- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-CLIC1
CLIC1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 14545-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
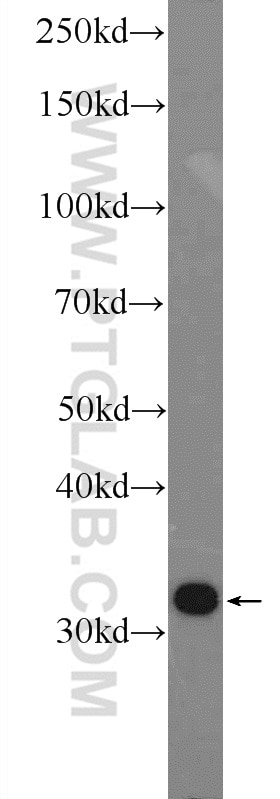
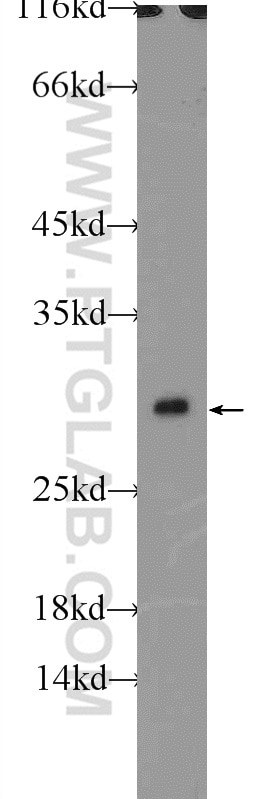
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HL-60, cellules HeLa |
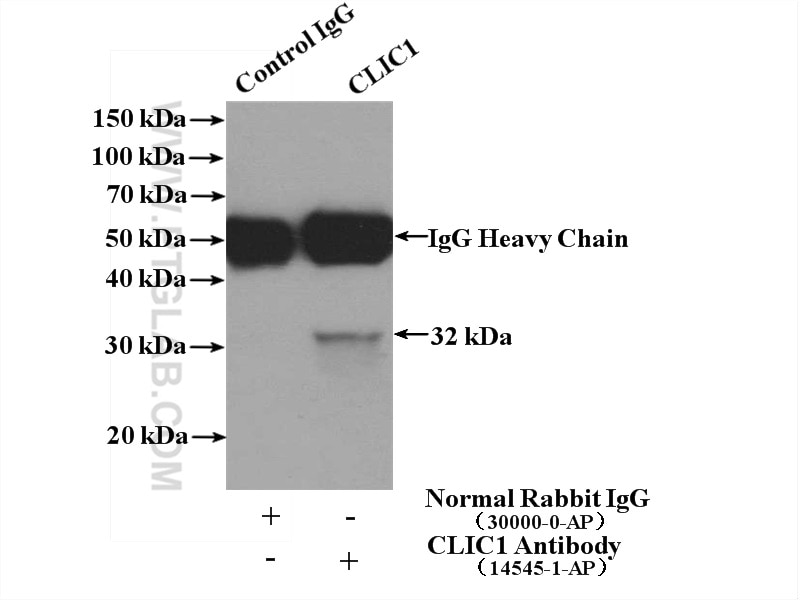
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HeLa |
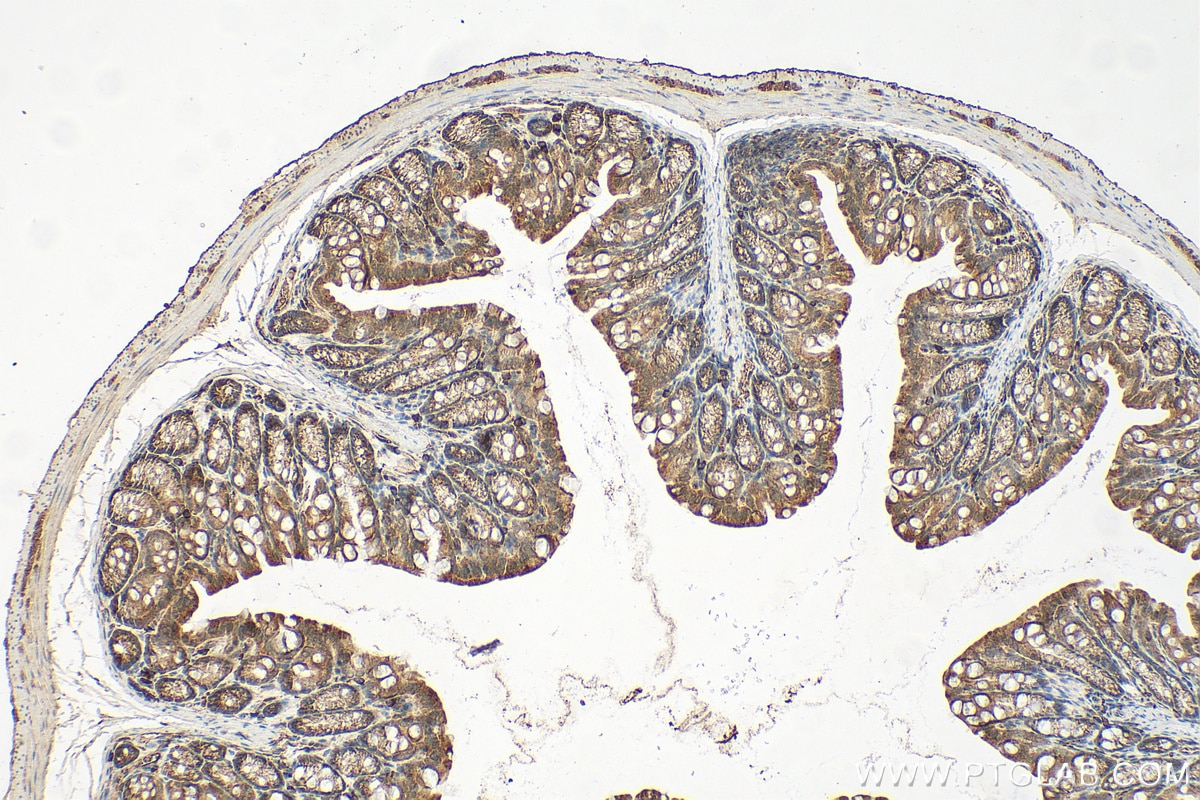
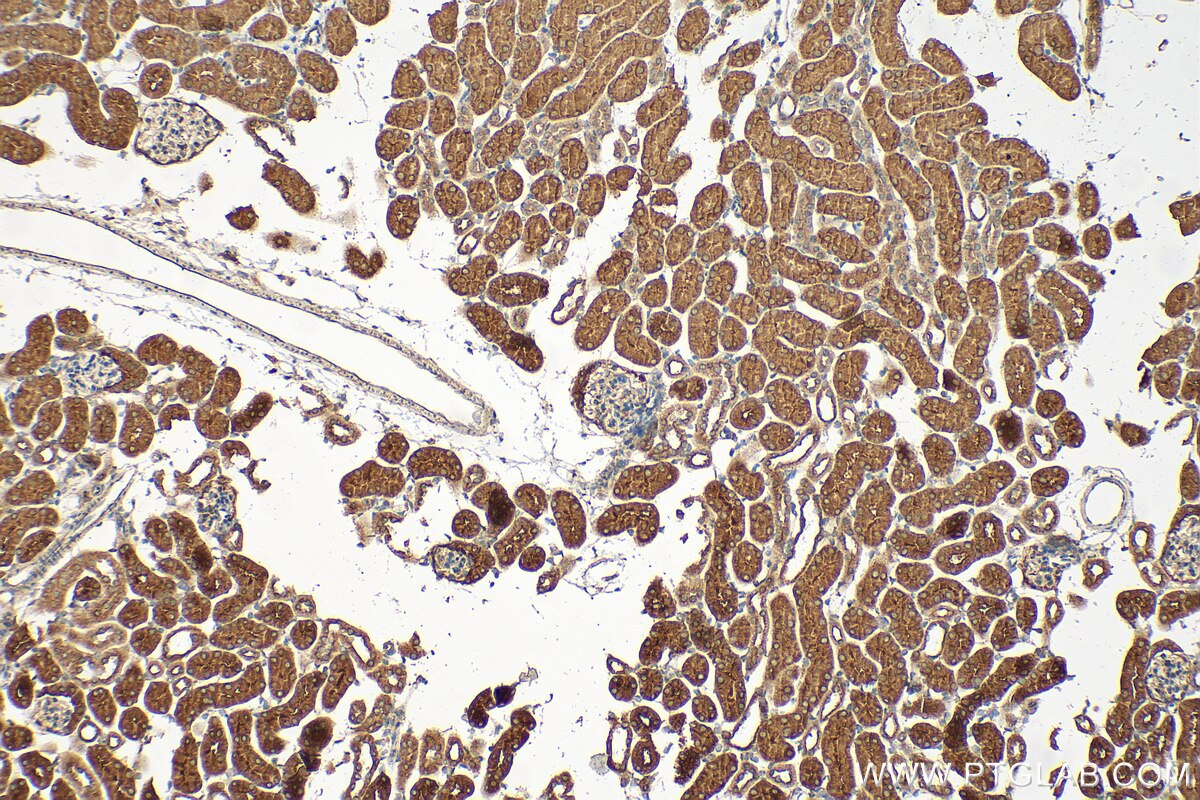
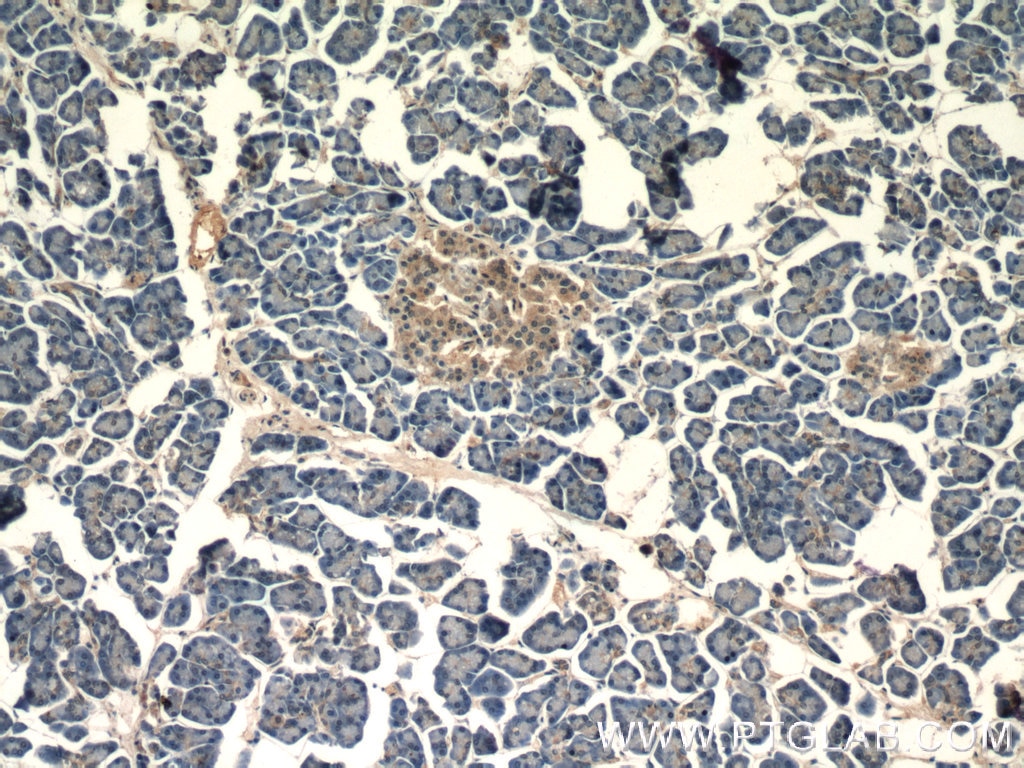
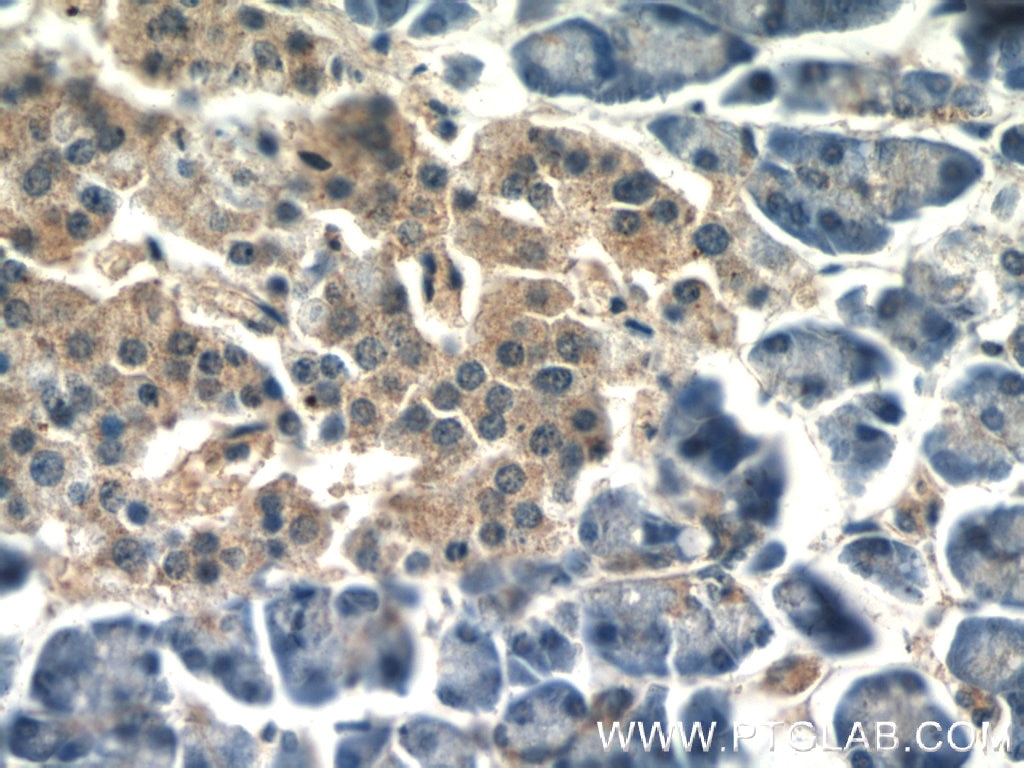
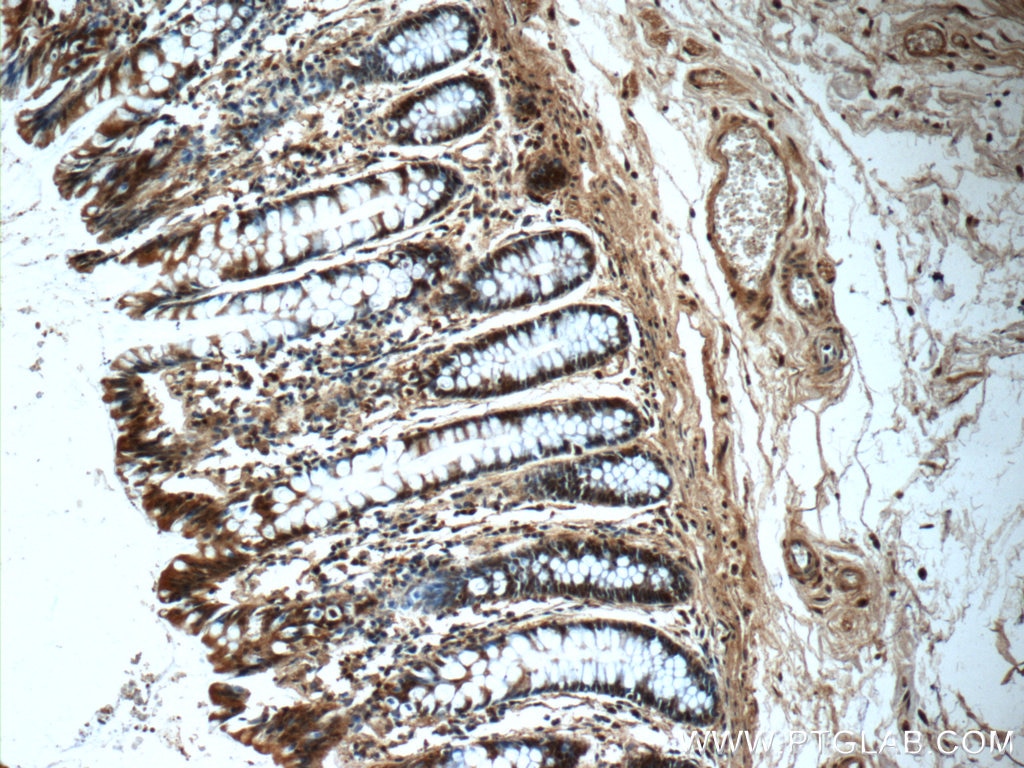
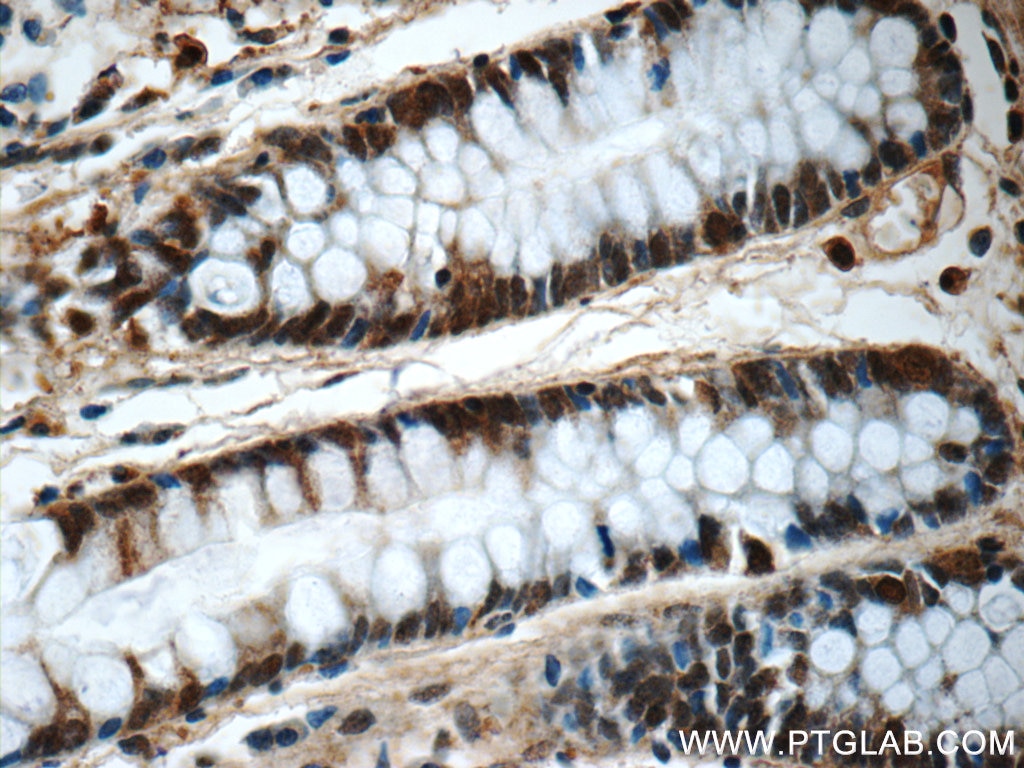
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de côlon de souris, tissu de côlon humain, tissu pancréatique humain, tissu rénal de souris il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
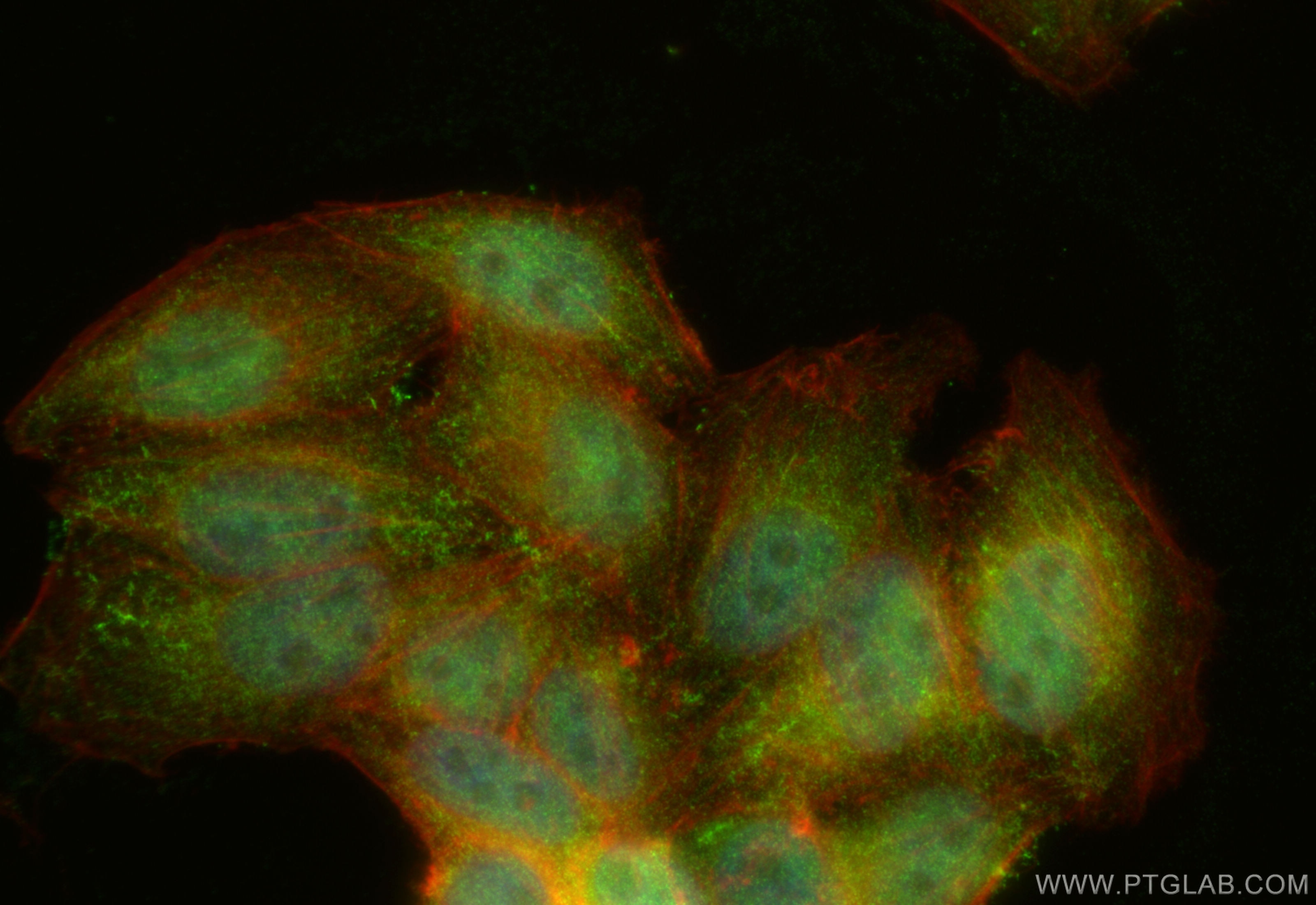
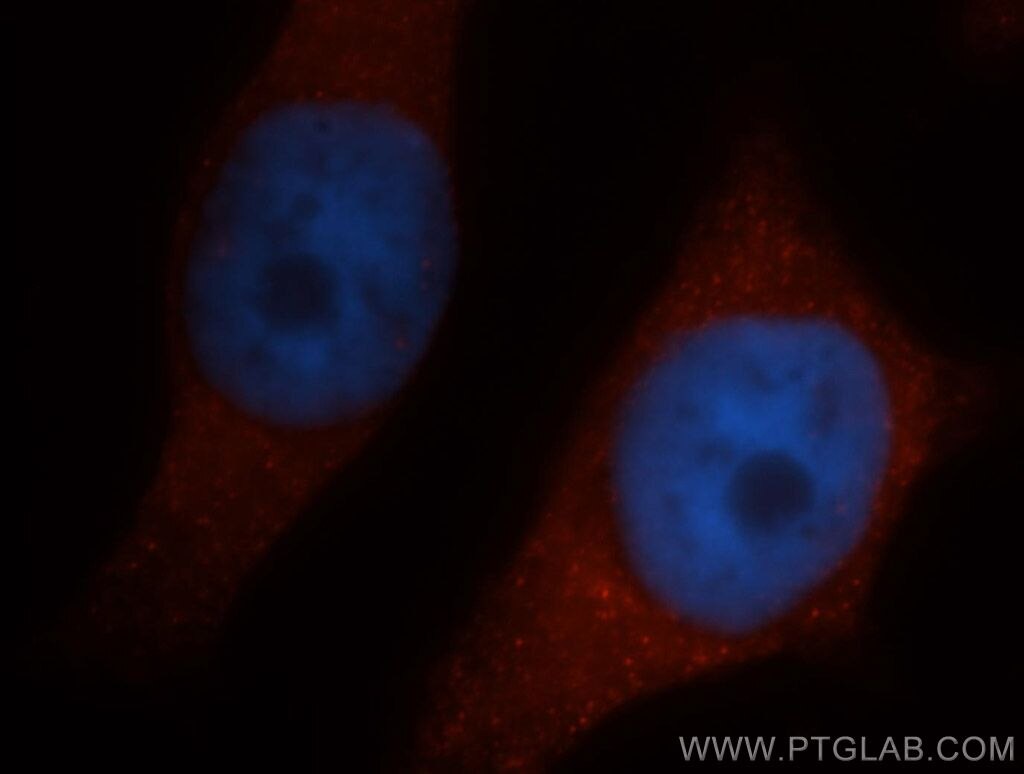
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HepG2, cellules HeLa |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
14545-1-AP cible CLIC1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CLIC1 Protéine recombinante Ag6049 |
| Nom complet | chloride intracellular channel 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 27 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 27-32 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC064527 |
| Symbole du gène | CLIC1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 1192 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 (CLIC1) is a member of the chloride intracellular channel protein family. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including the regulation of chloride ion transport, cell viability, and mitochondrial function. CLIC1 is involved in the formation of membrane-inserted channels that facilitate chloride ion movement, which is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and function (PMID: 32116799). Additionally, CLIC1 has been implicated in cancer progression, where it influences cell proliferation, migration, and invasion (PMID: 38027011).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CLIC1 antibody 14545-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CLIC1 antibody 14545-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CLIC1 antibody 14545-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for CLIC1 antibody 14545-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun CLICs-dependent chloride efflux is an essential and proximal upstream event for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. | ||
Alzheimers Res Ther Circular RNA APP contributes to Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis by modulating microglial polarization via miR-1906/CLIC1 axis | ||
Oxid Med Cell Longev Attenuation of ROS/Chloride Efflux-Mediated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Contributes to Alleviation of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in Rats after Sleeve Gastrectomy. | ||
Transl Oncol Chloride intracellular channel 1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation via mTOR signalling
| ||
Cell Biochem Biophys CLIC1 Inhibition Protects Against Cellular Senescence and Endothelial Dysfunction Via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. | ||
Anticancer Res Chloride Intracellular Channel 1 Expression Is Associated With Poor Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. |