- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-PD-L1/CD274
PD-L1/CD274 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 17952-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
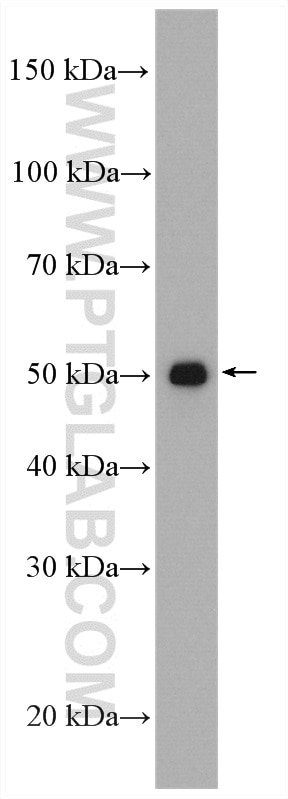
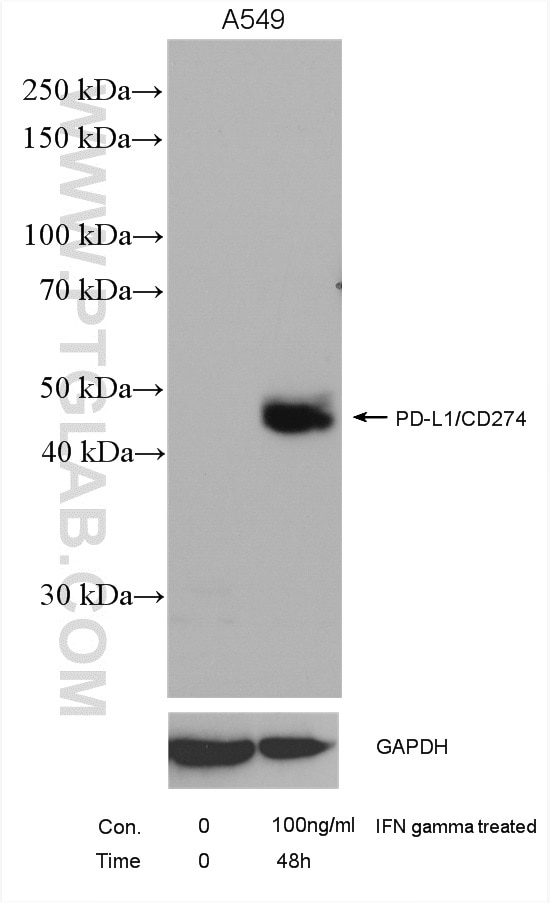
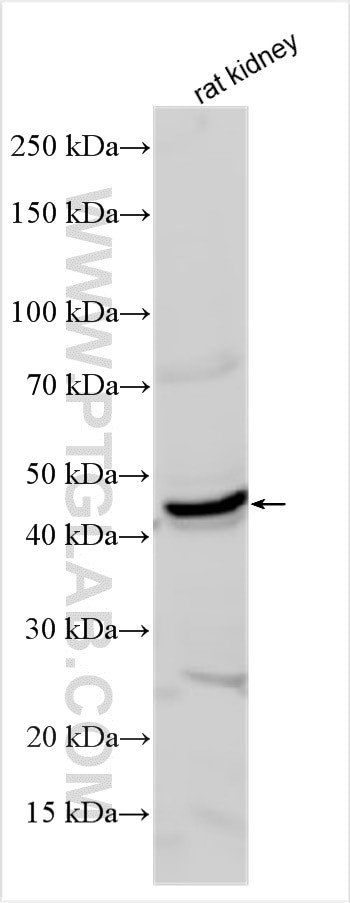
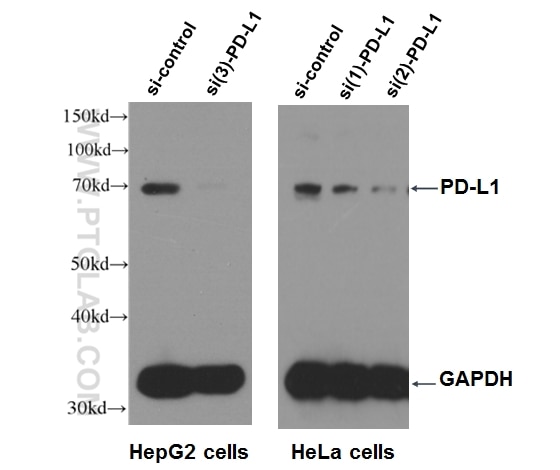
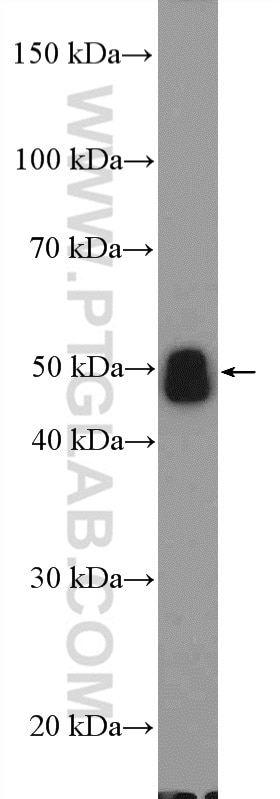
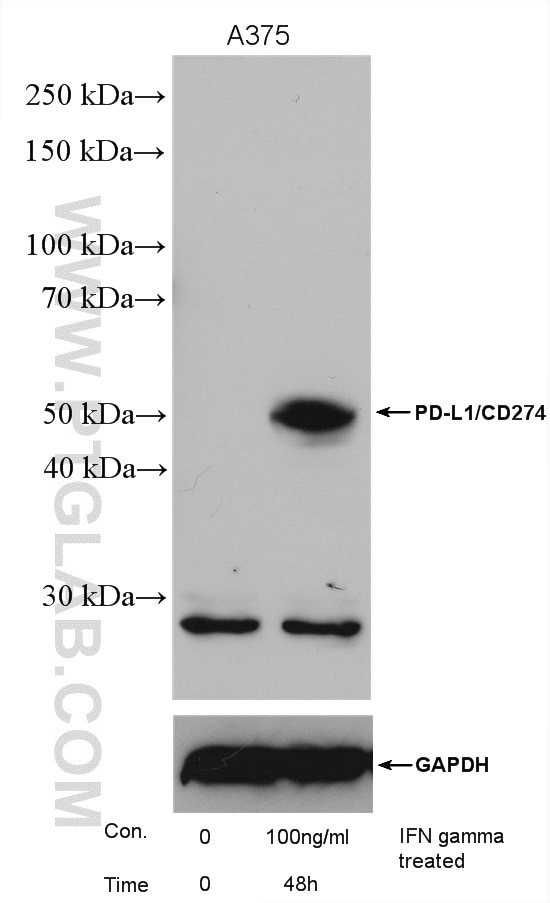
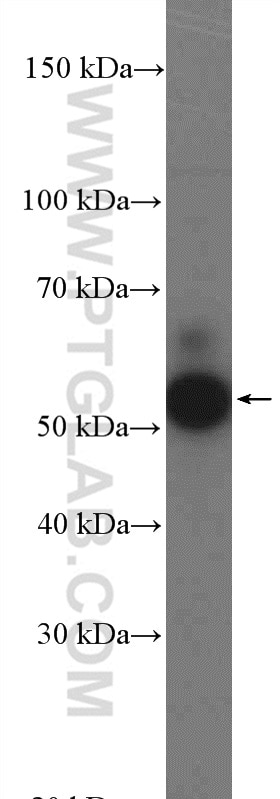
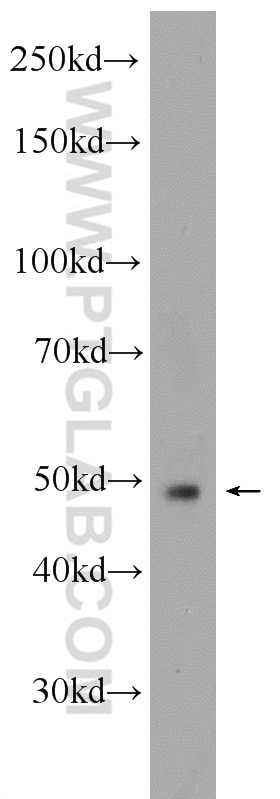
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu placentaire humain, cellules A375, cellules A549 traitées par IFN gamma, cellules HepG2, cellules K-562, tissu cardiaque de souris, tissu de muscle squelettique de souris, tissu rénal de rat |
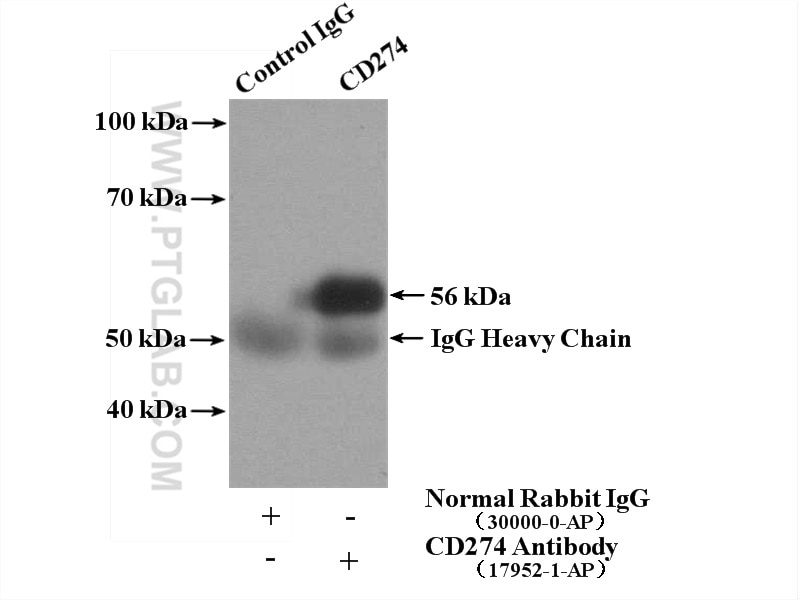
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu cardiaque de souris |
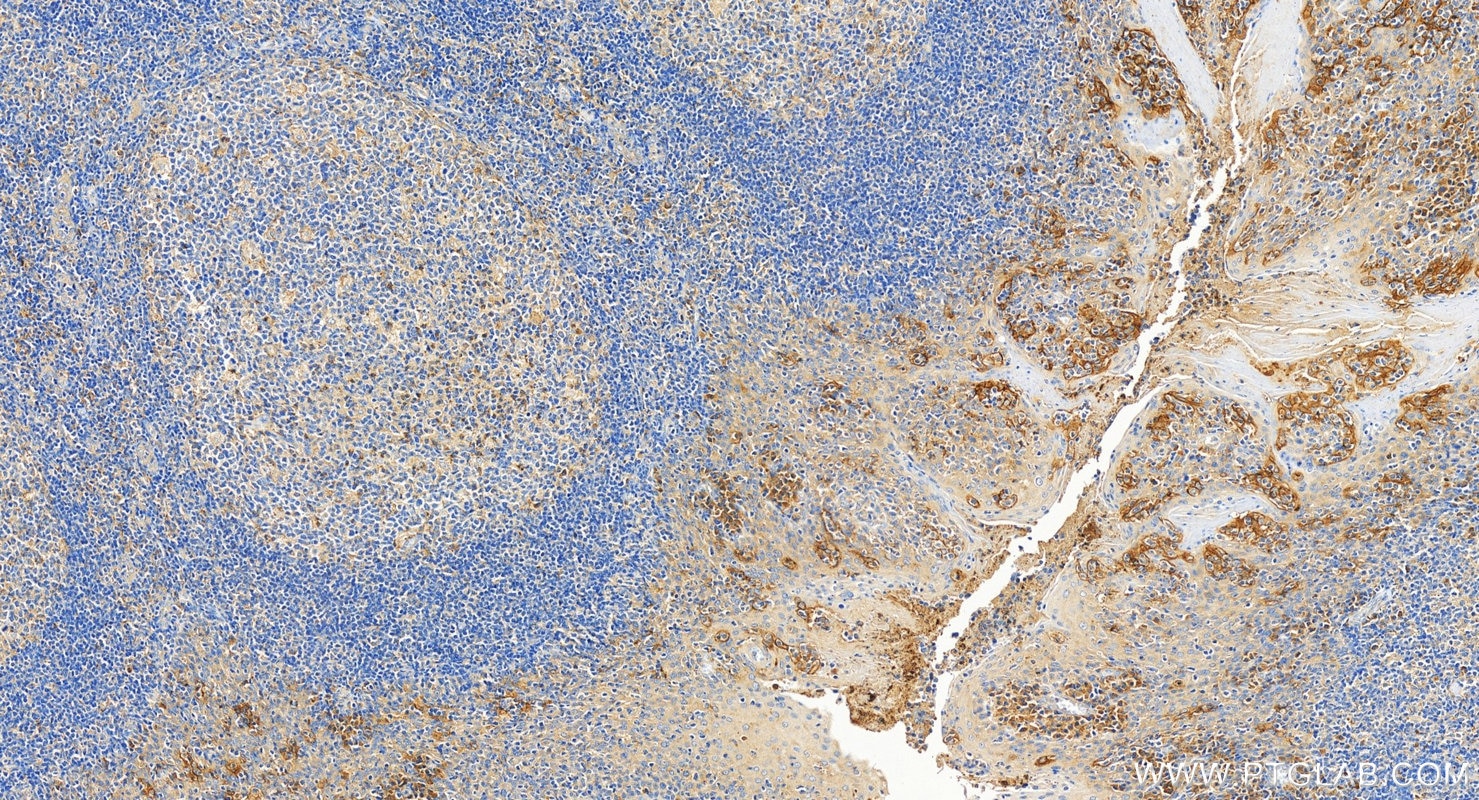
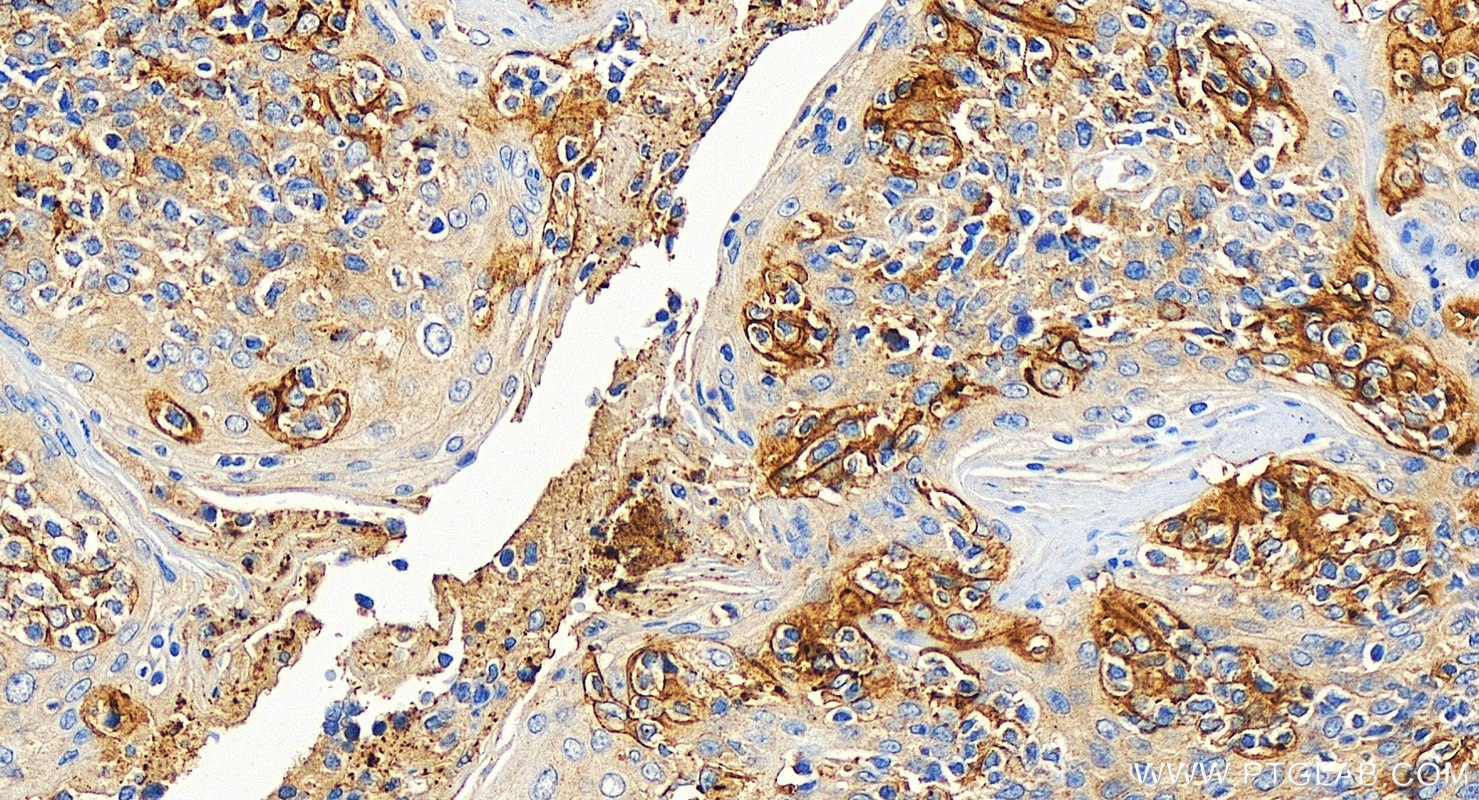
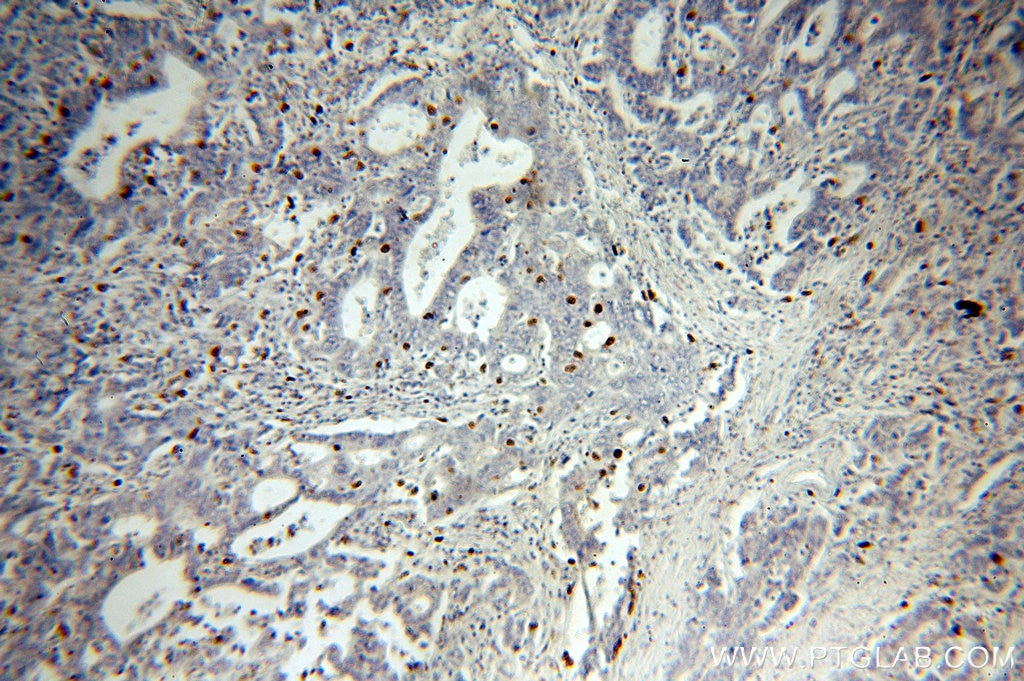
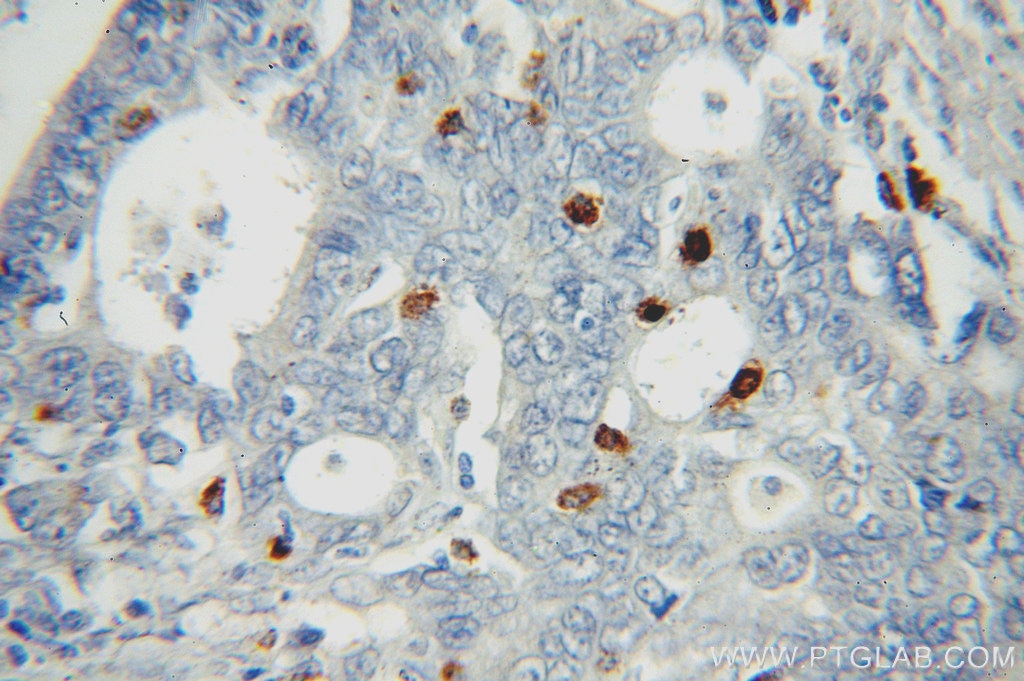
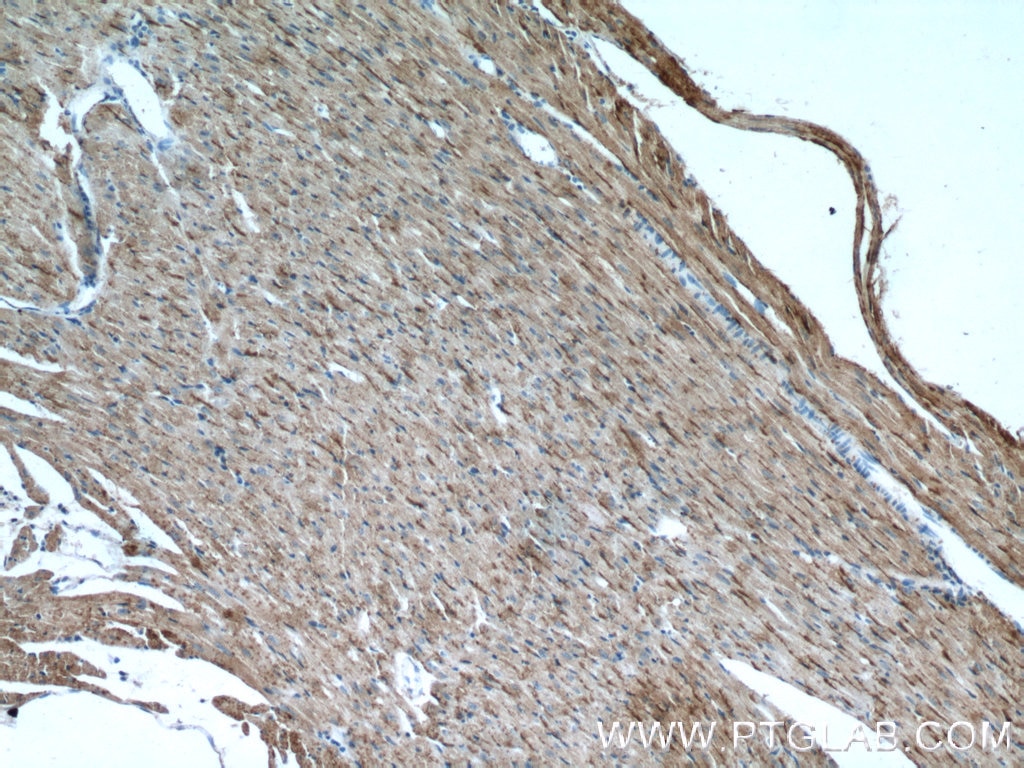
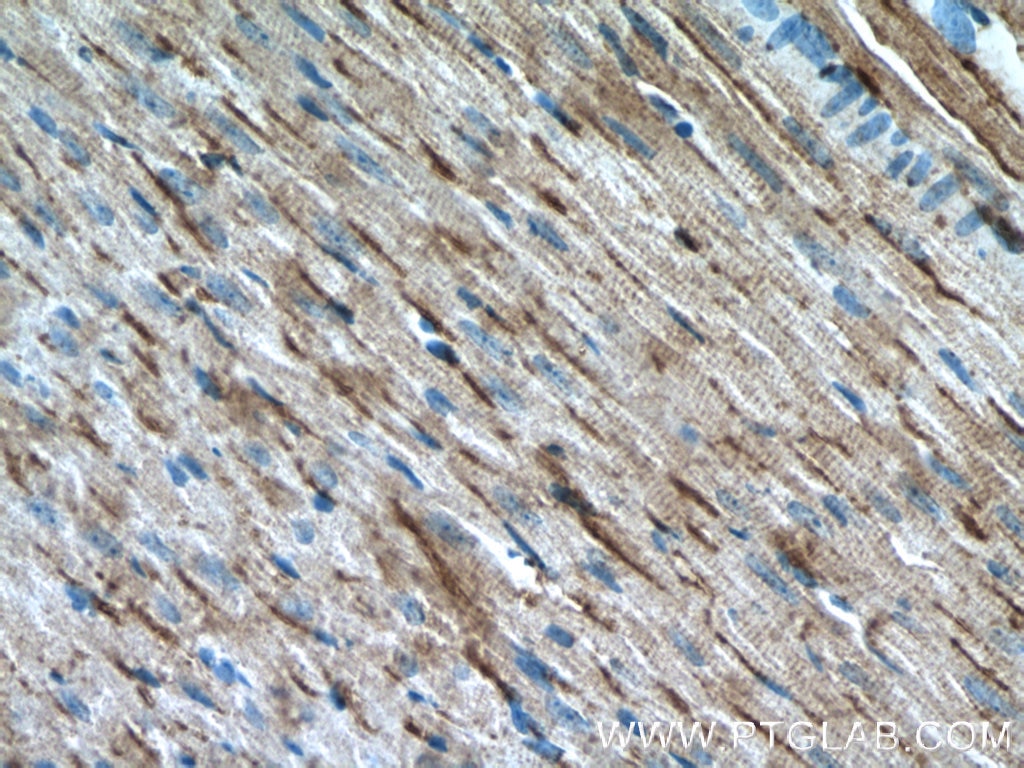
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu d'amygdalite humain, tissu cardiaque de souris, tissu de cancer de l'estomac humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
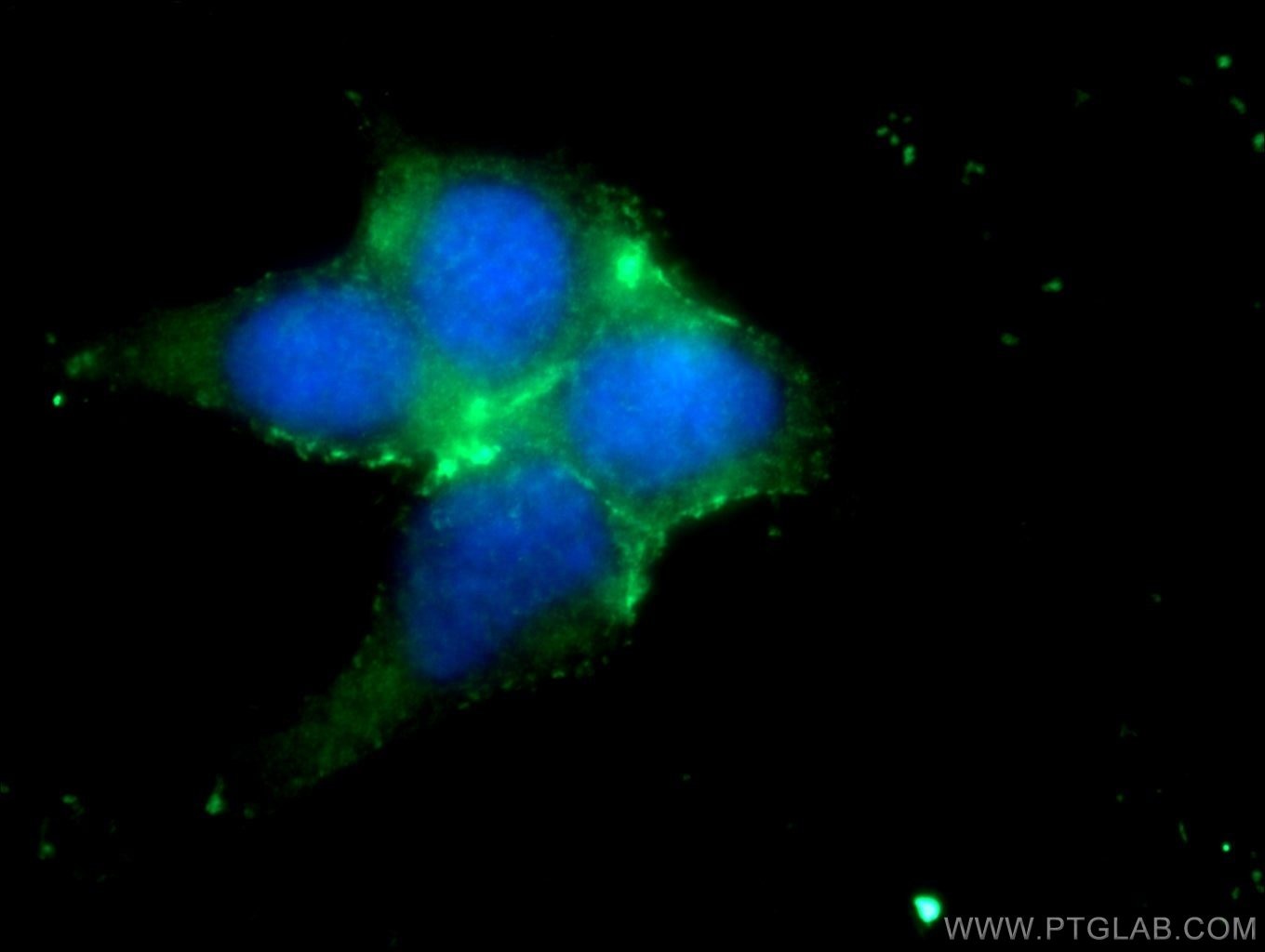
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HEK-293 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
17952-1-AP cible PD-L1/CD274 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | PD-L1/CD274 Protéine recombinante Ag12432 |
| Nom complet | CD274 molecule |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 290 aa, 33 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 45-56 kDa, 65-70 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC074984 |
| Symbole du gène | PD-L1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 29126 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
PD-L1, also known as CD274 or B7H1, stands for programmed cell death ligand 1. It is a type I transmembrane protein that is thought to repress immune responses by binding to its receptor (PD1), thus inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. It contains V-like and C-like immunoglobulin domains. PD-L1 expression is regulated by various cytokines, such as TNF-α or LPS (ISSN: 1848-7718). Increased expression of this protein in certain types of cancers, e.g., renal cell carcinoma or colon cancer, correlates with poor prognosis.
What is the molecular weight of PD-L1?
Depending on the isoform, the calculated molecular weight of the protein varies between 20 and 33 kDa (176-290 aa).
What are the isoforms of PD-L1?
According to NCBI, three different isoforms have been identified. There are significant differences in the untranslated and protein coding regions.
What is the subcellular localization and tissue specificity of PD-L1?
It is predicted to localize in the plasma membrane of various cell types, with a particularly high expression in placental trophoblast and subsets of immune cells. High levels of PD-L1 protein have also been detected in lung and colon tissues.
What is the function of PD-L1 in immune responses?
PD-L1 is critical for the induction and maintenance of immune self-tolerance during infection or inflammation in normal tissues. The interaction of PD-L1 and its receptors is responsible for preventing auto-immune phenotypes and balancing the overall immune response in situations such as pregnancy or tissue allografts. The interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 or B7.1 starts an inhibitory signaling cascade, which results in the decreased proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells and increased survival of regulatory T-cells (PMID: 15240681).
How can PD-L1's implication in cancer be used as a drug target?
In certain tumors, high expression of PD-L1 serves as a stop-sign to inhibit the recognition of cancer cells by T-cells (PMID: 23087408). The interaction between PD-L1 and its receptors (PD1 and B7.1) is a mechanism for the tumor to evade the host immune response (PMID: 29357948). Several mAbs have been developed to target that interaction and thus prevent the inactivation of cytotoxic T-cells by the tumor (PMIDs: 23890059, 18173375).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PD-L1/CD274 antibody 17952-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for PD-L1/CD274 antibody 17952-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for PD-L1/CD274 antibody 17952-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for PD-L1/CD274 antibody 17952-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Biomed Eng Inhibiting PD-L1 palmitoylation enhances T-cell immune responses against tumours. | ||
Nat Commun Pharmaceutical targeting of OTUB2 sensitizes tumors to cytotoxic T cells via degradation of PD-L1 | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) BiTE-Secreting CAR-γδT as a Dual Targeting Strategy for the Treatment of Solid Tumors | ||
Acta Pharm Sin B Whole-body PET tracking of a d-dodecapeptide and its radiotheranostic potential for PD-L1 overexpressing tumors. | ||
Mol Cell Phosphorylated RB Promotes Cancer Immunity by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation and PD-L1 Expression. | ||
Mol Ther Targeting leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 sensitizes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy |