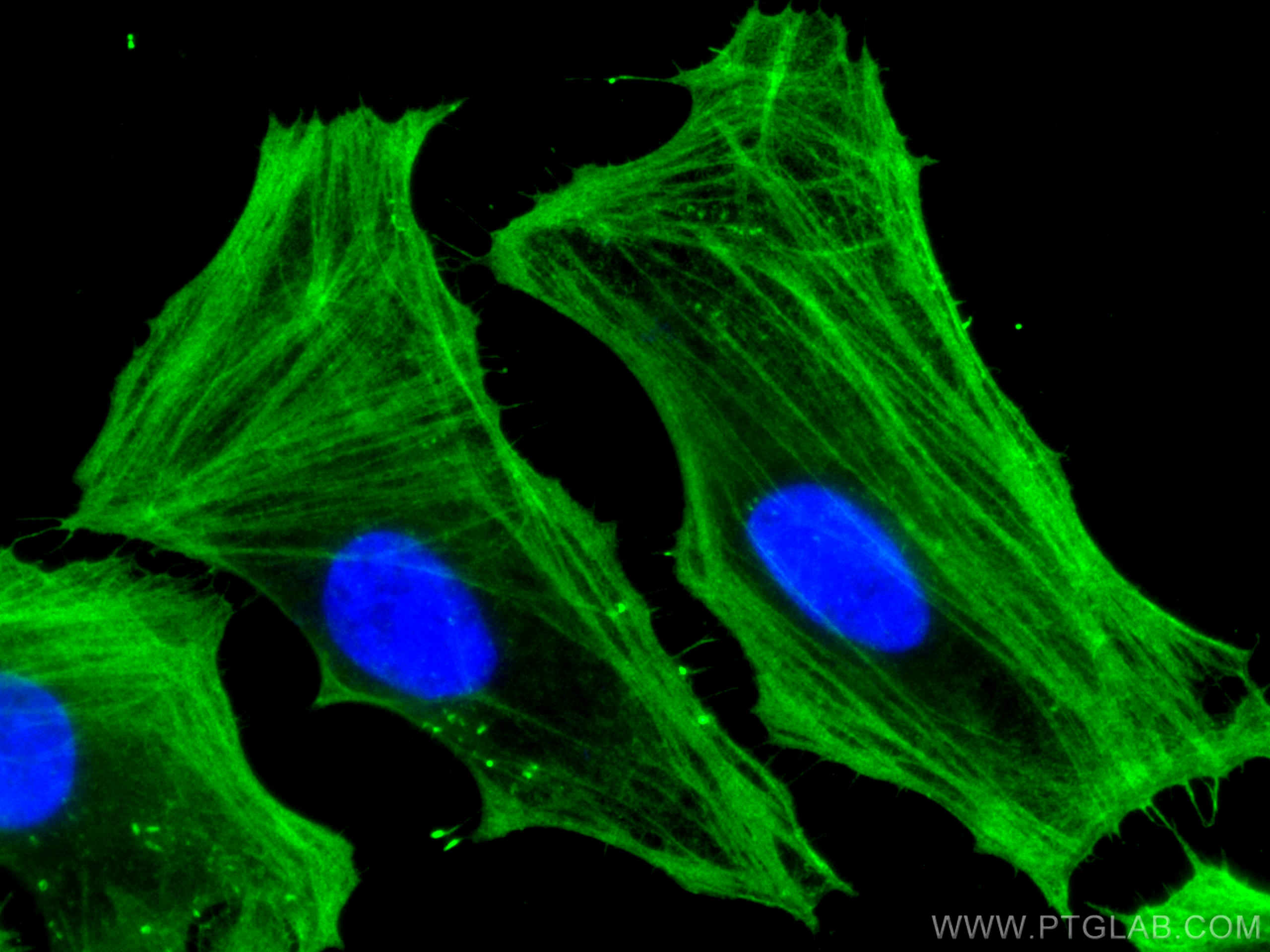
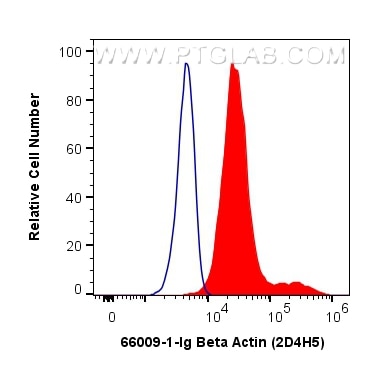
- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Beta Actin
Beta Actin Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
canin, Humain, Lapin, poisson-zèbre, porc, poulet, rat, singe, souris, Hamster
Applications
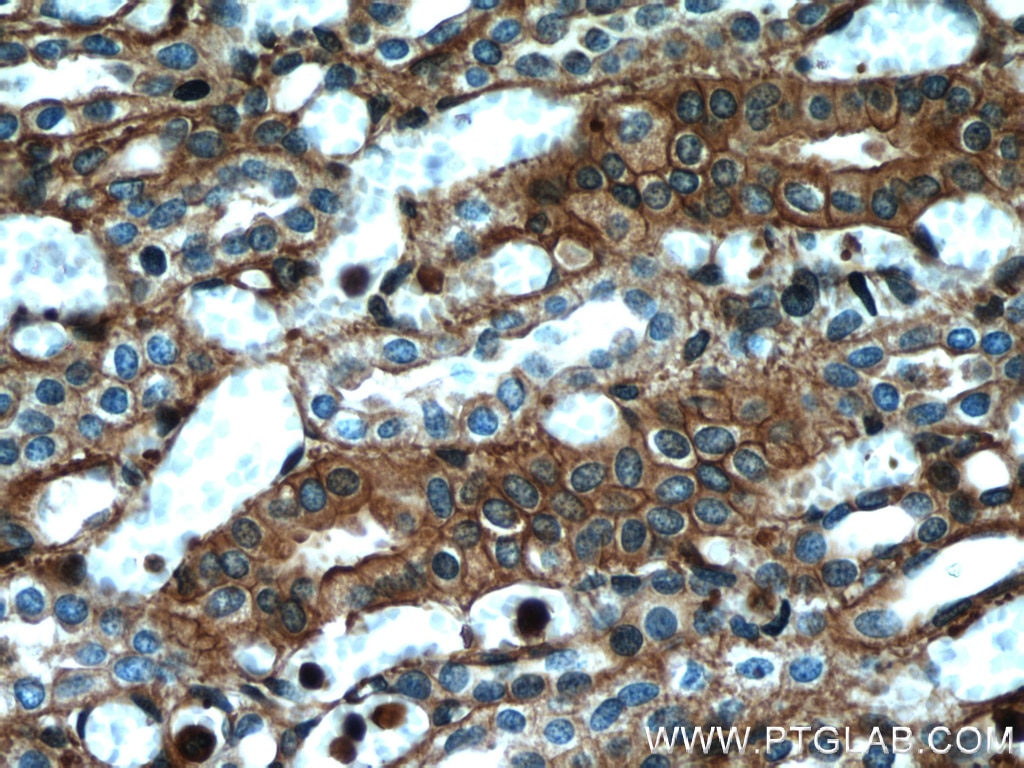
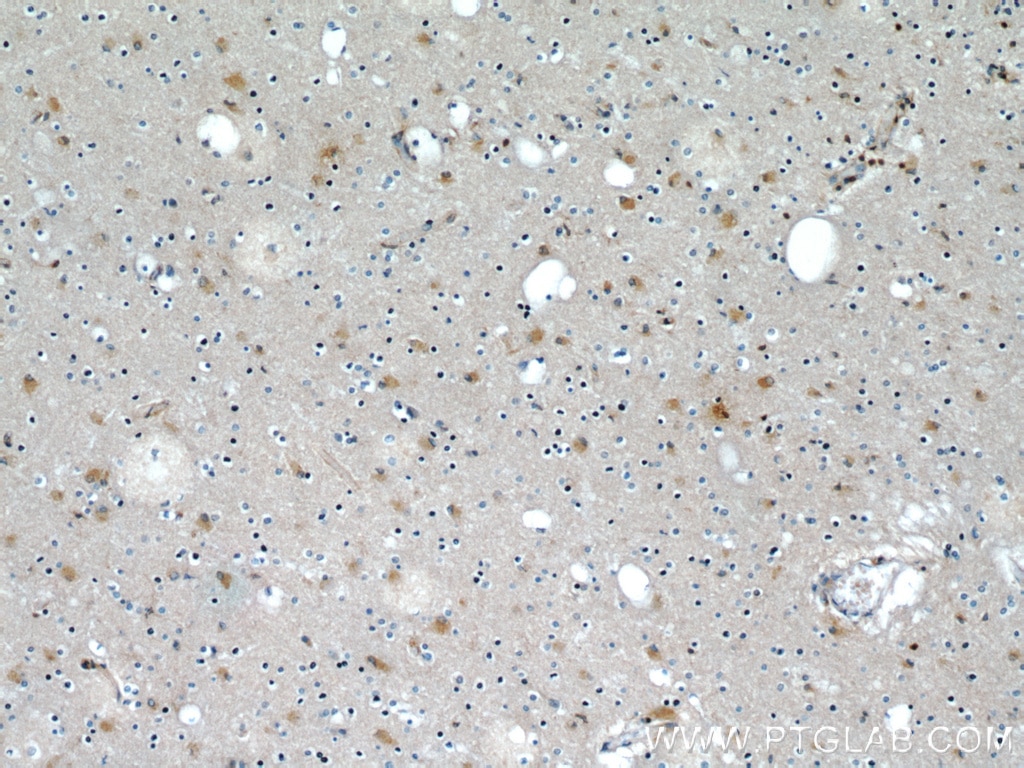
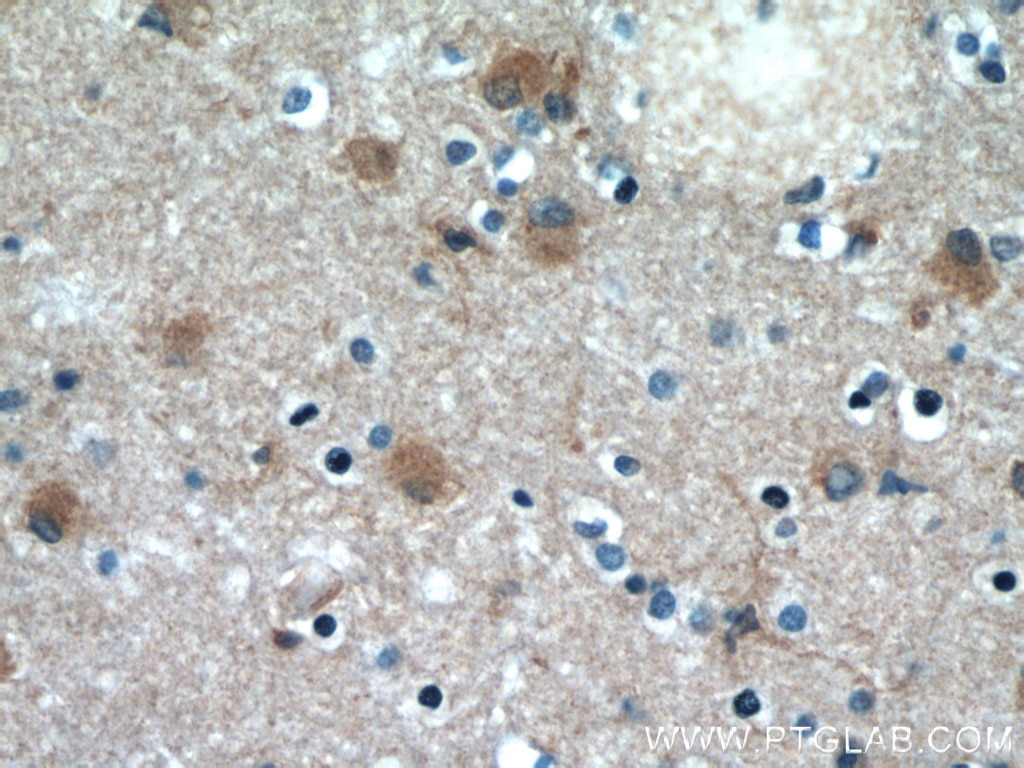
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2D4H5
N° de cat : 66009-1-PBS
Synonymes
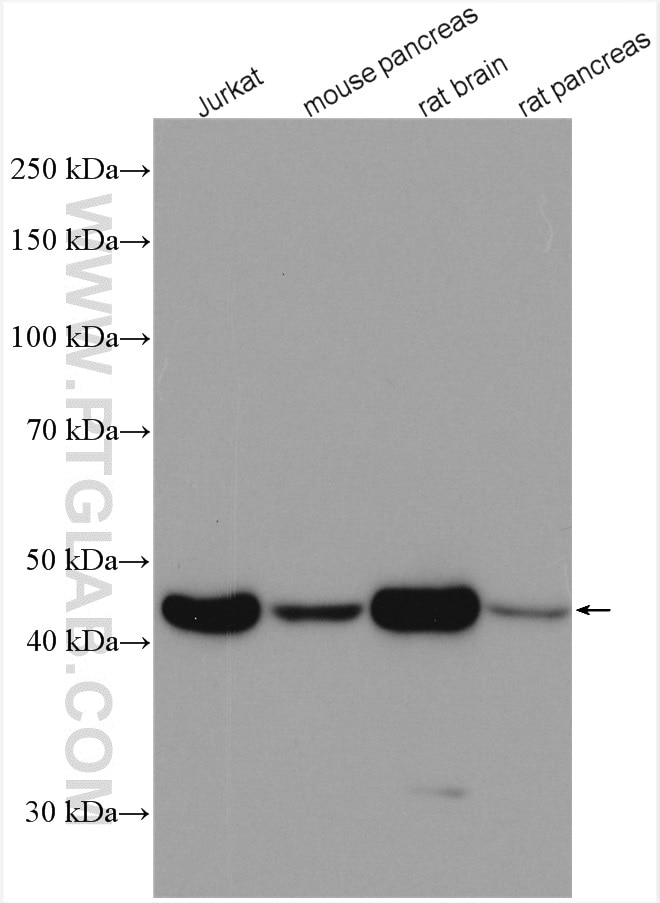
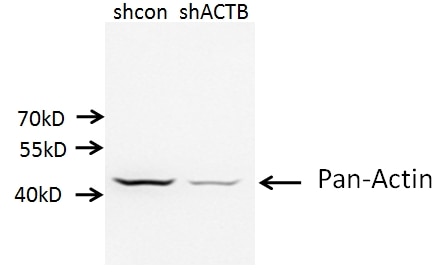
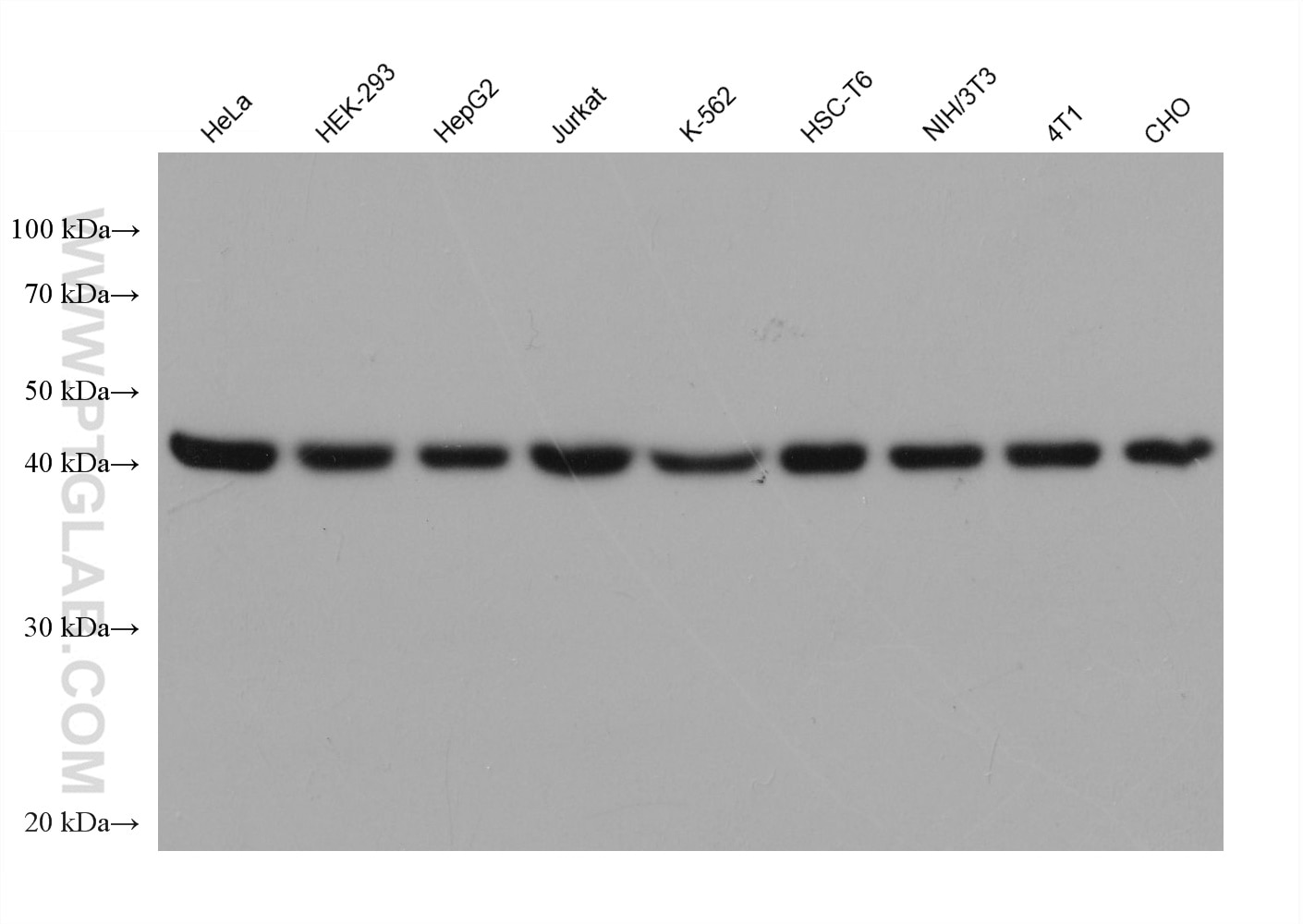
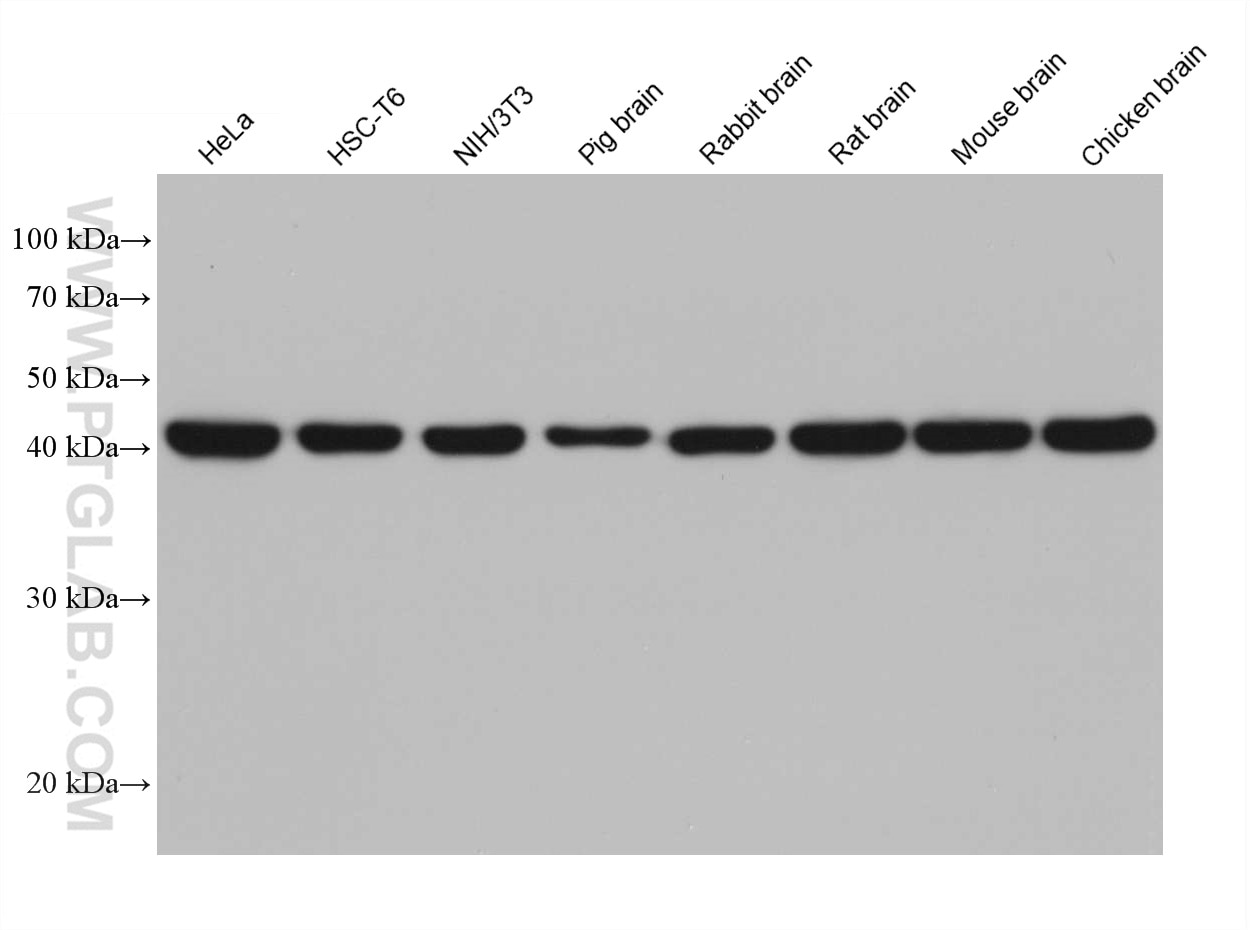
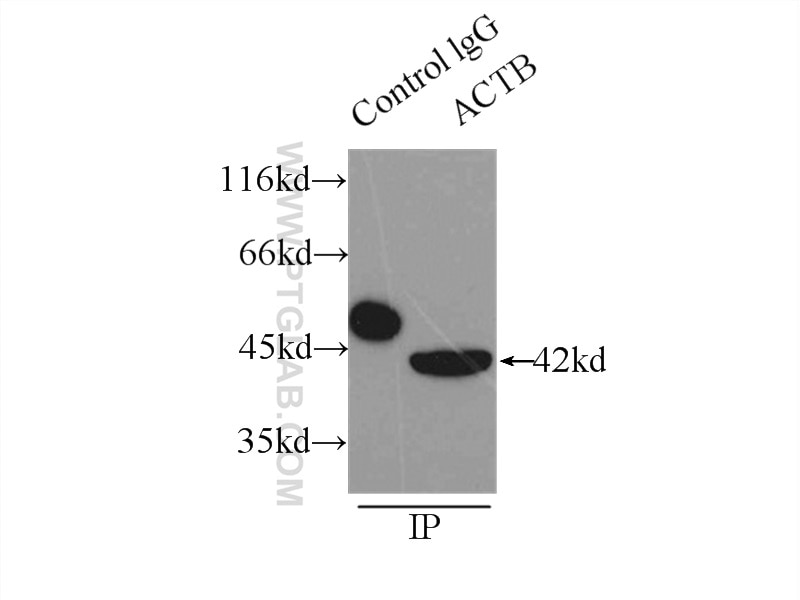
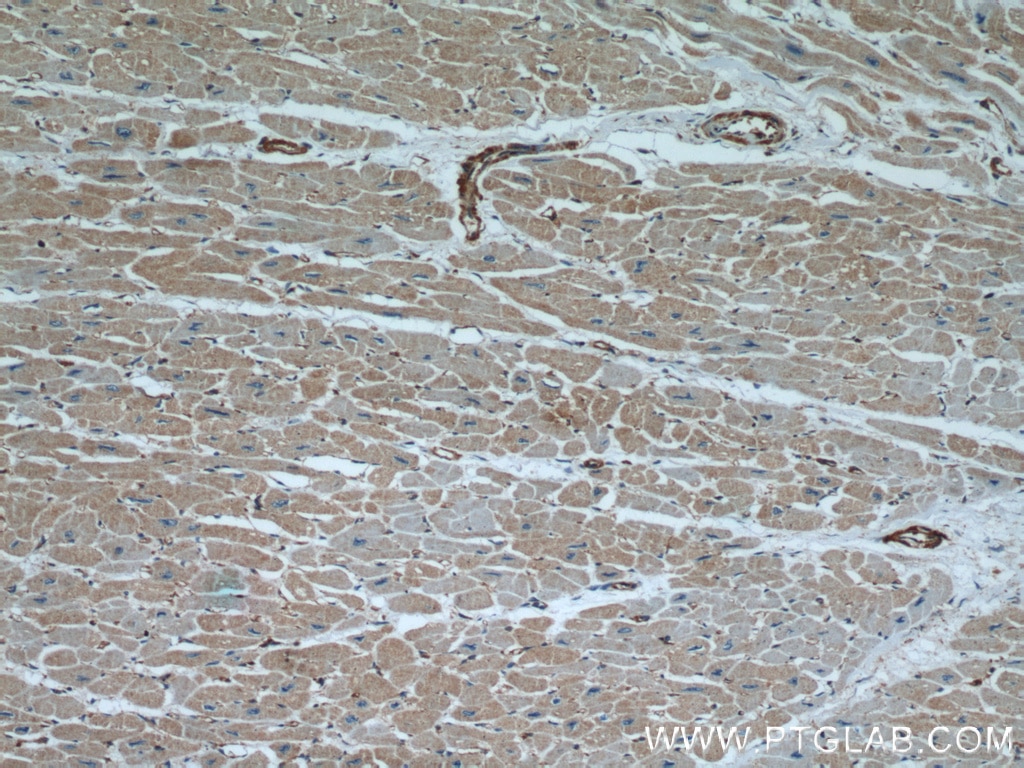
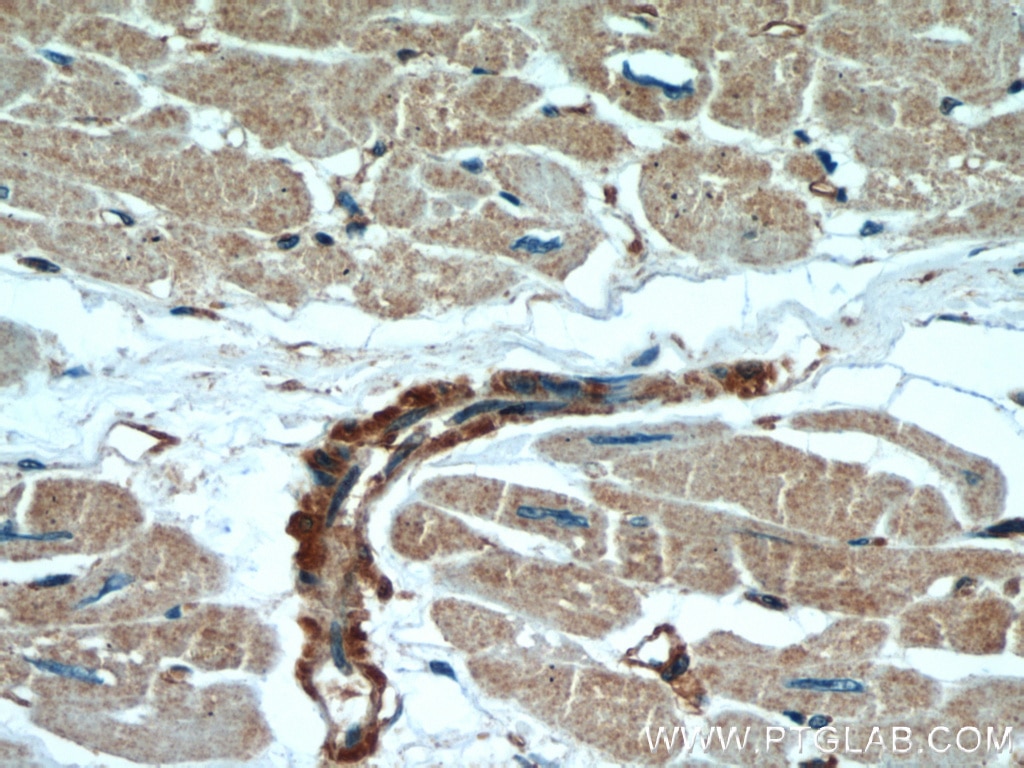
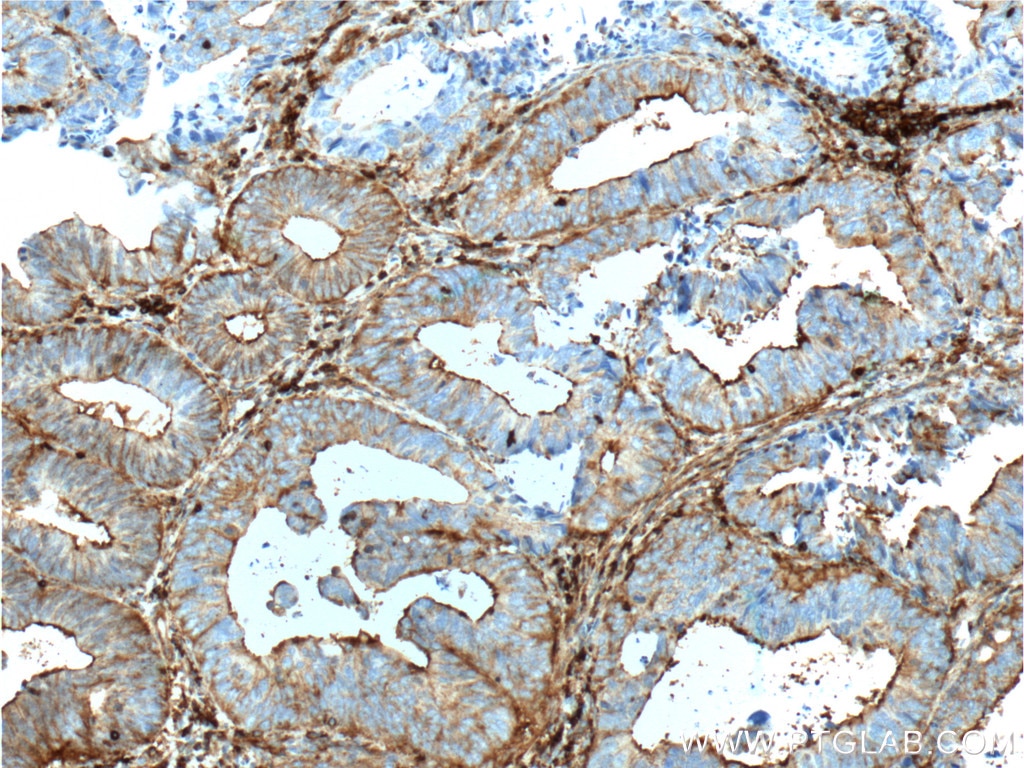
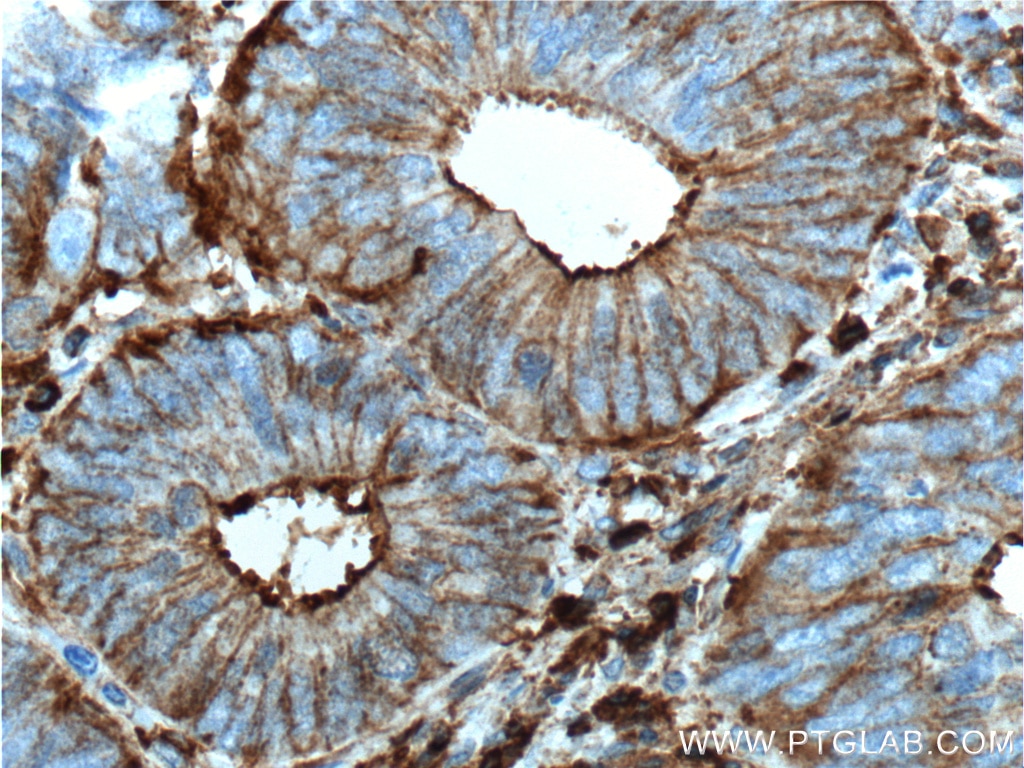
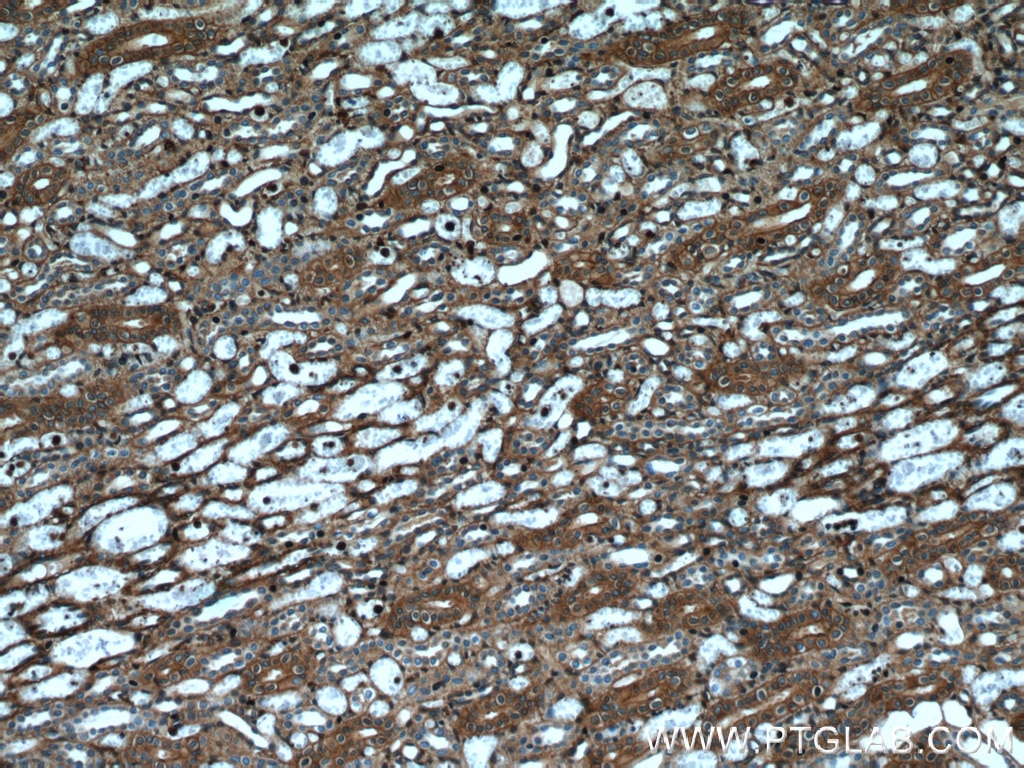
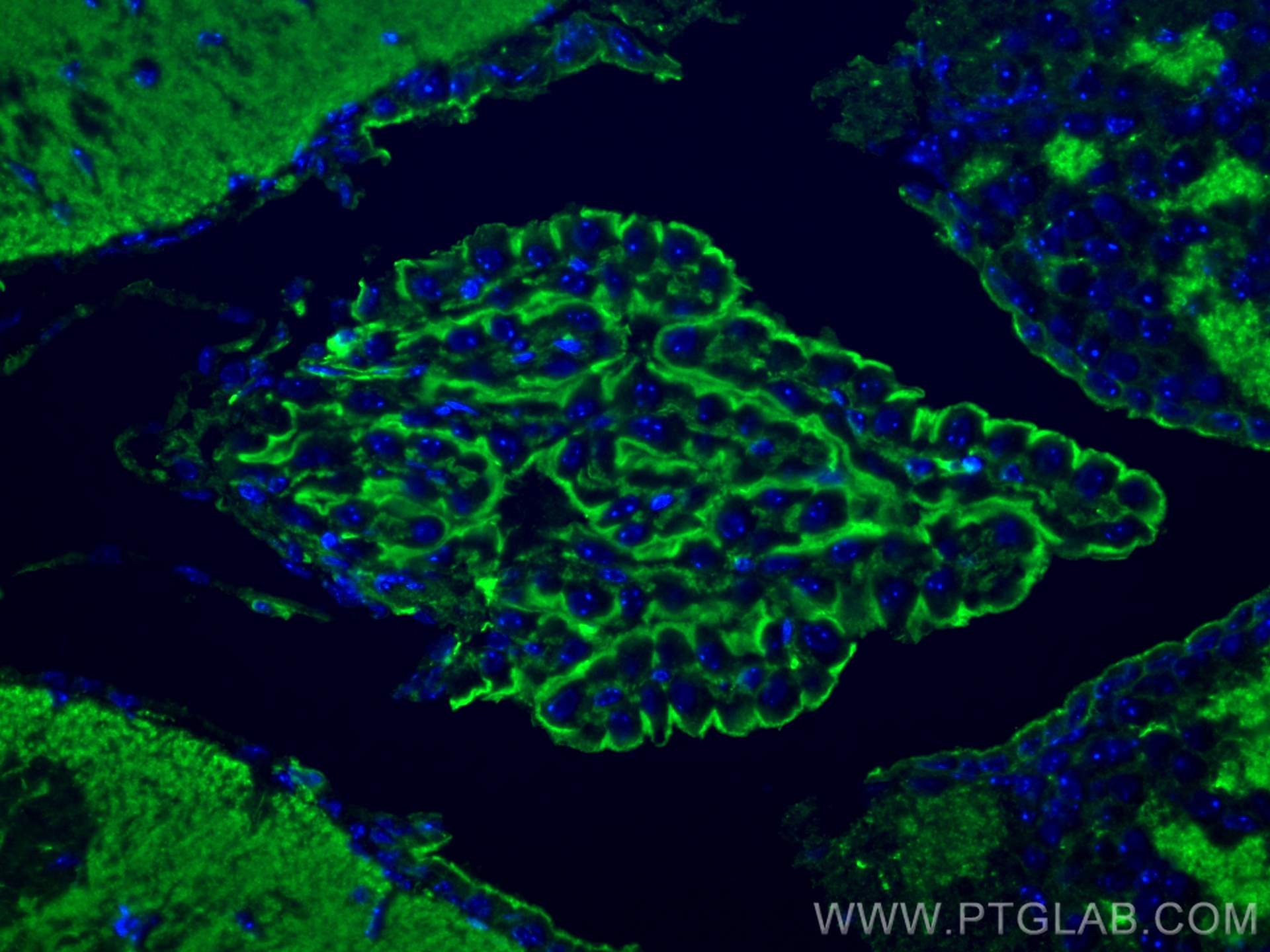
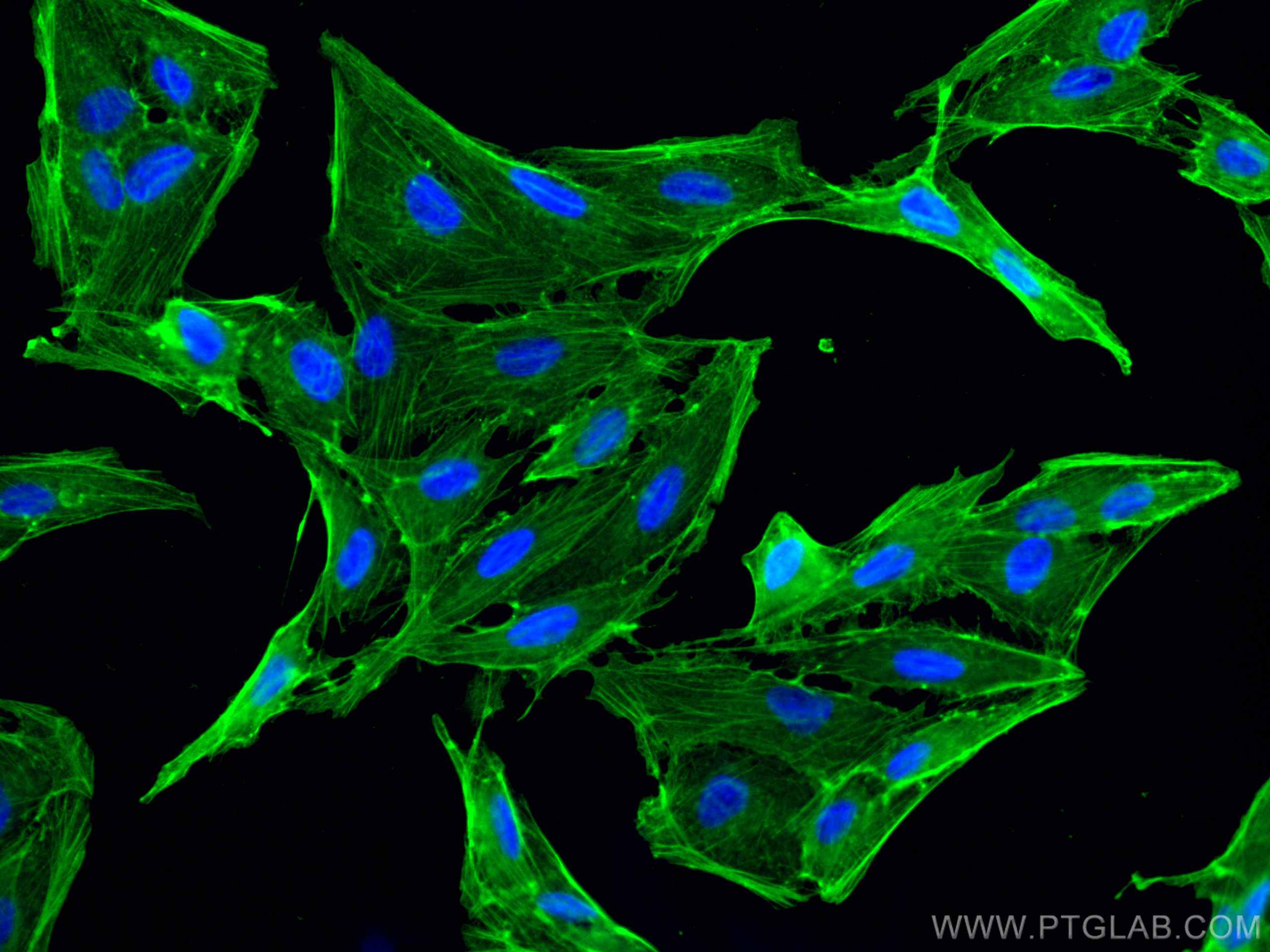
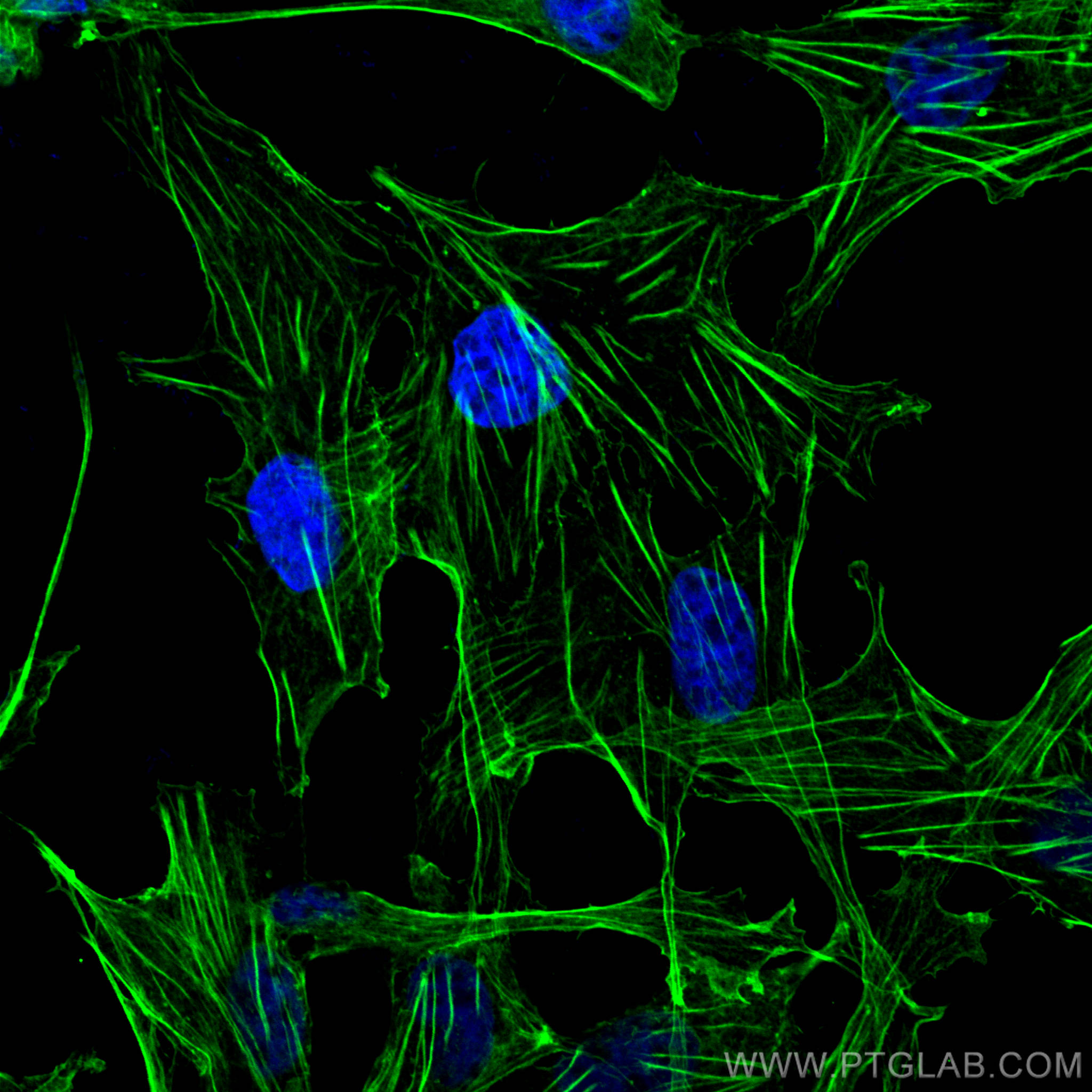
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
66009-1-PBS cible Beta Actin dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons canin, Humain, Lapin, poisson-zèbre, porc, poulet, rat, singe, souris, Hamster
| Réactivité | canin, Humain, Lapin, poisson-zèbre, porc, poulet, rat, singe, souris, Hamster |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Protéine recombinante |
| Nom complet | actin, beta |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 42 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 42 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM_001101 |
| Symbole du gène | Beta Actin |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 60 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Actins are highly conserved globular proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. At least six isoforms of actins are known in mammals and other vertebrates. Beta-actin (or β-actin) is a cytoskeletal actin isoform, highly conserved and ubiquitously expressed in eukaryotic organisms, making it a commonly used "housekeeping gene" in many laboratory techniques. It has been widely used as the internal control in RT-PCR and Western Blotting. The isotype of this antibody is IgG2b.
What is the molecular weight of beta-actin?
42 kDa
What is the function of beta-actin?
Actins are a key part of the cytoskeleton and are involved in cell motility, structure, and signaling, with beta-actin as part of the contractile apparatus. Beta-actin is located in the cytoplasm of non-muscle cells, particularly where the plasma membrane meets the cytoskeleton (PMID: 1993736) and is found co-distributed with alpha-actin (PMID: 9490838).
What are the applications for beta-actin?
As it is ubiquitously and constitutively expressed, beta-actin is a useful loading control in techniques such as RT-PCR and Western Blots to measure baseline expression and degradation. Beta-actin can be used as a reference gene to normalize mRNA or protein levels in quantitative studies of expression. Although some evidence suggests variation in tissue types and developing embryos (PMID: 23099774) if expression is stable across conditions, beta-actin is still considered by many to be a suitable gene for normalization.
Beyond its role as a housekeeping gene, it has been shown that beta-actin associates with endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) and can therefore regulate nitric oxide activity in endothelial cells (PMID: 12734108).
What are the post-transcriptional modifications (PTMs) to beta actin?
Alterations to actin proteins can modulate their properties and function. While small molecules are known to alter actin, post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation and acetylation can also affect actin (PMID: 23195437). Modifications to actin have been associated with diseases including but not limited to age-related macular degeneration (PMID: 17652714), cardiovascular disease (PMID: 21232667), and Alzheimer's disease (PMID: 11246152).
For murine tissue sample, conjugated antibody (HRP-66009) or rabbit antibody (20536-1-AP) is preferable.