Anticorps Monoclonal anti-androgen receptor
androgen receptor Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1F7C12
N° de cat : 66747-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
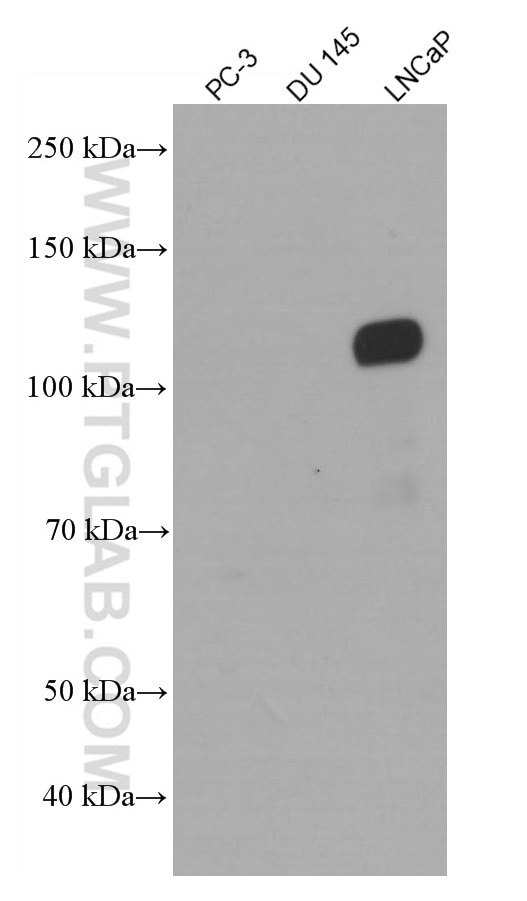
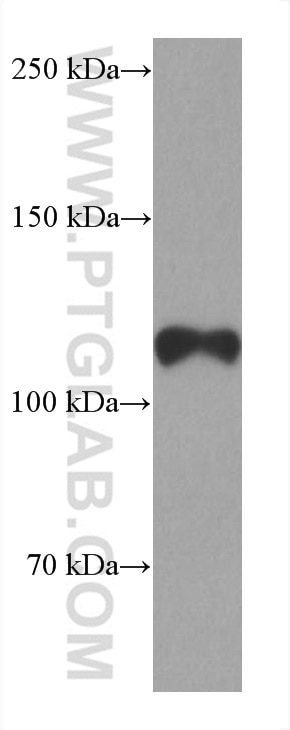
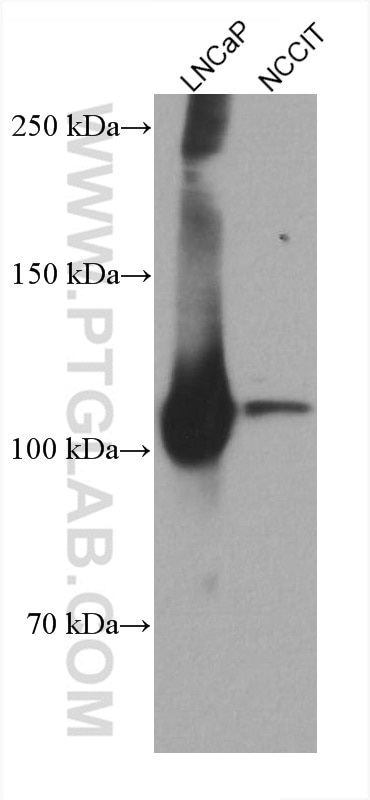
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules LNCaP, cellules NCCIT, tissu testiculaire humain |
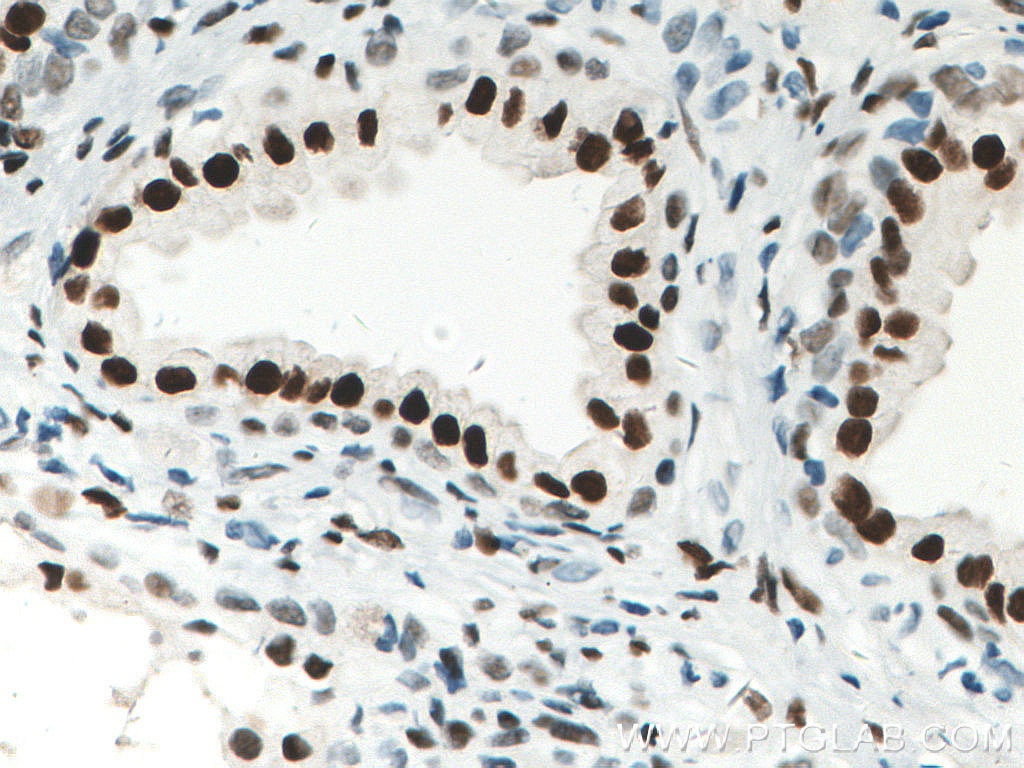
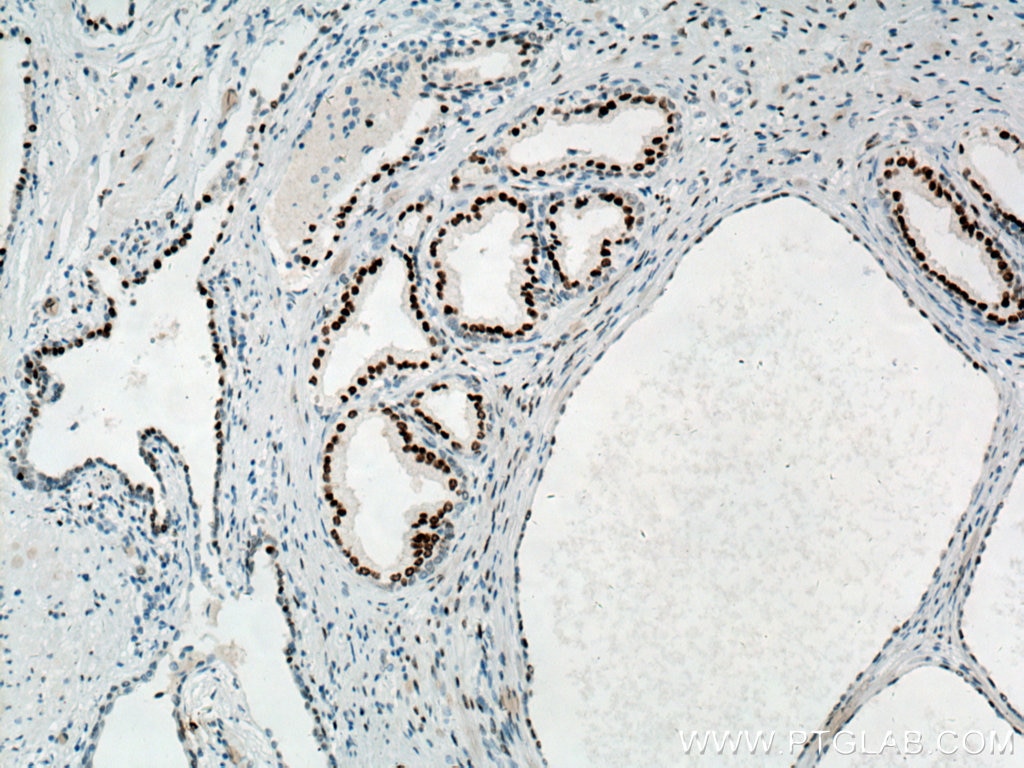
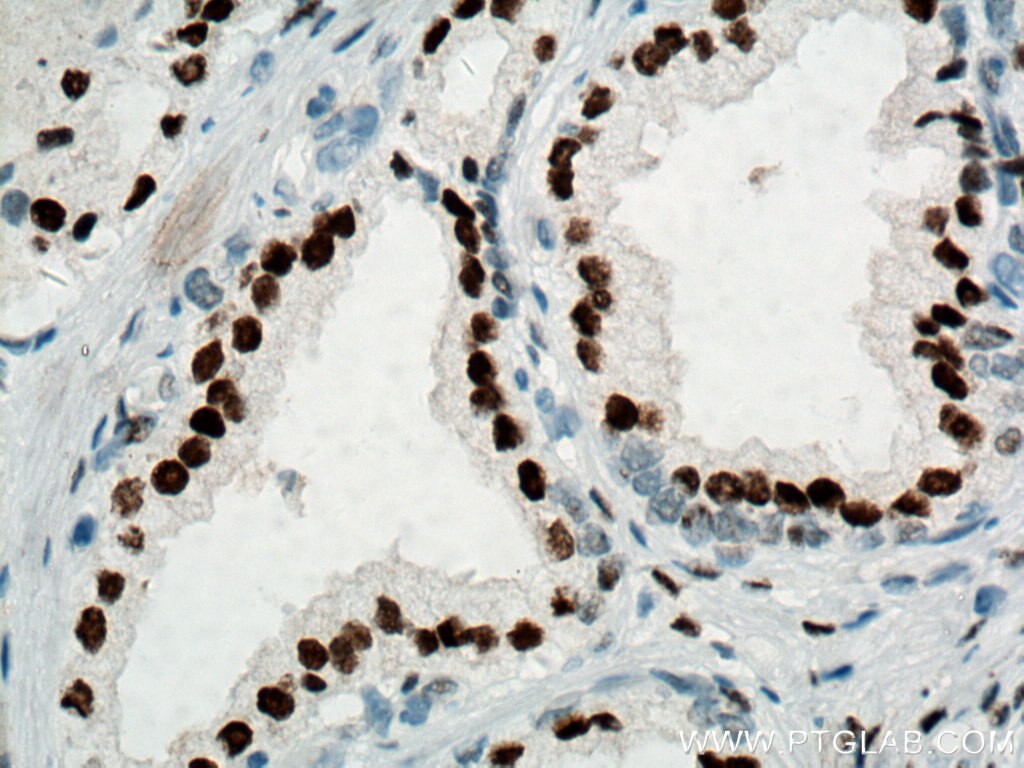
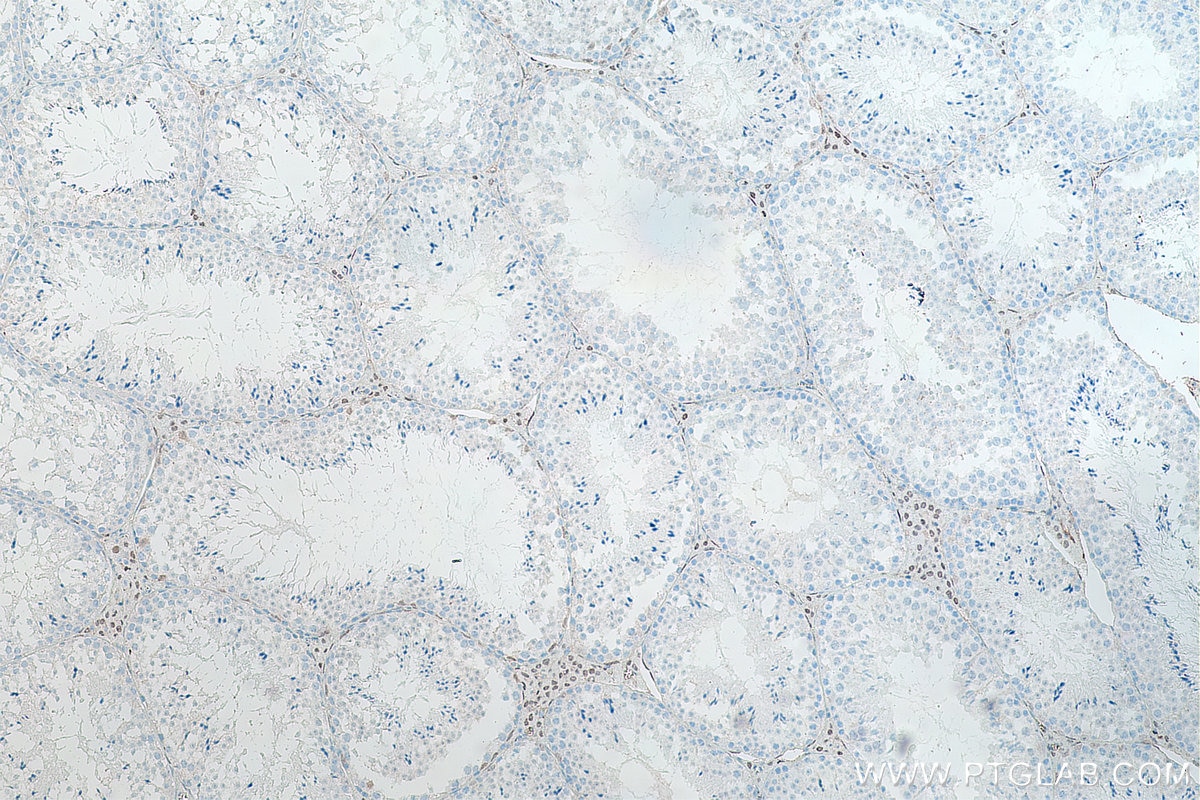
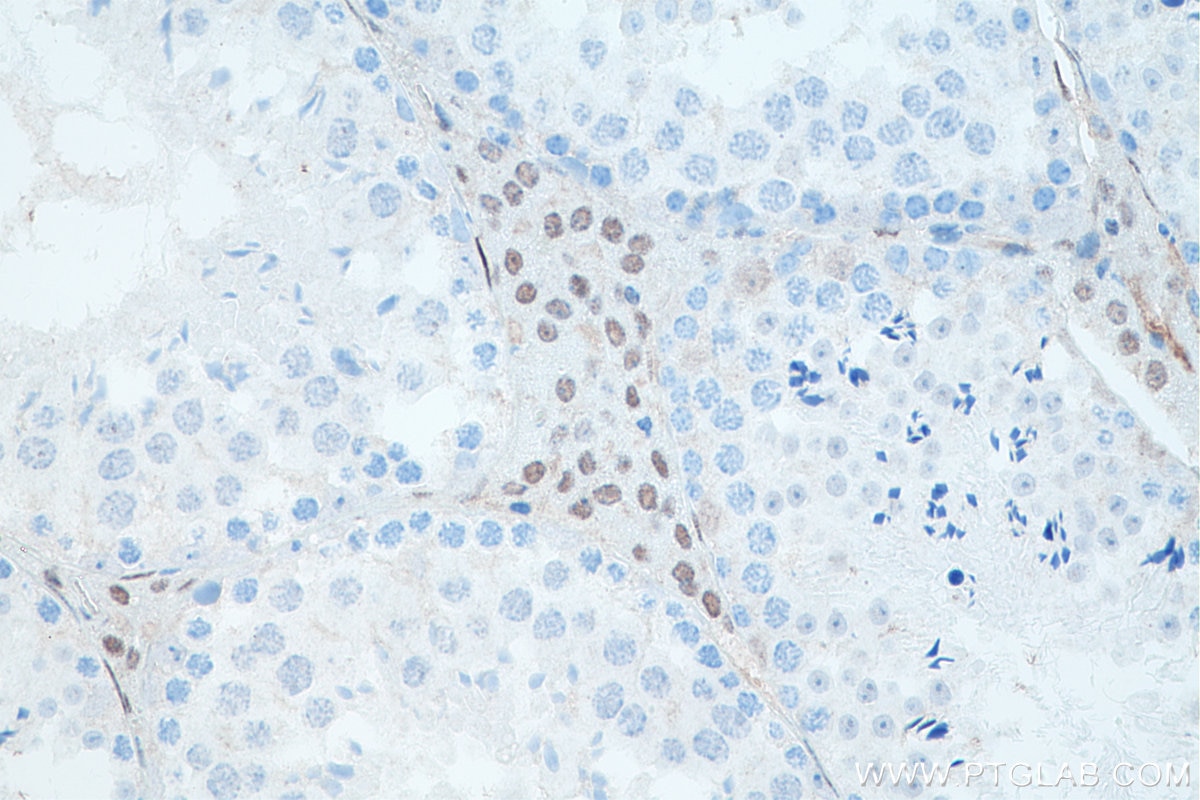
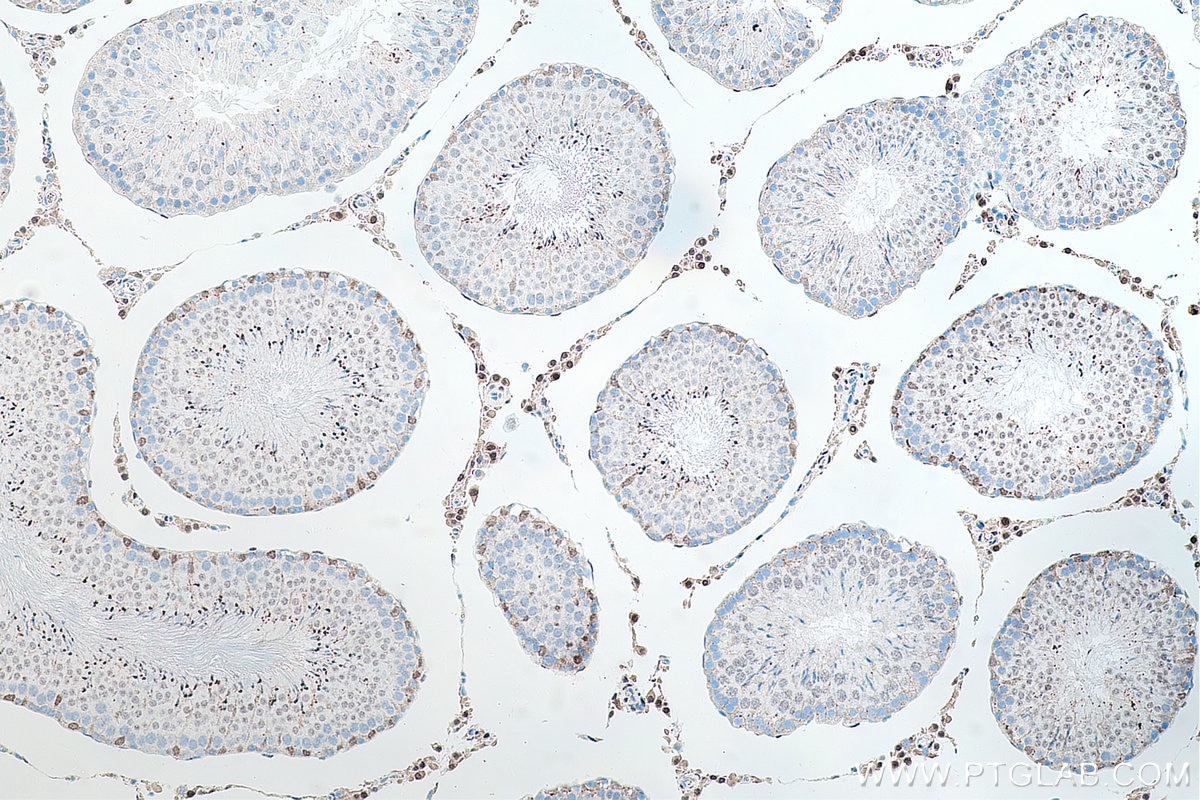
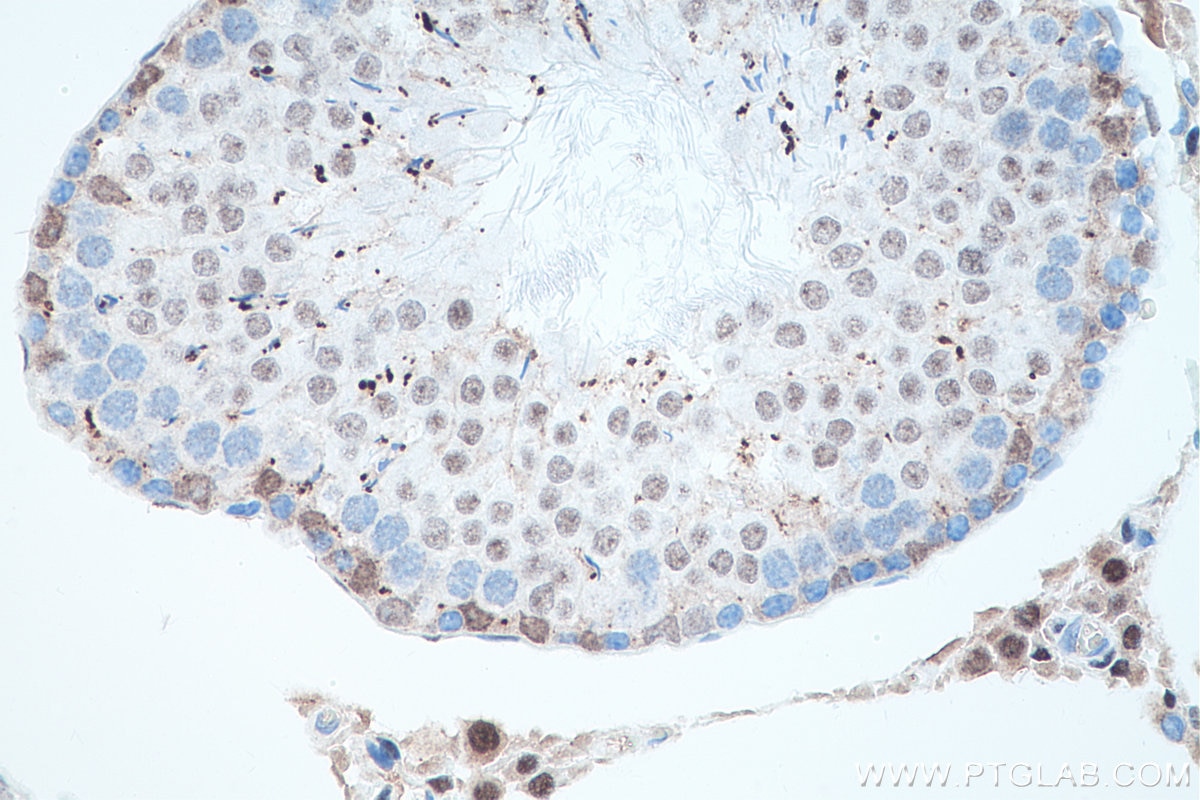
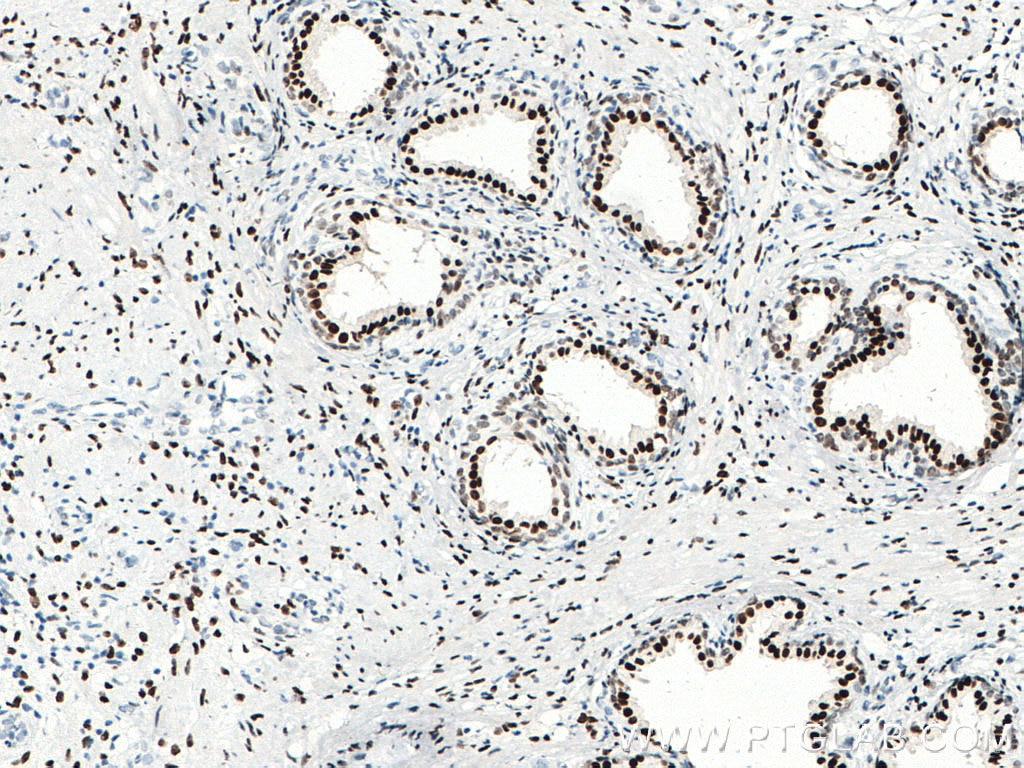
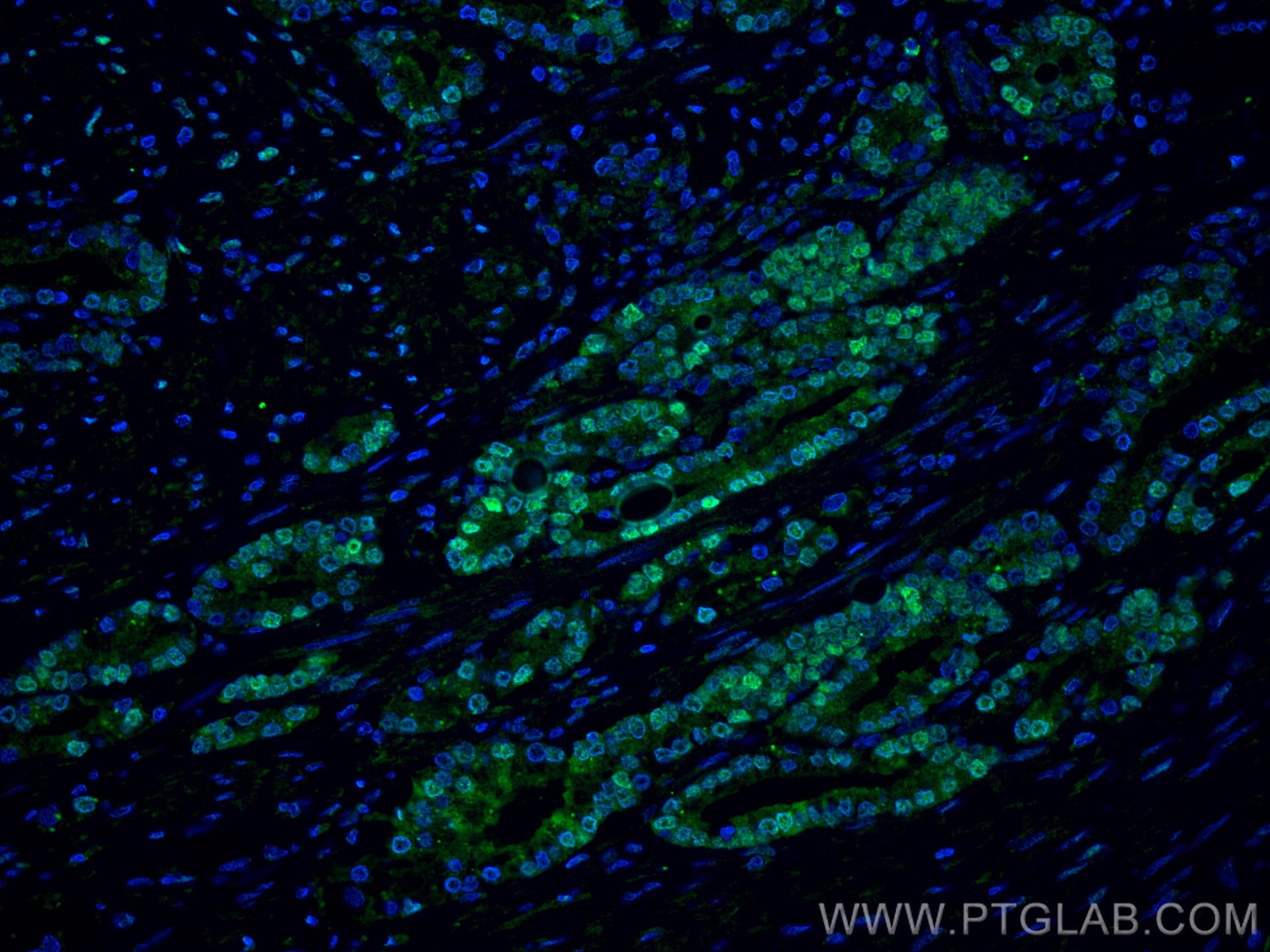
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer de la prostate humain, tissu testiculaire de rat, tissu testiculaire de souris il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
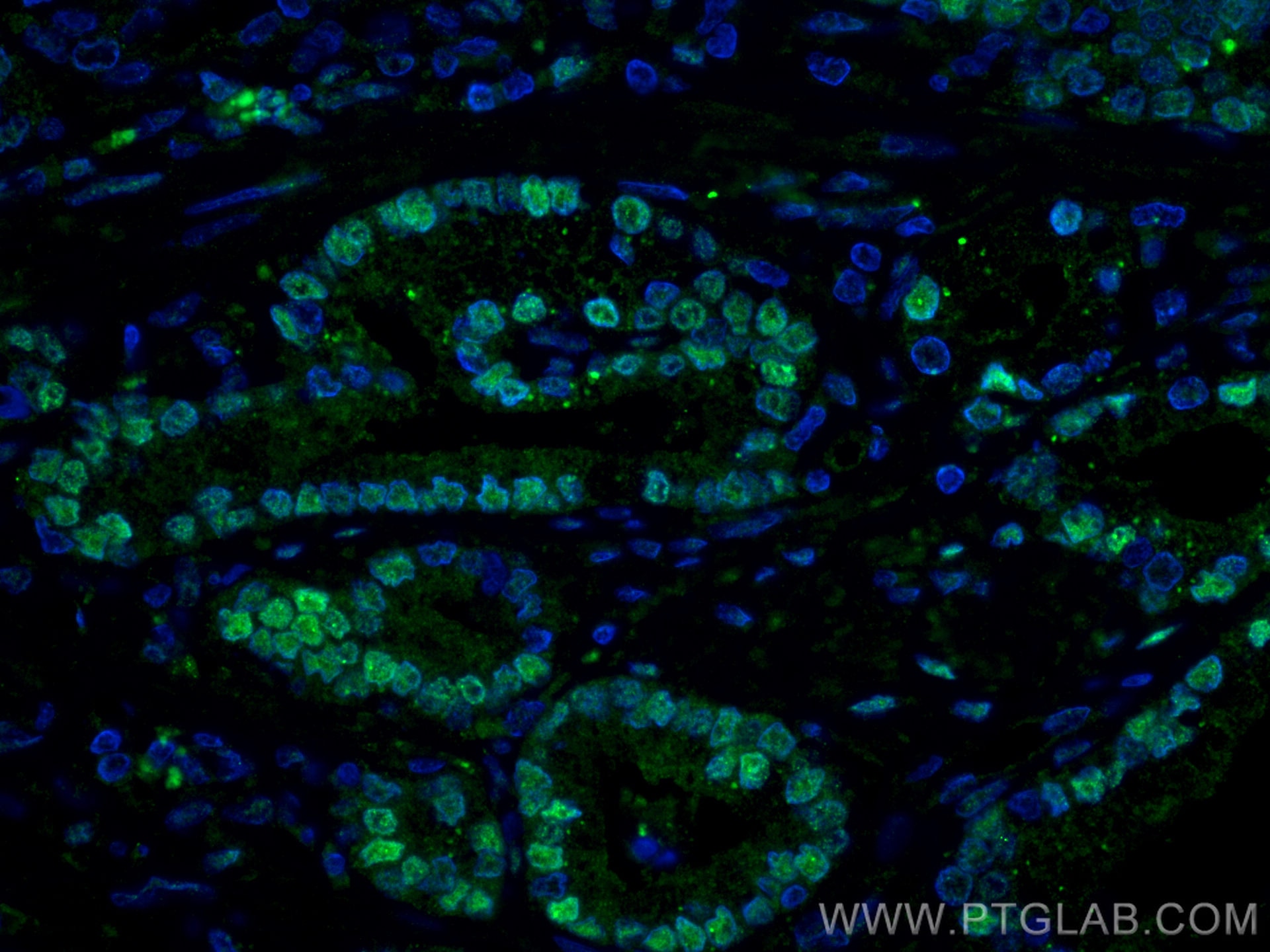
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu de cancer de la prostate humain |
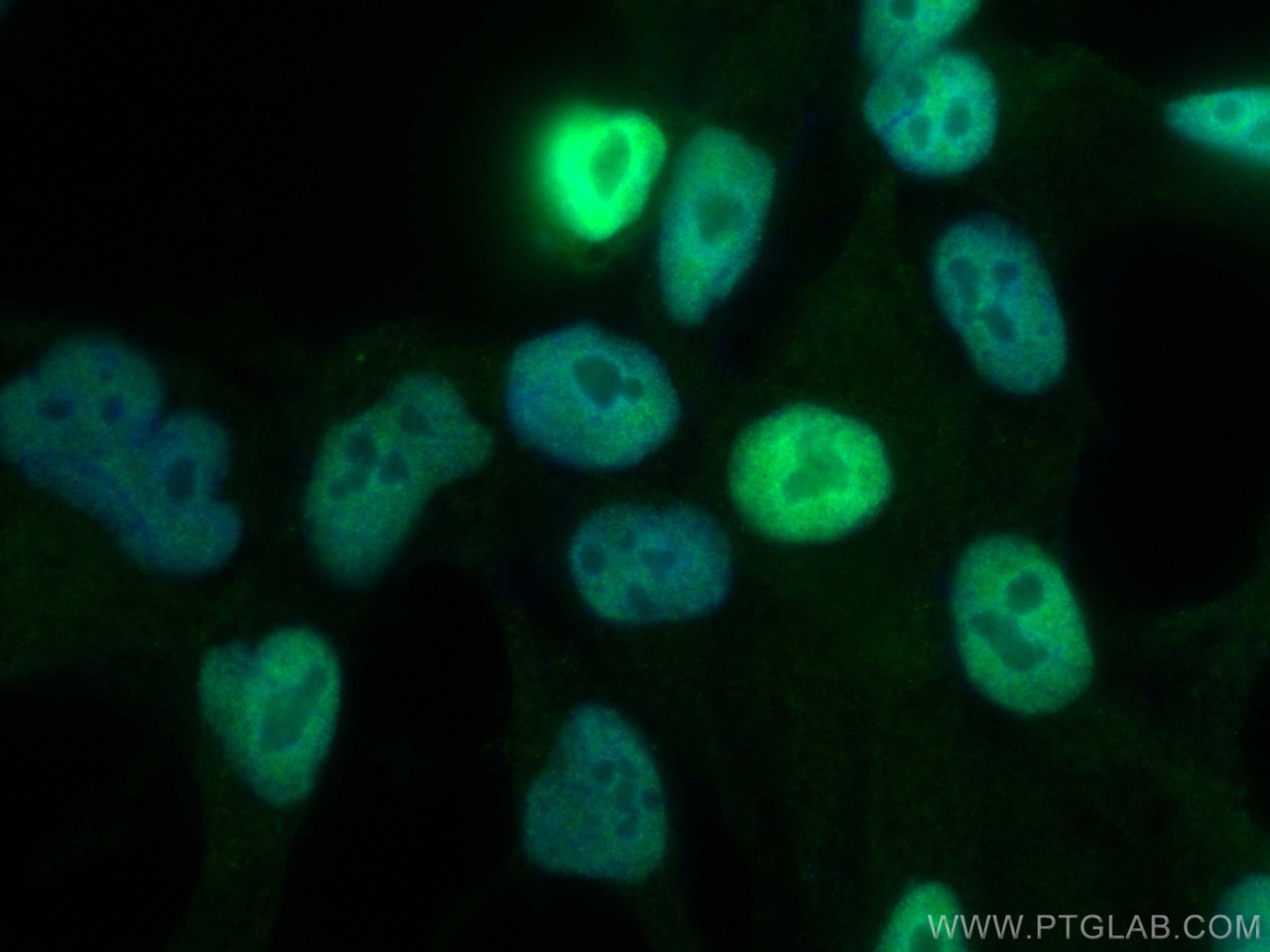
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules LNCaP, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:600-1:3000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:5000-1:20000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 7 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66747-1-Ig cible androgen receptor dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Chèvre, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | androgen receptor Protéine recombinante Ag17291 |
| Nom complet | androgen receptor |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 914 aa, 99 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 110-120 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC132975 |
| Symbole du gène | AR |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 367 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
AR, also named as DHTR and NR3C4, belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family and NR3 subfamily. AR is a ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins. AR is activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3. Defects in AR are the cause of androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS), previously known as testicular feminization syndrome (TFM), which is an X-linked recessive form of pseudohermaphroditism due end-organ resistance to androgen. Defects in AR are the cause of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy X-linked type 1 (SMAX1) which also known as Kennedy disease. Defects in AR may play a role in metastatic prostate cancer. Defects in AR are the cause of androgen insensitivity syndrome partial (PAIS) which also known as Reifenstein syndrome. AR exists various isoforms with MW 110-120 kDa and 75-80 kDa. (PMID: 19244107 )
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for androgen receptor antibody 66747-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for androgen receptor antibody 66747-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for androgen receptor antibody 66747-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Stem Cell Androgen Signaling Regulates SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Levels and Is Associated with Severe COVID-19 Symptoms in Men. | ||
Development Human prostate organoid generation and the identification of prostate development drivers using inductive rodent tissues | ||
Chin J Nat Med Eucommia lignans alleviate the progression of diabetic nephropathy through mediating the AR/Nrf2/HO-1/AMPK axis in vivo and in vitro | ||
iScience WTAP boosts lipid oxidation and induces diabetic cardiac fibrosis by enhancing AR methylation | ||
Gynecol Endocrinol N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO related to hyperandrogenism in PCOS via AKT pathway | ||
Psychoneuroendocrinology Effects of testosterone dose on depression-like behavior among castrated adult male rats |