- Phare
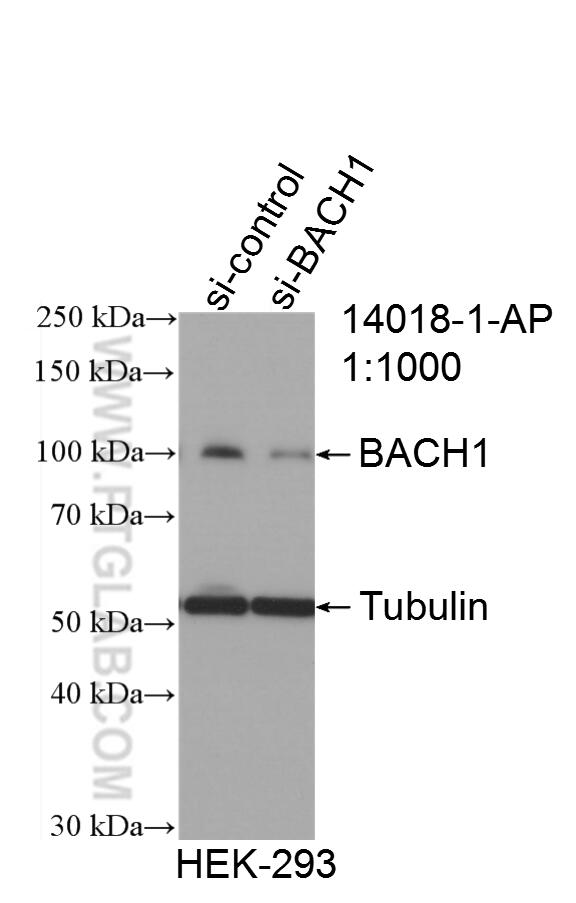
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-BACH1
BACH1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
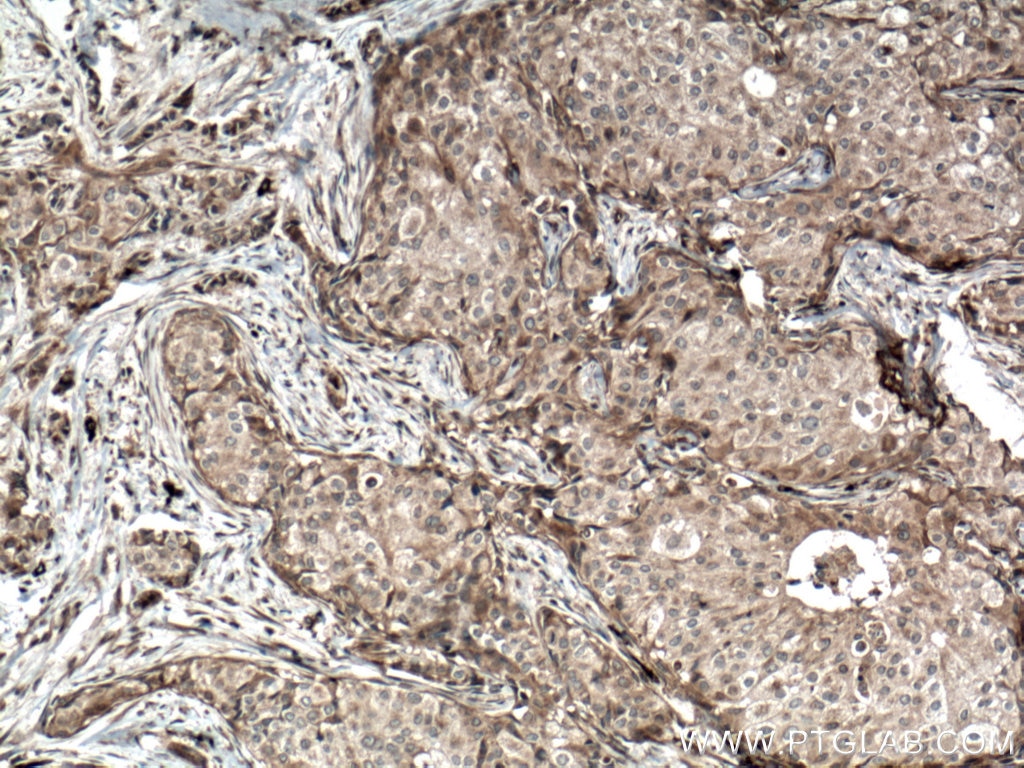
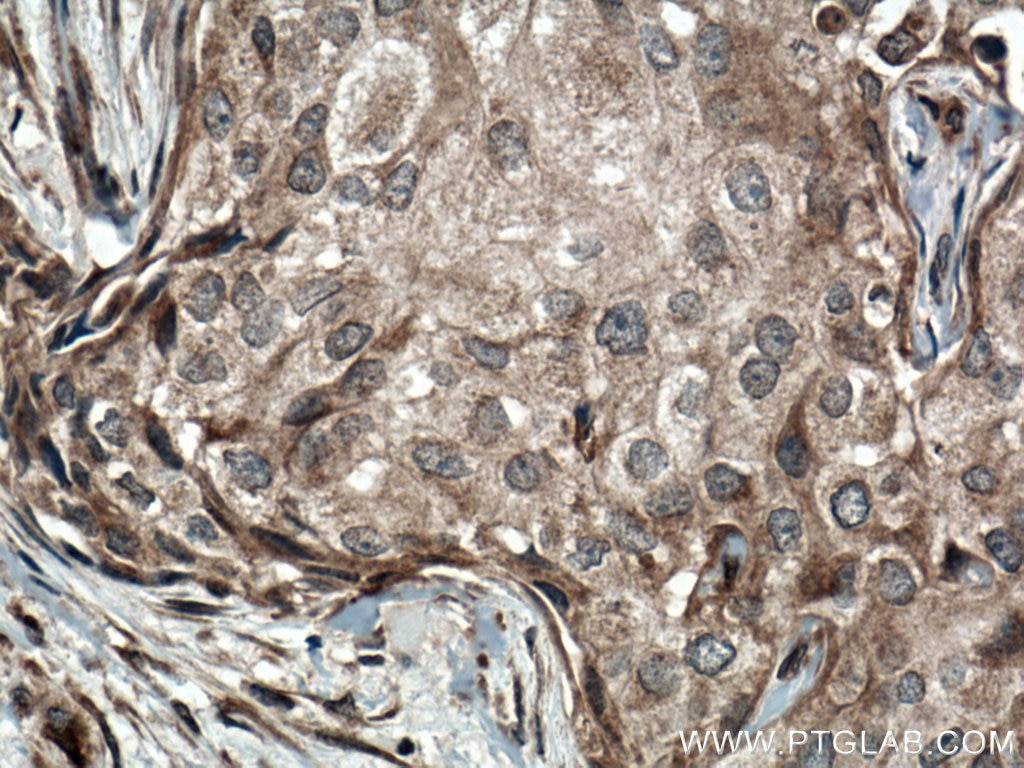
WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 14018-1-PBS
Synonymes
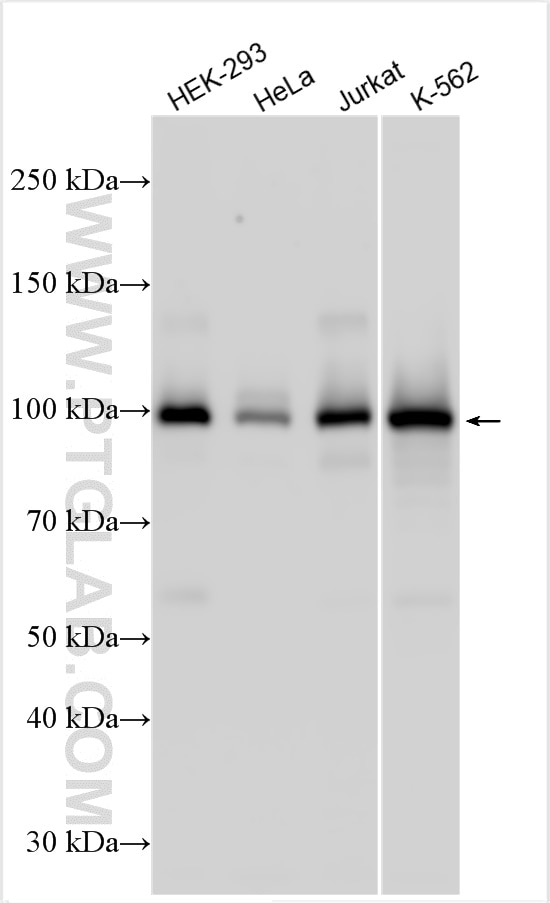
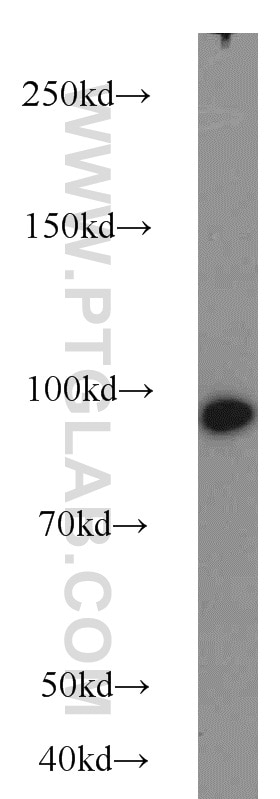
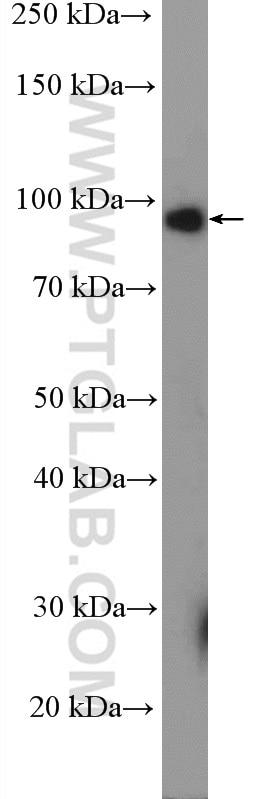
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
14018-1-PBS cible BACH1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | BACH1 Protéine recombinante Ag5128 |
| Nom complet | BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 82 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 100-110 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC063307 |
| Symbole du gène | BACH1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 571 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
BTB and CNC homology 1 (Bach1) is a transcription factor expressed in many tissues, with key roles in cell cycle
regulation in homeostasis and in cancer in disease.
What is the molecular weight of BACH1?
Bach1 consists of 736 amino acids and is a member of the cap'n'collar type of basic region leucine zipper factor
family (CNC-bZip) with several atypical protein domains. Although its predicted MW is 82 kDa, it runs
anomalously at 100-110 kDa in SDS-PAGE.
What is the cellular localization of BACH1?
As it is a transcription factor, BACH1 is found in the nucleus of a number of mammalian cells, where it forms a
heterodimer with small Maf proteins. Once it has formed part of a heterodimer, BACH1 is able to bind to the
Maf recognition elements (MAREs) of target genes. During oxidative stress, BACH1 can be inactivated either by
heme or by cadmium, at which point it is exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where it localizes to
microtubules (PMID: 15809329).
What is the function of BACH1?
BACH1 regulates the production of reactive oxygen species, with many of its downstream targets such as heme
oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) (PMID: 12356737; PMID: 15734732) involved
in the oxidative stress response. When the cell undergoes oxidative stress, BACH1 is displaced by nuclear factor
(erythroid-derived2)-like-2 (Nrf2), as both compete in binding to the MAREs in target genes. BACH1 also plays a
role in cell proliferation and survival, as it regulates several cell cycle genes such as cyclin-dependent kinase 6
(CDK6) and BCL2-like 11 (BCL2L11).
What is the role of BACH1 in disease?
BACH1 has been described in a number of cancer types, including breast, prostate, and melanoma. The function
of BACH1 appears varied in these tissues, with evidence that it may both promote and repress metastasis,
influence epigenetics, and regulate the growth of cancer cells (PMID: 22875853; PMID: 28889753; PMID: 26787
892). BACH1 may act on the same gene in different contexts to repress or activate it (PMID: 8887638).