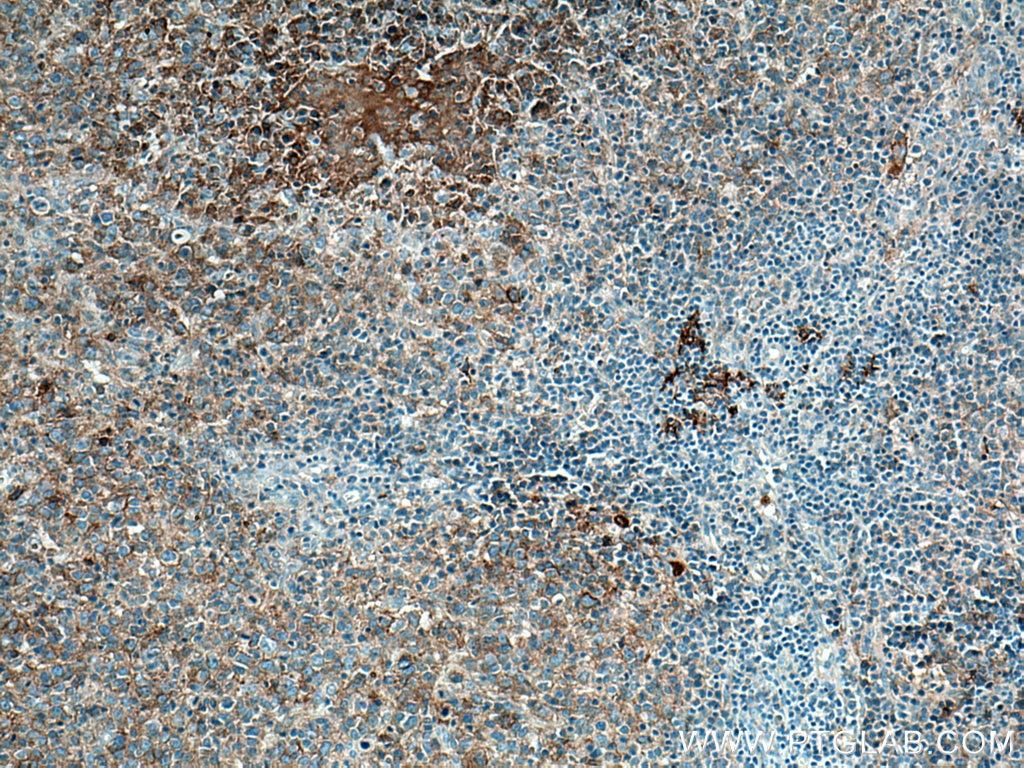
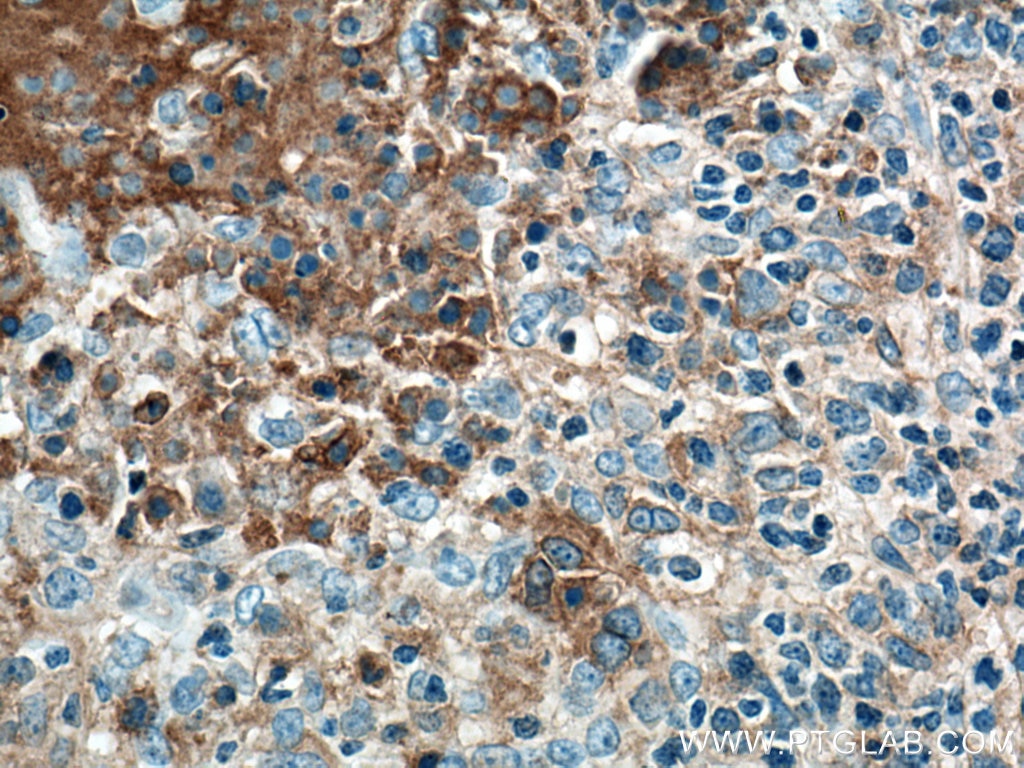
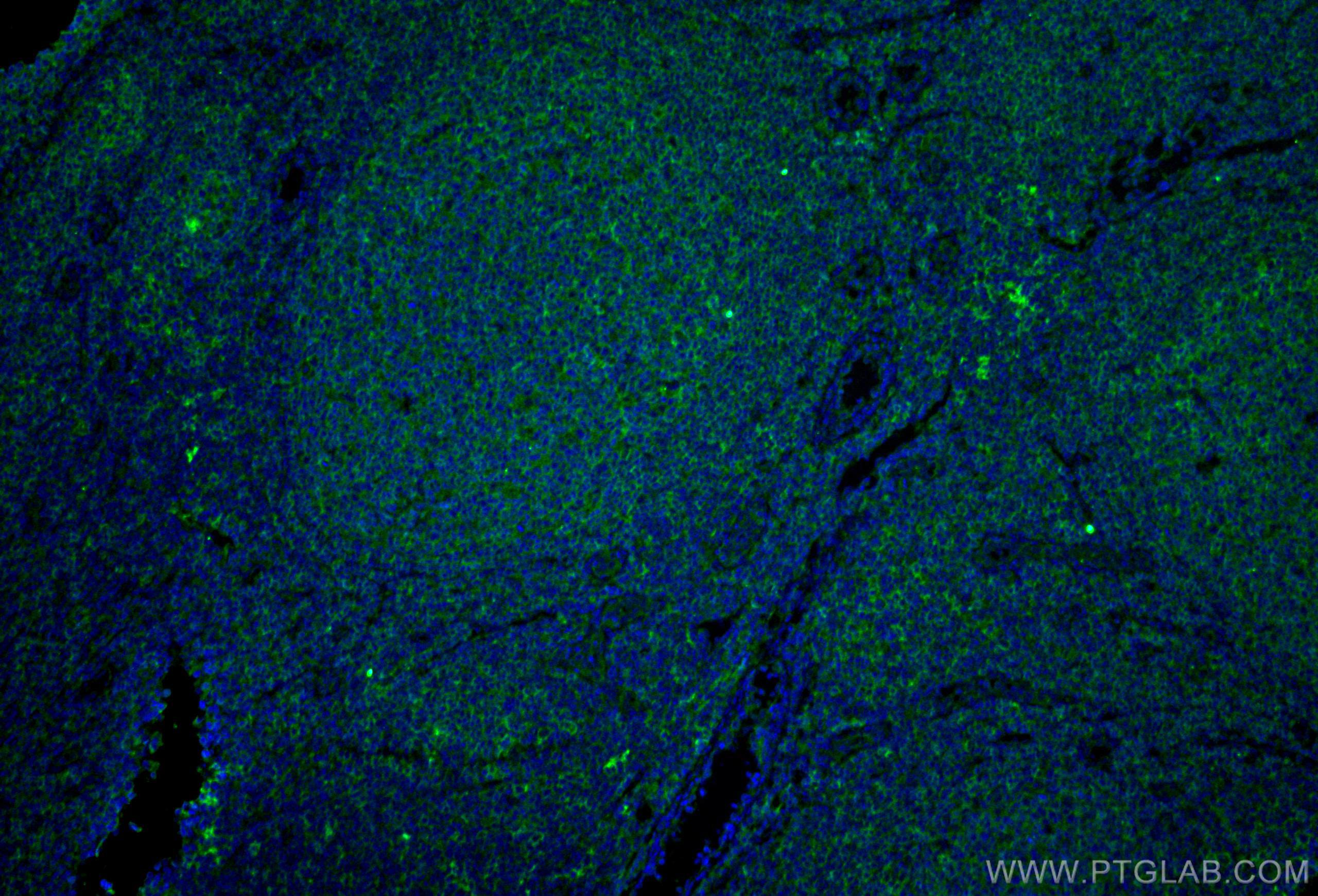
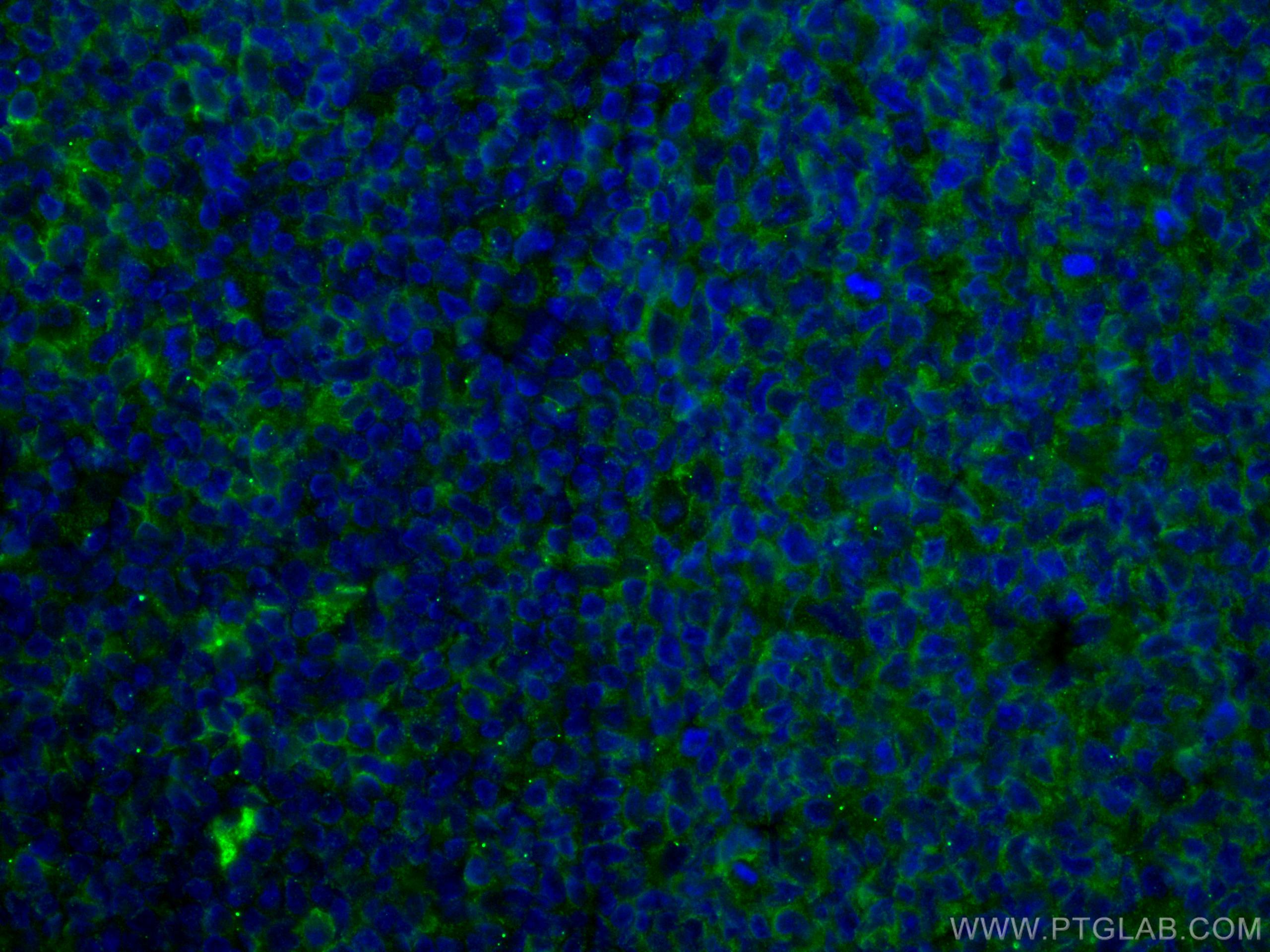
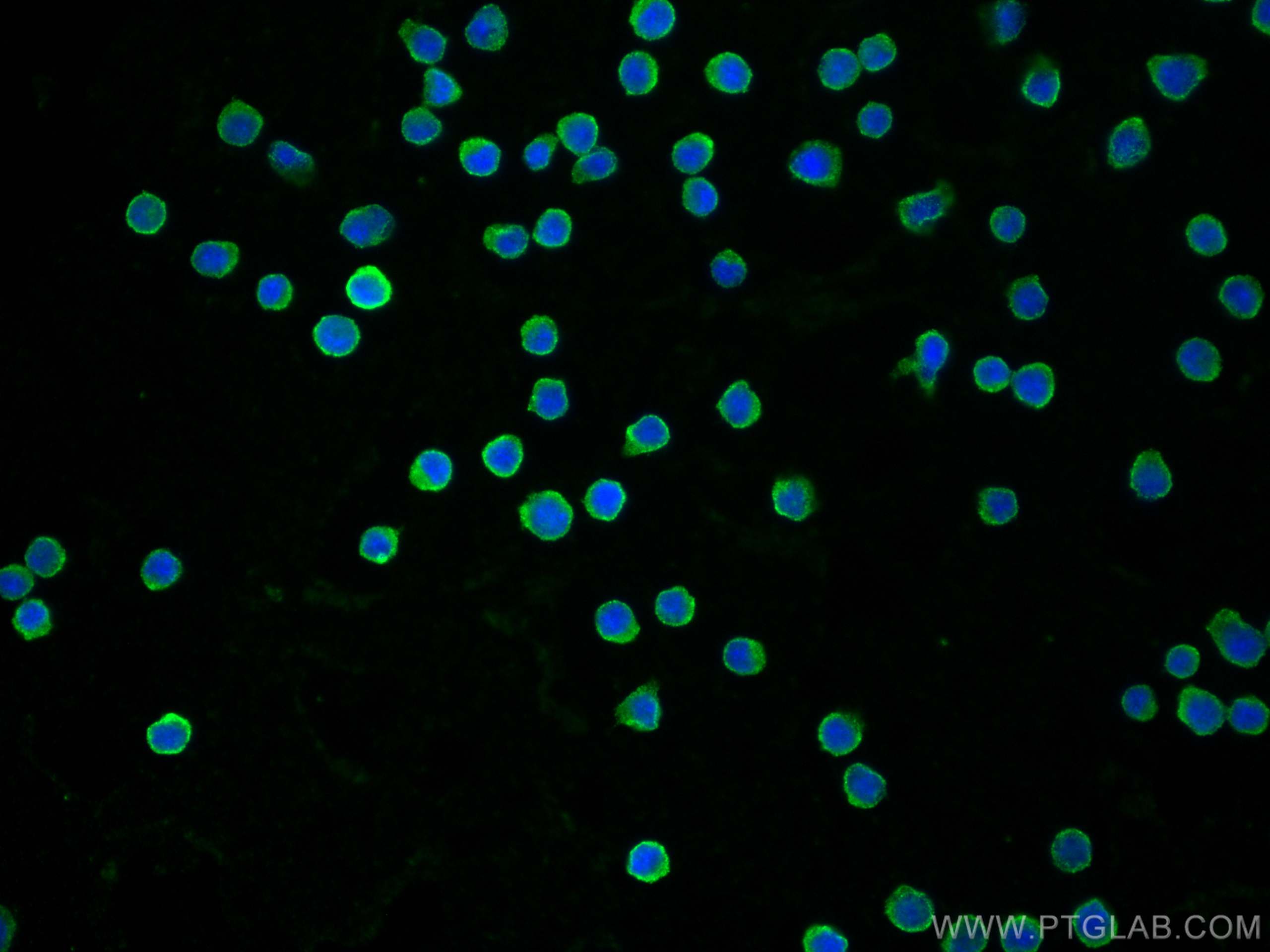
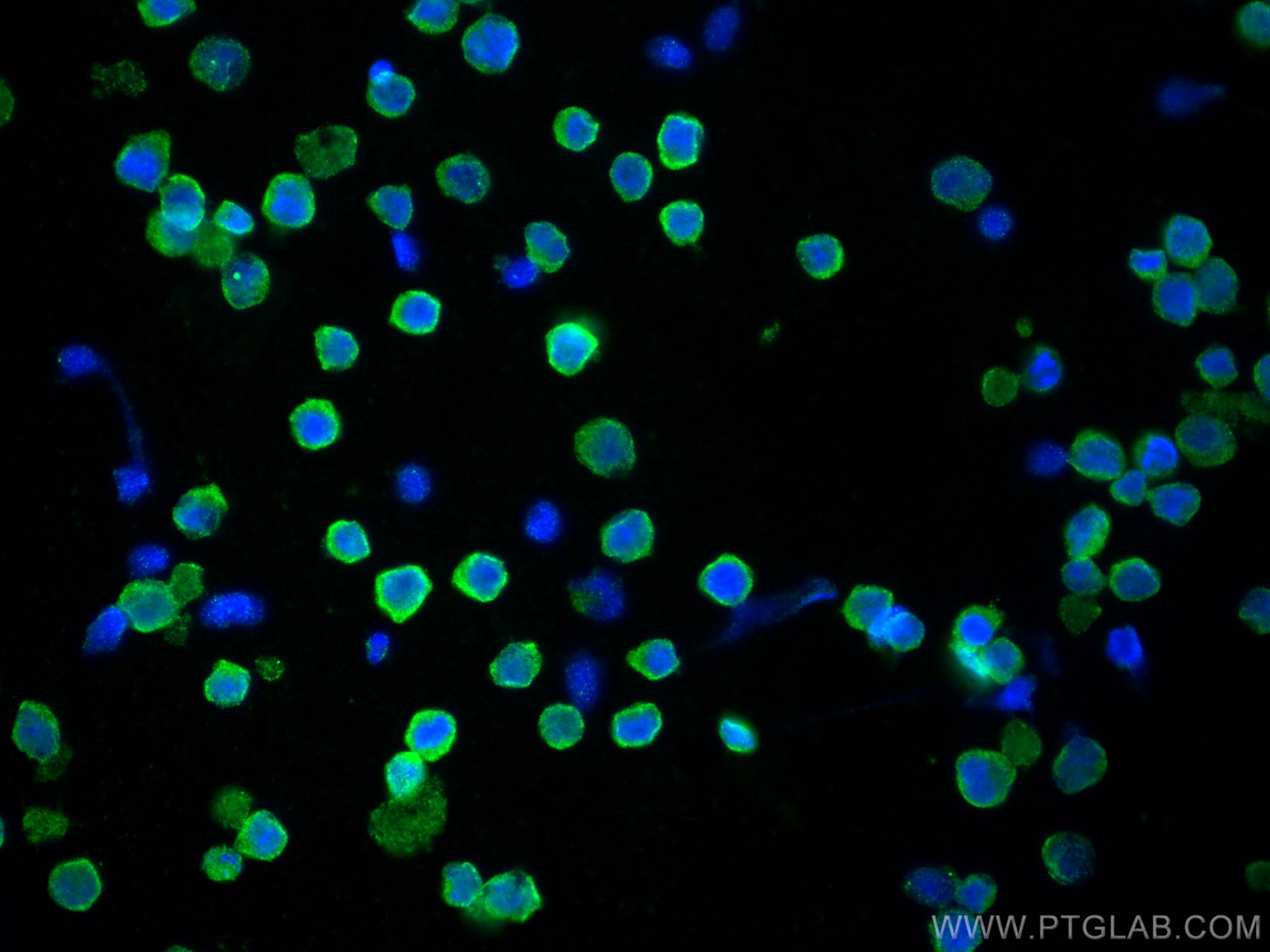
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-CD40
CD40 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2A8G5
N° de cat : 66965-1-PBS
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Informations sur le produit
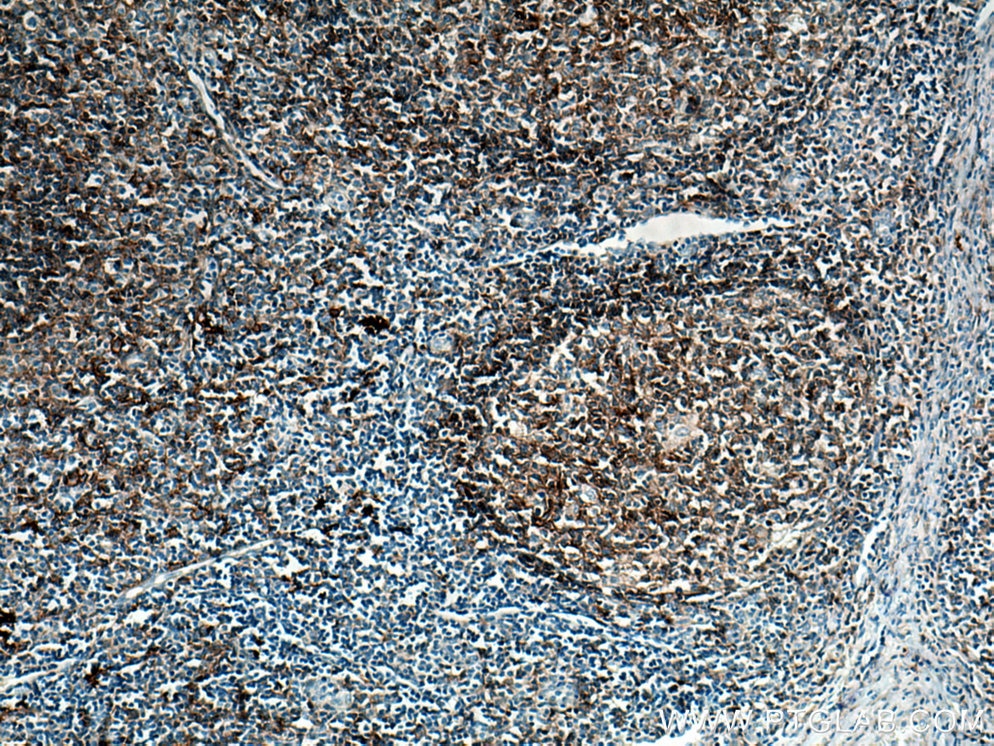
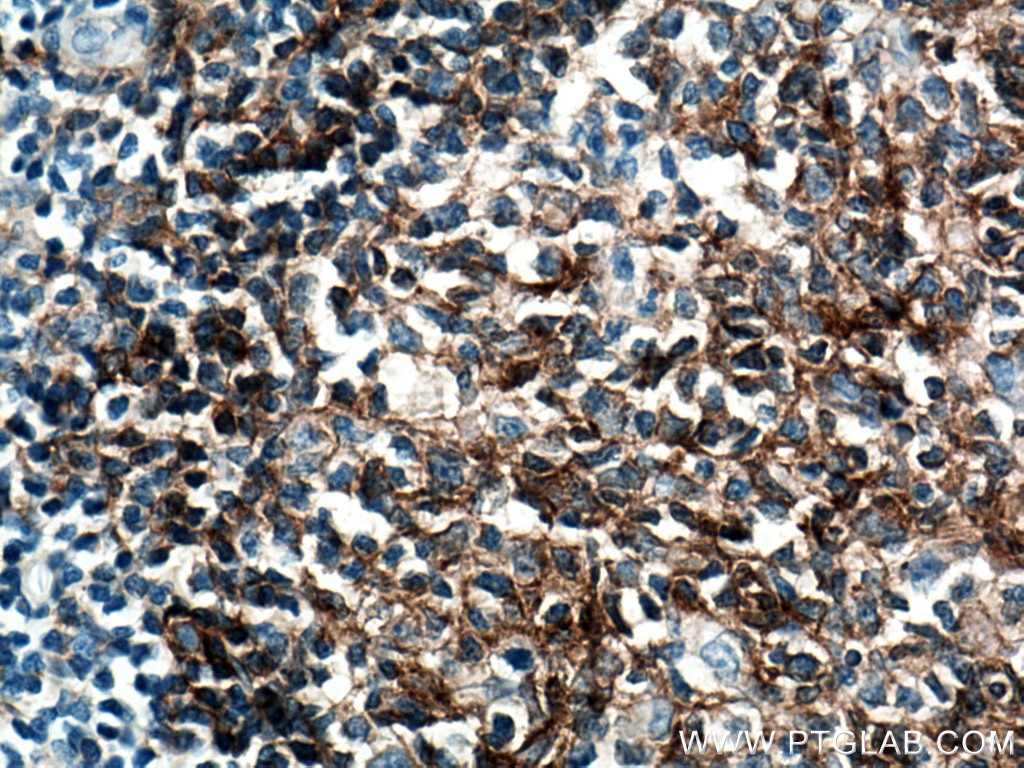
66965-1-PBS cible CD40 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CD40 Protéine recombinante Ag28040 |
| Nom complet | CD40 molecule, TNF receptor superfamily member 5 |
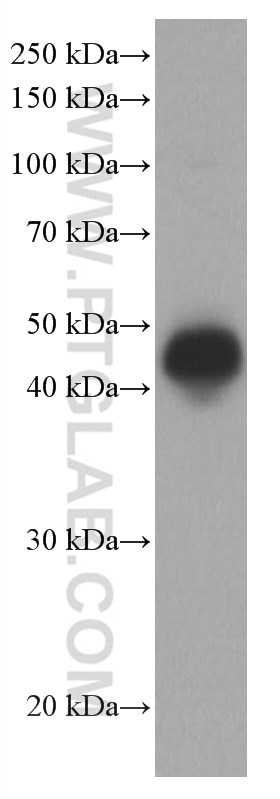
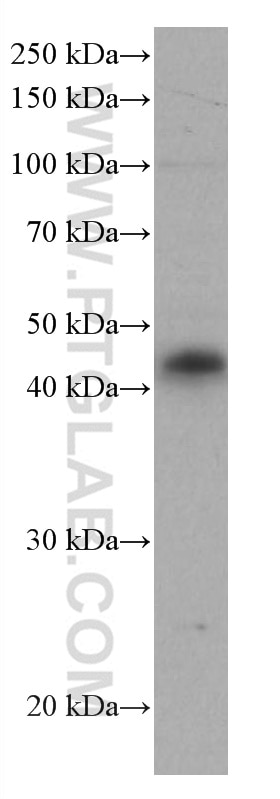
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 277 aa, 31 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 43 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC012419 |
| Symbole du gène | CD40 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 958 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS only |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at -80°C. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Cluster of differentiation 40 (CD40) is a costimulatory protein located on antigen presenting cells and is required for their activation. CD40 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor (TNFR) family.
What is the molecular weight of CD40?
The molecular weight of CD40 is 43 kDa.
What is the cellular localization of CD40?
CD40 can be secreted by cells or found in the cell membrane.
What is the tissue specificity of CD40?
CD40 is expressed in B cells and primary carcinoma cells but is also found in dendritic cells and macrophages (PMID: 10209159).
What is the function of CD40?
CD40 acts as a receptor for TNFSF5/CD40LG, which is expressed on activated T cells. This interaction is essential for B cell proliferation, expression of activation markers, immunoglobulin production, and isotype switching (PMID: 8809473). This interaction is also crucial for the formation of memory B cells and germinal centers, and signaling through CD40 prevents apoptosis of germinal center B cells.
What is the role of CD40 in disease?
Defects in CD40 lead to hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome type 3 (HIGM3) (PMID: 11675497). This is an autosomal recessive disorder that includes the inability of B cells to undergo isotype switching, a key step in the final differentiation of the humoral immune response, and an inability to mount an antibody-specific immune response.