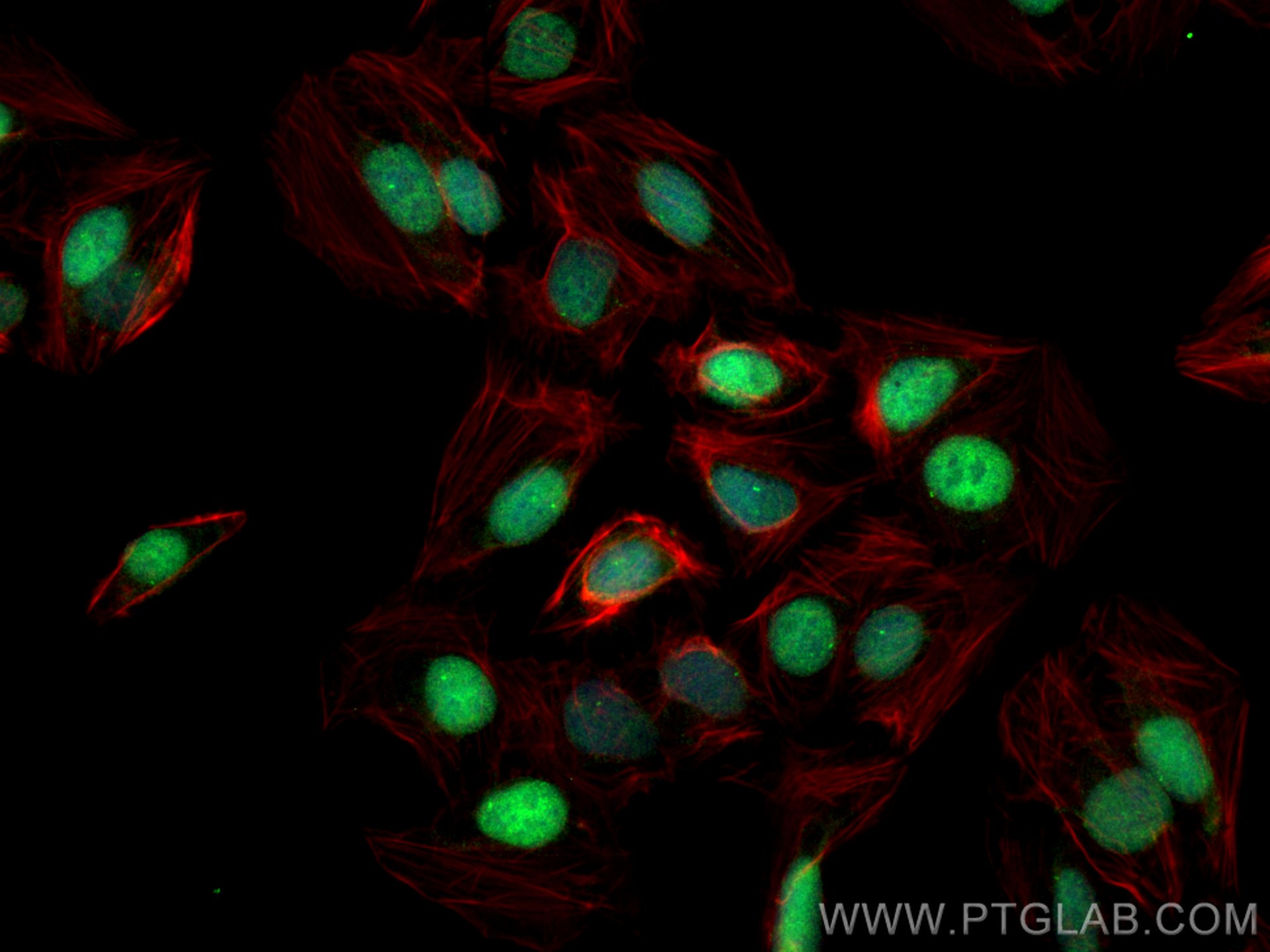
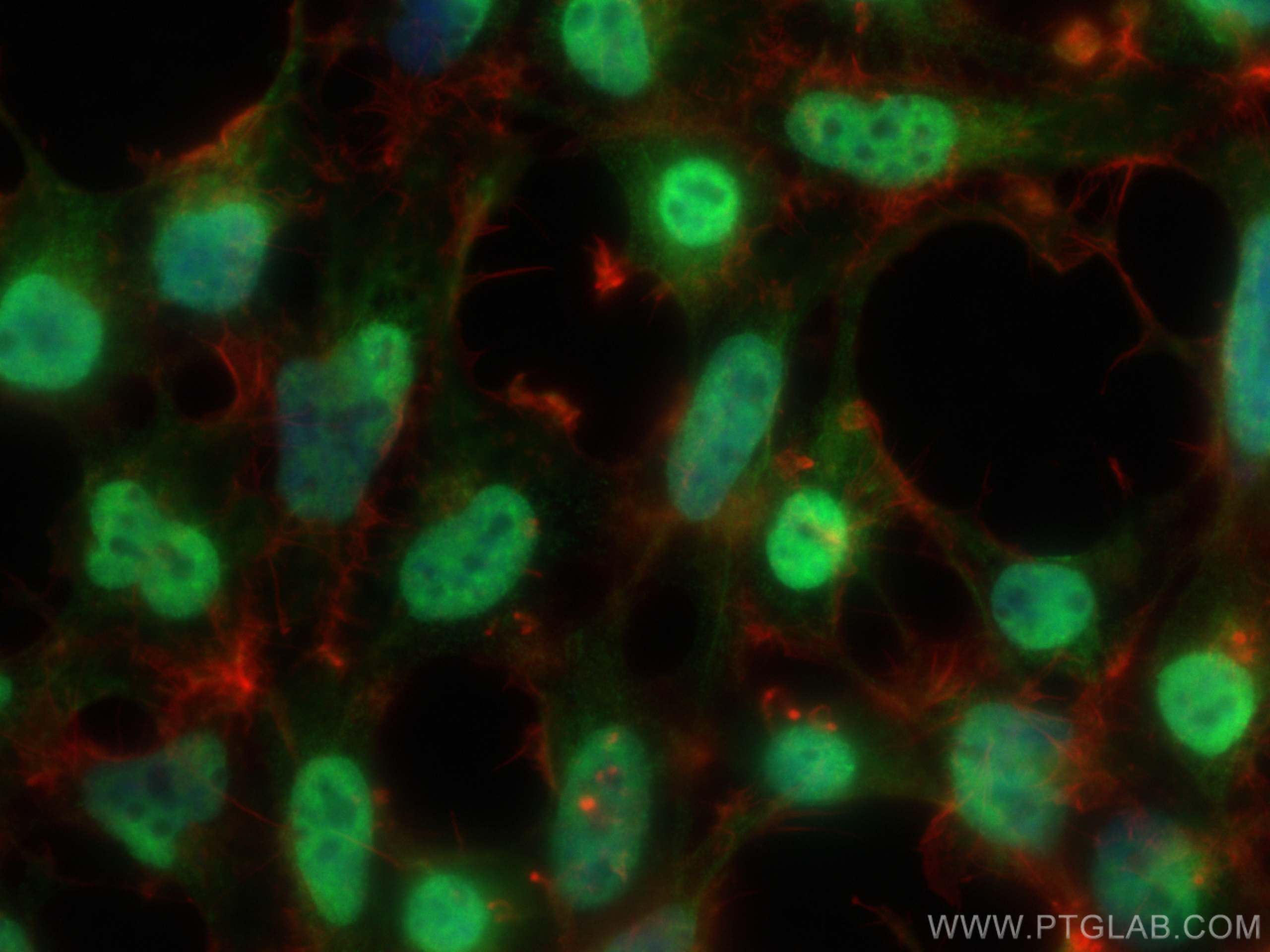
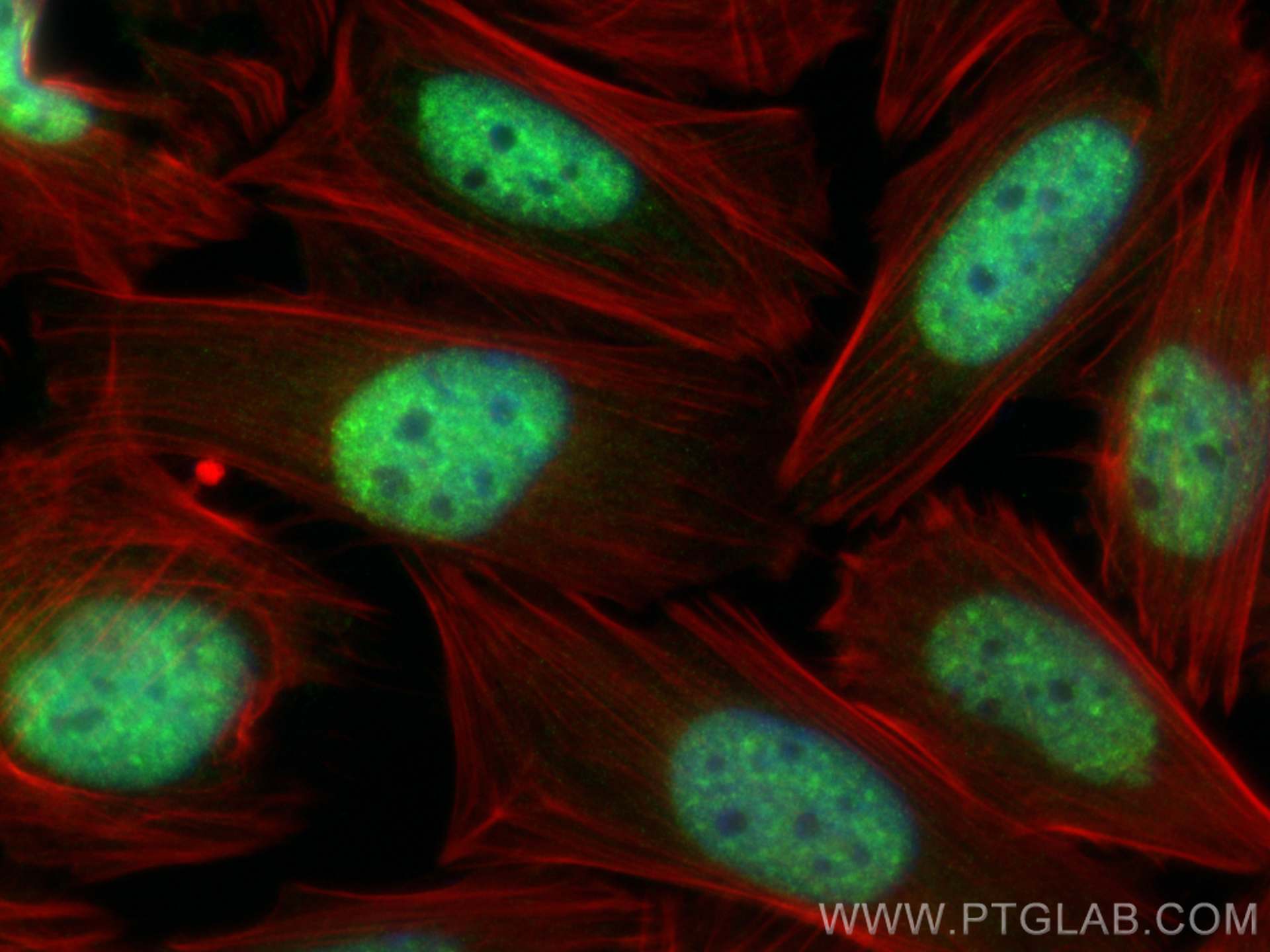
10828-1-PBS bindet in WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA c-MYC und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | c-MYC fusion protein Ag1263 |
| Vollständiger Name | v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 49 kDa |
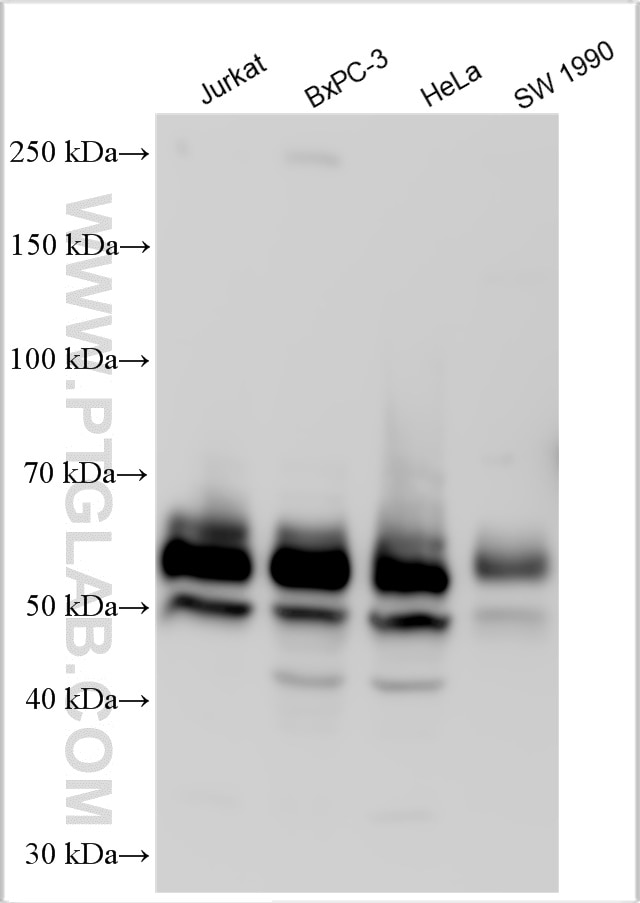
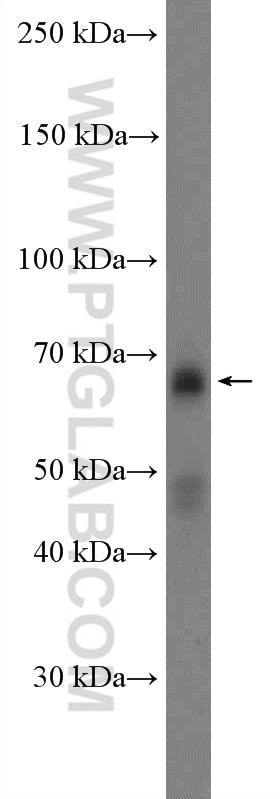
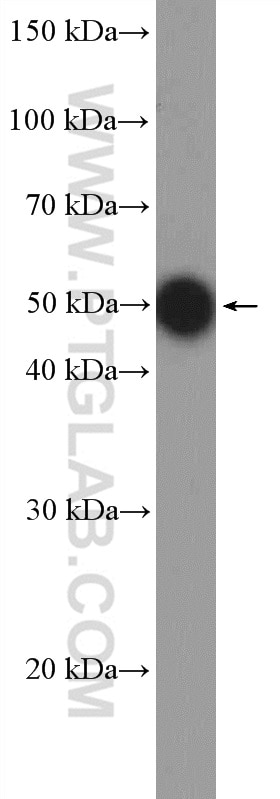
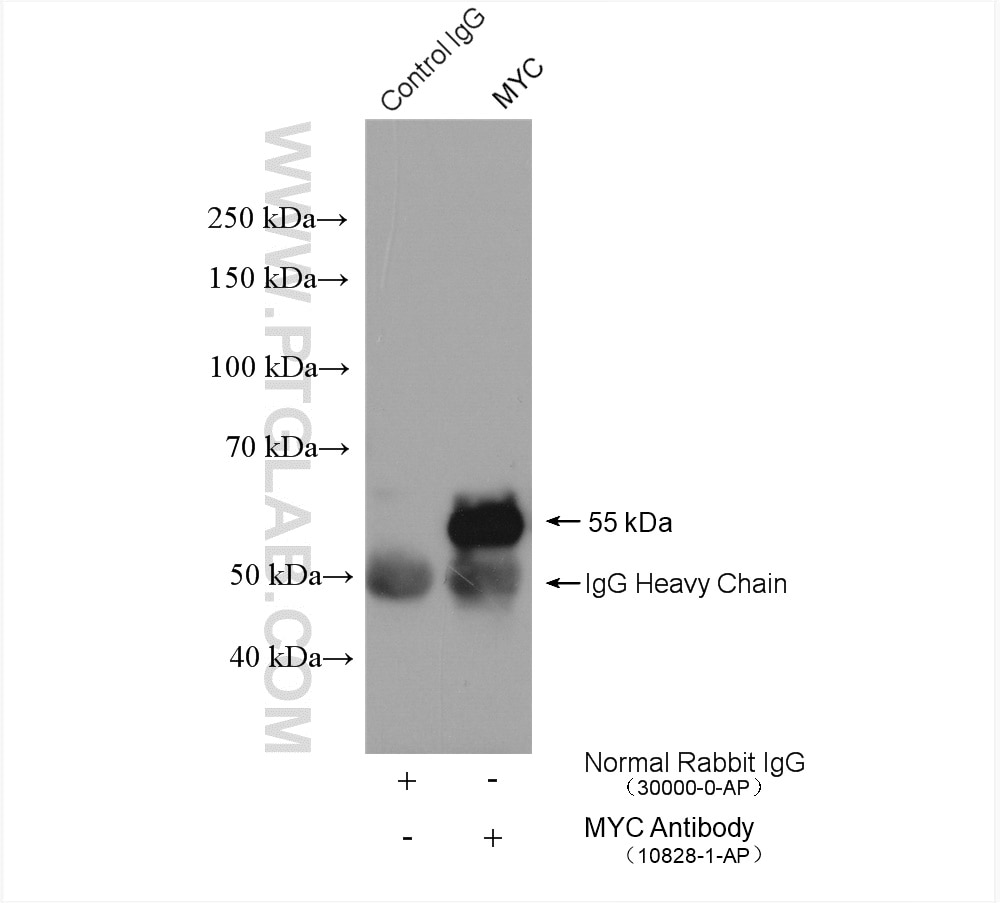
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 62-65 kDa, 50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC000141 |
| Gene symbol | MYC |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4609 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS only |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at -80°C. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Function
c-Myc (also known as Myc), together with l-Myc and n-Myc, belongs to the Myc family of transcription factors. c-Myc has a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper domain and through heterodimerization can bind and regulate the transcriptional activity of genes, either by repression or activation. It is a key player in the regulation of cell growth and cell cycle progression and acts as a proto-oncogene.
Tissue specificity
c-Myc is ubiquitously expressed in almost all cell types and its expression positively correlates with tissue proliferative capacity. c-Myc is also expressed during embryogenesis and is upregulated in many cancer types.
Involvement in disease
· Upregulated in many cancer types, especially in aggressive, poorly differentiated tumors.
· Mutations in the MYC gene and breakpoint translocations within the MYC gene cause Burkitt lymphoma.
Isoforms
There are 3 different isoforms of c-Myc: c-Myc1, c-Myc2, and c-MycS (PMID: 16260605). They differ in molecular size, can be preferentially expressed during cell growth, and are reported to be functionally distinct. The 50kDa band recognized by antibody is the native form of MYC, while the other bands, between 60-70kDa, are the phosphorylated form of MYC (PMID: 12189186).
Post-translational modifications
c-Myc is subject to various post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitinylation (PMID: 16987807), which regulate its activity.
Cellular localization
c-Myc localizes to the nucleus but can also be present in the cytoplasm of certain cancer types.